Abstract
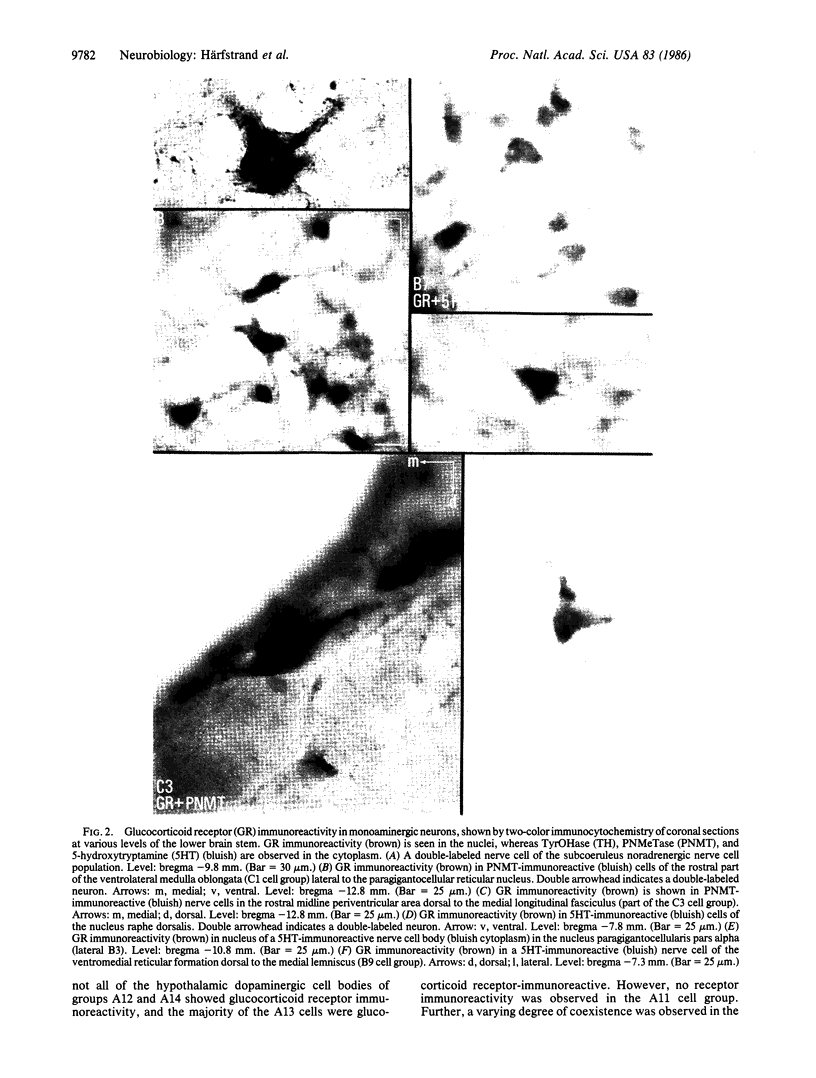
A monoclonal antibody against the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor was used in combination with rabbit antibodies against tyrosine hydroxylase, phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, and 5-hydroxytryptamine to demonstrate strong glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactivity in large numbers of central monoaminergic nerve cell bodies of the male rat. The receptor immunoreactivity was predominantly located in the nucleus, whereas the tyrosine hydroxylase, phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, and 5-hydroxytryptamine were detected mainly in the cytoplasm. The vast majority of the noradrenergic nerve cell bodies of groups A1-A7 and of the 5-hydroxytryptaminergic cell bodies of groups B1-B9 were found to contain strong glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactivity. The majority of the phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase-immunoreactive nerve cells of the adrenergic cell groups C1-C3 and of the dorsal subnuclei of the nucleus tractus solitarius in the medulla oblongata were also strongly immunoreactive for glucocorticoid receptor. In the midbrain dopaminergic groups A8-A10, moderately (A8, A9) to strongly (A10) glucocorticoid receptor-immunoreactive cells were found, ranging from 40 to 75% of the total population. In the hypothalamic dopaminergic cell groups, all the cells of groups A12 and A14, as well as the majority of the dopaminergic cells of the zona incerta (A13), were found to contain moderate to strong glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactivity, but none of the large dopaminergic cells of the posterior hypothalamus (A11) showed such immunoreactivity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnati L. F., Fuxe K., Yu Z. Y., Härfstrand A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Goldstein M., Zoli M., Vale W., Gustafsson J. A. Morphometrical analysis of the distribution of corticotrophin releasing factor, glucocorticoid receptor and phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase immunoreactive structures in the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Mar 15;54(2-3):147–152. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(85)80070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll B. J. The dexamethasone suppression test for melancholia. Br J Psychiatry. 1982 Mar;140:292–304. doi: 10.1192/bjp.140.3.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T. The effect of immobilization stress on the activity of central monoamine neurons. Life Sci. 1968 Jan 1;7(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(68)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLSTROEM A., FUXE K. EVIDENCE FOR THE EXISTENCE OF MONOAMINE-CONTAINING NEURONS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. I. DEMONSTRATION OF MONOAMINES IN THE CELL BODIES OF BRAIN STEM NEURONS. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1964:SUPPL 232–23355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan G. E., Stumpf W. E. A combined autoradiographic and immunocytochemical study of 3H-corticosterone target neurons and catecholamine neurons in rat and mouse lower brain stem. Neuroendocrinology. 1985 Mar;40(3):262–271. doi: 10.1159/000124083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe K., Goldstein M., Hökfelt T., Joh T. H. Immunohistochemical localization of dopamine- -hydroxylase in the peripheral and central nervous system. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1970 Sep;1(5):627–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe K., Härfstrand A., Agnati L. F., Yu Z. Y., Cintra A., Wikström A. C., Okret S., Cantoni E., Gustafsson J. A. Immunocytochemical studies on the localization of glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactive nerve cells in the lower brain stem and spinal cord of the male rat using a monoclonal antibody against rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Sep 16;60(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe K., Wikström A. C., Okret S., Agnati L. F., Härfstrand A., Yu Z. Y., Granholm L., Zoli M., Vale W., Gustafsson J. A. Mapping of glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactive neurons in the rat tel- and diencephalon using a monoclonal antibody against rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):1803–1812. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-1803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T. Characterization and tissue localization of catecholamine synthesizing enzymes. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Jun;24(2):293–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höktelt T., Everitt B. J., Fuxe K., Kalia M., Agnati L., Johansson O., Härfstrand A., Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Theodorsson-Norheim E. Transmitter and peptide systems in areas involved in the control of blood pressure. Clin Exp Hypertens A. 1984;6(1-2):23–41. doi: 10.3109/10641968409062549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvet M. Biogenic amines and the states of sleep. Science. 1969 Jan 3;163(3862):32–41. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3862.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalia M., Fuxe K., Goldstein M. Rat medulla oblongata. II. Dopaminergic, noradrenergic (A1 and A2) and adrenergic neurons, nerve fibers, and presumptive terminal processes. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Mar 15;233(3):308–332. doi: 10.1002/cne.902330303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y., Bloom F. E. Central catecholamine neuron systems: anatomy and physiology of the norepinephrine and epinephrine systems. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:113–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertel W. H., Tappaz M. L., Berod A., Mugnaini E. Two-color immunohistochemistry for dopamine and GABA neurons in rat substantia nigra and zona incerta. Brain Res Bull. 1982 Jul-Dec;9(1-6):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(82)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okret S., Wikström A. C., Wrange O., Andersson B., Gustafsson J. A. Monoclonal antibodies against the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis D. J., Fuxe K. Brain norepinephrine: evidence that neuronal release is essential for sham rage behavior following brainstem transection in cat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):108–112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbusch H. W. Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat-cell bodies and terminals. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):557–618. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbusch H. W., Verhofstad A. A., Joosten H. W. Localization of serotonin in the central nervous system by immunohistochemistry: description of a specific and sensitive technique and some applications. Neuroscience. 1978;3(9):811–819. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry A. M., Tassin J. P., Blanc G., Stinus L., Scatton B., Glowinski J. Discovery of the mesocortical dopaminergic system: some pharmacological and functional characteristics. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1977;16:5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. Purification of the glucocorticoid receptor from rat liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9284–9290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Okret S., Radojćić M., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. Characterization of the purified activated glucocorticoid receptor from rat liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4534–4541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]