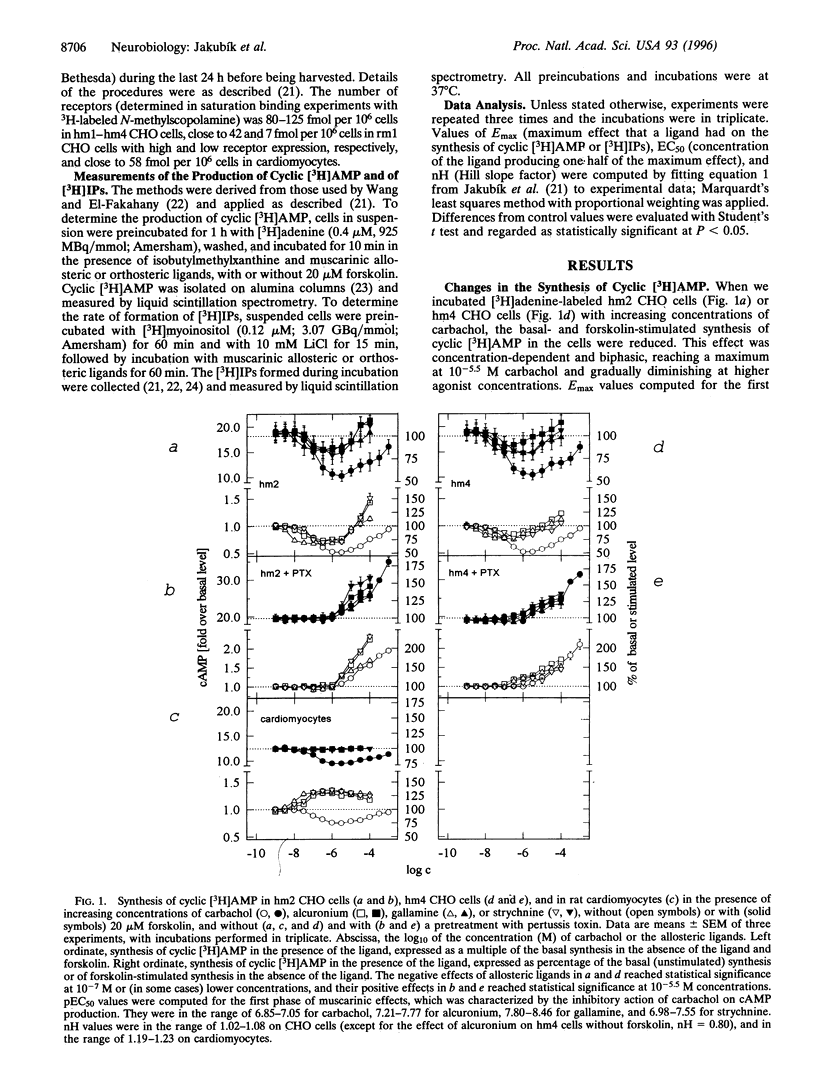
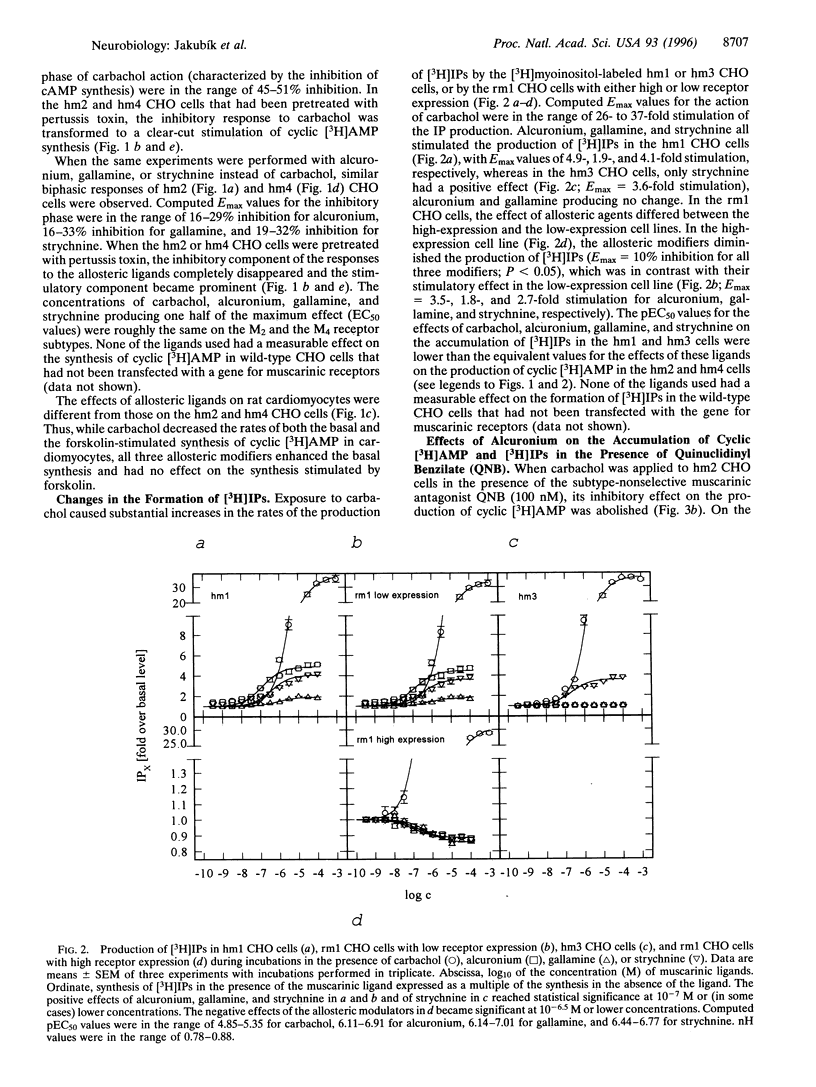
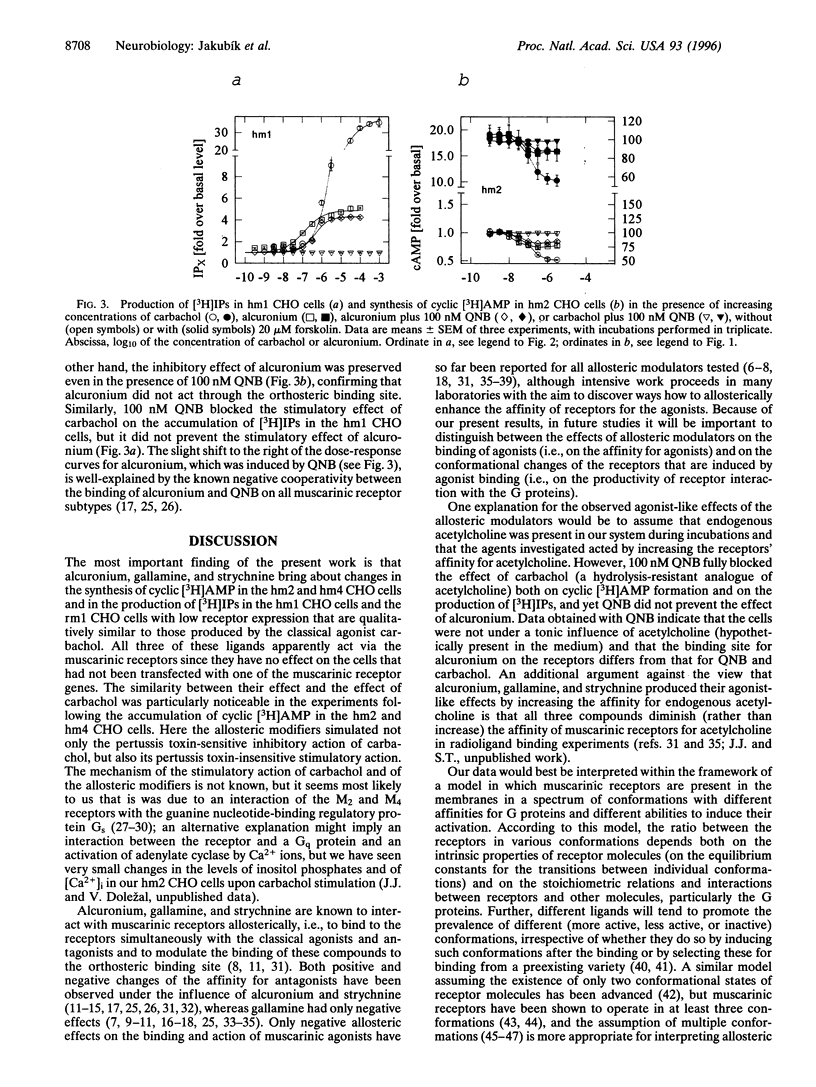
Abstract
Ligands that bind to the allosteric-binding sites on muscarinic acetylcholine receptors alter the conformation of the classical-binding sites of these receptors and either diminish or increase their affinity for muscarinic agonists and classical antagonists. It is not known whether the resulting conformational change also affects the interaction between the receptors and the G proteins. We have now found that the muscarinic receptor allosteric modulators alcuronium, gallamine, and strychnine (acting in the absence of an agonist) alter the synthesis of cAMP in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing the M2 or the M4 subtype of muscarinic receptors in the same direction as the agonist carbachol. In addition, most of their effects on the production of inositol phosphates in CHO cells expressing the M1 or the M3 muscarinic receptor subtypes are also similar to (although much weaker than) those of carbachol. The agonist-like effects of the allosteric modulators are not observed in CHO cells that have not been transfected with the gene for any of the subtypes of muscarinic receptors. The effects of alcuronium on the formation of cAMP and inositol phosphates are not prevented by the classical muscarinic antagonist quinuclidinyl benzilate. These observations demonstrate for the first time that the G protein-mediated functional responses of muscarinic receptors can be evoked not only from their classical, but also from their allosteric, binding sites. This represents a new mechanism of receptor activation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birdsall N. J., Cohen F., Lazareno S., Matsui H. Allosteric regulation of G-protein-linked receptors. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995 Feb;23(1):108–111. doi: 10.1042/bst0230108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley N. J., Bonner T. I., Buckley C. M., Brann M. R. Antagonist binding properties of five cloned muscarinic receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;35(4):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burford N. T., Tobin A. B., Nahorski S. R. Differential coupling of m1, m2 and m3 muscarinic receptor subtypes to inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate accumulation in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jul;274(1):134–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgen A. S. Conformational changes and drug action. Fed Proc. 1981 Nov;40(13):2723–2728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgen A. S. The effects of agonists on the components of the cardiac muscarinic receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;92(2):327–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein E. S., Spalding T. A., Braüner-Osborne H., Brann M. R. Constitutive activation of muscarinic receptors by the G-protein Gq. FEBS Lett. 1995 Apr 24;363(3):261–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield M. P. Muscarinic receptors--characterization, coupling and function. Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Jun;58(3):319–379. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90027-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. L., Mitchelson F. The inhibitory effect of gallamine on muscarinic receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;58(3):323–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1976.tb07708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittman A. H., Weber J. P., Hinds T. R., Choi E. J., Migeon J. C., Nathanson N. M., Storm D. R. A novel mechanism for coupling of m4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors to calmodulin-sensitive adenylyl cyclases: crossover from G protein-coupled inhibition to stimulation. Biochemistry. 1994 Feb 1;33(4):943–951. doi: 10.1021/bi00170a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong G. Z., Kameyama K., Rinken A., Haga T. Ligand binding properties of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes (m1-m5) expressed in baculovirus-infected insect cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jul;274(1):378–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorofeeva N. A., Shelkovnikov S. A., Starshinova L. A., Danilov A. F., Nedoma J., Tucek S. Quest for agonist and antagonist selectivity at muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig smooth muscles and cardiac atria. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;346(4):383–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00171078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap J., Brown J. H. Heterogeneity of binding sites on cardiac muscarinic receptors induced by the neuromuscular blocking agents gallamine and pancuronium. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Jul;24(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlert F. J. Gallamine allosterically antagonizes muscarinic receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity in the rat myocardium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Nov;247(2):596–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Huyler J., Brann M. R. Allosteric regulation of cloned m1-m5 muscarinic receptor subtypes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 24;42(10):1927–1932. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90591-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J., Seidenberg M. Two allosteric modulators interact at a common site on cardiac muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;42(4):638–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felder C. C. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: signal transduction through multiple effectors. FASEB J. 1995 May;9(8):619–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner B. Molecular mechanisms of agonism. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Aug;16(8):259–260. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)89039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanf R., Li Y., Szabo G., Fischmeister R. Agonist-independent effects of muscarinic antagonists on Ca2+ and K+ currents in frog and rat cardiac cells. J Physiol. 1993 Feb;461:743–765. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilf G., Jakobs K. H. Agonist-independent inhibition of G protein activation by muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists in cardiac membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 12;225(3):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90026-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulme E. C., Birdsall N. J., Buckley N. J. Muscarinic receptor subtypes. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:633–673. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högger P., Shockley M. S., Lameh J., Sadée W. Activating and inactivating mutations in N- and C-terminal i3 loop junctions of muscarinic acetylcholine Hm1 receptors. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7405–7410. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubík J., Bacáková L., el-Fakahany E. E., Tucek S. Constitutive activity of the M1-M4 subtypes of muscarinic receptors in transfected CHO cells and of muscarinic receptors in the heart cells revealed by negative antagonists. FEBS Lett. 1995 Dec 18;377(2):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubík J., Bacáková L., el-Fakahany E. E., Tucek S. Subtype selectivity of the positive allosteric action of alcuronium at cloned M1-M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Sep;274(3):1077–1083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubík J., Tucek S. Positive allosteric interactions on cardiac muscarinic receptors: effects of chemical modifications of disulphide and carboxyl groups. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Apr 28;289(2):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(95)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubík J., Tucek S. Protection by alcuronium of muscarinic receptors against chemical inactivation and location of the allosteric binding site for alcuronium. J Neurochem. 1994 Nov;63(5):1932–1940. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63051932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Alvarez R., Salomon Y. Determination of adenylyl cyclase catalytic activity using single and double column procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1994;238:31–56. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)38005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. V., Heilman C. J., Brann M. R. Functional responses of cloned muscarinic receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. Agonist-receptor efficacy. I: Mechanisms of efficacy and receptor promiscuity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Jun;16(6):188–192. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)89020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. Agonist-receptor efficacy. II. Agonist trafficking of receptor signals. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Jul;16(7):232–238. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)89032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T., Boselli C. Pharmacologic discrimination between receptor heterogeneity and allosteric interaction: resultant analysis of gallamine and pirenzepine antagonism of muscarinic responses in rat trachea. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Sep;250(3):944–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T., Morgan P., Lutz M. On the importance of the "antagonist assumption" to how receptors express themselves. Biochem Pharmacol. 1995 Jun 29;50(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(95)00137-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazareno S., Birdsall N. J. Detection, quantitation, and verification of allosteric interactions of agents with labeled and unlabeled ligands at G protein-coupled receptors: interactions of strychnine and acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;48(2):362–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N. H., el-Fakahany E. E. Allosteric antagonists of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 5;42(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90703-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P. The two-state model of receptor activation. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Mar;16(3):89–97. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)88989-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppik R. A., Miller R. C., Eck M., Paquet J. L. Role of acidic amino acids in the allosteric modulation by gallamine of antagonist binding at the m2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 May;45(5):983–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui H., Lazareno S., Birdsall N. J. Probing of the location of the allosteric site on m1 muscarinic receptors by site-directed mutagenesis. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;47(1):88–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migeon J. C., Nathanson N. M. Differential regulation of cAMP-mediated gene transcription by m1 and m4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Preferential coupling of m4 receptors to Gi alpha-2. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9767–9773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proska J., Tucek S. Mechanisms of steric and cooperative actions of alcuronium on cardiac muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):709–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki K., Haga T. Effects of magnesium ion on the interaction of atrial muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and GTP-binding regulatory proteins. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 3;31(43):10634–10642. doi: 10.1021/bi00158a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockton J. M., Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. Modification of the binding properties of muscarinic receptors by gallamine. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 May;23(3):551–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucek S., Musílková J., Nedoma J., Proska J., Shelkovnikov S., Vorlícek J. Positive cooperativity in the binding of alcuronium and N-methylscopolamine to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):674–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucek S., Proska J. Allosteric modulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Jun;16(6):205–212. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)89023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W. K., Mosser V. A., Bulseco D. A., Schimerlik M. I. Porcine m2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-effector coupling in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 30;270(26):15485–15493. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.26.15485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelbroeck M. Identification of drugs competing with d-tubocurarine for an allosteric site on cardiac muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Oct;46(4):685–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Z., el-Fakahany E. E. Application of transfected cell lines in studies of functional receptor subtype selectivity of muscarinic agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu S. Z., Wang S. Z., Hu J., el-Fakahany E. E. An arginine residue conserved in most G protein-coupled receptors is essential for the function of the m1 muscarinic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Mar;45(3):517–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



