Abstract
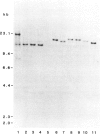
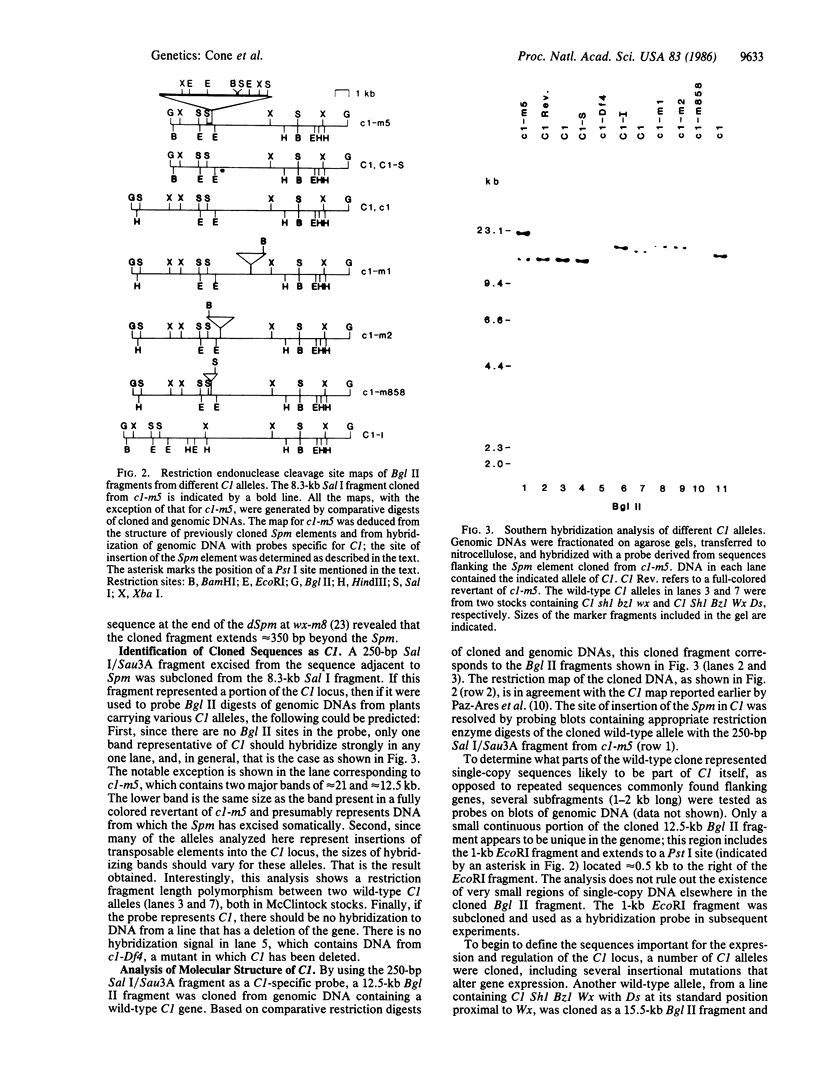
The C1 gene of maize plays a regulatory role in the production of anthocyanin pigments in the aleurone layer of the endosperm. As an initial step toward understanding the molecular details of how C1 controls pigment biosynthesis, we cloned the C1 gene. This was accomplished by first cloning a mutable allele of C1, c1-m5, which contains the transposable element Spm. A combination of molecular and genetic analysis was used to identify the Spm at the C1 locus. Individual genomic DNAs from a population in which the c1-mutable phenotype was segregating with the recessive c1 phenotype were digested with methyl-sensitive restriction enzymes and probed with a small DNA fragment derived from a defective Spm. One Sal I restriction fragment complementary to the Spm probe was shown to be present in the DNA of individuals with the c1-m5 phenotype but absent from DNA of individuals with a recessive c1 phenotype. Subsequent cloning and restriction analysis of this fragment revealed sequences flanking the Spm that proved to be C1-specific. A DNA fragment derived from the flanking sequences was then used as a probe to clone the wild-type C1 gene and several additional alleles of C1, including one stable recessive, two mutations caused by Ds insertions, one mutation induced by insertion of a defective Spm, and two dominant mutations, C1-S and C1-I. RNA blot hybridization analysis of three C1 alleles indicates that C1 regulation of the Bz1 and A1 structural genes in the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway is at the transcriptional level.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chandler V. L., Walbot V. DNA modification of a maize transposable element correlates with loss of activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1767–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooner H. K., Nelson O. E. Genetic control of UDPglucose:flavonol 3-O-glucosyltransferase in the endosperm of maize. Biochem Genet. 1977 Jun;15(5-6):509–519. doi: 10.1007/BF00520194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N. V., Furtek D. B., Nelson O. E. Cloning of the bronze locus in maize by a simple and generalizable procedure using the transposable controlling element Activator (Ac). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3825–3829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wessler S., Shure M. Isolation of the transposable maize controlling elements Ac and Ds. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Saedler H. Molecular interactions between the components of the En-I transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):579–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isackson P. J., Bertrand K. P. Dominant negative mutations in the Tn10 tet repressor: evidence for use of the conserved helix-turn-helix motif in DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6226–6230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly C., Shepherd N. S., Pereira A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Bertram I., Robertson D. S., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Molecular cloning of the a1 locus of Zea mays using the transposable elements En and Mu1. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):877–882. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ares J., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Molecular cloning of the c locus of Zea mays: a locus regulating the anthocyanin pathway. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):829–833. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04291.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Bertram I., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Genetic and molecular analysis of the Enhancer (En) transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):17–23. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02311.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Genes encoding actin in higher plants: intron positions are highly conserved but the coding sequences are not. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):111–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]