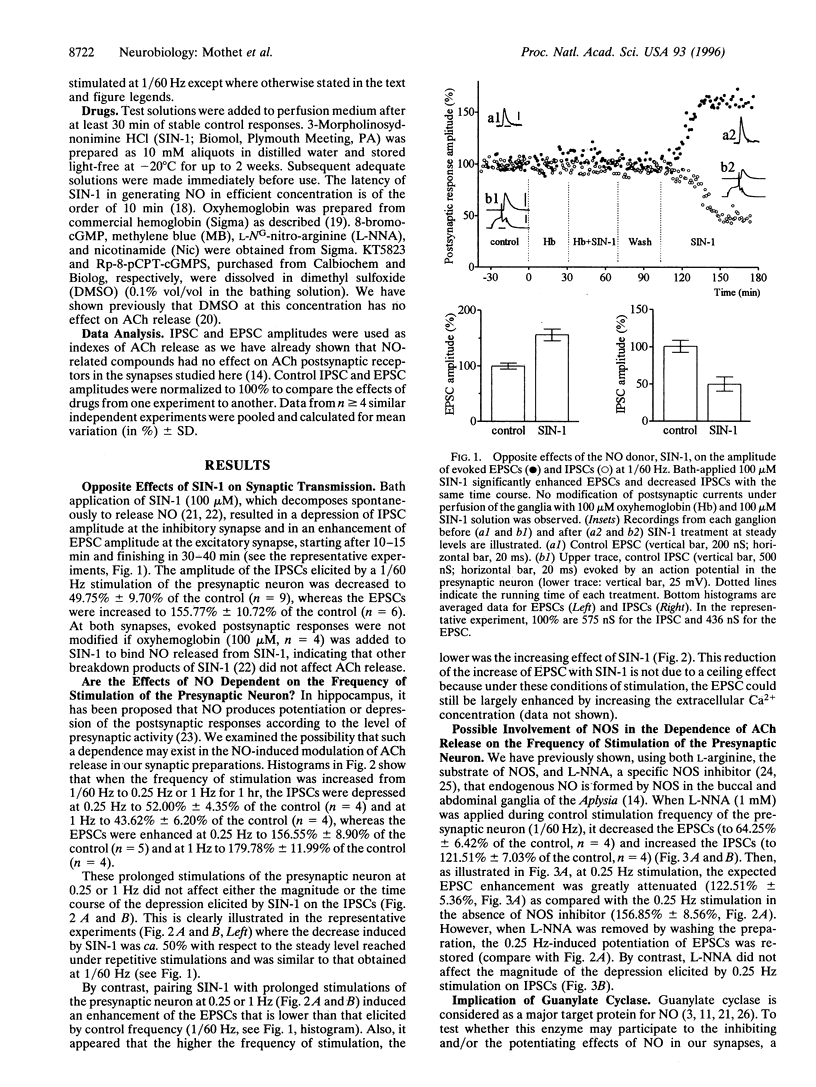
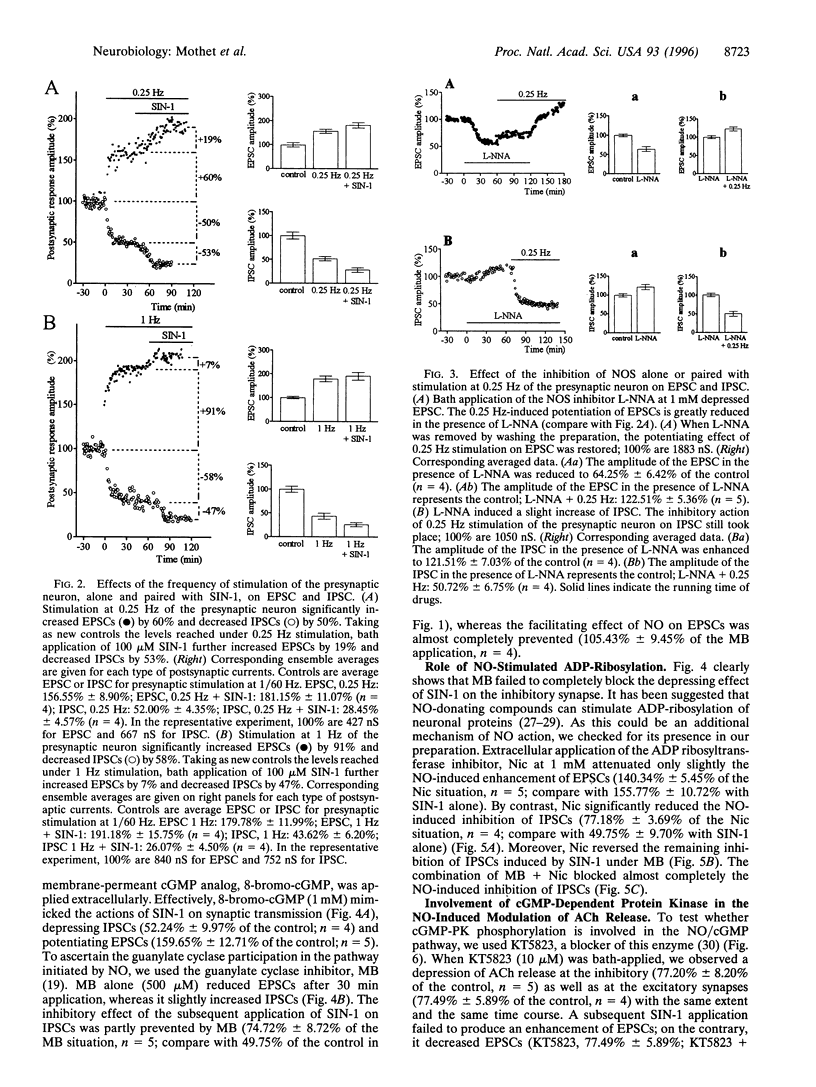
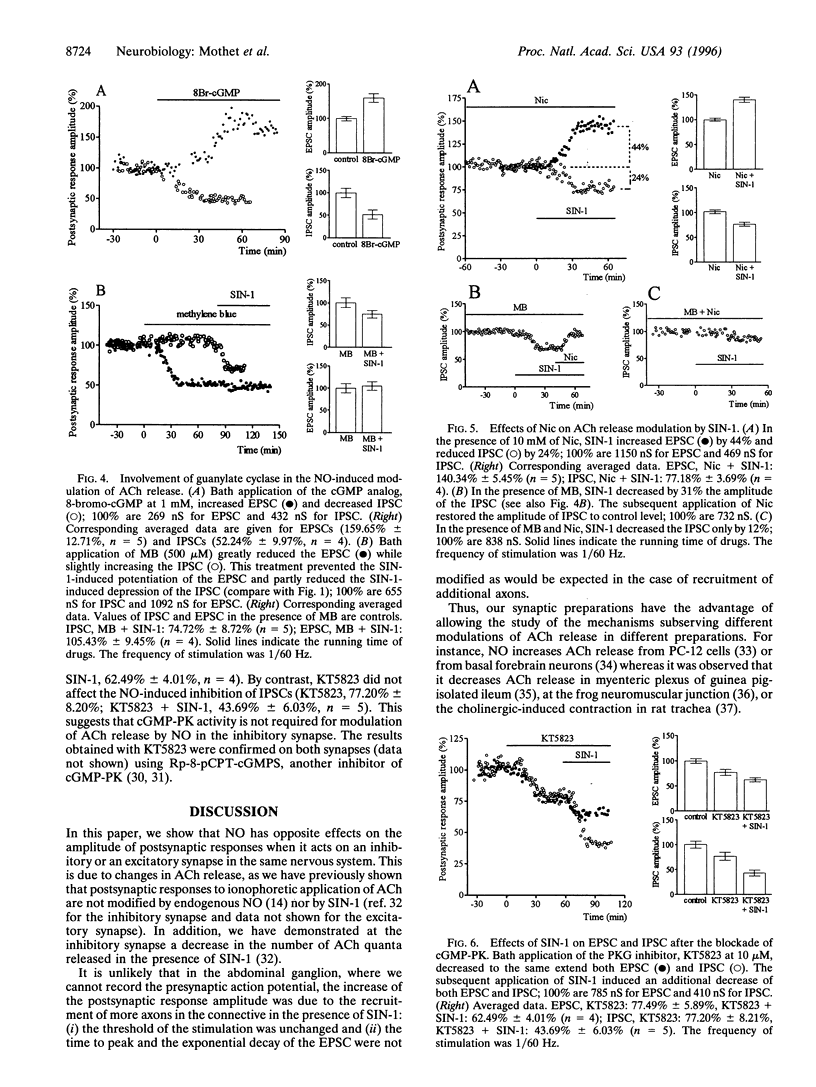
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) produced opposite effects on acetylcholine (ACh) release in identified neuroneuronal Aplysia synapses depending on the excitatory or the inhibitory nature of the synapse. Extracellular application of the NO donor, SIN-1, depressed the inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) and enhanced the excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) evoked by presynaptic action potentials (1/60 Hz). Application of a membrane-permeant cGMP analog mimicked the effect of SIN-1 suggesting the participation of guanylate cyclase in the NO pathway. The guanylate cyclase inhibitor, methylene blue, blocked the NO-induced enhancement of EPSCs but only reduced the inhibition of IPSCs indicating that an additional mechanism participates to the depression of synaptic transmission by NO. Using nicotinamide, an inhibitor of ADP-ribosylation, we found that the NO-induced depression of ACh release on the inhibitory synapse also involves ADP-ribosylation mechanism(s). Furthermore, application of SIN-1 paired with cGMP-dependent protein kinase (cGMP-PK) inhibitors showed that cGMP-PK could play a role in the potentiating but not in the depressing effect of NO on ACh release. Increasing the frequency of stimulation of the presynaptic neuron from 1/60 Hz to 0.25 or 1 Hz potentiated the EPSCs and reduced the IPSCs. In these conditions, the potentiating effect of NO on the excitatory synapse was reduced, whereas its depressing effect on the inhibitory synapse was unaffected. Moreover the frequency-dependent enhancement of ACh release in the excitatory synapse was greatly reduced by the inhibition of NO synthase. Our results indicate that NO may be involved in different ways of modulation of synaptic transmission depending on the type of the synapse including synaptic plasticity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey C. H., Chen M. Morphological basis of long-term habituation and sensitization in Aplysia. Science. 1983 Apr 1;220(4592):91–93. doi: 10.1126/science.6828885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baux G., Fossier P., Tauc L. Histamine and FLRFamide regulate acetylcholine release at an identified synapse in Aplysia in opposite ways. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:147–168. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton C. L., Southam E., Garthwaite J. Nitric oxide-dependent long-term potentiation is blocked by a specific inhibitor of soluble guanylyl cyclase. Neuroscience. 1995 Dec;69(3):699–703. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00349-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide mediates glutamate-linked enhancement of cGMP levels in the cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9030–9033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel neuronal messenger. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90104-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüne B., Lapetina E. G. Activation of a cytosolic ADP-ribosyltransferase by nitric oxide-generating agents. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8455–8458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt E., Eigenthaler M., Genieser H. G. (Rp)-8-pCPT-cGMPS, a novel cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Oct 14;269(2):265–268. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhme E., Grossmann G., Herz J., Mülsch A., Spies C., Schultz G. Regulation of cyclic GMP formation by soluble guanylate cyclase: stimulation by NO-containing compounds. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:259–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementi E., Vecchio I., Sciorati C., Nisticò G. Nitric oxide modulation of agonist-evoked intracellular Ca2+ release in neurosecretory PC-12 cells: inhibition of phospholipase C activity via cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase I. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Mar;47(3):517–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. M., Snyder S. H. Gases as biological messengers: nitric oxide and carbon monoxide in the brain. J Neurosci. 1994 Sep;14(9):5147–5159. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-09-05147.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duman R. S., Terwilliger R. Z., Nestler E. J. Endogenous ADP-ribosylation in brain: initial characterization of substrate proteins. J Neurochem. 1991 Dec;57(6):2124–2132. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb06431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer M. A., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase: irreversible inhibition by L-NG-nitroarginine in brain in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1136–1141. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90403-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feelisch M., Noack E. A. Correlation between nitric oxide formation during degradation of organic nitrates and activation of guanylate cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 2;139(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossier P., Baux G., Tauc L. N- and P-type Ca2+ channels are involved in acetylcholine release at a neuroneuronal synapse: only the N-type channel is the target of neuromodulators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4771–4775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossier P., Baux G., Trudeau L. E., Tauc L. Involvement of Ca2+ uptake by a reticulum-like store in the control of transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1992 Sep;50(2):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90434-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fossier P., Baux G., Trudeau L. E., Tauc L. Pre- and postsynaptic actions of nifedipine at an identified cholinergic central synapse of Aplysia. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Nov;422(2):193–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00370420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furfine E. S., Harmon M. F., Paith J. E., Garvey E. P. Selective inhibition of constitutive nitric oxide synthase by L-NG-nitroarginine. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 24;32(33):8512–8517. doi: 10.1021/bi00084a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galione A., Lee H. C., Busa W. B. Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release in sea urchin egg homogenates: modulation by cyclic ADP-ribose. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1143–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.1909457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galione A., White A., Willmott N., Turner M., Potter B. V., Watson S. P. cGMP mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ in sea urchin eggs by stimulating cyclic ADP-ribose synthesis. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):456–459. doi: 10.1038/365456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. Bilateral symmetry and interneuronal organization in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia. Science. 1971 Aug 6;173(3996):550–553. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3996.550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Boulton C. L. Nitric oxide signaling in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:683–706. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.003343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Charles S. L., Chess-Williams R. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release on activation of NMDA receptors suggests role as intercellular messenger in the brain. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):385–388. doi: 10.1038/336385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelperin A. Nitric oxide mediates network oscillations of olfactory interneurons in a terrestrial mollusc. Nature. 1994 May 5;369(6475):61–63. doi: 10.1038/369061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead D. C., Jacklet J. W. Effects of calcium and magnesium on facilitation of a unitary synaptic potential in neuron R15 of Aplysia. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1974 Mar 1;47(3):991–1003. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(74)90473-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess D. T., Lin L. H., Freeman J. A., Norden J. J. Modification of cysteine residues within G(o) and other neuronal proteins by exposure to nitric oxide. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Nov;33(11):1283–1292. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch D. B., Steiner J. P., Dawson T. M., Mammen A., Hayek E., Snyder S. H. Neurotransmitter release regulated by nitric oxide in PC-12 cells and brain synaptosomes. Curr Biol. 1993 Nov 1;3(11):749–754. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90022-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacklet J. W. Nitric oxide is used as an orthograde cotransmitter at identified histaminergic synapses. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Aug;74(2):891–895. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.74.2.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Shapiro E., Kandel E. R. Synaptic plasticity and the modulation of the Ca2+ current. J Exp Biol. 1980 Dec;89:117–157. doi: 10.1242/jeb.89.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. C., Aarhus R. ADP-ribosyl cyclase: an enzyme that cyclizes NAD+ into a calcium-mobilizing metabolite. Cell Regul. 1991 Mar;2(3):203–209. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.3.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. Q., Bennett M. R. Nitric oxide modulation of quantal secretion in chick ciliary ganglia. J Physiol. 1994 Dec 1;481(Pt 2):385–394. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren C. A., Laird M. V. Nitroprusside inhibits neurotransmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. Neuroreport. 1994 Oct 27;5(16):2205–2208. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199410270-00054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Gruner J. A., Sugimori M., McGuinness T. L., Greengard P. Regulation by synapsin I and Ca(2+)-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II of the transmitter release in squid giant synapse. J Physiol. 1991 May;436:257–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M., Silver R. B. The concept of calcium concentration microdomains in synaptic transmission. Neuropharmacology. 1995 Nov;34(11):1443–1451. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(95)00150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallart A., Martin A. R. An analysis of facilitation of transmitter release at the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):679–694. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulemans A., Mothet J. P., Schirar A., Fossier P., Tauc L., Baux G. A nitric oxide synthase activity is involved in the modulation of acetylcholine release in Aplysia ganglion neurons: a histological, voltammetric and electrophysiological study. Neuroscience. 1995 Dec;69(3):985–995. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00316-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S. The 1991 Ulf von Euler Lecture. The L-arginine: nitric oxide pathway. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Jul;145(3):201–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroz L. L., Chen D., Gillette M. U., Gillette R. Nitric oxide synthase activity in the molluscan CNS. J Neurochem. 1996 Feb;66(2):873–876. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.66020873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroz L. L., Winlow W., Turner R. W., Bulloch A. G., Lukowiak K., Syed N. I. Nitric oxide synthase-immunoreactive cells in the CNS and periphery of Lymnaea. Neuroreport. 1994 Jun 2;5(10):1277–1280. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199406020-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mothet J. P., Fossier P., Tauc L., Baux G. NO decreases evoked quantal ACh release at a synapse of Aplysia by a mechanism independent of Ca2+ influx and protein kinase G. J Physiol. 1996 Jun 15;493(Pt 3):769–784. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Bicker G. Calcium-activated release of nitric oxide and cellular distribution of nitric oxide-synthesizing neurons in the nervous system of the locust. J Neurosci. 1994 Dec;14(12):7521–7528. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-12-07521.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape H. C., Mager R. Nitric oxide controls oscillatory activity in thalamocortical neurons. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90182-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prast H., Philippu A. Nitric oxide releases acetylcholine in the basal forebrain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 May 27;216(1):139–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90223-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randriamampita C., Ciapa B., Trautmann A. Cyclic-GMP-dependent refilling of calcium stores in macrophages. Pflugers Arch. 1991 Feb;417(6):633–637. doi: 10.1007/BF00372962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Benfenati F., Poulain B., Rossetto O., Polverino de Laureto P., DasGupta B. R., Montecucco C. Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):832–835. doi: 10.1038/359832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlapfer W. T., Woodson P. B., Tremblay J. P., Barondes S. H. Depression and frequency facilitation at a synapse in Aplysia californica: evidence for regulation by availability of transmitter. Brain Res. 1974 Aug 16;76(2):267–280. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H. NO., CO and .OH. Endogenous soluble guanylyl cyclase-activating factors. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jul 27;307(1):102–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80910-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuman E. M., Madison D. V. Nitric oxide and synaptic function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:153–183. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.001101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuman E. M., Meffert M. K., Schulman H., Madison D. V. An ADP-ribosyltransferase as a potential target for nitric oxide action in hippocampal long-term potentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):11958–11962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.11958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. R., Bennett M. R. The effect of nitric oxide on the efficacy of synaptic transmission through the chick ciliary ganglion. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):627–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13857.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekizawa K., Fukushima T., Ikarashi Y., Maruyama Y., Sasaki H. The role of nitric oxide in cholinergic neurotransmission in rat trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):816–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13885.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauc L. Transmission in invertebrate and vertebrate ganglia. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):521–593. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R. Nitric oxide: a radical neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1994 Jan;42(1):129–160. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(94)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund C. U., Olgart C., Wiklund N. P., Gustafsson L. E. Modulation of cholinergic and substance P-like neurotransmission by nitric oxide in the guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):833–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. B., Li X., Gu X., Jope R. S. Modulation of endogenous ADP-ribosylation in rat brain. Brain Res. 1992 Oct 2;592(1-2):49–56. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91657-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo M., Hu Y., Schultz C., Kandel E. R., Hawkins R. D. Role of guanylyl cyclase and cGMP-dependent protein kinase in long-term potentiation. Nature. 1994 Apr 14;368(6472):635–639. doi: 10.1038/368635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo M., Kandel E. R., Hawkins R. D. Nitric oxide and cGMP can produce either synaptic depression or potentiation depending on the frequency of presynaptic stimulation in the hippocampus. Neuroreport. 1994 May 9;5(9):1033–1036. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199405000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:13–31. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



