Abstract
The outcome of an infection with any given pathogen varies according to the dosage and route of infection, but, in addition, the physiological state of the host can determine the efficacy of clearance, the severity of infection and the extent of immunopathology. Here we propose that the forkhead box O (FOXO) transcription factor family — which is central to the integration of growth factor signalling, oxidative stress and inflammation — provides connections between physical well-being and the form and magnitude of an immune response. We present a case that FOXO transcription factors guide T cell differentiation and function in a context-driven manner, and might provide a link between metabolism and immunity.
The signal transduction of metazoans seems to be both complex beyond understanding and simple, in that a limited number of pathways, which are conserved across vast evolutionary time, control most cell fate decisions. Many of these signalling pathways were first traced in yeast, worms, flies or dedifferentiated cells in tissue culture, and this has provided a starting point for understanding cellular and organismal responses to environmental change. We imagine that with increasing organismal complexity, new differentiated cell types arose, and the fundamental signalling pathways of single-cell organisms were redirected to integrate new inputs and compute selectable, advantageous results. Thus, similarly rooted pathways in different cell types may or may not serve a common purpose or programme of gene expression.
Forkhead box O (FOXO) transcription factors are central to many aspects of metazoan physiology (BOX 1). They are named for their forkhead domain, a DNA-binding domain of ~100 amino acids, and for their membership of the O subclass1. They regulate cell-cycle progression, DNA repair and apoptosis and, as such, are considered to be tumour suppressor proteins2–5. They also respond to oxidative stress and regulate ageing, in part through the detoxification of reactive oxygen species and the control of DNA repair pathways6,7. Furthermore, they affect metabolism and the anerobic or aerobic generation of ATP at multiple control points8. More recently, FOXO1 was shown to control a programme of pluripotency in human and mouse embryonic stem cells, probably by directly controlling the transcriptional activity of OCT4 (also known as POU5F1) and SOX2 (REF. 9). It is possible, although not proven, that most if not all cell fates are in some manner regulated by FOXO transcription factors. This great variety of cellular functions seemingly directed by FOXO transcription factors illustrates the principle that individual transcription factors do not determine cell-type specification. Rather, a given transcription factor functions as a scaffold that is post-transcriptionally modified as a result of cellular context, and thus common signalling modules direct different programmes of gene expression. No gene is always activated by a given transcription factor, and conversely there is no circumstance under which a transcription factor activates every one of its target genes10. Specifically, the expression of a FOXO transcription factor itself is not predictive of a cellular function or state of differentiation; rather, it enables the amplification of cellular potential. It can provide an integration point for several inputs and induce distinct programmes of gene expression while retaining conserved mechanisms and pathway connections.
Box 1. The FOXO transcription factor family.
In jawed vertebrates, possibly excluding cartilaginous fish, there are four major forkhead box O (FOXO) paralogues that are orthologous to the single-copy genes found in urochordates, nematodes (in which this gene is known as daf-16) and arthropods (in which this gene is known as foxo). The four paralogues arose from an initial duplication event that produced the FOXO1/FOXO4 gene lineage and the FOXO3/FOXO6 gene lineage, followed by a second pair of duplication events that produced the four separate, unlinked genes: FOXO1, FOXO3, FOXO4 and FOXO6 (REF. 165). FOXO1, FOXO3 and FOXO4 are widely expressed, and the encoded proteins have many of the same post-translational regulatory mechanisms. By contrast, FOXO6 is largely expressed in the nervous system and is the most diverged evolutionarily, and the protein it encodes is subject to alternative mechanisms of post-translational regulation165,166. In mammals, FOXO1 is most highly expressed in B cells, T cells and ovaries66, although genetic analyses have shown it to have an important function in many tissues5,167. Foxo1-mutant mice exhibit embryonic lethality at embryonic day 10.5 owing to impaired vascular development168,169. FOXO3 expression is found in most tissues, including lymphocytes and myeloid cells, and Foxo3-mutant mice are largely without a noticeable phenotype with the exception that female mice exhibit early depletion of functional ovarian follicles168,170. One mouse strain with an insertional mutation in Foxo3 seemed to develop spontaneous immunopathology15; however, this was not apparent in two other Foxo3-mutant strains43,168,170. FOXO4 is similarly expressed across human tissues at an apparently low level66. Mice with loss-of-function mutations in Foxo4 have no known phenotypic differences from wild-type mice.
As reviewed extensively elsewhere11–14, and briefly below, FOXO transcription factors respond to growth factors, oxidative stress, inflammation and nutritional abundance — physiological conditions that influence the magnitude and effectiveness of an immune response. In turn, FOXO transcription factors regulate cell survival, division and energy utilization, and these activities of FOXO transcription factors would be predicted to strongly affect the expansion and contraction of antigen-responsive lymphocyte populations.
In addition, more recent work has shown that FOXO transcription factors have been co-opted to regulate specialized characteristics of lymphocyte homeostasis, including turnover, homing and differentiation12,15–17. In this Review, we address the possibility that FOXO transcription factors programme lymphocytes to respond to diverse physiological changes, some of which are advantageous whereas others may contribute to immune pathology. We also highlight recent work showing that FOXO transcription factors are central to multiple processes of T cell differentiation, including the formation of memory T cells. The study of FOXO transcription factors now affords an opportunity to begin to understand the integration of immunity with the physiological state of an organism, which includes metabolic function, inflammation and oxidative stress.
Control of FOXO transcriptional activity
Cell type-specific expression
FOXO paralogues are expressed widely, although each has a unique pattern of tissue-specific expression. Several transcription factors have been shown to directly affect the expression of FOXO genes. Such factors include FOXC1, E2F1, p53, E2A, HEB (also known as TCF12) and, interestingly, FOXO1 and FOXO3 themselves, implying a positive-feedback control mechanism18–20. Through such feedback, post-translational inhibitory modifications to FOXO transcription factors (as discussed below) could reduce the transcription of FOXO genes. The transcriptional basis for the preferential expression of FOXO1 in lymphocytes is not understood, but signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) seems to bind to the promoters of Foxo1 and Foxo3, and Stat3−/− naive T cells have low levels of both Foxo1 and Foxo3 mRNA21. In the determination of B cell fate, E2F1 and E2A have been shown to bind to the Foxo1 locus22. Currently, the field awaits a comprehensive analysis of the general and lymphocyte-specific promoter and enhancer binding sites that are active in the Foxo1 and Foxo3 genes.
Post-translational modifications
FOXO transcription factors are subject to extensive and varied post-translational modifications that affect their abundance, localization and transcriptional activity. Together these modifications have been described as a FOXO code11,13. Such modifications have been found in various cell types, but, although they are assumed to be generally applicable, they have not been extensively studied in T cells.
A major pathway of FOXO regulation is initiated by growth factors, such as insulin, and results in the activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) (FIG. 1). The activity of PI3K causes the recruitment of the kinases AKT and SGK1 to the cell membrane and their phosphorylation by 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1)23,24. AKT and SGK1 can directly phosphorylate FOXO transcription factors on three sites, but to mediate this activity they must also be phosphorylated by mTORC2 (REFS 25–27). Until recently, the activation requirements for mTORC2 were not understood, but a genetic screen in yeast followed by studies in mammalian cell lines have shown that PI3K enhances a (translation-independent) interaction between mTORC2 and the ribosome, and it is this interaction that allows mTORC2 to phosphorylate AKT within its hydrophobic motif (at S473)28. The result of the triple phosphorylation of FOXO transcription factors by AKT or SGK1 (at T24, S256 and S319) (FIG. 2) is nuclear export and degradation7,29,30, and this basic mechanism is conserved across all the phyla that have been examined31. This mechanism is partially mimicked by cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), which is important for the transition from G1 phase to S phase in the cell cycle and which has been shown to phosphorylate FOXO1 at S249 to induce nuclear export. This export presumably promotes cell survival during cell-cycle progression, and it is abrogated by DNA damage in a p53-independent manner32. The inhibitory mechanism mediated by AKT or SGK1 functions in T cells stimulated through the T cell receptor (TCR), common γ-chain (γc) cytokine receptors or homing receptors2,3,33–35.
Figure 1. A signalling scheme regulating FOXO transcription factors.
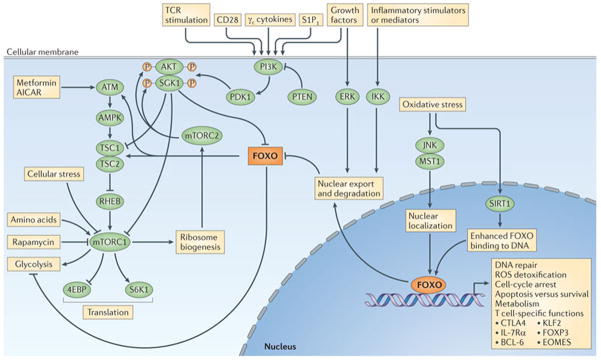
Forkhead box O (FOXO) transcription factors make multiple connections with the cellular signalling network. Examples of connecting proteins include: phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and AKT29,30,173–175; ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM)176,177; tuberous sclerosis protein 2 (TSC2)178; extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)179; JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK)180; mammalian STE20-like kinase 1 (MST1)49,181; IκB kinase (IKK)42,182; mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)25; and CREB-binding protein (CBP)183. The mTOR pathway is inhibited in T cells by metformin, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside (AICAR)159 and rapamycin160. FOXO transcription factors also affect glycolysis54. γc, γ-chain; 4EBP, EIF4E-binding protein 1; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; BCL-6, B cell lymphoma 6; CTLA4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; EOMES, eomesodermin; IL-7Rα, interleukin-7 receptor subunit-α; KLF2, Krüppel-like factor 2; mTORC, mTOR complex; PDK1, 3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; S1P1, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1; S6K1, S6 kinase 1; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; TCR, T cell receptor.
Figure 2. Inhibitory and activating post-translational modifications of FOXO1 transcription factors mapped onto a schematic diagram of the functional domains.
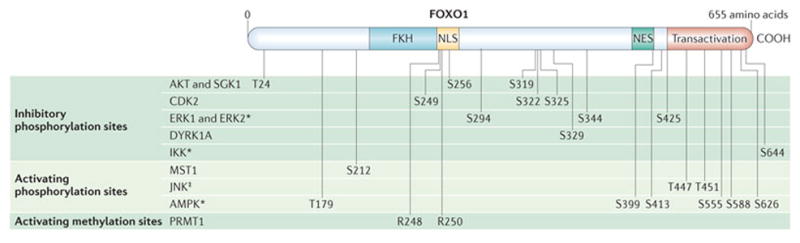
Unless indicated the post-translational modifications were demonstrated for forkhead box O1 (FOXO1). See the FIG. 1 legend for references with the exception of dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A)184. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; CDK2, cyclin-dependent kinase 2; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FKH, forkhead domain; IKK, IκB kinase; JNK, JUN N-terminal kinase; MST1, mammalian STE20-like kinase 1; NES, nuclear export signal; NLS, nuclear localization signal; PRMT1, protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1; transactivation, transcriptional activation domain. *Shown for FOXO3. ‡Shown for FOXO4.
An additional growth factor-controlled inhibitory pathway is mediated through the phosphorylation of FOXO3 at three unique sites by extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) (FIG. 2), and this results in MDM2-mediated ubiquitylation and proteosomal degradation of FOXO3 (REF. 36). This pathway also seems to operate in T cells. Under conditions of regulatory T (TReg) cell differentiation, deletion of Erk2 resulted in a threefold or greater increase in the expression of 20 genes, and three of these genes were direct FOXO1 targets: interleukin-7 receptor subunit-α (Il7ra), L-selectin (Sell) and Krüppel-like factor 2 (Klf2)37. Similarly to growth factors, pro-inflammatory cytokines — such as tumour necrosis factor (TNF) — can also affect the course of an immune response, and a central inflammatory pathway results in the nuclear localization of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) through the activity of IκB kinase (IKK)38,39. Studies have shown that IKK is the key survival factor for acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) blast cells40,41, and it functions through the inactivation of FOXO3 (REF. 42). An implication is that inflammatory processes, however they are induced, inactivate FOXO3 (through increased IKK activity), and this could affect T cell or dendritic cell (DC) function (as described later)15,43. Another mode of FOXO turnover may be regulated by GTPases of the immunity-associated protein family (GIMAPs), which are associated with human autoimmunity44–46. T cells from mice with a mutation in Gimap5 displayed a progressive loss of FOXO1, FOXO3 and FOXO4 and a concomitant loss of TReg cell function47. The authors speculated that GIMAP5 regulates the turnover of FOXO transcription factors through an increase in the expression of S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2) and thus proteasomal degradation.
In opposition to these FOXO-inhibitory pathways is oxidative stress, the effects of which are propagated through several post-translational FOXO modifications. These include alternative phosphorylations by JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK) or mammalian STE20-like kinase 1 (MST1); both prevent the interaction of 14-3-3 scaffold proteins with FOXO transcription factors, thereby promoting FOXO nuclear localization48,49. The JNK phosphorylation sites have been identified for FOXO4 but are not conserved in other paralogues; however, JNK also phosphorylates 14-3-3 proteins. As this too interferes with FOXO binding, one possibility is that JNK indirectly regulates the nuclear localization of all FOXO transcription factors50. In addition, arginine methylation of FOXO transcription factors by protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) inhibits AKT-mediated phosphorylation at S256, thereby preventing AKT-mediated nuclear exclusion51. Oxidative stress can also affect p300-mediated acetylation and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1)-mediated deacetylation of FOXO transcription factors in a temporally complex manner52,53. In some cases, these modifications can supersede growth factor-mediated inhibition of FOXO transcriptional activity; however, we note that not all of these mechanisms have been verified in T cells.
FOXO transcription factors in the liver are also regulated by nutrient levels and metabolic control mechanisms54. The energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) enhances the transcriptional activity of FOXO3 directly through phosphorylation at six unique sites55, and indirectly through inhibition of the mTORC2 pathway56. In response to nutrient availability, FOXO transcription factors are also modified and activated by O-linked glycosylation with N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), which is catalysed by a single enzyme, O-GlcNAc transferase. This modification functions as an energy sensor because it is highly sensitive to the concentration of the donor sugar, UDP-GlcNAc, which is the end product of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway57–59. As the amount of UDP-GlcNAc is regulated by nearly every metabolic pathway, a prediction is that FOXO activity is responsive to the overall metabolic state of the cell. These modifications by AMPK and O-GlcNAc transferase have been described in liver, muscle and fat, but we still do not know how they control FOXO transcription factors in lymphocytes, macrophages or DCs. We also do not yet know how FOXO transcription factors integrate metabolism with T cell responses or the overall state of inflammation.
miRNAs
FOXO transcription factors are also subject to post-transcriptional control by multiple microRNAs (miRNAs). For example, miR-27a, miR-96 and miR-182 decrease FOXO1 mRNA expression in breast cancer cells60. A contemporaneous report showed that melanoma metastasis depends on miR-182-mediated inhibition of FOXO3 expression61, whereas the expression of FOXO1 in endometrial cancer cells seems to be regulated by as many as five miRNAs62. In antigen- or mitogen-stimulated mouse T cells, miR-182 is induced by IL-2 and decreases FOXO1 expression, allowing T cell proliferation to continue even after growth factor-induced, AKT-mediated inhibition of FOXO transcription factor activity wanes63. Conversely, inhibition of miR-182 causes increased levels of Foxo1 mRNA and decreased T cell proliferation secondary to increased cell death.
Another miRNA that potentially inhibits FOXO expression is miR-155. Studies have identified miR-155 as a signature of natural TReg cells and have shown it to be important for targeting mRNAs encoding suppressor of cytokine signalling 1 (SOCS1), PU.1, MAF, activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), SH2 domain-containing inositol 53-phosphatase 1 (SHIP1) and interferon-γ(IFNγ)64. In addition, miR-155 targets Foxo3 transcripts in a T cell line and in mouse T cells65. As genetic studies have shown that the dominant FOXO transcription factor in T cells is FOXO1 (REF. 66), we predict that dysregulation of FOXO3 expression in T cells through gain or loss of miR-155 would not be immediately discernable43. However, a recent report showed that loss of Foxo3 caused a twofold increase in the proliferation of CD8+ T cells in some tissues in response to infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus67. This suggests that miR-155 could contribute to the regulation of T cell clonal expansion and memory. As FOXO1 and FOXO3 additively control the differentiation of TReg cells68,69, another possibility is that the balance between conventional T cells and TReg cells is determined, in part, by miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation.
Targets of FOXO transcriptional control
Direct DNA-binding transcriptional activity
The forkhead DNA-binding domain (also known as the winged-helix domain) of FOXO transcription factors is evolutionarily conserved and recognizes the sequence motif 53-GTAAA(T/C)AA-33 (or 53-TT(A/G) TTTAC-33), which is known as the DAF-16 binding element (DBE)70 (FIG. 3). The actual recognition sequence is somewhat broader, however, as FOXO1 has a fivefold higher affinity for a DBE sequence that includes T-rich 33 flanking sequences71. FOXO proteins also bind with lower affinity to the insulin response element (IRE), which has the sequence 53-(C/A)(A/C)AAA(C/T)AA-33 (REFS 71,72). Specific acetylation or phosphorylation of FOXO1 was shown to inhibit or entirely preclude DNA binding, directly demonstrating that post-translational modifications affect the transcriptional function of FOXO transcription factors in addition to their intracellular localization72.
Figure 3. Context-dependent FOXO transcriptional activity.
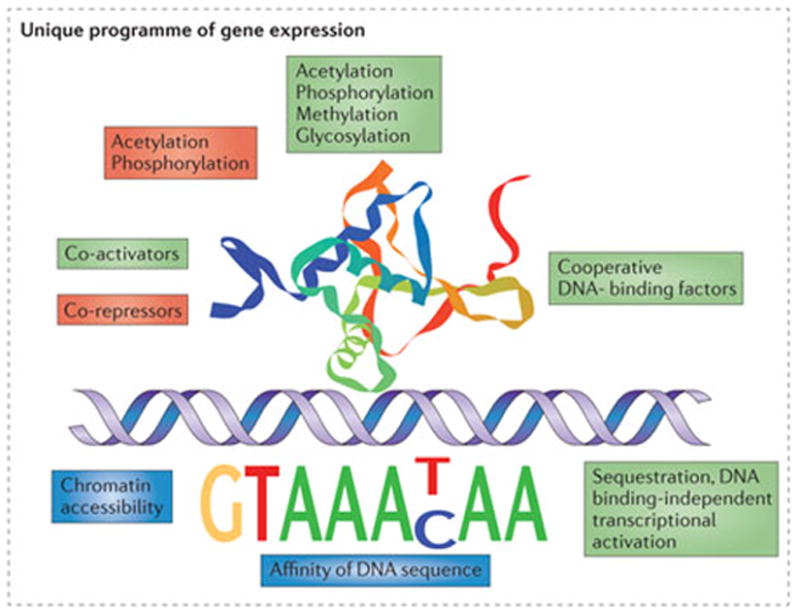
The figure shows a schematic representation of the forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) DNA-binding domain (amino acids 150–249) bound to the FOXO consensus DNA sequence (the structural data were obtained from Protein Data Bank entry 3C06 (REF. 71)). The transcriptional activity depends on recruited cofactors, post-translational modifications and cooperative binding, which can have positive (green) or negative (red) effects. FOXO transcription factors bind with differing affinities to DNA sequences related to the consensus site. FOXO factors can also affect chromatin conformation, thereby acting as gateway factors to make gene loci accessible for further regulation. The expectation is that FOXO factors offer unique programmes of gene expression in each distinct cell type.
FOXO transcription factors that are bound to DNA function as independent transcriptional activators, as deduced from their roles in oncogenesis73,74. FOXO1 was originally identified as part of a fusion protein with paired box protein 3 (PAX3) resulting from a chromosomal translocation that is responsible for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma75. The DNA-binding domain and thus target gene specificity was derived from PAX3, whereas the transcriptional activation domain came from FOXO1 (the reverse, which might enhance the gene expression programme of the FOXO1 tumour suppressor, would not be expected to lead to oncogenesis). Both FOXO3 and FOXO4 are also targets of chromosomal translocations in mixed-lineage leukaemias76; the fusions mainly occur within and disrupt the FOXO DNA-binding domain, resulting in chimeric proteins that derive transcriptional activity from the FOXO factors. It would seem that the FOXO transactivation domains are particularly potent.
Other forms of transcriptional activity
FOXO transcription factors might also regulate transcription in a DNA-binding-independent manner, as mutant FOXO variants with inactivated DNA-binding domains were still able to regulate a subset of FOXO target genes77. A caveat is that these results were derived using an overexpressed and constitutively nuclear form of FOXO1 in PTEN-deficient cells. FOXO transcription factors also have chromatin binding and remodelling functions, endowing them with the ability to modulate active chromatin states78. In this regard, the transcriptional activity of FOXO transcription factors is often or always achieved by association with other transcriptional activators or repressors. FOXO transcription factors have been shown to associate with SMAD proteins, histone deacetylases and acetyltransferases, many nuclear hormones, β-catenin and other transcriptional regulators79. The mechanisms of co-regulation include direct binding interactions, sequestration and cooperative promoter binding sites (FIG. 3). FOXO transcription factors in collaboration with other factors are thus able to integrate extrinsic information from many different pathways to coordinately initiate or facilitate varied programmes of transcriptional regulation. As stated above, the target genes of FOXO factors might be widely disparate in different tissues owing to differences in chromatin accessibility, available cofactors and post-translational modifications. Thus, our ability to extrapolate specific roles for FOXO transcription factors between different tissues is likely to be limited.
Control of T cell gene expression
The identification of FOXO target genes in T cells has depended on multiple avenues of investigation (BOX 2). Published studies show that several direct FOXO gene targets are actively transcribed in T cells. One important target is Il7ra66,68,80, which encodes IL-7Rα, a subunit of the primary survival receptor for naive T cells81. FOXO1 binds to an enhancer approximately 3 kb upstream of the Il7ra start site, and acute deletion of Foxo1 causes the loss of Il7ra expression in naive T cells66. A second important target is Klf2, which in turn controls the expression of Sell (which encodes L-selectin) and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1pr1, which encodes S1P1). These receptors are important for lymphocyte entry into and exit from lymphatic tissues66,82,83. In addition, FOXO transcription factors control Klf4, a tumour suppressor gene that is particularly active in B cells84,85. As discussed below, FOXO transcription factors also directly regulate the expression of Foxp3 (REFS 86,87) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (Ctla4)69, which are essential for the differentiation and function of TReg cells. Furthermore, there is evidence that FOXO transcription factors directly control the expression of B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6)88–90, which encodes a transcriptional repressor that is required for the differentiation of CD4+ T follicular helper cells (TFH cells), B cells, TReg cells, CD8+ T cells and natural killer T (NKT) cells91–95. In each case, BCL6-expressing cells have a tendency to localize to lymphoid follicles, and one of the roles of BCL-6 is to direct B and T cells into close proximity as part of the multifaceted germinal centre response. More recently, FOXO transcription factors were shown to bind to a promoter site in the eomesodermin (Eomes) gene and to control its expression in differentiated CD8+ T cells96. Together, the known cell type-specific FOXO target genes profoundly affect the survival, homing, proliferation and differentiation of T cells. By targeting these genes, together with numerous other, more widely expressed genes, FOXO transcription factors control the immune system in varied and diverse ways14 (TABLE 1).
Box 2. Analysis of FOXO transcription factor target genes.
Several criteria for identifying forkhead box O (FOXO) target genes can be used to assess the participation of FOXO transcription factors in lymphocyte-specific gene expression. One is the evolutionarily conserved presence of a FOXO-binding consensus motif in the promoter or enhancer regions of a gene of interest. A second criterion is the specific binding of FOXO transcription factors to such a site in T cells, as shown by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA), chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) or ChIP followed by sequencing (ChIP–seq) experiments. A third is the demonstration that a sequence containing the FOXO-binding consensus motif can function as an active regulatory region in T cell-specific reporter experiments. A fourth means of identifying a role for FOXO transcription factors in the transcriptional regulation of a particular gene is to show that acute genetic deletion of one or more FOXO genes results in the loss of target gene expression. The fifth commonly presented form of evidence is that constitutively nuclear mutant forms of FOXO transcription factors induce the expression of a given gene. Combinations of one or more of these criteria have identified several important FOXO target genes in T cells, but new technologies will undoubtedly establish target genes more definitively. Such an analysis would consist of global gene expression analyses (using a microarray or mRNA sequencing) with and without the acute deletion of a FOXO gene, ChIP–seq to identify FOXO-bound regulatory sequences (enhancers and silencers), and 3C techniques to identify the physical associations between regulatory sequences and 53 proximal promoters171,172.
Table 1.
Cell type-specific phenotypes of Foxo1- and Foxo3-knockout cells
| Cell type | Foxo1 knockout | Foxo3 knockout | Notes | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thymic TReg cells | Strongly depleted | No effect | FOXO1 may control part of the TReg cell gene expression programme, including Ctla4 | 69,86 |
| TReg cells in secondary lymphoid organs | Present with Ki67+ phenotype | No effect | In Foxo1-knockout mice, the small TReg cell population that develops may homeostatically expand | 69,86 |
| Induced TReg cells (in culture) | No induction, TH1 cells result | Reduced induction | FOXO1 is required for the TGFβ-induced downregulation of T-bet expression | 69,86,87 |
| CD4+ T cells | Decreased numbers of naive T cells; increased numbers of activated CD4+ T cells | No effect | The reduction in naive T cells is due to the loss of IL-7Rα and homing receptor expression; the increase in activated T cells is secondary to a loss of functional TReg cells | 66,68,83 |
| TFH cells | High numbers of TFH cells and spontaneous germinal centre formation | No effect | The effects in Foxo1-knockout mice may depend on the loss of TReg cells; FOXO transcription factors may regulate BCL-6, which is necessary for TFH cell differentiation, although the direction of regulation is the reverse of that expected | 69 |
| CD8+T cells | Decreased numbers of naive CD8+ T cells (owing to a loss of IL-7 Rα, L-selectin and S1P1 expression); no increase in spontaneously activated CD8+T cells | No effect | Activation of FOXO1-deficient naive CD8+ T cells progresses normally, in contrast to that of CD4+T cells | 66,68,83 |
| CD8+ effector T cells | FOXO1 inhibits T-bet expression and thus the CD8+ T cell effector molecules IFNγ and granzyme B | Increased approximately twofold owing to enhanced survival | IL-12 promotes T-bet expression through the inactivation of FOXO1 in culture | 67,96 |
| CD8+ memory T cells | Unknown | Increased, approximately twofold | FOXO1 inhibits T-bet expression and promotes eomesodermin expression and hallmarks of memory cell formation in culture | 67,96,164 |
BCL-6, B cell lymphoma 6; CTLA4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4; FOXO, forkhead box O; IFNγ. interferon-γ; IL, interleukin; IL-7Rα, IL-7 receptor subunit-α; S1P1, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β; TFH, T follicular helper; TH1, T helper 1;TReg, regulatory T.
Role in T cell survival and cell-cycle progression
One of the characteristic features of FOXO transcription factors is their control of the cell cycle and apoptosis. Specifically, evidence has been presented that FOXO transcription factors (mainly FOXO3) positively control the expression of several cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, including p15 (also known as INK4B), p19 (also known as INK4D), p21 (also known as CIP1) and p27 (also known as KIP1), as well as that of the pro-apoptotic molecules BIM (also known as BCL2L11), PUMA (also known as BBC3) and FAS ligand (also known as CD95L)3,4,29,97–100. Most of these studies were carried out in non-lymphoid cell lines and so their relevance to T cells is not clear, although FOXO3 was shown to induce the expression of p27 and BIM in the CTLL cell line3 and that of PUMA in T cells following the withdrawal of IL-2 (REF. 98). The concept is that signalling through growth-inducing receptors (such as the TCR or cytokine receptors) transiently activates the PI3K pathway, which inactivates FOXO transcription factors, and this is the primary signal promoting cell division and survival101. A caveat is that constitutively active AKT (as a result of a PTEN deficiency) does not completely rescue the loss of viability following IL-2 withdrawal98, and thus there may be redundant death pathways operative in T cells. In fact, FOXO1- and FOXO3-deficient naive T cells do not spontaneously enter the cell cycle, and mice with a haematopoietic deletion of Foxo1, Foxo3 and Foxo4 do not develop lymphomas until 22 weeks of age, with almost 75% of the mice remaining disease-free for 75 weeks5.
A further complication is that FOXO1 seems to have a role distinct from that of FOXO3. FOXO1 promotes the survival of naive T cells through the expression of IL-7Rα and thus BCL-2 (REFS 66,68). Furthermore, CD4+ but not CD8+ T cells require FOXO1 for antigen-or mitogen-stimulated population expansion, both in culture and in vivo. In particular, following the acute deletion of Foxo1 and cell activation through CD3 and CD28, CD4+ T cells progress through multiple rounds of cell division, but undergo apoptosis at a very high rate (Y. Kerdiles and E.L.S., unpublished data). This defect in survival was not rescued by the transgenic expression of Il7ra, and the mechanism underlying a requirement for FOXO1 in T cell survival is currently unknown. Similar experiments with FOXO3-mutant T cells stimulated in vitro revealed no differences compared with wild-type T cells43. The unique roles for FOXO1 and FOXO3 in T cell survival and division have so far not been resolved; however, these studies suggest that FOXO1 expression is required for naive T cell survival and that its nuclear expression is attenuated, but not ablated, following T cell activation. By contrast, increased FOXO3 activity induced by a growth factor deficiency is pro-apoptotic. The underlying basis for these intricately controlled and opposing functions is presently unknown.
Changes in FOXO3 expression are apparent in T cells from HIV-infected patients. HIV induces the apoptosis of primary CD4+ T cells, and the presence of the HIV protein Tat alone is sufficient to recapitulate this effect. Tat was proposed to function through the activation of PTEN and FOXO3, and, given its propensity to cross the plasma membrane, it may not act in a cell-autonomous manner102–104. In addition, CD4+ memory T cells from HIV-infected individuals who control HIV replication (elite controllers) have increased amounts of phosphorylated FOXO3, and this is correlated with the increased survival of memory CD4+ T cells105. Another study showed that preventing FOXO3 phosphorylation in CD4+ central memory T cells increased apoptosis106. The proposed model is that an increase in FOXO3 activity, possibly owing to Tat signalling in patients with HIV, results in T cell apoptosis, whereas attenuation of FOXO3 through phosphorylation (as occurs in elite controllers) results in enhanced memory T cell survival. From this we conclude that the amount, localization, activity and specificity of FOXO transcription factors, as regulated by some or all of the mechanisms already described, are important in determining the outcome of an immune response. In particular, the balance between persistent pathogen infections and clearance may be influenced by the precise physiological state of the infected individual as interpreted by FOXO transcription factors.
TReg cell development and function
Natural TReg cell development
In addition to having defects in naive T cell survival and homing (owing to decreased expression of Il7Ra and Klf2)66,68,83, mice with a T cell-specific conditional mutation in Foxo1 have substantial immunopathology that is not cell autonomous but rather is associated with decreased numbers of FOXP3+ natural TReg cells in the thymus69,86. This diminution in numbers is even more pronounced when FOXO1-deficient T cell precursors have to compete with wild-type precursors in a mixed bone marrow chimaera69. Furthermore, mice lacking both FOXO1 and FOXO3 in T cells have few natural TReg cells in the thymus and decreased TReg cell numbers in secondary lymphoid organs when at a young age but have normal numbers of FOXP3+ T cells as adults. Mortality from excessive immunopathology was seen starting at 8 weeks of age, and experiments showed that FOXO1-deficient bone marrow cells were unable to complement a loss of FOXP3 in mixed bone marrow chimaeras. The conclusion drawn from these studies is that both the development and function of natural TReg cells are retarded in the absence of FOXO1, with an additive contribution from FOXO3 (REFS 66,86,87).
These results highlight the suggestion that FOXP3, although essential for TReg cell function, is not a lineage specification factor. Studies have shown that it is only one of the essential transcription factors required for the development of a TReg cell phenotype107–111. In fact, an analysis of genes expressed by various TReg cells showed that FOXP3 expression positively correlated with the expression of only a small number of TReg cell signature genes108. Additional studies indicate that the AKT–mTOR axis might regulate a substantial portion of the TReg cell gene signature independently of FOXP3 (REFS 112,113). A conclusion of these studies was that a higher level of regulation, upstream of FOXP3, determines the TReg cell lineage108, and one possibility is that FOXO transcription factors, which are inhibited by AKT, constitute an essential aspect of this higher level of control.
Induced TReg cell development
Mature naive CD4+ FOXP3− T cells can give rise to induced TReg cells in the presence of transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ)114. When naive CD4+ T cells lacking FOXO1 or both FOXO1 and FOXO3 were cultured in this manner, few FOXP3+ induced TReg cells developed69,86,87. FOXO3-deficient CD4+ T cells also showed a decreased ability to develop into induced TReg cells, although the effect was less pronounced than for FOXO1 deficiency87.
Although there are some discrepancies, in general conditions that favour activation of the PI3K–AKT pathway retard the differentiation of induced TReg cells, whereas inhibition of the PI3K–AKT pathway promotes TReg cell differentiation87,112,115–119. We thus propose that inhibition of PI3K–AKT signalling is specifically required for the nuclear localization and activity of FOXO transcription factors69. This is also in accord with the activity of vitamin A metabolites and vitamin D, both of which have been shown to induce nuclear localization of FOXO transcription factors in myeloid leukaemia and squamous carcinoma cells116,120 and, in separate studies, the induction of TReg cells121–123.
At the heart of these effects is the mTOR pathway — the master regulator of protein synthesis124,125. mTOR forms two distinct kinase complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2, and these complexes are intricately related in terms of their activity as well as their structure126. mTORC1 is activated downstream of AKT by the inhibitory phosphorylation of the mTORC1 inhibitor, tuberous sclerosis protein 2 (TSC2). Activated mTORC1 promotes protein translation in several ways, including through an increase in ribosome biogenesis (FIG. 1). We can therefore deduce that this would sequentially activate mTORC2, stabilize AKT and thus lead to inactivating phosphorylations of FOXO transcription factors.
Genetic or pharmacological inhibition of mTOR leads to the generation of induced TReg cells in the absence of added cytokines, and naive T cells in which mTOR is inhibited do not differentiate into T helper 1 (TH1), TH2 or TH17 cells127. In particular, rapamycin — which inhibits mTORC1 and, with prolonged application, mTORC2 — causes activated T cells to differentiate into TReg cells113,128–130. Likewise, a T cell-specific deletion of the gene encoding mTOR causes activated T cells to assume a TReg cell phenotype131. Furthermore, mTOR signalling is decreased when the availability of essential amino acids is limited, and this decrease synergizes with TGFβ in promoting the differentiation of induced TReg cells132. Genetic ablations leading to the individual loss of mTORC1 or mTORC2 are not sufficient to cause TReg cell differentiation, implying that both pathways have to be abrogated for TReg cell differentiation to occur131. We conclude that TReg cell differentiation requires the inhibition of mTOR signalling, and we propose that this is mediated in part through an increase in the nuclear localization and activity of FOXO transcription factors.
Mechanisms of FOXO transcription factors in the function of TReg cells
The mechanisms underlying the requirement for FOXO transcription factors in TReg cell differentiation are not yet understood. The simplest idea is that FOXO transcription factors are required for the transcription of Foxp3, as studies have shown that FOXO transcription factors can bind to and transcriptionally activate a previously mapped Foxp3 promoter sequence86,87 (FIG. 4). However, we found that TReg cells are present in the secondary lymphoid organs of adult Foxo1−/−Foxo3−/− mice and have only slightly decreased FOXP3 expression69. Nonetheless, these cells are not sufficient to prevent immunopathology69,86. As TReg cells are all but absent in the thymus in the absence of Foxo1 and Foxo3, we deduce that a small number of FOXP3+ TReg cells proliferate over time to produce TReg cells in normal numbers. One proposal is that FOXO transcription factors together with REL (which binds to the CNS3 enhancer in Foxp3) facilitate chromosome accessibility within the Foxp3 locus133 to promote the eventual accumulation of other transcription factors133 (FIG. 4). Such factors include STAT1 (REF. 134), STAT5 (REF. 135), Helios136 and, notably, FOXP3 itself, which implies self-reinforcing gene expression18,133. Without REL or FOXO factors, the Foxp3 locus might be relatively inaccessible, but over time it could achieve close to full activity owing to this self-reinforcing mechanism.
Figure 4. The Foxp3 locus.
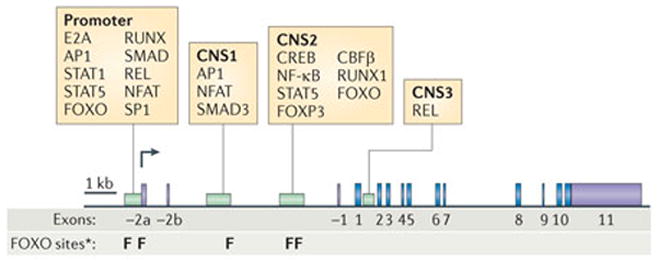
The forkhead box P3 (Foxp3) promoter and enhancers may be controlled by activator protein 1 (AP1), forkhead box O1 (FOXO1), nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT), SMAD3 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5), as well as by other factors identified through evolutionarily conserved consensus sites185. The enhancer nomenclature for Foxp3 is from REF. 133. CBFβ, core-binding factor-β; CREB, cAMP-responsive element-binding protein; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB. *Evolutionarily conserved DAF-16 binding elements.
Given the presence of FOXP3+ T cells in secondary lymphoid organs, what is the basis for the immunopathology seen in mice deficient for FOXO1 and FOXO3? It does not seem to be intrinsic to the expanded populations of effector T cells, but rather results from a lack of TReg cell function. Thus, one possibility is that a small diminution of FOXP3 expression is sufficient to handicap the extant TReg cells. Another possibility is that, in the absence of FOXO transcription factors, FOXP3+ TReg cells lack the suppressive function required for immune quiescence. Consistent with this idea, active AKT prevents FOXP3+ TReg cell differentiation, whereas it does not affect established FOXP3 expression in TReg cells112. Another study has shown that enforced expression of an active allele of AKT in human CD4+CD25+ T cells (which is presumed to constrain FOXO activity) inhibits their suppressive function137. In addition, FOXP3+ TReg cells that are deficient in both FOXO1 and FOXO3 are less efficient than wild-type cells in a suppression assay in cell culture86. One key feature of TReg cells is their expression of CTLA4, an indispensable co-receptor for TReg cell function138–140. We found that FOXO1 is required for CTLA4 expression (whether directly or indirectly) in all T cells tested, and it binds to a DBE located 193 base pairs upstream of the Ctla4 transcriptional start site69. Although there are likely to be other genes crucial for TReg cell function that are under the control of FOXO transcription factors, the requirement for FOXO1 in CTLA4 expression would itself be sufficient to explain the immunopathology seen in both Foxo1−/− and Foxo1−/−Foxo3−/− mutant mice.
TH1 cell differentiation
Recently, the mTOR–FOXO pathway has emerged as a key pathway regulating TH1 cell versus TReg cell differentiation. S1P1 (which is encoded by S1pr1) activates AKT and also activates S6 kinases downstream of the mTORC1 pathway. Experiments have shown that a loss-of-function mutation in S1pr1 promotes TReg cell development, whereas an S1pr1 gain-of-function mutation inhibits the differentiation of induced TReg cells. Instead, under conditions that promote TReg cell induction in wild-type T cells (such as the presence of TGFβ), the presence of an S1pr1 transgene diverted naive T cell differentiation towards the generation of TH1 cells141,142. In particular, the ability of TGFβ to maintain the phosphorylation of SMAD3 for between 24 and 48 hours and to induce TReg cells was lost in the presence of the S1pr1 transgene. A conclusion based on these results could be that S1P1 signalling interferes directly with the TGFβ– SMAD3 pathway, which is an important component of TReg cell differentiation. An alternative explanation could involve FOXO1. Naive FOXO1-deficient CD4+ T cells that are activated with antibodies specific for CD3 and CD28 in the presence of TGFβ do not differentiate into FOXP3+ TReg cells, as would be expected for wild-type T cells, but instead become T-bet+IFNγ+ TH1 cells69. Consistent with this result, FOXO1 is required for the TGFβ-induced inhibition of the expression of T-bet (which is encoded by Tbx21) that occurs in wild-type T cells. However, FOXO1 deficiency does not simply inhibit TGFβ signalling, as Foxo1−/− cells have normal levels of SMAD3 phosphorylation at early time points, and activation of FOXO1-deficient cells in the absence of TGFβ does not induce TH1 cell differentiation69. As SMAD proteins form transcriptional complexes with FOXO transcription factors4, the loss of sustained SMAD3 phosphorylation at later times may be indirect and result from the inactivation of FOXO1 through S1P1 signalling. We conclude that, under some conditions, TH1 cells and TReg cells constitute alternative fates that depend on S1P1 signalling, mTOR activation and FOXO transcription factor activity.
T follicular helper cells
FOXO transcription factors clearly have a role in regulating the differentiation of CD4+ T cells into TReg cells and TH1 cells; however, the potential role of FOXO transcription factors in regulating the differentiation of other T cell subsets is just beginning to be studied. Mice with a T cell-specific deletion of Foxo1 spontaneously accumulate a large number of CXCR5+PD1+ TFH cells, and this corresponds with the appearance of germinal centres, class-switched B cells and DNA-specific antibodies69. The differentiation of TFH cells from naive CD4+ T cells normally depends on signalling through the co-stimulatory molecule inducible T cell co-stimulator (ICOS) and on sequential antigen presentation by DCs and B cells143–146. Signalling through ICOS is dependent on PI3K, such that a mutation in the cytoplasmic tail of ICOS that prevents PI3K recruitment decreases TFH cell development147. Furthermore, mice with a T cell-specific deletion of the gene encoding the p110γ subunit of PI3K have greatly decreased numbers of TFH cells after immunization with foreign proteins adsorbed to alum adjuvant148. These studies clearly establish the role of the ICOS and PI3K pathway in the differentiation or survival of TFH cells and, on the basis of the emergence of TFH cells in Cd4Cre Foxo1f/f mice, we speculate that a role of ICOS signalling is to inactivate FOXO transcription factors. However, as described above, FOXO3 has been shown to positively regulate the expression of BCL6, which encodes the essential transcription factor for TFH cell differentiation91–93. Thus, the enigma is that in some cells FOXO3 positively regulates BCL-6, even though ICOS signalling (which is required for TFH cell differentiation) would be predicted to negatively regulate all FOXO transcription factors. A recent study showed that strong IL-2 signalling inhibits the expression of a profile of TFH cell-associated genes, including Bcl6, and this was correlated with decreased binding of FOXO1 to the Bcl6 promoter149. The manner by which FOXO1 regulates BCL-6 expression, and how this relates to ICOS signalling and TFH cell differentiation, requires further study.
CD8+ T cell differentiation and function
Following host infection with an intracellular pathogen, antigen-specific naive CD8+ T cells accumulate in draining lymphatic organs, proliferate and differentiate into effector T cells. The expanding T cell population diversifies, such that a small proportion of cells acquires characteristics of memory cell precursors, whereas most cells maintain an effector phenotype. At the peak of the expansion phase (usually around 8 days after infection in mouse models of acutely infectious agents), this T cell diversity is evident on the basis of the differential expression of key cell-surface molecules. Memory precursor effector cells have a KLRG1lowCD127hi phenotype, whereas effector cells have a KLRG1hiCD127low phenotype150,151. The differentiation of activated T cells into T cell memory precursors and then long-lived memory T cells is thought to be based on a progressive and self-reinforcing programme of gene expression that may originate with stochastic changes in the expression of a few genes150–153. One part of this gene expression programme is the transcription factor EOMES154,155, and EOMES expression depends on WNT-mediated conversion of the transcription factor TCF7 (also known as TCF1) into an active complex with β-catenin156,157.
As described earlier, FOXO1 regulates programmes of homing, self-renewal, cell-cycle entry and progression, and cell survival, all of which are essential components in the control of memory versus effector T cell differentiation. In accord with this, recent work has shown that FOXO1 and FOXO3 might each have a role in CD8+ T cell differentiation. CD8+ T cells acquire some of the hallmarks of effector function (such as a KLRG1hi phenotype) through the expression of Tbx21 (which encodes T-bet), and this is amplified by antigen-induced stimulation in the presence of IL-12 (REF. 152). Reminiscent of the role of FOXO1 in the TGFβ-mediated inhibition of T-bet69, a recent study showed that IL-12 promotes Tbx21 expression by inactivating FOXO1, and Tbx21 expression can be inhibited indirectly by FOXO1 overexpression96. Furthermore, FOXO1 seems to directly target Eomes, and thus constitutes a second pathway that converges on Eomes expression in order to promote a memory cell phenotype. T cells that were adoptively transferred following in vitro activation and knockdown of Foxo1 expression survived poorly after 40 days and showed no ability to be reactivated in vivo96. Thus, FOXO1 activity may be at least one deciding factor in effector versus memory precursor CD8+ T cell differentiation. This is consistent with a report describing the effects of sustained AKT activation in CD8+ T cells, a condition that would induce the inactivation of FOXO1. Indeed, these cells had decreased levels of EOMES and TCF7 and a reduced potential to survive and adopt a memory phenotype compared with control cells158. These studies may help to explain the mechanism underlying the ability of metformin or rapamycin to promote CD8+ memory T cell formation159,160. Both drugs inhibit the mTORC1 and mTORC2 pathways161–163 and, as such, they might function in part or even entirely through their ability to promote FOXO transcription factor activity.
Other studies have shown that the maintenance of a memory T cell phenotype is an active process dependent on T cell interactions with DCs, and these interactions are mediated through CD27 and 4-1BB164. CD27 signalling correlates with decreased FOXO1 activity, leading to the conclusion that inhibition of FOXO1 is required for the maintenance of a memory T cell phenotype. Although this might seem to be inconsistent with the role of FOXO1 inactivation in inducing an effector T cell phenotype, these studies probe different stages in T cell differentiation. The exact amount of nuclear FOXO1, its available cofactors and its post-translational modifications might differ between newly emerging activated CD8+ T cells and long-term memory T cells.
Experiments also support a role for FOXO3 in CD8+ T cell proliferation. In our studies, there was a clear increase in the expansion of CD8+ T cell populations in FOXO3-deficient mice, but at early time points we found the increase to originate with the DC population. In the absence of FOXO3, DCs produced excess IL-6, TNF and CC-chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2; also known as MCP1), and the additional IL-6 was sufficient to cause higher than normal levels of T cell population expansion owing to an increase in survival43. However, a more recent study showed that in mice with a T cell-specific deletion of Foxo3, there was up to a twofold increase in the number of antigen-specific T cells present in the spleen at day 8 after virus infection67. Furthermore, one possibility is that FOXO1 and FOXO3 have overlapping, but possibly distinct, functions in CD8+ T cell proliferation and differentiation, and future studies will elucidate the specific programmes of gene expression mediated by these two paralogues.
Conclusion
In almost every aspect of T cell biology so far examined, there is a role for FOXO transcription factors. They respond to a wide range of extrinsic signals to fundamentally alter the trajectory of a T cell-dependent immune response. The programmes of gene expression affected include cell type-specific genes involved in differentiated functions, as well as genes that control the essential aspects of general cellular physiology, such as cell division, survival and metabolism. The challenge will be to isolate the direct effects of FOXO transcriptional regulation from the indirect effects that ripple and echo throughout the signalling network of the cell. Given the right antibodies or tagged versions of FOXO transcription factors, the technology is now available to definitively characterize the FOXO1 and FOXO3 gene targets at each stage of T cell differentiation.
To what end? In addition to providing a map of gene connections, we contend that such an analysis will unveil the relationships between inflammation, metabolism and oxidative stress, and the manner by which these conditions affect the strength and effectiveness of an immune response. How does hyperinsulinaemia affect the course of an acute, persistent or latent infection? Do pathogens that provoke an oxidative burst experience a different response from those that elicit high levels of inflammation? Do these physiological changes act directly on T cells, or are the effects on DCs and macrophages more important? We think that a broad analysis of the part played by FOXO transcription factors in the immune system will illuminate and eventually bring resolution to these issues of medical significance.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank D. R. Beisner, A. S. Dejean, and Y. M. Kerdiles for contributing to this work with their many experimental and conceptual insights.
Glossary
- Tumour suppressor proteins
Proteins that limit the generation of cancer. Many of these proteins regulate scheduled entry to the cell cycle or promote the apoptosis of damaged cells. Loss-of-function mutations in tumour suppressor genes increase susceptibility to cancer.
- Reactive oxygen species
Highly reactive oxygen-containing molecules that can be produced by the mitochondria in eukaryotic cells. Examples include hydrogen peroxide, ions such as hypochlorite, and free radicals such as superoxide and nitric oxide. They can be inactivated by enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase.
- mTORC2
(Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2). A complex consisting of: mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR); rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR (RICTOR); mammalian stress-activated MAP kinase-interacting protein 1 (mSIN1; also known as MAPKAP1); protein observed with RICTOR 1 (PROTOR1); PROTOR2; DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein (DEPTOR); and mLST8 (also known as GβL).
- MDM2
An E3 ubiquitin ligase that can cause the proteasomal degradation of p53 as well as of other tumour suppressor proteins such as FOXO3.
- MicroRNAs
(miRNAs). Non-coding RNA molecules that provide recognition for the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which has inhibitory effects on transcription and/or translation. This large, multisubunit, nucleoprotein complex includes DICER, which is essential for processing precursor RNA molecules, and Argonaute, which is central to silencing.
- T follicular helper cells
(TFH cells). CD4+ T cells that migrate to the B cell-rich follicles in an active immune response and provide helper functions that promote the differentiation of B cells into antibody-producing cells. They are variously described as a separate T cell subset or a further differentiation of TH1, TH2 and TH17 cells.
- CTLL cell line
A T cell line that grows indefinitely in the presence of interleukin-2 (IL-2) with no requirement for stimulation through the T cell receptor (TCR). This is not a feature of freshly explanted T cells, which require a cycle of TCR and IL-2 stimulation followed by rest before re-stimulation.
- Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
(EMSA). An assay used to measure DNA–protein interactions. Short stretches of double-stranded, radio-labelled DNA are mixed with nuclear extracts and subjected to sizing by gel electrophoresis. In the presence of bound proteins, the labelled DNA will migrate more slowly. To determine the identity of the bound proteins, specific antibodies can be added to see whether the migration of the complex is altered — either becoming even slower (‘supershifted’) or being prevented altogether.
- Chromatin immunoprecipitation
(ChIP). An assay used to determine whether specific transcription factors are bound to chromatin. DNA–protein complexes are stabilized by reversible crosslinking, the DNA is sheared to an average size of about 500 bp, an antibody specific for a suspected chromatin-associated factor is used to carry out immunoprecipitation, and the complexes are isolated. Following dissolution of the crosslinks and protein digestion, PCR is used to determine whether specific DNA sequences were co-isolated. A positive signal using appropriate controls indicates that a given factor is within proximity (about 500 bp) of the primers used to amplify the DNA.
- ChIP–seq
An assay similar to chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with the exception that the immunoprecipitated DNA is modified by the addition of coded oligonucleotides, and the resulting libraries of DNA are sequenced using massively parallel sequencing techniques.
- mRNA sequencing
In this technique, poly(A)-containing mRNA isolated by hydridization to oligo-dT columns may be fragmented and is then converted to complementary DNA (cDNA) using the enzyme reverse transcriptase. The cDNA is then prepared for parallel sequencing. The number of sequencing reads specific for each gene correlates with mRNA abundance. Information can also be obtained pertaining to alternative splicing or transcriptional start isoforms of each gene. This technique yields accurate and abundant data, and is rapidly superseding microarray technologies.
- 3C techniques
Chromosome conformation capture (3C) is used to determine whether a distal enhancer sequence is in proximity to a promoter in a given state of a particular cell type. The basic concept is that DNA–protein and protein– protein interactions in the nucleus are reversibly crosslinked to stabilize interacting regions of DNA. The DNA is digested to completion with a restriction enzyme, and intramolecular ligation is carried out to link promoter and enhancer sequences. The resulting complex can be analysed by sequencing in several ways to identify known or unknown interacting regulatory elements.
- mTORC1
(Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1). A complex consisting of: mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), which is a serine/threonine kinase; regulatory-associated protein of mTOR (RAPTOR); proline-rich AKT substrate of 40 kDa (PRAS40), which is an mTORC1 inhibitor; mLST8 (also known as GβL), which is of unknown function; and DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein (DEPTOR), which is an mTOR inhibitor.
- CNS3 enhancer
One of four DNA regulatory regions in the Foxp3 gene (together with the promoter, CNS1 and CNS2) that was initially defined by histone modifications that are permissive for transcription. CNS1, CNS2 and CNS3 were then analysed for activity by generating mice with deletions spanning each region of the chromosome.
- Cd4Cre Foxo1f/f mice
Mice in which both alleles of the Foxo1 gene are modified to include loxP sites flanking exon 2 and in which the Cre recombinase gene from the P1 bacteriophage is expressed from a transgene using control elements of the Cd4 gene. In such mice, the Foxo1 gene is inactivated in the T cell lineage during the CD4+CD8+ stage of thymic development
Footnotes
Competing interests statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.Kaestner KH, Knochel W, Martinez DE. Unified nomenclature for the winged helix/forkhead transcription factors. Genes Dev. 2000;14:142–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dijkers PF, et al. Forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1 modulates cytokine-dependent transcriptional regulation of p27(KIP1) Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:9138–9148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.24.9138-9148.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stahl M, et al. The forkhead transcription factor FoxO regulates transcription of p27Kip1 and Bim in response to IL-2. J Immunol. 2002;168:5024–5031. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.10.5024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Seoane J, Le HV, Shen L, Anderson SA, Massague J. Integration of Smad and forkhead pathways in the control of neuroepithelial and glioblastoma cell proliferation. Cell. 2004;117:211–223. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Paik JH, et al. FoxOs are lineage-restricted redundant tumor suppressors and regulate endothelial cell homeostasis. Cell. 2007;128:309–323. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lin K, Dorman JB, Rodan A, Kenyon C. daf-16: an HNF-3/forkhead family member that can function to double the life-span of Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1997;278:1319–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5341.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Salih DA, Brunet A. FoxO transcription factors in the maintenance of cellular homeostasis during aging. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:126–136. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kousteni S. FoxO1, the transcriptional chief of staff of energy metabolism. Bone. 2012;50:437–443. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.06.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhang X, et al. FOXO1 is an essential regulator of pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Nature Cell Biol. 2011;13:1092–1099. doi: 10.1038/ncb2293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barolo S, Posakony JW. Three habits of highly effective signaling pathways: principles of transcriptional control by developmental cell signaling. Genes Dev. 2002;16:1167–1181. doi: 10.1101/gad.976502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Calnan DR, Brunet A. The FoxO code. Oncogene. 2008;27:2276–2288. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hedrick SM. The cunning little vixen: Foxo and the cycle of life and death. Nature Immunol. 2009;10:1057–1063. doi: 10.1038/ni.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.van den Berg MC, Burgering BM. Integrating opposing signals toward Forkhead box O. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14:607–621. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.van der Vos KE, Coffer PJ. The extending network of FOXO transcriptional target genes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14:579–592. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lin L, Hron JD, Peng SL. Regulation of NF-κB, Th activation, and autoinflammation by the forkhead transcription factor Foxo3a. Immunity. 2004;21:203–213. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dejean AS, Hedrick SM, Kerdiles YM. Highly specialized role of Forkhead box O transcription factors in the immune system. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;14:663–674. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ouyang W, Li MO. Foxo: in command of T lymphocyte homeostasis and tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2011;32:26–33. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2010.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Essaghir A, Dif N, Marbehant CY, Coffer PJ, Demoulin JB. The transcription of FOXO genes is stimulated by FOXO3 and repressed by growth factors. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:10334–10342. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808848200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Al-Mubarak B, Soriano FX, Hardingham GE. Synaptic NMDAR activity suppresses FOXO1 expression via a cis-acting FOXO binding site: FOXO1 is a FOXO target gene. Channels (Austin) 2009;3:233–238. doi: 10.4161/chan.3.4.9381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Welinder E, et al. The transcription factors E2A and HEB act in concert to induce the expression of FOXO1 in the common lymphoid progenitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:17402–17407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111766108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Oh HM, et al. STAT3 protein promotes T-cell survival and inhibits interleukin-2 production through up-regulation of Class O Forkhead transcription factors. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:30888–30897. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.253500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lin YC, et al. A global network of transcription factors, involving E2A, EBF1 and Foxo1, that orchestrates B cell fate. Nature Immunol. 2010;11:635–643. doi: 10.1038/ni.1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Alessi DR, et al. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Bα. Curr Biol. 1997;7:261–269. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00122-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stokoe D, et al. Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in the activation of protein kinase B. Science. 1997;277:567–570. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5325.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Guertin DA, et al. Ablation in mice of the mTORC components raptor, rictor, or mLST8 reveals that mTORC2 is required for signaling to Akt-FOXO and PKCα, but not S6K1. Dev Cell. 2006;11:859–871. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2006.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Facchinetti V, et al. The mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 controls folding and stability of Akt and protein kinase C. EMBO J. 2008;27:1932–1943. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Brunet A, et al. Protein kinase SGK mediates survival signals by phosphorylating the forkhead transcription factor FKHRL1 (FOXO3a) Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:952–965. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.3.952-965.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zinzalla V, Stracka D, Oppliger W, Hall MN. Activation of mTORC2 by association with the ribosome. Cell. 2011;144:757–768. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Brunet A, et al. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell. 1999;96:857–868. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80595-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kops GJ, et al. Direct control of the Forkhead transcription factor AFX by protein kinase B. Nature. 1999;398:630–634. doi: 10.1038/19328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Bridge D, et al. FoxO and stress responses in the cnidarian Hydra vulgaris. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e11686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Huang H, Regan KM, Lou Z, Chen J, Tindall DJ. CDK2-dependent phosphorylation of FOXO1 as an apoptotic response to DNA damage. Science. 2006;314:294–297. doi: 10.1126/science.1130512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Burgering BM, Medema RH. Decisions on life and death: FOXO Forkhead transcription factors are in command when PKB/Akt is off duty. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;73:689–701. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1202629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Charvet C, et al. Vav1 promotes T cell cycle progression by linking TCR/CD28 costimulation to FOXO1 and p27kip1 expression. J Immunol. 2006;177:5024–5031. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.8.5024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wood JE, Schneider H, Rudd CE. TcR and TcR-CD28 engagement of protein kinase B (PKB/AKT) and glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) operates independently of guanine nucleotide exchange factor VAV-1. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:32385–32394. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M604878200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yang JY, et al. ERK promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting FOXO3a via MDM2-mediated degradation. Nature Cell Biol. 2008;10:138–148. doi: 10.1038/ncb1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chang CF, et al. Polar opposites: Erk direction of CD4 T cell subsets. J Immunol. 2012;189:721–731. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 2010;140:883–899. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hayden MS, Ghosh S. NF-κB, the first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev. 2012;26:203–234. doi: 10.1101/gad.183434.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Guzman ML, et al. Nuclear factor-κB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood. 2001;98:2301–2307. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.8.2301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Frelin C, et al. Targeting NF-κB activation via pharmacologic inhibition of IKK2-induced apoptosis of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood. 2005;105:804–811. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hu MC, et al. IκB kinase promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of forkhead FOXO3a. Cell. 2004;117:225–237. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00302-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dejean AS, et al. Transcription factor Foxo3 controls the magnitude of T cell immune responses by modulating the function of dendritic cells. Nature Immunol. 2009;10:504–513. doi: 10.1038/ni.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Shin JH, et al. IA-2 autoantibodies in incident type I diabetes patients are associated with a polyadenylation signal polymorphism in GIMAP5. Genes Immun. 2007;8:503–512. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6364413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hellquist A, et al. The human GIMAP5 gene has a common polyadenylation polymorphism increasing risk to systemic lupus erythematosus. J Med Genet. 2007;44:314–321. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2006.046185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cousins L, et al. Eosinophilic bowel disease controlled by the BB rat-derived Lymphopenia/Gimap5 gene. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:1475–1485. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.09.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Aksoylar HI, Lampe K, Barnes MJ, Plas DR, Hoebe K. Loss of immunological tolerance in Gimap5-deficient mice is associated with loss of Foxo in CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 2012;188:146–154. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Brunet A, et al. 14-3-3 transits to the nucleus and participates in dynamic nucleocytoplasmic transport. J Cell Biol. 2002;156:817–828. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200112059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lehtinen MK, et al. A conserved MST-FOXO signaling pathway mediates oxidative-stress responses and extends life span. Cell. 2006;125:987–1001. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sunayama J, Tsuruta F, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y. JNK antagonizes Akt-mediated survival signals by phosphorylating 14-3-3. J Cell Biol. 2005;170:295–304. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200409117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yamagata K, et al. Arginine methylation of FOXO transcription factors inhibits their phosphorylation by Akt. Mol Cell. 2008;32:221–231. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kitamura YI, et al. FoxO1 protects against pancreatic β cell failure through NeuroD and MafA induction. Cell Metab. 2005;2:153–163. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hatta M, Liu F, Cirillo LA. Acetylation curtails nucleosome binding, not stable nucleosome remodeling, by FoxO1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;379:1005–1008. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhang W, et al. FoxO1 regulates multiple metabolic pathways in the liver: effects on gluconeogenic, glycolytic, and lipogenic gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:10105–10117. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600272200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Greer EL, et al. The energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase directly regulates the mammalian FOXO3 transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:30107–30119. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705325200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Reiling JH, Sabatini DM. Stress and mTORture signaling. Oncogene. 2006;25:6373–6383. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Haltiwanger RS, Holt GD, Hart GW. Enzymatic addition of O-GlcNAc to nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins. Identification of a uridine diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine:peptide β-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:2563–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Marshall S, Bacote V, Traxinger RR. Discovery of a metabolic pathway mediating glucose-induced desensitization of the glucose transport system. Role of hexosamine biosynthesis in the induction of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:4706–4712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hart GW, Slawson C, Ramirez-Correa G, Lagerlof O. Cross talk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: roles in signaling, transcription, and chronic disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:825–858. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060608-102511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Guttilla IK, White BA. Coordinate regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:23204–23216. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.031427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Segura MF, et al. Aberrant miR-182 expression promotes melanoma metastasis by repressing FOXO3 and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:1814–1819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808263106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Myatt SS, et al. Definition of microRNAs that repress expression of the tumor suppressor gene FOXO1 in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70:367–377. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-1891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Stittrich AB, et al. The microRNA miR-182 is induced by IL-2 and promotes clonal expansion of activated helper T lymphocytes. Nature Immunol. 2010;11:1057–1062. doi: 10.1038/ni.1945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lu LF, et al. Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive fitness to regulatory T cells by targeting SOCS1 protein. Immunity. 2009;30:80–91. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yamamoto M, et al. miR-155, a modulator of FOXO3a protein expression, is underexpressed and cannot be upregulated by stimulation of HOZOT, a line of multifunctional treg. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e16841. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kerdiles YM, et al. Foxo1 links homing and survival of naive T cells by regulating L-selectin, CCR7 and interleukin 7 receptor. Nature Immunol. 2009;10:176–184. doi: 10.1038/ni.1689. This study shows that FOXO1 regulates naive T cell survival and homing through the control of IL-7Rα and KLF2 expression, respectively. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sullivan JA, Kim EH, Plisch EH, Peng SL, Suresh M. FOXO3 regulates CD8 T cell memory by T cell-intrinsic mechanisms. PLos Pathog. 2012;8:e1002533. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002533. In this study, the authors show that a T cell-specific deletion of Foxo3 results in increased numbers of effector and memory CD8+ T cells. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ouyang W, Beckett O, Flavell RA, Li MO. An essential role of the Forkhead-box transcription factor Foxo1 in control of T cell homeostasis and tolerance. Immunity. 2009;30:358–371. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.02.003. This paper shows that FOXO1 controls naive T cell survival by regulating a programme of gene expression that includes IL-7Rα expression. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kerdiles YM, et al. Foxo transcription factors control regulatory T cell development and function. Immunity. 2010;33:890–904. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.12.002. This paper shows that FOXO1, with a contribution from FOXO3, controls TReg cell function at least partially through the control of CTLA4 expression. In addition, the experiments show that in the absence of FOXO1, TGFβ signalling does not inhibit T-bet expression and instead induces TH1 cell differentiation. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Furuyama T, Nakazawa T, Nakano I, Mori N. Identification of the differential distribution patterns of mRNAs and consensus binding sequences for mouse DAF-16 homologues. Biochem J. 2000;349:629–634. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3490629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Brent MM, Anand R, Marmorstein R. Structural basis for DNA recognition by FoxO1 and its regulation by posttranslational modification. Structure. 2008;16:1407–1416. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2008.06.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Obsil T, Obsilova V. Structural basis for DNA recognition by FOXO proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:1946–1953. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.11.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Fredericks WJ, et al. The PAX3-FKHR fusion protein created by the t(2;13) translocation in alveolar rhabdomyosarcomas is a more potent transcriptional activator than PAX3. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:1522–1535. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bennicelli JL, Fredericks WJ, Wilson RB, Rauscher FJ, 3rd, Barr FG. Wild type PAX3 protein and the PAX3-FKHR fusion protein of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma contain potent, structurally distinct transcriptional activation domains. Oncogene. 1995;11:119–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Galili N, et al. Fusion of a fork head domain gene to PAX3 in the solid tumour alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Nature Genet. 1993;5:230–235. doi: 10.1038/ng1193-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.So CW, Cleary ML. Common mechanism for oncogenic activation of MLL by forkhead family proteins. Blood. 2003;101:633–639. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Ramaswamy S, Nakamura N, Sansal I, Bergeron L, Sellers WR. A novel mechanism of gene regulation and tumor suppression by the transcription factor FKHR. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:81–91. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Hatta M, Cirillo LA. Chromatin opening and stable perturbation of core histone:DNA contacts by FoxO1. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:35583–35593. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704735200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.van der Vos KE, Coffer PJ. FOXO-binding partners: it takes two to tango. Oncogene. 2008;27:2289–2299. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Dengler HS, et al. Distinct functions for the transcription factor Foxo1 at various stages of B cell differentiation. Nature Immunol. 2008;9:1388–1398. doi: 10.1038/ni.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Schluns KS, Kieper WC, Jameson SC, Lefrancois L. Interleukin-7 mediates the homeostasis of naive and memory CD8 T cells in vivo. Nature Immunol. 2000;1:426–432. doi: 10.1038/80868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Fabre S, et al. FOXO1 regulates L-Selectin and a network of human T cell homing molecules downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Immunol. 2008;181:2980–2989. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.5.2980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Gubbels Bupp MR, et al. T cells require Foxo1 to populate the peripheral lymphoid organs. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:2991–2999. doi: 10.1002/eji.200939427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Yusuf I, et al. KLF4 is a FOXO target gene that suppresses B cell proliferation. Int Immunol. 2008;20:671–681. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxn024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Cao Z, Sun X, Icli B, Wara AK, Feinberg MW. Role of Kruppel-like factors in leukocyte development, function, and disease. Blood. 2010;116:4404–4414. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-285353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ouyang W, et al. Foxo proteins cooperatively control the differentiation of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. Nature Immunol. 2010;11:618–627. doi: 10.1038/ni.1884. This paper reported that FOXO1 and FOXO3 are required for TReg cell development and function, and may directly control the expression of Foxp3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Harada Y, et al. Transcription factors Foxo3a and Foxo1 couple the E3 ligase Cbl-b to the induction of Foxp3 expression in induced regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 2010;207:1381–1391. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Fernandez de Mattos S, et al. FoxO3a and BCR-ABL regulate cyclin D2 transcription through a STAT5/ BCL6-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:10058–10071. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.22.10058-10071.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Glauser DA, Schlegel W. The FoxO/Bcl-6/cyclin D2 pathway mediates metabolic and growth factor stimulation of proliferation in Min6 pancreatic β-cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2009;29:293–298. doi: 10.3109/10799890903241824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Duy C, et al. BCL6 enables Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells to survive BCR-ABL1 kinase inhibition. Nature. 2011;473:384–388. doi: 10.1038/nature09883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Johnston RJ, et al. Bcl6 and Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular helper cell differentiation. Science. 2009;325:1006–1010. doi: 10.1126/science.1175870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Nurieva RI, et al. Bcl6 mediates the development of T follicular helper cells. Science. 2009;325:1001–1005. doi: 10.1126/science.1176676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Yu D, et al. The transcriptional repressor Bcl-6 directs T follicular helper cell lineage commitment. Immunity. 2009;31:457–468. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Vinuesa CG, Cyster JG. How T cells earn the follicular rite of passage. Immunity. 2011;35:671–680. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Cui W, Liu Y, Weinstein JS, Craft J, Kaech SM. An interleukin-21-interleukin-10-STAT3 pathway is critical for functional maturation of memory CD8+ T cells. Immunity. 2011;35:792–805. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Rao RR, Li Q, Gubbels Bupp MR, Shrikant PA. Transcription factor Foxo1 represses T-bet-mediated effector functions and promotes memory CD8+ T cell differentiation. Immunity. 2012;36:374–387. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.01.015. In this study, the authors show that IL-12 promotes Tbx21 expression in vitro by inactivating FOXO1. FOXO1 binds to a site in the Eomes gene and affects EOMES expression. A loss of FOXO1 prevented memory CD8+ T cell reactivation. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Dijkers PF, et al. FKHR-L1 can act as a critical effector of cell death induced by cytokine withdrawal: protein kinase B-enhanced cell survival through maintenance of mitochondrial integrity. J Cell Biol. 2002;156:531–542. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200108084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.You H, et al. FOXO3a-dependent regulation of Puma in response to cytokine/growth factor withdrawal. J Exp Med. 2006;203:1657–1663. doi: 10.1084/jem.20060353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Bosque A, et al. The induction of Bim expression in human T cell blasts is dependent on non-apoptopic Fas/CD95 signalling. Blood. 2006;109:1627–1635. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-022319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Katayama K, Nakamura A, Sugimoto Y, Tsuruo T, Fujita N. FOXO transcription factor-dependent p15(INK4b) and p19(INK4d) expression. Oncogene. 2008;27:1677–1686. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Ho KK, Myatt SS, Lam EW. Many forks in the path: cycling with FoxO. Oncogene. 2008;27:2300–2311. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Gump JM, Dowdy SF. TAT transduction: the molecular mechanism and therapeutic prospects. Trends Mol Med. 2007;13:443–448. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2007.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Dabrowska A, Kim N, Aldovini A. Tat-induced FOXO3a is a key mediator of apoptosis in HIV-1-infected human CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2008;181:8460–8477. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.12.8460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Kim N, Kukkonen S, Gupta S, Aldovini A. Association of Tat with promoters of PTEN and PP2A subunits is key to transcriptional activation of apoptotic pathways in HIV-infected CD4+ T cells. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1001103. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.van Grevenynghe J, et al. Transcription factor FOXO3a controls the persistence of memory CD4+ T cells during HIV infection. Nature Med. 2008;14:266–274. doi: 10.1038/nm1728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Riou C, et al. Convergence of TCR and cytokine signaling leads to FOXO3a phosphorylation and drives the survival of CD4+ central memory T cells. J Exp Med. 2007;204:79–91. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Sugimoto N, et al. Foxp3-dependent and -independent molecules specific for CD25+CD4+ natural regulatory T cells revealed by DNA microarray analysis. Int Immunol. 2006;18:1197–1209. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxl060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Hill JA, et al. Foxp3 transcription-factor-dependent and -independent regulation of the regulatory T cell transcriptional signature. Immunity. 2007;27:786–800. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Gavin MA, et al. Foxp3-dependent programme of regulatory T-cell differentiation. Nature. 2007;445:771–775. doi: 10.1038/nature05543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Lin W, et al. Regulatory T cell development in the absence of functional Foxp3. Nature Immunol. 2007;8:359–368. doi: 10.1038/ni1445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Feuerer M, Hill JA, Mathis D, Benoist C. Foxp3+ regulatory T cells: differentiation, specification, subphenotypes. Nature Immunol. 2009;10:689–695. doi: 10.1038/ni.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Haxhinasto S, Mathis D, Benoist C. The AKT-mTOR axis regulates de novo differentiation of CD4+Foxp3+ cells. J Exp Med. 2008;205:565–574. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071477. This paper shows that the AKT–mTOR pathway inhibits TReg cell development and controls a subset of the TReg cell gene expression signature, including CTLA4 expression. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Sauer S, et al. T cell receptor signaling controls Foxp3 expression via PI3K, Akt, and mTOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:7797–7802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800928105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Chen W, et al. Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25– naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-β induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med. 2003;198:1875–1886. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Pierau M, et al. Protein kinase B/Akt signals impair Th17 differentiation and support natural regulatory T cell function and induced regulatory T cell formation. J Immunol. 2009;183:6124–6134. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Sakoe Y, Sakoe K, Kirito K, Ozawa K, Komatsu N. FOXO3A as a key molecule for all-trans retinoic acid-induced granulocytic differentiation and apoptosis in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 2010;115:3787–3795. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-222976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Turner MS, Kane LP, Morel PA. Dominant role of antigen dose in CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cell induction and expansion. J Immunol. 2009;183:4895–4903. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Gottschalk RA, Corse E, Allison JP. TCR ligand density and affinity determine peripheral induction of Foxp3 in vivo. J Exp Med. 2010;207:1701–1711. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Francisco LM, et al. PD-L1 regulates the development, maintenance, and function of induced regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 2009;206:3015–3029. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.An BS, et al. Stimulation of Sirt1-regulated FoxO protein function by the ligand-bound vitamin D receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:4890–4900. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00180-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Mucida D, et al. Reciprocal TH17 and regulatory T cell differentiation mediated by retinoic acid. Science. 2007;317:256–260. doi: 10.1126/science.1145697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Jeffery LE, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 and IL-2 combine to inhibit T cell production of inflammatory cytokines and promote development of regulatory T cells expressing CTLA-4 and FoxP3. J Immunol. 2009;183:5458–5467. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ghoreishi M, et al. Expansion of antigen-specific regulatory T cells with the topical vitamin d analog calcipotriol. J Immunol. 2009;182:6071–6078. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Brown EJ, et al. Control of p70 s6 kinase by kinase activity of FRAP in vivo. Nature. 1995;377:441–446. doi: 10.1038/377441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Gingras AC, Kennedy SG, O’Leary MA, Sonenberg N, Hay N. 4E-BP1, a repressor of mRNA translation, is phosphorylated and inactivated by the Akt(PKB) signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 1998;12:502–513. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.4.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012;149:274–293. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Delgoffe GM, et al. The mTOR kinase differentially regulates effector and regulatory T cell lineage commitment. Immunity. 2009;30:832–844. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.04.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Battaglia M, Stabilini A, Roncarolo MG. Rapamycin selectively expands CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. Blood. 2005;105:4743–4748. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-3932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Kang J, Huddleston SJ, Fraser JM, Khoruts A. De novo induction of antigen-specific CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in vivo following systemic antigen administration accompanied by blockade of mTOR. J Leukoc Biol. 2008;83:1230–1239. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1207851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Kopf H, de la Rosa GM, Howard OM, Chen X. Rapamycin inhibits differentiation of Th17 cells and promotes generation of FoxP3+ T regulatory cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007;7:1819–1824. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2007.08.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Delgoffe GM, et al. The kinase mTOR regulates the differentiation of helper T cells through the selective activation of signaling by mTORC1 and mTORC2. Nature Immunol. 2011;12:295–303. doi: 10.1038/ni.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Cobbold SP, et al. Infectious tolerance via the consumption of essential amino acids and mTOR signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:12055–12060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903919106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Zheng Y, et al. Role of conserved non-coding DNA elements in the Foxp3 gene in regulatory T-cell fate. Nature. 2010;463:808–812. doi: 10.1038/nature08750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Ouaked N, et al. Regulation of the foxp3 gene by the Th1 cytokines: the role of IL-27-induced STAT1. J Immunol. 2009;182:1041–1049. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.182.2.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Zorn E, et al. IL-2 regulates FOXP3 expression in human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells through a STAT-dependent mechanism and induces the expansion of these cells in vivo. Blood. 2006;108:1571–1579. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-004747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Getnet D, et al. A role for the transcription factor Helios in human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Mol Immunol. 2010;47:1595–1600. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Crellin NK, Garcia RV, Levings MK. Altered activation of AKT is required for the suppressive function of human CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Blood. 2007;109:2014–2022. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-035279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Bachmann MF, Kohler G, Ecabert B, Mak TW, Kopf M. Cutting edge: lymphoproliferative disease in the absence of CTLA-4 is not T cell autonomous. J Immunol. 1999;163:1128–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nature Immunol. 2005;6:345–352. doi: 10.1038/ni1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Wing K, et al. CTLA-4 control over Foxp3+ regulatory T cell function. Science. 2008;322:271–275. doi: 10.1126/science.1160062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Liu G, et al. The receptor S1P1 overrides regulatory T cell-mediated immune suppression through Akt-mTOR. Nature Immunol. 2009;10:769–777. doi: 10.1038/ni.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Liu G, Yang K, Burns S, Shrestha S, Chi H. The S1P1–mTOR axis directs the reciprocal differentiation of TH1 and Treg cells. Nature Immunol. 2010;11:1047–1056. doi: 10.1038/ni.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Akiba H, et al. The role of ICOS in the CXCR5+ follicular B helper T cell maintenance in vivo. J Immunol. 2005;175:2340–2348. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.4.2340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Choi YS, et al. ICOS receptor instructs T follicular helper cell versus effector cell differentiation via induction of the transcriptional repressor Bcl6. Immunity. 2011;34:932–946. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Linterman MA, Vinuesa CG. Signals that influence T follicular helper cell differentiation and function. Semin Immunopathol. 2010;32:183–196. doi: 10.1007/s00281-009-0194-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Crotty S. Follicular helper CD4 T cells (TFH) Annu Rev Immunol. 2011;29:621–663. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-031210-101400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Gigoux M, et al. Inducible costimulator promotes helper T-cell differentiation through phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:20371–20376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911573106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Rolf J, Fairfax K, Turner M. Signaling pathways in T follicular helper cells. J Immunol. 2010;184:6563–6568. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Oestreich KJ, Mohn SE, Weinmann AS. Molecular mechanisms that control the expression and activity of Bcl-6 in TH1 cells to regulate flexibility with a TFH-like gene profile. Nature Immunol. 2012;13:405–411. doi: 10.1038/ni.2242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Kaech SM, Wherry EJ. Heterogeneity and cell-fate decisions in effector and memory CD8+ T cell differentiation during viral infection. Immunity. 2007;27:393–405. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Lefrancois L, Obar JJ. Once a killer, always a killer: from cytotoxic T cell to memory cell. Immunol Rev. 2010;235:206–218. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Arens R, Schoenberger SP. Plasticity in programming of effector and memory CD8 T-cell formation. Immunol Rev. 2010;235:190–205. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00899.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Rutishauser RL, Kaech SM. Generating diversity: transcriptional regulation of effector and memory CD8 T-cell differentiation. Immunol Rev. 2010;235:219–233. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2010.00901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Pearce EL, et al. Control of effector CD8+ T cell function by the transcription factor Eomesodermin. Science. 2003;302:1041–1043. doi: 10.1126/science.1090148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Intlekofer AM, et al. Effector and memory CD8+ T cell fate coupled by T-bet and eomesodermin. Nature Immunol. 2005;6:1236–1244. doi: 10.1038/ni1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Zhou X, et al. Differentiation and persistence of memory CD8+ T cells depend on T cell factor 1. Immunity. 2010;33:229–240. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.08.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Jeannet G, et al. Essential role of the Wnt pathway effector Tcf-1 for the establishment of functional CD8 T cell memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:9777–9782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914127107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Kim EH, et al. Signal integration by Akt regulates CD8 T cell effector and memory differentiation. J Immunol. 2012;188:4305–4314. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Pearce EL, et al. Enhancing CD8 T-cell memory by modulating fatty acid metabolism. Nature. 2009;460:103–107. doi: 10.1038/nature08097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Araki K, et al. mTOR regulates memory CD8 T-cell differentiation. Nature. 2009;460:108–112. doi: 10.1038/nature08155. In this study, the authors show that inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin increases memory CD8+ T cell formation. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Jacinto E, et al. Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nature Cell Biol. 2004;6:1122–1128. doi: 10.1038/ncb1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Sarbassov DD, et al. Prolonged rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol Cell. 2006;22:159–168. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.03.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Lamming DW, et al. Rapamycin-induced insulin resistance is mediated by mTORC2 loss and uncoupled from longevity. Science. 2012;335:1638–1643. doi: 10.1126/science.1215135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Allam A, et al. The CD8+ memory T-cell state of readiness is actively maintained and reversible. Blood. 2009;114:2121–2130. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-220087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Wang M, Zhang X, Zhao H, Wang Q, Pan Y. FoxO gene family evolution in vertebrates. BMC Evol Biol. 2009;9:222. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Jacobs FM, et al. FoxO6, a novel member of the FoxO class of transcription factors with distinct shuttling dynamics. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:35959–35967. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302804200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Tothova Z, et al. FoxOs are critical mediators of hematopoietic stem cell resistance to physiologic oxidative stress. Cell. 2007;128:325–339. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Hosaka T, et al. Disruption of forkhead transcription factor (FOXO) family members in mice reveals their functional diversification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:2975–2980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400093101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Furuyama T, et al. Abnormal angiogenesis in Foxo1 (Fkhr)-deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:34741–34749. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M314214200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Castrillon DH, Miao L, Kollipara R, Horner JW, DePinho RA. Suppression of ovarian follicle activation in mice by the transcription factor Foxo3a. Science. 2003;301:215–218. doi: 10.1126/science.1086336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Simonis M, et al. High-resolution identification of balanced and complex chromosomal rearrangements by 4C technology. Nature Methods. 2009;6:837–842. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.de Wit E, de Laat W. A decade of 3C technologies: insights into nuclear organization. Genes Dev. 2012;26:11–24. doi: 10.1101/gad.179804.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Rena G, Guo S, Cichy SC, Unterman TG, Cohen P. Phosphorylation of the transcription factor forkhead family member FKHR by protein kinase B. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:17179–17183. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.24.17179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Biggs WHr, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, Cavenee WK, Arden KC. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:7421–7426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.13.7421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Nakae J, Park BC, Accili D. Insulin stimulates phosphorylation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR on serine 253 through a Wortmannin-sensitive pathway. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:15982–15985. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.23.15982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Tsai WB, Chung YM, Takahashi Y, Xu Z, Hu MC. Functional interaction between FOXO3a and ATM regulates DNA damage response. Nature Cell Biol. 2008;10:460–467. doi: 10.1038/ncb1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Yalcin S, et al. Foxo3 is essential for the regulation of ataxia telangiectasia mutated and oxidative stress-mediated homeostasis of hematopoietic stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:25692–25705. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800517200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Khatri S, Yepiskoposyan H, Gallo CA, Tandon P, Plas DR. FOXO3a regulates glycolysis via transcriptional control of tumor suppressor TSC1. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:15960–15965. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.121871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Yang W, Dolloff NG, El-Deiry WS. ERK and MDM2 prey on FOXO3a. Nature Cell Biol. 2008;10:125–126. doi: 10.1038/ncb0208-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Wang MC, Bohmann D, Jasper H. JNK extends life span and limits growth by antagonizing cellular and organism-wide responses to insulin signaling. Cell. 2005;121:115–125. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Choi J, et al. Mst1-FoxO signaling protects naive T lymphocytes from cellular oxidative stress in mice. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e8011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Chapuis N, et al. IκB kinase overcomes PI3K/Akt and ERK/MAPK to control FOXO3a activity in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2010;116:4240–4250. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-260711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Matsuzaki H, et al. Acetylation of Foxo1 alters its DNA-binding ability and sensitivity to phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:11278–11283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502738102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Arimoto-Ishida E, et al. Inhibition of phosphorylation of a forkhead transcription factor sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin. Endocrinology. 2004;145:2014–2022. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Burchill MA, Yang J, Vogtenhuber C, Blazar BR, Farrar MA. IL-2 receptor β-dependent STAT5 activation is required for the development of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2007;178:280–290. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.1.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


