Abstract
Acute hepatic failure during pregnancy is a life-threatening situation for the mother and fetus and might need a super-urgent liver transplantation. Many pregnancies with positive outcomes are reported after a previous liver transplantation before the pregnancy, but only a few of them are mentioned with transplantation during pregnancy. In these few cases, fetal outcome is mostly adverse. Experience with liver failure during pregnancy and its management is still deficient and needs to be approved. For sure, patients need to be treated in highly qualified centers in a multidisciplinary approach. We present a case of successful super-urgent liver transplantation during the second trimester of pregnancy after acute hepatic failure due to an acute hepatitis B infection with positive maternal and fetal outcome. Liver transplantation during pregnancy due to an acute liver failure can be a life-saving procedure for the mother and fetus. An early initiated maternal therapy with antiviral drugs and immunoglobulins seems to be safe and able to prevent fetal infection and immunosuppressive therapy after transplantation seems to be well tolerated. Nevertheless, fetal outcome differs widely and long-term outcome is deficiently known.
1. Introduction
Acute hepatic failure is always a life-threatening situation. Sometimes, the only solution solving the problem is a super-urgent liver transplantation. An ongoing pregnancy aggravates such a situation, as two people's lives are involved, the one of the mother and the fetus. Many pregnancies with positive outcomes are reported after liver transplantation before getting pregnant, but only a few cases are mentioned with transplantation during pregnancy [1–21].
2. Case Presentation
A 30-year-old primigravida at 22 0/7 gestational weeks (GW) was admitted to our hospital in suspicion of an acute hepatitis B infection. She had presented herself in another hospital with slight nausea and vomiting, pruritus, slight jaundice, dark urine, a fairly affected overall condition, and a positive blood test for acute hepatitis B infection. The source of the infection remained unknown. Her blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation were normal, as well as her urine analysis besides an elevated bilirubin level. She showed no signs of edema or hyperreflexia but slight jaundice and icteric sclera. Her cardiac and pulmonary status was unaffected, and her temperature was elevated to 38.8°C. Her laboratory work-up showed a progressive hepatic failure (Table 1). HELLP syndrome, intoxication with acetaminophen, Wilson's disease, hepatic neoplasia, acute fatty liver of pregnancy, autoimmune hepatitis, and alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency as other potential etiologies of acute liver failure were excluded by laboratory testing. The infection screening revealed an acute hepatitis B infection with a viral load of 170.000.000 IU/mL. Other infections as hepatitis A, hepatitis C, HIV, cytomegalovirus (CMV), epstein barr virus, herpes simplex virus, varicella zoster virus, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, and parvovirus B19 could be excluded. Her personal medical history showed only an infection with chlamydia trachomatis in early pregnancy, which had been treated with azithromycin. Her family history revealed no cases of known hepatitis B infections. The fetus was sonographically unaffected and well developed according to her gestational age at admission. A multidisciplinary team of hepatologists, surgeons, and obstetricians took care of the patient. An antiviral therapy with tenofovir, 245 mg orally once a day, was initiated immediately. But the patient, who dearly wanted to keep the pregnancy, had to be added to the super-urgent liver transplantation list two days after admission according to Clichy criteria because of rapid progression of hepatic failure and encephalopathy (lab MELD 33) (Table 1). After graft allocation and within 24 hours, an orthotopic liver transplantation with cava preserving technique (piggy back) and intermittent portocaval shunt was performed to avoid any cava clamping during transplantation. The operation was uneventful (six-hour surgery, transfusion of 2 U red blood cells, and low pressors). Intraoperatively, an additional treatment with hepatitis B immunoglobulin was started and continued for 10 days in a dose of 10.000 IU per day intravenously. Thereafter, it was continued to maintain the anti-HBs titer >100 IU/mL. Postoperatively, treatment with tenofovir was continued until 28 6/7 GW. Afterwards, it was changed to lamivudine 100 mg p.o. daily because of an increase of liver enzymes. Immunosuppression consisted of corticosteroids and tacrolimus. The corticosteroids were applied intravenously for the first five days postoperatively in declining doses of methylprednisolone from 250 to 40 mg, followed by decreasing doses of prednisolone orally from 20 mg to 5 mg until delivery. Tacrolimus was applied orally in doses between 5 mg and 12 mg with the goal to achieve a blood level of six to eight ng/mL. On the first postoperative day, the patient could be extubated without any problems and recovered quickly. The histopathological examination of the explanted liver confirmed subtotal necrosis of the liver with extensive cholestasis and predominantly lymphocytic hepatitis. Subsequent maternal sonographic controls and laboratory testing showed normal liver function and perfusion. Subsequent biopsies of the transplanted liver due to elevated liver enzymes at day six after transplantation, could exclude a graft rejection. Eleven days after liver transplantation fetal sonography revealed hepatomegaly and intracranial ventriculomegaly (Figure 1(a)). Additionally, small hematomas in the plexus choroideus on both sides and a subdural bleeding in the posterior cranial fossa were detected (Figure 1(b)). Therefore, an additional MRI of the fetus was arranged five days later and confirmed a mild ventriculomegaly on both sides. However, the hepatomegaly could not be confirmed. Repeated sonographic and MRI examinations showed total restitution of the former findings during the course of pregnancy (Figure 1(c)). Because the patient suffered from preterm uterine contractions, tocolytic agents in form of nifedipine 60 mg orally twice a day in an off-label-use were applied and had to be changed to intravenous admission of hexoprenaline at 28 4/7 GW because of ongoing contractions. The patient developed gestational diabetes, which could be well controlled by diet. With 34 GW a CMV reactivation was detected and treated with CMV immunoglobulins intravenously. An elective cesarean delivery was performed at 36 0/7 GW due to increasing discomfort and strong demand of the patient. A healthy male newborn of 2700 g (42. percentile) was delivered with an APGAR score of 6-4-7 and an umbilical artery pH of 7.39. The child was transferred to our neonatal intensive care unit for better surveillance. A fetal hepatitis B and CMV infection could be excluded by serological testing of the fetal blood and urine. The mother's and child's course were uneventful and they were dismissed eight and 20 days after the cesarean section, respectively.
Table 1.
Maternal laboratory values.
| Day of admission, 22 0/7 GW | Day of transplantation, 22 3/7 GW | Two days after transplantation, 22 5/7 GW | Discharge of hospital (110 days after transplantation) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hb in g/L (117–153) | 111 | 83 | 64 | 133 |
| Tc in G/L (143–400) | 173 | 194 | 137 | 249 |
| INR (<1.2) | 1.6 | 4.6 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| Factor 5 in % (50–150) | 27 | 15 | 79 | |
| Bilirubin in mcM/L (<21) | 129 | 184 | 37 | 7 |
| Ammoniac in mcM/L (9–30) | 17 | 49 | 14 | |
| AST in U/L (<35) | 4030 | 1749 | 347 | 20 |
| ALT in U/L (10–35) | 2775 | 2272 | 824 | 12 |
| GGT in U/L (5–36) | 19 | 17 | ||
| HBV-DNA IU/mL (0) | 117 × 106 | 110 × 106 | 6.2 × 106 | <20 |
| HBs-Ag in U/mL (<0.05) | pos | 2748.68 | 0 | |
| Anti-HBs U/L (<10) | neg | 17 | 787 | |
| HBe-Ag (neg) | pos | neg | ||
| Anti-HBe (neg) | pos | pos | ||
| Anti-HBc-IgM (neg) | pos | pos |
Figure 1.
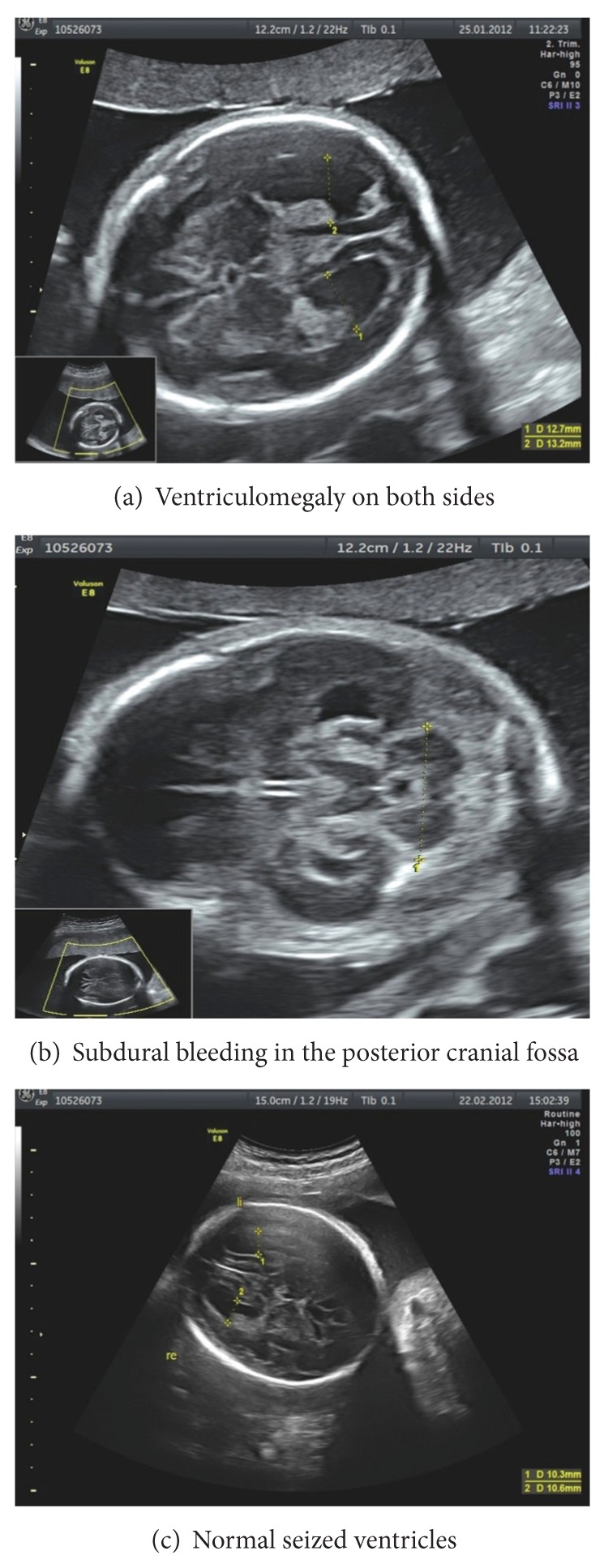
Sonographic images.
3. Discussion
Acute liver failure during pregnancy is a rare but potentially life-threatening disease. Causes of acute liver failure can be pre-existing, pregnancy related, or can occur during pregnancy without being directly related to it (Table 2). Depending on the age of gestation and the viability of the fetus, termination of pregnancy before or during transplantation or maintaining pregnancy has to be discussed with the patient. A multidisciplinary approach is mandatory and the treatment of patients with acute liver failure during pregnancy should take place in a highly qualified and specialized center.
Table 2.
Causes of acute hepatic failure during pregnancy.
| Causes of hepatic failure | Pregnancy related | Nonpregnancy related | Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| HELLP syndrome | x | Thrombocytes, liver enzymes, hemolysis parameters (LDH, haptoglobin) | |
| Acute fatty liver of pregnancy | x | Long-chain fatty acids (LCHAD), acylcarnitine | |
| Infections | x | Serological blood testing | |
| Intoxications (drugs, medication) | x | Urine/blood testing (qualitative/quantitative drug proof) | |
| Metabolic disorders (e.g., M. Wilson) | x | Special markers (e.g., ceruloplasmin, alpha-1-antitrypsin), biopsy | |
| Tumors | x | Imaging, biopsy, tumor markers (e.g., AFP) | |
| Autoimmune disorders | x | Autoantibodies, biopsy |
Besides our case, 18 other cases of liver transplantation during pregnancy were described (Table 3). The reasons for transplantation were acute liver failure due to different etiologies (Table 3). All liver transplantation procedures were performed with piggy back technique. According to current guidelines, immunosuppressive treatment mostly consists of a combination of a calcineurin inhibitor (e.g., tacrolimus) and corticosteroids [19, 21, 22], as it was in our patient. She tolerated the medication without any problems.
Table 3.
Eighteen other cases of liver transplantation during pregnancy in the literature.
| Publication | GW at transplantation | Etiology | Maternal outcome | Delivery mode, GW | Fetal outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anders et al. [1] | 20 | Unknown | Survived | Curettage, 20 GW | Intrauterine fetal death (IUFD) |
| Catnach et al. [2] | 20 | Autoimmune | Survived, PPROM | Spontaneous, 28 GW | Survived |
| Eguchi et al. [3] | 15 | Unknown | Survived, cytomegaly infection | Curettage, 20 GW | Abortion |
| Fair et al. [4] | 22 | Hepatitis B | Survived, Retransplantation | Cesarean, 30 GW | Survived, intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) |
| Finlay et al. [5] | 17.5 | Unknown | Survived | Spontaneous, 28.5 GW | IUFD |
| Hamilton et al. [6] | 21 | Hepatitis B | Survived | Spontaneous, 22 GW | IUFD |
| Jarufe et al. [7] | 22 | Unknown | Survived, reoperation (biliary stenosis), mild graft reaction, preterm contractions | Spontaneous, 27 GW | Survived, no compromises |
| Laifer et al. [8] | 26 | Hepatitis B | Survived, Retransplantation | Cesarean, 28 GW | Neonatal death |
| Laifer et al. [9] | 23 | Autoimmune | Survived; infection, renal insufficiency, anemia, thrombozytopenia, hypotension graft reaction | Spontaneous, 23 GW | IUFD |
| Lo et al. [10] | 26 | Unknown | Survived | Spontaneous, 26 GW | IUFD 26 |
| Kato et al. [11] | 13 | Unknown | Survived, reoperation (insufficient biliary anastomosis) | Miscarriage, 13 GW | Miscarriage |
| Moreno et al. [12] | 27 | Unknown | Survived | Cesarean, term | Survived |
| Morris et al. [13] | 27 | Drug (PTU) | Survived | Spontaneous, 27 GW | Neonatal death |
| Sequeira et al. [14] | 18 | Drug (PTU) | Survived | Cesarean, 37 GW | IUGR, microcephaly, oligohydramnion, ventriculomegaly, ischemic enzephalopathy, seizures |
| Jankovic et al. [15] | 13.5 | Autoimmune | Survived | Spontaneous, 36 GW | No compromises |
| Maddukuri et al. [16] | 11 | Unknown | Survived | Spontaneous, 30 GW | Normally developed at age of 4 years |
| Simsek et al. [17] | 18 | Hepatitis A | Survived | Induced abortion 18 GW | Abortion, growth restriction, oligohydramnion |
| Thornton and Minns [18] | 20 5/7 | Drug | Survived | Induced abortion | Abortion, hydrops, bilateral ventriculomegaly |
Described side effects during pregnancy after liver transplantation, when transplantation was performed before the begin of a pregnancy, are hypertension (26–46%), preeclampsia (9–26%), cholestasis (3–27%), graft rejection (7–12%), diabetes (5–13%), osteoporosis, neurotoxicity, impaired maternal renal function, maternal infections (9–27%), cesarean delivery (23–47%), preterm delivery (31–39%), fetal growth restriction (17–34%), indistinct fetal malformations (0–3%), and complications of the newborn (17–33%) with a perinatal mortality of 0–4% [19–24].
Side effects after transplantation during the ongoing pregnancy in the 18 cases differed little, with cholestasis (22%), graft rejections (25%), impaired maternal renal function (6%), maternal infections (13%), cesarean delivery (25%), preterm delivery (44%), fetal growth restriction (22%), complications of the newborn (19%), and perinatal mortality (50%) [1–18]. Concerning our case, maternal complications in form of a steroid induced gestational diabetes, a reactivation of CMV-infection due to the immunosuppressive medication and preterm contractions, well controlled by tocolysis, took place. No serious complications were found. Concerning the fetus, intermittent intracranial ventriculomegaly and intracranial bleeding with a total restitution in the further course of pregnancy were documented. The reason for these intermittent changes was unclear. By treating the mother with antiviral drugs and immunoglobulins against hepatitis B and CMV, an infection of the newborn could be successfully prevented. In the end, a normally sized and developed newborn was delivered almost at term. Its development a year after the birth its absolutely normal and uncomplicated, but the neurological long-term outcome is still unknown. In comparison, fetal outcome in the other 18 cases described in the literature showed a wide range from abortion to delivery of a normal fetus (Table 3).
We conclude that super-urgent liver transplantation due to an acute hepatitis B infection during pregnancy can be a life-saving procedure for the mother and fetus. An early initiated maternal therapy with antiviral drugs and immunoglobulins seems to be safe and able to prevent fetal infection. Although perinatal mortality is high, on one hand, because of intrauterine fetal death in the course and on the other hand, because of induced abortion for fear of fetal complications, maintaining the pregnancy should always be discussed with the mother. As especially our case and few others show, maintaining the pregnancy is an option in case of acute liver failure with the necessity of transplantation and positive outcome is possible. Nevertheless, fetal outcomes after transplantation during pregnancy are diverse and long-term outcomes are deficiently known. But as our case shows, there are good chances of positive outcome for affected patients and their offspring as long as they are treated in highly specialized centers with intense treatment and observation.
References
- 1.Anders M, Quiñonez E, Goldaracena N, Osatnik J, Fernández JL, Viola L. Liver transplantation during pregnancy in a patient with acute liver failure. Acta Gastroenterologica Latinoamericana. 2010;40:268–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Catnach SM, McCarthy M, Jauniaux E, et al. Liver transplantation during pregnancy complicated by cytomegalovirus infection. Transplantation. 1995;60(5):510–511. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199509000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Eguchi S, Yanaga K, Fujita F, et al. Living-related right lobe liver transplantation for a patient with fulminant hepatic failure during the second trimester of pregnancy: report of a case. Transplantation. 2002;73(12):1970–1971. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200206270-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fair J, Klein AS, Feng T, Merritt WT, Burdick JF. Intrapartum orthotopic liver transplantation with successful outcome of pregnancy. Transplantation. 1990;50(3):534–535. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199009000-00041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Finlay DE, Foshager MC, Longley DG, Letourneau JG. Ischemic injury to the fetus after maternal liver transplantation. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine. 1994;13(2):145–148. doi: 10.7863/jum.1994.13.2.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hamilton MIR, Alcock R, Magos L, Mallett S, Rolles K, Burroughs AK. Liver transplantation during pregnancy. Transplantation Proceedings. 1993;25(5):2967–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jarufe N, Soza A, Pérez-Ayuso RM, et al. Successful liver transplantation and delivery in a woman with fulminant hepatic failure occurring during the second trimester of pregnancy. Liver International. 2006;26(4):494–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01246.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Laifer SA, Darby MJ, Scantlebury VP, Harger JH, Caritis SN. Pregnancy and liver transplantation. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1990;76(6):1083–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Laifer SA, Abu-Elmagd K, Fung JJ. Hepatic transplantation during pregnancy and the puerperium. Journal of Maternal-Fetal and Neonatal Medicine. 1997;6(1):40–44. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6661(199701/02)6:1<40::AID-MFM8>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lo CM, Gertsch P, Fan ST. Living unrelated liver transplantation between spouses for fulminant hepatic failure. British Journal of Surgery. 1995;82(8):1036–1037. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800820811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kato T, Nery JR, Morcos JJ, et al. Successful living related liver transplantation in an adult with fulminant hepatic failure. Transplantation. 1997;64(3):415–417. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199708150-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Moreno EG, Garcia GI, Gomez SR, et al. Fulminant hepatic failure during pregnancy successfully treated by orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1991;52(5):923–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Morris CV, Goldstein RM, Cofer JB, Solomon H, Klintmalm GB. An unusual presentation of fulminant hepatic failure secondary to propylthiouracil therapy. Clinical Transplants. 1989, article 311 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sequeira E, Wanyonyi S, Dodia R. Severe propylthiouracil-induced hepatotoxicity in pregnancy managed successfully by liver transplantation: a case report. Journal of Medical Case Reports. 2011;5, article 461 doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jankovic Z, Stamenkovic D, Duncan B, Prasad R, Davies M. Successful outcome after a technically challenging liver transplant during pregnancy. Transplantation Proceedings. 2007;39(5):1704–1706. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2007.02.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Maddukuri VC, Stephenson CD, Eskind L, Ahrens WA, Purdum P, Russo MW. Liver transplantation for acute liver failure at 11-week gestation with successful maternal and fetal outcome. Case Reports in Transplantation. 2012;2012:7 pages. doi: 10.1155/2012/484080.484080 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Simsek Y, Isik B, Karaer A, Celik O, Kutlu R, Aydin NE. Fulminant hepatitis A infection in second trimester of pregnancy requiring living-donor liver transplantation. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research. 2012;38(4):745–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.2011.01757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Thornton SL, Minns AB. Unintenional chronic acetaminophen poisoning during pregnancy resulting in liver transplantation. Journal of Medical Toxicology. 2012;8(2):176–178. doi: 10.1007/s13181-012-0218-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Parolin MB, Coelho JCU, Urbanetz AA, Pampuch M. Contraception and pregnancy after liver transplantation—an update overview. Arquivos de Gastroenterologia. 2009;46(2):154–158. doi: 10.1590/s0004-28032009000200015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.dei Malatesta MF, Rossi M, Rocca B, et al. Pregnancy after liver transplantation: report of 8 new cases and review of the literature. Transplant Immunology. 2006;15(4):297–302. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Radomski JS, Moritz MJ, Muñoz SJ, Cater JR, Jarrell BE, Armenti VT. National Transplantation Pregnancy Registry: analysis of pregnancy outcomes in female liver transplant recipients. Liver Transplantation and Surgery. 1995;1(5):281–284. doi: 10.1002/lt.500010502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mukherjee S, Mukherjee U. A comprehensive review of immunosuppression used for liver transplantation. Journal of Transplantation. 2009;2009:20 pages. doi: 10.1155/2009/701464.701464 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Armenti VT, Constantinescu S, Moritz MJ, Davison JM. Pregnancy after transplantation. Transplantation Reviews. 2008;22(4):223–240. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2008.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Armenti VT, Herrine SK, Radomski JS, Moritz MJ. Pregnancy after liver transplantation. Liver Transplantation. 2000;6(6):671–685. doi: 10.1053/jlts.2000.18703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


