Abstract
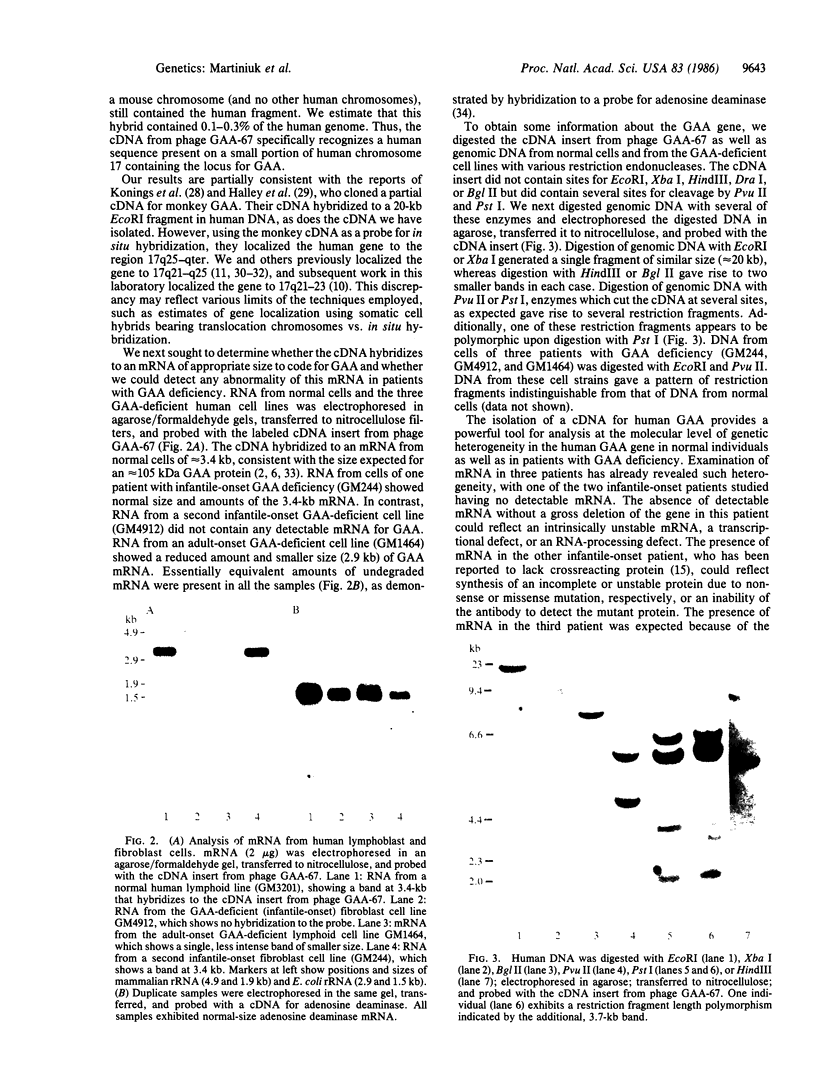
Lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.3) hydrolyzes 1,4-linked alpha-D-glucose polymers present in glycogen. Genetic deficiency of acid alpha-glucosidase results in glycogen-storage disease type II, encompassing a spectrum of disorders of varying severity. To study the molecular basis for this heterogeneity, we sought to clone the coding sequence for human acid alpha-glucosidase. We screened 10(6) recombinant phage from a human liver cDNA expression library with an affinity-purified polyclonal antibody to human acid alpha-glucosidase. When we retested positive phage for reactivity to monoclonal antibodies, we identified a single phage, containing a 2-kilobase (kb) cDNA insert, that reacted with both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. The 2-kb cDNA hybridized to a 20-kb EcoRI fragment of human genomic DNA. This 20-kb EcoRI fragment was present only in DNA from somatic cell hybrids that retained the human chromosome 17 segment q21-q23, which contains the gene for human acid alpha-glucosidase. The cDNA also hybridized to a 3.4-kb mRNA, consistent with the size (approximately 105 kDa) of the acid alpha-glucosidase protein. Finally, in one of two infantile-onset acid alpha-glucosidase-deficient cell lines tested, the 3.4-kb mRNA was not detectable, whereas in an adult-onset cell line, an mRNA of reduced size and amount was found. Examination of DNA digested with restriction enzymes did not reveal any major deletions in the genomic DNA of these patients.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian G. S., Hutton J. J. Adenosine deaminase messenger RNAs in lymphoblast cell lines derived from leukemic patients and patients with hereditary adenosine deaminase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1649–1660. doi: 10.1172/JCI110920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beratis N. G., LaBadie G. U., Hirschhorn K. An isozyme of acid alpha-glucosidase with reduced catalytic activity for glycogen. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Mar;32(2):137–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beratis N. G., LaBadie G. U., Hirschhorn K. Genetic heterogeneity in acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Jan;35(1):21–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. I., Brown D. H. The subcellular distribution of enzymes in type II glycogenosis and the occurrence of an oligo-alpha-1,4-glucan glucohydrolase in human tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 25;110(1):124–133. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni C. B., Auricchio F., Covelli I. Acid alpha-D-glucosidase glucohydrolase from cattle liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 10;244(17):4735–4742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. H., Bishop D. F., Bernstein H. S., Quinn M., Hantzopoulos P., Desnick R. J. Fabry disease: isolation of a cDNA clone encoding human alpha-galactosidase A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7364–7368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Gomez M. R., Seybold M. E., Lambert E. H. The spectrum and diagnosis of acid maltase deficiency. Neurology. 1973 Jan;23(1):95–106. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima H., de Wet J. R., O'Brien J. S. Molecular cloning of a cDNA for human alpha-L-fucosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1262–1265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginns E. I., Choudary P. V., Martin B. M., Winfield S., Stubblefield B., Mayor J., Merkle-Lehman D., Murray G. J., Bowers L. A., Barranger J. A. Isolation of cDNA clones for human beta-glucocerebrosidase using the lambda gt11 expression system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 17;123(2):574–580. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G. alpha-Glucosidase deficiency in generalized glycogenstorage disease (Pompe's disease). Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86:11–16. doi: 10.1042/bj0860011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halley D. J., Konings A., Hupkes P., Galjaard H. Regional mapping of the human gene for lysosomal alpha-glucosidase by in situ hybridization. Hum Genet. 1984;67(3):326–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00291362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Neufeld E. F. Biosynthesis of lysosomal enzymes in fibroblasts. Synthesis as precursors of higher molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4937–4945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig J., Martiniuk F., D'Eustachio P., Zamfirescu C., Desnick R., Hirschhorn K., Hirschhorn L. R., Hirschhorn R. Confirmation of the regional localization of the genes for human acid alpha-glucosidase (GAA) and adenosine deaminase (ADA) by somatic cell hybridization. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;48(Pt 1):49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings A., Hupkes P., Versteeg R., Grosveld G., Reuser A., Galjaard H. Cloning a cDNA for the lysosomal alpha-glucosidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):252–258. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91645-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. Trafficking of lysosomal enzymes in normal and disease states. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI112262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiniuk F., Ellenbogen A., Hirschhorn K., Hirschhorn R. Further regional localization of the genes for human acid alpha glucosidase (GAA), peptidase D (PEPD), and alpha mannosidase B (MANB) by somatic cell hybridization. Hum Genet. 1985;69(2):109–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00293278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiniuk F., Hirschhorn R. Characterization of neutral isozymes of human alpha-glucosidase: differences in substrate specificity, molecular weight and electrophoretic mobility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Apr 14;658(2):248–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiniuk F., Pellicer A., Mehler M., Hirschhorn R. Detection, frequency, and stability of cotransformants expressing nonselectable human enzymes. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Jan;12(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01560722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehler M., DiMauro S. Residual acid maltase activity in late-onset acid maltase deficiency. Neurology. 1977 Feb;27(2):178–184. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel B. E., McAlpine P. J. Extension of human acid alpha-glucosidase polymorphism by isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel. Ann Hum Genet. 1982 May;46(Pt 2):97–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1982.tb00700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Daddona P. E., Shewach D. S., Markham A. F., Bruns G. A., Goff S. C., Kelley W. N. Molecular cloning of human adenosine deaminase gene sequences. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):12753–12756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oude Elferink R. P., Brouwer-Kelder E. M., Surya I., Strijland A., Kroos M., Reuser A. J., Tager J. M. Isolation and characterization of a precursor form of lysosomal alpha-glucosidase from human urine. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 15;139(3):489–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salafsky I. S., Nadler H. L. A fluorometric assay of alpha-glucosidase and its application in the study of Pompe's disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Mar;81(3):450–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandison A., Broadhead D. M., Bain A. D. Elucidation of an unbalanced chromosome translocation by gene dosage studies. Clin Genet. 1982 Jul;22(1):30–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb01407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Swallow D., Burgess S., Evans L. Assignment of the human acid alpha-glucosidase gene (alphaGLU) to chromosome 17 using somatic cell hybrids. Ann Hum Genet. 1979 Jan;42(3):273–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1979.tb00661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. M., Corney G., Harris H., Hirschhorn R. Acid alpha-glucosidase: a new polymorphism in man demonstrable by 'affinity' electrophoresis. Ann Hum Genet. 1975 May;38(4):391–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1975.tb00629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Van Cong N., Gross M. S., Frézal J. Localisation du gene de l'alpha-glucosidase acide (alpha-GLUa) sur le segment q21 à qter du chromosome 17 par l'hybridation cellulaire interspecifique. Hum Genet. 1979 Nov;52(2):249–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Fukushima H., Dewji N. N., Wilcox E., O'Brien J. S., Helinski D. R. Chromogenic immunodetection of human serum albumin and alpha-L-fucosidase clones in a human hepatoma cDNA expression library. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):437–447. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]