Abstract
Acute and chronic myeloid leukemia (AML, CML) are hematologic malignancies arising from oncogene-transformed hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells known as leukemia stem cells (LSCs). LSCs are selectively resistant to various forms of therapy including irradiation or cytotoxic drugs. The introduction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors has dramatically improved disease outcome in patients with CML. For AML, however, prognosis is still quite dismal. Standard treatments have been established more than 20 years ago with only limited advances ever since. Durable remission is achieved in less than 30% of patients. Minimal residual disease (MRD), reflected by the persistence of LSCs below the detection limit by conventional methods, causes a high rate of disease relapses. Therefore, the ultimate goal in the treatment of myeloid leukemia must be the eradication of LSCs. Active immunotherapy, aiming at the generation of leukemia-specific cytotoxic T cells (CTLs), may represent a powerful approach to target LSCs in the MRD situation. To fully activate CTLs, leukemia antigens have to be successfully captured, processed, and presented by mature dendritic cells (DCs). Myeloid progenitors are a prominent source of DCs under homeostatic conditions, and it is now well established that LSCs and leukemic blasts can give rise to “malignant” DCs. These leukemia-derived DCs can express leukemia antigens and may either induce anti-leukemic T cell responses or favor tolerance to the leukemia, depending on co-stimulatory or -inhibitory molecules and cytokines. This review will concentrate on the role of DCs in myeloid leukemia immunotherapy with a special focus on their generation, application, and function and how they could be improved in order to generate highly effective and specific anti-leukemic CTL responses. In addition, we discuss how DC-based immunotherapy may be successfully integrated into current treatment strategies to promote remission and potentially cure myeloid leukemias.
Keywords: dendritic cells, immunotherapy, active, myeloid leukemia, minimal residual disease, leukemia stem cells
Introduction
During the last century our molecular and mechanistic understanding of the immune system and the immunosurveillance of solid and hematological tumors has advanced extensively. For hematological tumors especially, the demonstration of the graft-vs.-leukemia (GvL) effect of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (aHSCT) and donor lymphocyte infusions (DLIs), as well as the discovery of leukemia-associated antigens (LAAs) was of fundamental importance in order to translate, implement, and optimize immunotherapies against myeloid leukemias. Consequently, active and passive immunotherapy approaches, such as peptide- and dendritic cell (DC)-based vaccines using LAAs, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), and the in vitro-generation of leukemia-specific cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) for adoptive transfer have recently yielded promising results in pre-clinical models and clinical trials (1–4). To maximize their efficacy, these immunotherapies have to be implemented into the treatment strategy in conjunction with standard treatments of care for each patient individually. Here, we summarize recent advances in DC-based active vaccination using LAAs and discuss this method as an attractive supplementary immunotherapeutic strategy in the context of current standard treatments for myeloid leukemias.
Classification, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations of CML and AML
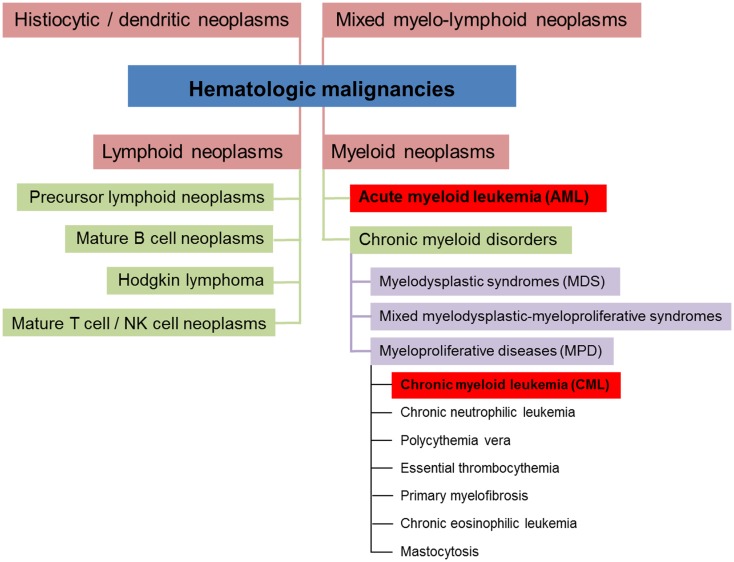
Hematologic malignancies are neoplasms of the blood-forming system. Conceptually, these neoplasms can be divided into four different subsets (myeloid, lymphoid, mixed myelo-lymphoid, and histiocytic/dendritic neoplasms, see Figure 1) (5, 6). Myeloid neoplasms can be further grouped into acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and chronic myeloid disorders depending on the percentage of bone marrow (BM) infiltration by immature blasts. 20% and more infiltrating immature blasts define the cut-off criterion for AML. Chronic myeloid disorders such as chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) bear the risk of evolving into AML. Experimental studies revealed that myeloid leukemias in general are of clonal origin, suggesting genesis from a single leukemia stem cell [LSC, reviewed in Ref. (7)].
Figure 1.
Conceptual classification of hematologic neoplasms [based on data from Ref. (5, 6)].
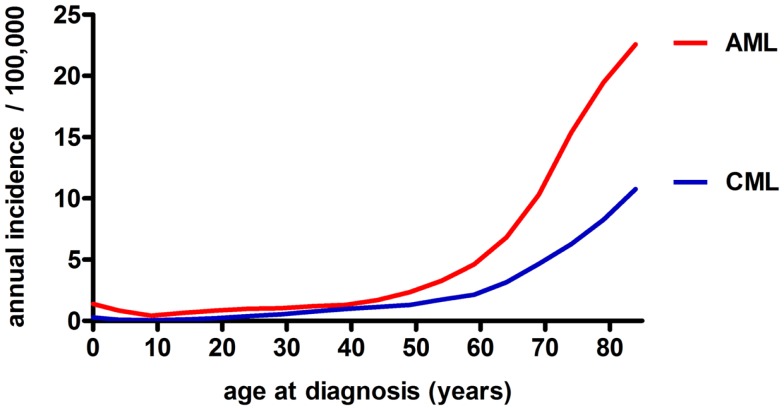
Chronic myeloid leukemia is caused by translocation of chromosomes 9 and 22 in a hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) resulting in the formation of the constitutively active tyrosine kinase BCR/ABL1 and the subsequent generation of an LSC (8). CML is characterized by the overproduction and accumulation of mature, functionally impaired myeloid cells, predominantly granulocytes. CML represents about 15–20% of all leukemias in adulthood, affecting slightly more men than women (ratio ~1.8–1) (9). Its annual incidence is 1–2 cases per 100,000 for all age groups (10). This incidence is rising with age to 10–12 cases per 100,000 for people older than 80 years of age (Figure 2) (11). Without treatment, chronic phase CML inevitably evolves via an accelerated phase (12) into blast crisis, which is characterized by the presence of ≥20% blasts in the blood or BM or the presence of extramedullary infiltrating blasts. In two thirds of cases, the blasts are of myeloid origin and the disease phenotype is similar to AML. The other third is of lymphoid origin. Blast crisis CML is highly resistant to treatment, and median survival of patients is approximately 4–8 months. The most common causes of death in blast crisis CML are bleedings and infections due to lack of a functional hematopoietic system (13). Because BCR/ABL1 is necessary and sufficient for the malignant phenotype, attempts to inhibit this kinase using small molecules have led to the discovery of the specific tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) Imatinib (14). Since its introduction into clinics in 2001, Imatinib became the gold standard in CML therapy and has replaced cytarabin/interferon (IFN)-α combination therapy (15). Imatinib is the first-line therapy of choice for nearly all newly diagnosed CML patients (16). Second- and third-generation TKIs with superior efficacy, also against mutated forms of BCR/ABL1, are currently tested in clinical trials (17–20). Even though TKI treatment stabilizes the disease during the chronic phase, a small percentage of patients will progress to accelerated phase and blast crisis (21). Besides TKIs, which have demonstrated long-term disease control and very good tolerability, the only other treatment option that may be considered for CML is aHSCT. Today, aHSCT is the only treatment with proven ability to cure CML (22).
Figure 2.
Annual incidence of AML and CML in the USA among different age groups (both sexes, all race groups, years 1992–2010), based on data from the NCI/SEER (11).
In contrast to CML, AML is an aggressive and fatal disease caused by an increased proliferation and a block in differentiation capacity of myeloid blasts. With an annual incidence of three to five cases per 100,000 (m:f ratio, 3:2), AML is the most frequent myeloid leukemia in adults (10). Compared to CML, the age-dependent rise in AML incidence is even more drastic to peak at 20–23 cases per 100,000 in the geriatric population (Figure 2) (11). Besides age and sex, known risk factors for myeloid leukemias include exposure to ionizing radiation, benzene (e.g., cigarette smoking) and previous cytotoxic chemotherapy (23, 24). Despite the tremendous efforts that have been made to classify AML based on cytogenetic and molecular markers (25), AML treatment basically remained unimproved in the last 20 years and consists of induction cytotoxic chemotherapy (“3 + 7” scheme with cytarabin and an anthracycline), with minor modifications for elderly patients, therapy-related AML, and relapsed or therapy-resistant disease. The only exception is t(15;17)-associated acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), which is treated with a differentiating agent, all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) in combination with standard chemotherapy (23, 26). In face of these highly toxic chemotherapies, on average less than 30% of AML patients survive long-term. The prognosis for “elderly” patients (defined by the age of 65 or more in most studies) is even more dismal. Treatment failure may occur due to therapy-related complications, such as infections, toxicity, and tumor lysis syndrome. More importantly, the high disease relapse rate after a first remission is the major problem clinicians are confronted with in AML therapy (23). Relapse is thought to be caused by a therapy-resistant neoplastic cell reservoir slumbering in the BM, a situation referred to as minimal residual disease (MRD). It is likely that MRD represents the persistence of quiescent, therapy-resistant LSCs in the BM. Therefore, after a first remission is achieved, post-remission chemotherapy and/or aHSCT is needed to control LSCs (27).
Leukemia stem cells and the problem of minimal residual disease
The goal of therapy in myeloid leukemia is to induce a durable complete remission (CR). For chronic phase CML, this is most often relatively easily achieved by TKI treatment; however, this therapy only eliminates the bulk of leukemia cells, whereas LSCs are spared. It is thought that CML LSCs are not completely addicted to BCR/ABL1, and several studies have shown survival of CML LSCs in the presence of Imatinib in vitro and in vivo [(28) and reviewed in Ref. (20)].
For AML, induction poly-chemotherapy may result in a labile CR that has to be consolidated by aHSCT or post-remission chemotherapy. If this treatment is omitted, relapse will often occur rapidly due to persistence of MRD below the cytological detection limit of ~109 cells (23).
Whereas CML LSCs are relatively well characterized as lineage-negative (lin−) CD34+CD38− cells, the definition of the immunophenotype of AML LSCs is currently controversially discussed. Generally, LSCs are defined as a rare cell population with the capability of self-renewal, extensive proliferation, induction of leukemia, and serial transplantation capacity in xenografts as well as resistance to various treatments. Seminal studies by John Dick et al. using severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) or non-obese diabetic (NOD)/SCID mice in the 1990s revealed that AML stem cells reside within the lin− CD34+ CD38− fraction, as the initiation of AML of all subtypes (except APL) was only possible with purified lin− CD34+ CD38− cells, but not with purified lin− CD34+ CD38+ cells. The leukemias produced in these mouse models closely resembled the original human diseases, providing evidence that AML stem cells have long-term self-renewal capability and determine the leukemia’s phenotype (29, 30). Based on these experiments, the authors hypothesized that leukemias are hierarchically organized in a similar way as the normal blood-forming system and that the normal HSC would most likely be the cell-of-origin that is malignantly transformed during leukemogenesis. Subsequently, many groups tried to refine the immunophenotype of AML LSCs, and several additional markers were characterized (31–36). However, findings from a recent study by Sarry et al. have questioned this strict definition of LSCs by immunophenotype. These authors showed that CD34 expression in AML is highly variable, classifying their patients into 3 groups based on the extent of CD34 expression. Importantly, LSCs were found in all samples, even in CD34 negative ones, and in some patients also in a cell population expressing low amounts of lineage markers. Therefore, these authors suggest that the absolute distribution of LSCs does not necessarily correlate with their phenotypic distribution so that even though LSCs are enriched in certain fractions of cells, such as linnegCD38neg cells, the relative rarity of these populations implies that the absolute number of LSCs may be higher in other cell fractions (37). In addition, the incubation of leukemia cells with antibodies targeting surface markers, such as anti-CD38, may reduce the engraftment capacity of leukemia-initiating cells expressing these markers, even further complicating the analysis of human LSCs (37, 38).
In addition to the challenging task of characterizing an LSC phenotype in AML, there is no standard definition for MRD. MRD may well serve as an indicator for the quality of the response to the treatment and may be a prognostic parameter for disease relapse and the choice and effectiveness of post-remission treatment strategy (39). Whereas CR is conventionally defined by pathologists as the absence (≤5%) of blasts in the BM, the establishment of a definition for MRD is much more difficult. First, a significant proportion of AML patients lack molecular markers, such as FLT3-ITD, NPMmut, or chromosomal translocations that would allow monitoring MRD by molecular methods after induction chemotherapy. Second, the time point at which patients should first be tested for MRD and the time interval of serial monitoring is controversially discussed (40). Feller et al. suggested an interval of 3 months for MRD testing by flow cytometry (41). Third, the best method to quantify MRD is still a matter of debate. At the moment, real-time RT-PCR for molecular markers and immunophenotype using multi-parameter flow cytometry are comparable in terms of sensitivity and specificity; however, therapy-related changes in these parameters may limit the clinical applicability (42). Fourth, the level of transcript as measured by RT-PCR or number of cells as measured by flow cytometry defining the threshold for MRD+ vs. MRD− has to be validated in prospective studies. And last, the question remains whether peripheral blood can replace BM as the source of cells, which is a relative prerequisite for the feasibility of such studies (39, 40). In summary, all these questions should be addressed during the design of future studies on MRD therapy.
Myeloid Leukemias and the Immune System
Clinical and experimental observations suggested that myeloid leukemias are partly controlled by the immune system (43). Leukemia cells express major histocompatibility class (MHC)-I and -II molecules and co-stimulatory ligands, such as CD80 and CD86, and therefore may be recognized by T cells and induce potent T cell responses (44–48). In addition, myeloid leukemias respond to unspecific immune-mediated therapies such as IFN-α and interleukin (IL)-2 (49, 50). Furthermore, aHSCT, a treatment with proven ability to cure myeloid leukemias, is in fact an immunotherapy exploiting the allogeneic T and NK cell-mediated GvL effect, which is absent in syngeneic HSCT (22, 51, 52). In addition, it was shown that patients receiving T cell depleted aHSCT grafts had a greater risk of disease relapse, and DLIs from original donors led to CR in most of the patients suffering from disease relapse (53–56).
An interesting example of endogenous immunosurveillance was observed in non-transplanted pediatric AML patients. Montagna et al. demonstrated that stable remission after cytotoxic chemotherapy was associated with the emergence of leukemia-specific CTL precursors in the BM. All patients that had high numbers of CTL precursors remained in remission, whereas the majority of patients with no CTL precursors relapsed (57).
Leukemic cells can be controlled either via specific major histocompatibility complex (MHC-restricted) mechanisms or via less specific incompatibilities in minor histocompatibility genes (58). Indeed, CTLs directed against leukemia antigens have been detected in the peripheral blood of chronic phase CML patients (59, 60) and have been shown to kill CML target cells in vitro via Fas-receptor triggering (61). Similar anti-leukemic CTL responses have also been documented in AML (62). In contrast, blast crisis CML cells are refractory to Fas-ligand induced apoptosis, regardless of the expression levels of Fas-receptor, suggesting that an immune-mediated selection by CTLs could result in the acquisition of Fas resistance (63). A further line of evidence that CML is controlled by CTLs comes from our own studies in a murine CML model using the glycoprotein of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) as a model tumor-antigen. CML-specific CTLs were present in CML-bearing mice and displayed an exhausted phenotype as analyzed by low cytotoxicity, absence of IFN-γ and TNF-α production and expression of programed death-1 (PD-1). Nevertheless, these CTLs contributed to disease control, as depletion of CD8+ T cells led to rapid disease progression and death (64). We documented that leukemia-specific CTLs are able to interact with and kill CML LSCs in vitro and in vivo in a setting with minimal leukemia load. In contrast, in a clinically relevant setting of high leukemia load, CTLs did not kill LSCs but promoted their proliferation by secreting high amounts of IFN-γ (65). In addition, we demonstrated that CD70-expressing T cells stimulate CD27-expressing LSCs in a cell-contact-dependent manner: ligation of CD27 on LSCs by CD70 on T cells reinforced the Wnt-pathway in LSCs, leading to LSC proliferation and disease progression (66). Thus, as it has been shown for other tumors, the immune system interacts with leukemia (stem) cells and may as well play a paradoxical role in promoting disease progression (67).
The role of CD4+ T cells in the control of CML has been studied less intensively (68). CD4+ T cells isolated from the BM of CML patients were able to suppress autologous hematopoietic progenitor cells in a contact-dependent manner (69). DLIs, depleted of CD8+ T cells to reduce the side effects of GvHD, were able to induce remissions in aHSCT-treated CML patients after disease relapse. This led to the hypothesis that CD4+ T cells are the main effectors of the GVL effect, whereas CD8+ T cells are mainly responsible for GVHD (70). Endogenous CD4+ T cells, however, might be dysfunctional in vivo, as they have a normal intrinsic cytokine-producing ability only in vitro, but not in the leukemia environment (71). However, CD4+ T cells may be important in the setting of aHSCT. CD8+ T cell-depleted DLI, administered to patients after aHSCT, induced a low rate of remissions and of GvHD (70). Therefore, CD4+ T cells are also potentially involved in the GvL effect in CML patients. On the other hand, CD8+ T cells may serve as important effectors of GvHD without being essential for GvL.
The roles of B cells and NK cells in the control of CML remain controversial. BCR/ABL1 junctional peptides could induce production of specific antibodies to BCR/ABL1 (72). In addition, it was noted that CD4+ DLIs increased the numbers of circulating B cells in patients at the time of clinical response (73). Although antibodies recognizing many distinct leukemia antigens were discovered (74), the impact of antibodies on malignant CML cells remains elusive. NK cells were shown to selectively lyse CML progenitor cells in vitro (75). In accelerated CML and blast crisis, NK cell frequency, proliferation, and lytic function seems to decline, but it is currently unclear whether this decline is a cause rather than an effect of disease progression (76, 77). Moreover, donor-vs.-recipient NK cell alloreactivity could eliminate leukemia in human transplants (78).
Chronic myeloid leukemia patients have significantly reduced numbers of circulating myeloid and plasmacytoid DCs (pDCs) compared to healthy volunteers (79, 80). However, BCR/ABL1-expressing DCs have been detected in the peripheral blood of CML patients suggesting that CML derived DCs may possibly contribute to anti-leukemic immunity (81, 82). BCR/ABL1-expressing DCs could be generated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) or CD34+ progenitor cells of CML patients and were shown to have an impaired capacity to capture and process antigens and an impaired migratory capacity compared to DCs derived from healthy controls (83–85). In addition, leukemic DCs were shown to produce TNF-α and IL-8 (86). However, contradictory results about the maturation status of BCR/ABL1 DCs have been published (81, 82).
In summary, it seems plausible that innate as well as adaptive immunity play an important role in the control of myeloid leukemias.
Immune evasion mechanisms
Myeloid leukemias employ several strategies to compromise anti-leukemic immune responses. DCs originating from myeloid leukemia progenitor cells have been found in vivo in leukemia patients and were shown to be abnormal in numbers and function (80–82, 87). Leukemia-derived DCs (L-DCs) displayed reduced antigen-capture and processing capacity, a low maturation status and an aberrant homing pattern when compared to normal DCs (86, 88). Furthermore, L-DCs promoted T cell anergy and the generation of regulatory T (Treg) cells instead of inducing CTLs (89–91). Tregs are increased in myeloid leukemias (92, 93), are associated with an unfavorable outcome (94), correlate with disease relapse after aHSCT (95) and impede the function of adoptively transferred CTLs (96). Leukemic blasts express high levels of co-inhibitory molecules and interact poorly with T cells due to an impaired formation of immune synapse (97, 98). AML and CML cells for example express the ligands for programed death-1 (PD-L1, PD-L2), which interact with PD-1 expressed on T cells (64, 65, 99, 100). Accordingly, we recently demonstrated that CML LSCs express PD-L1 and PD-L2 as well (65). A further mechanism leukemic cells use to interfere with the immune system is the presentation of MHC class II-associated invariant chain-derived peptide (CLIP). CLIP expression on AML blasts predicts poor clinical outcome (101) and disturbs the activation of leukemia-specific CD4+ T cells (102), most probably by interfering with the loading and presentation of LAAs (103). Interestingly, CLIP could also promiscuously bind to various MHC class I types in leukemia cells deficient of MHC class II, a feature that could hamper CTL-mediated leukemia immunosurveillance (104).
The role of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and TNF-receptor superfamily members in the pathophysiology of leukemia has recently been documented. Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein ligand (GITRL) was shown to be expressed in a majority of AML cell lines and blasts from patient samples. Reverse signaling of GITRL in AML cells induced the release of TNF and IL-10, and triggering of GITR expressed on NK cells impaired NK cell cytotoxic function and IFN-γ production (105). AML cells exploit further signaling axes of the TNF/TNFR superfamily, such as the 4-1BB-ligand/4-1BB (CD137L-CD137) pathway and the receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B (RANK)-ligand RANK pathway (106, 107) to inhibit the immune system in a similar way as described for GITR. Furthermore, we could recently document a role for the TNFR CD27 on proliferation of CML LSCs and CML progression (66). Blocking inhibitory pathways holds promise for clinical development. Among them are FAS-ligand that induces apoptosis of FAS-expressing T cells, CD200 that directly inhibits T and NK cells, reactive oxygen species (ROS) that induce lymphocyte apoptosis, killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) that suppress NK cells and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) that depletes tryptophan required for T cell expansion or IL-10 that potently suppresses T cell activation [reviewed in Ref. (27)]. Besides inhibiting the adaptive immune system, it was recently demonstrated that leukemic cells are able to block programed cell removal by innate immune cells, thereby overcoming a further regulatory mechanism that normally limits cancer growth. The up-regulation of so-called “don’t eat me” signals on blasts and leukemia stem cells (LSC), such as CD47 and CD200, precludes apoptosis-independent phagocytosis by macrophages. In addition to enable the propagation of the malignant cells, this mechanism likely allows metastatic circulating cancer cells to survive in niches rich in phagocytes, such as the spleen and lymph nodes (108, 109).
These and further immunosuppressive mechanisms remain major hurdles to be overcome in order to successfully implement DC-based immunotherapy in the treatment of leukemia. Interfering with negative immune regulators may effectively improve DC-based immunotherapy, as has been shown by silencing the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) or the immunosuppressive cytokine IL-10, which enhanced antigen-presentation and secretion of IL-12 by DCs and triggered an effective anti-tumoral immune response (110–112).
Cross-priming of CTLs by DCs
Cross-presentation is fundamental for the maintenance of peripheral tolerance and the induction of cross-priming. The concept of cross-presentation defines the processes of antigen uptake and processing and presentation on MHC class I by professional APCs to CTLs (113, 114), whereas cross-priming describes the stimulation and activation of naïve CTLs by this process (115). According to our current understanding that is primarily derived from viral infection models, CTL cross-priming takes place in secondary lymphoid organs (116). Antigen-experienced, matured DCs migrate and transport the viral antigen from the infection site for cross-presentation to secondary lymphoid structures (117).
The crucial factor for DCs to tune CTL activation is their maturation status (118). Several studies demonstrated that the presence of appropriate inflammatory and co-stimulatory maturation signals, such as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), TLR ligands, type I IFNs, CD80/CD86, and CD70 (119, 120) as well as CD40 ligand (CD154) provided by CD4+ T cells (“DC licensing”) is essential for DCs to properly activate CTLs in viral infections (118). It is well documented that solid and hematological tumor microenvironments contain DCs in mice and men [reviewed in Ref. (121)]. These microenvironments, however, lack DC-activating and DC migration-inducing factors (122) and harbors a multitude of immunosuppressive molecules such as TGFβ and IL-10 that impair DC maturation, migration and antigen (cross-) presentation [reviewed in Ref. (123)]. AML blasts can generate an immunosuppressive microenvironment that hinders effective adaptive as well as innate immune responses (124–127), such as by the secretion of arginase II resulting in T cell inhibition (124). Cross-presentation of the LAAs proteinase-3 and PR1 has also been shown in AML patients, but these antigens were presented by immature DCs resulting in tolerization of CTLs (128).
Therefore, even though there is compelling evidence that LAAs are cross-presented in vitro and in vivo, the question as to what extent the process of cross-priming contributes to anti-leukemic immunity is still highly controversial (114).
Nevertheless, fully functional CTLs are fundamental for the surveillance, control, and elimination of tumors (129, 130). Therefore, a better understanding of specific DC subsets in the anti-leukemic immune response and how cross-presentation of LAAs in vivo can be improved and consequently CTL dysfunction circumvented, may lead to improved vaccine-based immunotherapy against leukemia.
Leukemia Antigens
In order to achieve an optimal and effective immune response with a low rate of toxicity, leukemia antigens that are specifically expressed and presented by leukemia cells and not by healthy tissue have to be identified. In addition, these should be immunogenic and should critically account for the leukemic phenotype. Most importantly, however, these antigens should be expressed in LSCs, even though currently the phenotypic characterization of LSCs is controversial and elusive. The restricted numbers of clearly identified LAAs in leukemia remain a major obstacle for the use of these peptides in DC-based immunotherapy. In addition, the low affinity of these LAAs to bind MHC I, the short time of antigen-presentation on DCs as well as the lack of help by CD4+ T cells may limit the capacity of these LAAs to induce an anti-tumoral immune response (131, 132).
The most specific leukemia antigens are peptides from aberrant proteins created by mutations or translocations only present in leukemia cells, such as the BCR/ABL1 tyrosine kinase in CML. These peptides are known as leukemia-specific antigens (LSAs). However, most of the leukemia-specific mutations and translocations do not give rise to proteins (133). Among the numerous chromosomal translocation that were characterized in AML, only a minor fraction such as AML1-ETO (133), DEK-CAN (134), and PML-RARα (135) gives rise to proteins that generate LSAs. In addition, only two mutations involving the fms-related tyrosine kinase (FLT) and nucleophosmin 1 (NPM1) have been shown to give rise to LSAs (136, 137). Therefore, most immunotherapy approaches in myeloid leukemia target LAAs, that is, peptides from proteins that are expressed in leukemic cells and also healthy tissues, but are often overexpressed in leukemia and important for the malignant phenotype. Consequently, the induction of autoimmunity is a potential risk if such LAAs are chosen as targets for an immunotherapy. As an additional limitation, T cell receptors recognizing antigens that are broadly expressed on healthy tissues in the body are usually of low affinity. Therefore, it is crucial to characterize the degree of LAA expression on normal tissues in order to envisage the multitude and characteristics of potential autoimmune reactions.
For AML, a multitude of LAAs has been described during the last two decades and has been validated as target for immunotherapy [Table 1 and reviewed in Ref. (133)]. These LAAs comprise proteinase-3, Wilms tumor protein (WT1) (62, 138–141), the receptor for hyaluronic acid-mediated motility [RHAMM/CD168 (142)] human telomerase reverse transcriptase [hTert (143)], preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma [PRAME (144, 145)], and Aurora-A kinase (146) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Leukemia-associated antigens (LAAs) in myeloid leukemias.
| Myeloid leukemia | LAA | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| AML | Aurora-A kinase | (146, 153, 154) |
| BRAP | (160) | |
| Cyclin A1 | (161) | |
| hTert | (143) | |
| HSJ2 | (160) | |
| MPP11 | (160) | |
| Neutrophil elastase (NE) | (166) | |
| PRAME | (144, 145, 162) | |
| PR1 | (128, 139, 163, 164) | |
| Proteinase-3 | (62, 164, 165) | |
| RBPJκ | (160) | |
| RHAMM/CD168 | (142) | |
| WT1 | (62, 139, 141, 148, 149, 151, 152) | |
| CML | BRAP | (160) |
| CML-28 | (167–169) | |
| CML-66 | (167–169) | |
| HAGE | (168) | |
| HSJ2 | (160) | |
| MPP11 | (160) | |
| PRAME | (144) | |
| PR1 | (59, 139, 164, 169) | |
| Proteinase-3 | (164, 165, 169) | |
| RBPJκ | (160) | |
| Survivin | (167–169) | |
| WT1 | (139, 148, 149, 169–171) |
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; BRAP, BRCA1-associated protein; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; HAGE, helicase antigen; HSJ2, heat-shock 40 kDa protein 4; hTert, human telomerase reverse transcriptase; MPP11, M-phase phosphoprotein 11; PRAME, preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma; RBPJκ, recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region; RHAMM, receptor for hyaluronic acid-mediated motility; WT1, Wilms tumor protein.
The most attractive and promising LAA is the tumor-suppressor gene and zinc finger transcription factor WT1. WT1 is a regulator of cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. In leukemia, WT1 has been shown to have a fundamental oncogenic role for leukemogenesis resulting in differentiation arrest and aberrant cell growth (147). WT1 was demonstrated to be immunogenic as it elicits a naturally occurring anti-tumoral immune response in cancer patients (148, 149). In addition, in a WT1 directed immunotherapeutic study, off-target toxicity effects have not been observed, indicating that WT1-expressing normal tissues are omitted from the response (150). However, in some AML patients no WT1-specific CTL response has been triggered even though objective responses and remissions have been elicited (141). Importantly, WT1 is expressed to a much lesser extent on normal HSCs than on leukemic blasts and LSCs in a majority of AML patients which characterizes WT1 as attractive target for immunotherapy in AML (151, 152). Consequently, WT1 is currently targeted in clinical T cell therapy and vaccination studies.
Importantly, in a curative approach LAAs have to be expressed on LSCs (146, 153, 154). One LAA in AML that is expressed on CD34+CD38− AML “stem” cells compared to CD34+CD38+ AML progenitor cells and normal CD34+ stem/progenitor cells from healthy individuals is the serine/threonine kinase Aurora-A. Importantly, CD34+ leukemia progenitor cells but not normal CD34+ stem/progenitor cells were lysed by Aurora-A kinase-specific CTLs. Furthermore, blockade of Aurora-A kinase by a small-molecule inhibitors or shRNA impaired engraftment and improved survival of mice in an AML xenograft model (146, 153, 154).
In CML patients numerous LAAs such as WT1, proteinase-3, cancer-testis antigens like HAGE, minor histocompatibility antigens, hTert, CML-66, CML-28, and survivin were shown to be aberrantly expressed in the transformed CML cell (Table 1). Some LAAs such as hTert and survivin have a quite restricted expression pattern and are not or only marginally expressed on normal non-dividing or terminally differentiated cells (143, 155). This makes hTert and survivin promising targets for DC-based immunotherapy.
The most prominent LSA in CML is the chimeric BCR/ABL1 fusion protein, an ideal target for immunotherapy (8). An elegant paper by Yotnda et al. identified a BCR/ABL1 junctional nonapeptide (SSKALQRPV) that binds to human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A2.1 and elicits specific CTL responses in vitro in blood from healthy donors and CML patients. In 5 out of 21 CML patients, the investigators found high frequencies of junctional peptide-specific CTLs in the peripheral blood, suggesting an in vivo-immunogenicity of this peptide (156). Additional studies confirmed and extended the finding of immunogenic BCR/ABL1 junction peptides (157, 158). However, BCR/ABL1 is gives rise to a limited number of immunogenic epitopes due to only two chromosomal breakpoints (159). Furthermore the expression of the epitopes is restricted to HLA A2, A3, and B7 (158).
Since all the LAAs listed in Table 1 are expressed to a greater extent on malignant cells than on their healthy counterparts, they represent suitable antigens for immunotherapeutic approaches.
Immunotherapy for Myeloid Leukemias
Nowadays, immunotherapy covers a huge spectrum of distinct experimental procedures in order to specifically eliminate cancer cells while minimizing harm to normal tissue to limit side effects (172). However, up to now only few approaches have entered clinical routine such as unspecific immune stimulation by Bacillus Calmette–Guérin (BCG) instillations to treat non-muscle invasive bladder cancer after surgical ablation (173) or the immunomodulating anti-CTLA4 mAb Ipilimumab for metastatic melanoma or prostate cancer (174), as well as aHSCT for the treatment of myeloid leukemias (175) and the prostate antigen-specific DC-based vaccine Sipuleucel-T (Provenge®) for hormone-refractory prostate cancer (176).
The intention of active cancer immunotherapy is to mount an endogenous adaptive immune response against a tumor by directly injecting tumor-antigens together with adjuvants (“peptide vaccines”) or by ex vivo-generation of cancer-specific DCs (“DC vaccines”) and to form CTL memory in order to sustain remission (177). For AML and CML, numerous studies extensively investigated the clinical potential of this approach. Administration of autologous DCs loaded via electroporation with mRNA of the LAA WT1 resulted in CR in 50% of AML patients in a phase I/II study (141). Importantly, CR was achieved in two patients that only had partial remission after chemotherapy, indicating the feasibility and clinical potential of this approach. In contrast, in a clinical phase I study, autologous monocyte-derived DCs (mDCs) previously cultured in the presence of AML failed to induce a clinical response in relapsed AML patients (178).
Recently, a better understanding of immunosurveillance paved the way for the development of new immunotherapeutic approaches and their implementation in the clinics. Among these, immune checkpoint inhibition is most advanced in melanoma patients and anti-CTLA4 blockade was actually the first therapy that improved survival of patients suffering from metastatic melanoma (174). A recent hallmark immunotherapeutic study using a dual mAb treatment approach to block the immune checkpoint regulators CTLA-4 and programed death-1 (PD-1) using Ipilimumab and Nivolumab, respectively, resulted in persistent tumor regression in advanced melanoma patients (179). AML and CML cells also express the ligands for PD-1 (PD-L1, PD-L2), which interact with PD-1 expressed on T cells (64, 65, 99, 100). Accordingly, we recently demonstrated that CML LSCs express PD-L1 and PD-L2 as well (65). In addition, we recently demonstrated that blocking PD-1 signaling results in improved CML control in pre-clinical mouse models (64).
Furthermore, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells for adoptive T cell therapy (ACT) proved their clinical potential in leukemia patients. In addition, ACT with CAR T cells overcame the obstacle to generate sufficient numbers of high avidity LAA-specific T cells in vitro and long-term persistence, memory formation, and migration in vivo. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients treated with a low number of CAR T cells targeting CD19 and containing the co-stimulatory signaling domain of CD137 exhibited a CR. Importantly, CAR T cells extensively expanded and showed a CD19-specific immune response as well as long-term persistence with an effector memory phenotype in peripheral blood and BM without the need to trigger an anti-leukemic immune response by professional APCs. This phenotype consequently allows potential expansion upon secondary encounter with CLL cells and prevention of relapse (180). Furthermore, two children with relapsed and refractory pre-B cell ALL treated with CD19-specific CAR T cells were reported to have achieved CR (181). For myeloid leukemias a clinical application of CAR T cells has not yet been documented. However, CAR T cells targeting isoform 6 of CD44 (CD44v6) that is expressed by AML cells (182) but not by HSCs and at low levels on normal cells (183) mediated potent anti-tumor effects against primary AML in a pre-clinical AML model (184). In addition, clinical phase I/II studies (NCT01640301, NCT01621724) using ACT of T cells carrying a TCR specific for the LAA WT1 in AML patients are ongoing. These trials are essential to further determine if safety and efficacy of this promising immunotherapeutic approach also holds true for the treatment of AML patients.
DC-based immunotherapy in leukemia
Because of their excellent ability to activate T cells, DCs are considered as one of the most promising tools for tumor-antigen delivery in active cancer immunotherapy and they are ideal candidates to supply foreign tumor-antigen in the form of a DC-based vaccine or for the generation of tumor-antigen-specific CTLs in vitro (185). Clinical studies have used various precursor cells in order to manufacture sufficient ex vivo tumor-antigen loaded DCs for immunotherapeutic purposes (186). However, the different methods in manufacturing those DCs and the notion that the generated DCs differed in function and phenotype resulted in need for the standardization of DC vaccines.
To vaccinate AML patients with DCs in order to induce an optimal, long-lasting anti-leukemic CTL response, several issues have to be considered:
First, the type and origin of DCs used to treat the patient has to be defined. DCs can either be generated from patient-derived CD34+ cells or CD14+ monocytes in vitro. They can be directly positively selected from the patient’s PBMCs (ex vivo) and are differentiated in the presence of various cytokines which improves the LAA loading onto these DCs (177). Additionally, naturally circulating DCs can be loaded and activated in vivo using mAbs targeting SIGLEC H conjugated to an LAA in combination with CpG nucleotides (187, 188). In leukemia patients, especially in AML patients, the presence of blast-derived leukemic DCs was extensively documented (80–82, 87). Consequently, a promising method of generating L-DCs is to differentiate blasts from AML patients into DCs ex vivo. This method allows circumventing the loading of the DCs with LAAs. The application of these AML-derived DCs in a clinical setting is still poorly developed. Especially, the generation of sufficient numbers of AML-derived DCs is challenging. Only 25% of the initial AML cells cultured can be converted into AML-derived DCs. In addition, AML-derived DCs can only be generated in around 40% of AML patients due to AML-specific mutations (e.g., Flt-ITD) or the lack of CD14 expression that prevent the conversion of blasts into AML-derived DCs (189, 190). Nonetheless, the tolerability of this therapeutic approach and the induction of an anti-leukemic immune response in patients have been already reported. Despite these positive reports, the clinical benefit of the DC vaccine is only marginal (191). Therefore, the current DC-based cancer immunotherapy protocols using AML-derived DCs are optimized and standardized in order to allow generating sufficient AML-derived DCs (192, 193) with an improved potential to prime and activate CTLs and increase their cytolytic capacity (194, 195).
The other critical factors determining the success of DCs in AML immunotherapy besides the generation of sufficient numbers of DCs are (1) the selection of the proper LAA (discussed later), (2) the method applied for loading the respective leukemia antigen onto the DCs, and (3) the strong activation of DCs necessary to provide sufficient co-stimulatory signal for efficient T cell activation and to prevent T cell tolerization.
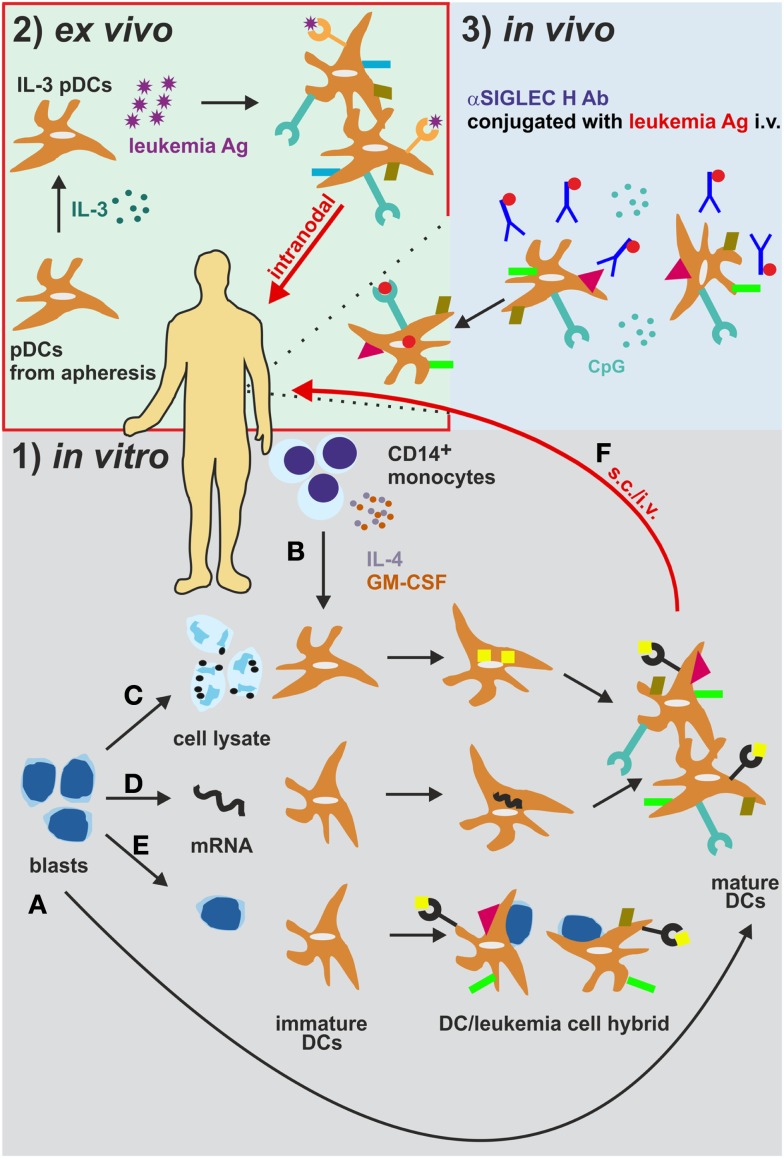
Originally, mDCs have been cultured together with AML cell lysates or immunogenic apoptotic/necrotic AML cells to ensure LAA loading [Figure 3 (185)]. As an additional approach, AML blast-mDC cell-fusion hybrids have been generated in vitro [Figure 3 (196)]. Importantly, all these multi-epitope approaches might deliver a variety of known and unknown LAAs to the DCs. In addition, these approaches circumvent the need for previous identification of the LAAs. On the other hand, co-culturing or fusion approaches might negatively impact the antigen uptake and processing and/or the maturation of DCs because of immunosuppressive factors stored in or produced by AML cells, such as TGF-β (185). Nevertheless, Herr et al. have shown that tumor cell lysate-loaded DCs were superior to DCs loaded with eluted peptides in inducing an anti-tumoral immune response against an EBV+ B lymphoblastic cell line (197). Nowadays, pre-clinical and clinical approaches favor the loading of DCs with peptides from LAAs or LSAs such as WT1, Survivin, PML-RARα, etc. via peptide pulsing or electroporation and mRNA loading [Figure 3 (191)]. Most of the studies using one of these loading methods reported activation and expansion of HLA-compatible CTLs in vitro resulting in killing and eliminating of the leukemia cells, indicating a reasonable rationale to apply mDC immunotherapy in a clinical setting irrespective of the antigen loading method. However, the use of single antigens poses the risk of immunoediting and the escape of antigen-loss variants (198). Especially, the technique of mRNA electroporation offers several advantages to overcome this issue: (1) simultaneous loading and presentation of multiple LAA epitopes without any risk for insertional mutagenesis due to the only transient mRNA expression (199); (2) expression of multiple patient-specific LAAs at once, when electroporation is performed with whole AML cell lysate mRNA (200); and (3) the possibility of combination with other loading methods (200).
Figure 3.
Different strategies for the generation and administration of DC-based vaccines in AML. (1) (A) Leukemia-derived DCs can be directly generated by isolation and differentiation from AML blasts in vitro. (B) CD14+ monocytes from patients or healthy donors are differentiated into monocyte-derived DCs (mDCs). These mDCs are cultured together with (C) AML cell lysates or immunogenic apoptotic/necrotic AML cells (185) or (D) are electroporated with mRNA from AML cells (191) to ensure leukemia antigen loading. (E) As an additional in vitro approach, AML blast-mDC cell-fusion hybrids are artificially generated (196). (F) The DCs are then injected s.c. or i.v. into AML patients. (2) DCs can also be loaded and activated in vivo (188). DCs express the endocytosis receptor SIGLEC. Intravenous administration of an αSIGLEC H mAb conjugated to a leukemia antigen in the presence of CpG results in DC activation, antigen uptake and presentation. (3) Plasmacytoid DCs isolated from AML patients are activated and loaded with leukemia antigens ex vivo and are re-injected intralymphatically into lymph nodes (201). Ab, antibody; Ag, antigen; i.v. intravenously; pDCs, plasmacytoid DCs. s.c., subcutaneously.
For optimal DC activation and antigen processing of in vitro generated DCs, different cocktails of cytokines and TLR ligands have been tested. Usually, patient-derived monocytes are cultured in the presence of IL-4 and granulocyte-monocyte colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) for several days, followed by a short course of DC maturation using TLRs, pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, prostaglandin E2, and/or CD40 ligand (202). Similar procedures have been applied for AML blast-derived DCs (185, 203–210). However, the effects of these in vitro culture and maturation conditions on the ability of DCs to capture, process and present antigen, on their T cell activating potential and on their in vivo migratory function are not fully understood (177). For example, the replacement of IL-4 by IL-15 during the differentiation phase was shown to enhance the immunostimulatory properties of DCs with a phenotype and characteristics of Langerhans cells (LCs), which are per se far more efficient in antigen-presentation and T cell priming in vitro. (211, 212). In addition, it was demonstrated that DCs matured conventionally in the presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines are unable to produce IL-12 in vivo, a cytokine that is essential for CD4+ TH1 cells differentiation. Maturation in the presence of the TLR7/8 agonist R848 restored IL-12 secretion, improved cell migration and led to more robust induction of anti-leukemic immune responses in vitro (202, 213, 214).
Tracking of labeled and intradermally administered DCs in patients revealed that less than 1% of the DCs are migrating into the adjacent lymph nodes (215). In order to circumvent the drawbacks of in vitro DC generation and their poor migration into lymph nodes, in a clinical study of DC-based immunotherapy in melanoma, Tel and colleagues directly isolated human pDCs and injected them intralymphatically into the inguinal lymph nodes after ex vivo activation and loading (201). pDCs, specialized DCs that are characterized by rapid and massive secretion of type I IFNs in response to foreign nucleic acids, have been shown to successfully mediate an interplay of innate and adaptive immune responses by activating other DCs and inducing cross-priming (216–218). Compared to subcutaneous injections, intralymphatic immunotherapy substantially reduces the amount of vaccine necessary and the duration of immunization. This approach has already proven effective for the treatment of allergies [Figure 3 (219)]. Therefore, pDCs and/or intralymphatic injection protocols may become crucial players in eliciting anti-leukemic immunity.
By now, it is unfortunately not fully elaborated which DC subset is most suitable for DC-based immunotherapy. The identification of this subset, the optimal route of administration, the optimal dose, the optimal antigen, and conditioning in order to maximize the efficacy of the treatment is pivotal for the success of treatment. Therefore, future studies have to fully aim at the functional characterization of different DC subsets in terms of T cell (cross-) priming, migration capacity, cytokine production, half-life etc. in order to maximize the clinical benefit of the therapy. The fundamental challenge in the treatment of AML remains the prevention of clinical relapse of the patients. The generation of clinical grade AML-derived DCs from AML patients in remission has been reported (220) and may consequently serve as a potential strategy in order to avoid a potential relapse (Figure 4). In addition, results from recent clinical phase I/II studies treating AML patients in remission with clinical grade DCs generated with different protocols highlight the importance of the selection of the antigen, the loading approach as well as the time of administration as fundamental success criteria for DC-based immunotherapy in AML.
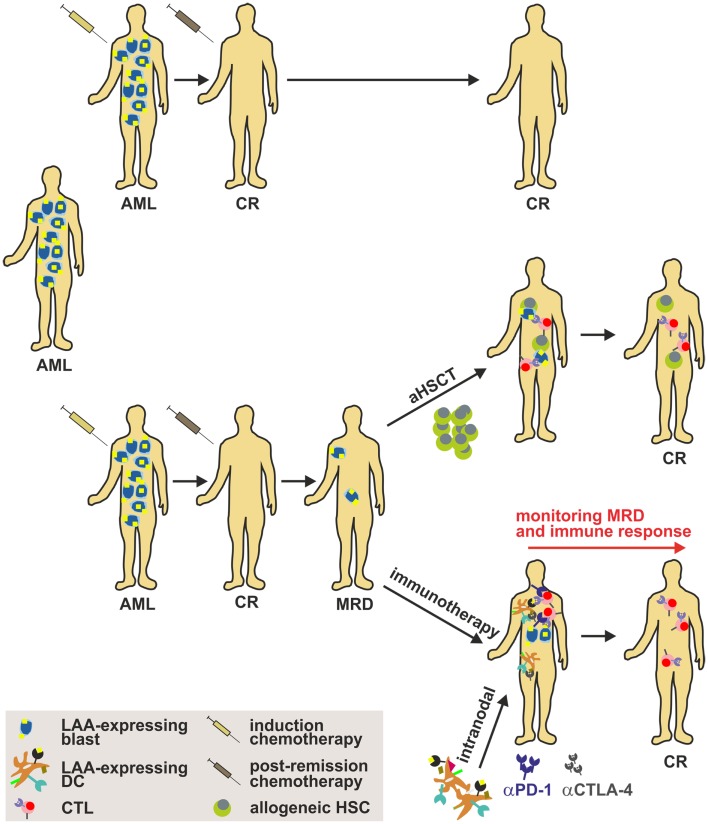
Figure 4.
Strategy to implement DC-based immunotherapy in the treatment of AML. Induction cytotoxic chemotherapy (“3 + 7” scheme with cytarabin and an anthracycline) results in a labile complete remission (CR) that has to be consolidated by post-remission chemotherapy. Nonetheless, many patients harbor persistent LSCs after a CR (referred to as MRD), which may cause disease relapse. Therefore, strategies such as aHSCT (only for a minor fraction of patients) or immunotherapy have to be implemented to sustain CR. Importantly, DC-based immunotherapy targeting AML-specific LAAs alone or in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-CTLA-4 or anti-PD-1 mAbs might be a promising approach to treat patients and to target and eliminate LSCs. aHSCT, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; CTL, cytotoxic lymphocyte; CR, complete response; DC, dendritic cell; LAA, leukemia-associated antigen; MRD, minimal residual disease.
Clinical Trials
Currently, several peptides derived from LAAs are under clinical investigation for myeloid leukemia patients in current vaccination trials. Ongoing or recruiting DC vaccination trials in phase I and II use either different WT1 derived peptides (NCT01686334, NCT00834002, NCT00672152, NCT01266083), the proteinase-3-derived peptide PR1 (NCT00454168), the peptides MAGE-A1, MAGE-A3, and NY-ESO-1 (NCT01483274) or a combination of WT1 and PR1 (NCT00433745, NCT00488592). These trials primarily include patients that just underwent aHSCT, elderly patients or patients in first remission. Interestingly, one study that has been completed recently applied a vaccination protocol with lethally irradiated autologous AML cells that were genetically modified to secrete human GM-CSF in order to enhance LAA presentation (NCT00136422). Another trial that aimed at up-regulating LAA presentation additionally administered the hypomethylating drug decitabine (NCT01483274). More and more studies use DC vaccination in combination with other drugs or cytokines. For example, in a clinical phase II study, CML patients in remission are treated with PR1 peptide vaccine in combination with pegylated IFN-α2b (PegIntron®, NCT00415857). Another approach combines a DC cell/AML fusion vaccine with the blockade of PD-1 (NCT01096602).
All these clinical trials have proven that DC-based immunotherapies in leukemia are safe and have hardly any side effects. Unfortunately, this good tolerability is accompanied by a rather minor clinical benefit in terms of response rate or other important clinical outcome parameters (191). From immunotherapy trials in solid tumors we have learned that the established response criteria for chemotherapy, such as the “RECIST criteria,” may not be appropriate for immunotherapy approaches. This may also hold true for leukemia. Reduction of leukemia load or remission in the BM shortly after the treatment may not be the appropriate readout to judge the efficacy of an active immunotherapy that needs time to be established and may contribute to a long-term control of the disease. In addition, suitable biomarkers that are predictive for a response to an immunotherapy are still lacking (177). Therefore, future studies also have to focus on the generation of adequate readouts and the identification of defined biomarkers for the monitoring of DC-based immunotherapy in leukemia. Furthermore, most clinical studies carried out so far enrolled leukemia patients with a high leukemia burden. In these studies, at least some of the patients showed a minor clinical benefit. Importantly, applying DC-based immunotherapy to patients with a lower leukemia burden or MRD might result in better responses.
Concluding Remarks
During the last decade, the combined efforts of researchers to treat myeloid leukemia unraveled a multitude of LAAs suitable for DC-based immunotherapy. Consequently, DC-based immunotherapy slowly progresses into the clinical treatment of leukemia.
The rapid development in the field allowed the design of phase I and II studies with different DC vaccination protocols. DC-based vaccination often resulted in the induction of potent anti-leukemic CTL responses. The benefit for the patient in these studies in terms of response to treatment was rather limited. Nevertheless, DC vaccination protocols remain a promising supplementary strategy in the treatment of leukemia, and future improvements will reveal their full potential. In order to improve DC-based vaccination for clinical routine, several issues still have to be solved. Most importantly, an optimal timing for the vaccination during the course of disease has to be defined. Current literature and our own experiments indicate that immunotherapy may be most effective in the state of MRD after successful induction and post-remission chemotherapy. In parallel, MRD has to be better defined, characterized, and especially quantified by the introduction of more sophisticated molecular and flow cytometry techniques. Simultaneously, it is of extreme importance to quantitatively and functionally assess the degree of the anti-leukemic CTL response. Furthermore, the vaccination procedure, including the choice of LAA (or multiple LAAs); the source of DCs (mDCs, LCs, pDCs, or AML-derived DCs); the DC maturation protocol and the way of application (i.v. vs. s.c. vs. intralymphatical) have to be defined and standardized. Finally, the timing and application of potential co-treatments, including chemotherapy, aHSCT and immunomodulating agents has to be considered. Especially, combining DC-based immunotherapy with the blockade of immune checkpoint regulators such as PD-1 and/or CTLA-4 may represent a powerful tool for the treatment of leukemia.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Adrian F. Ochsenbein is supported by grants from the Swiss National Science Foundation, the Swiss Cancer League, the Cancer League of the Canton of Bern, and the Werner und Hedy Berger-Janser-Stiftung. Christian M. Schürch is supported by the Gertrud Hagmann-Stiftung für Malignomforschung, the Fondazione Dr. Carlo Gianella and the Hans Altschüler-Stiftung. Carsten Riether is supported by the Sassella Foundation and the Fondation BIOS pour la Recherche.
Author Contributions
Christian M. Schürch and Carsten Riether wrote the manuscript and Adrian F. Ochsenbein revised the manuscript.
References
- 1.Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vacchelli E, Eggermont A, Fridman WH, Galon J, et al. Trial watch: dendritic cell-based interventions for cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology (2012) 1(7):1111–34 10.4161/onci.21494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Vacchelli E, Martins I, Eggermont A, Fridman WH, Galon J, Sautes-Fridman C, et al. Trial watch: peptide vaccines in cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology (2012) 1(9):1557–76 10.4161/onci.22428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vacchelli E, Eggermont A, Fridman WH, Galon J, Tartour E, Zitvogel L, et al. Trial watch: adoptive cell transfer for anticancer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology (2013) 2(5):e24238. 10.4161/onci.25595 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vacchelli E, Eggermont A, Galon J, Sautes-Fridman C, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G, et al. Trial watch: monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology (2013) 2(1):e22789. 10.4161/onci.24612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. editors. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haemopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon: IARC Press; (2008). [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tefferi A. Overview of the Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. UpToDate: Waltham, MA: (2013). [Google Scholar]
- 7.Huntly BJ, Gilliland DG. Leukaemia stem cells and the evolution of cancer-stem-cell research. Nat Rev Cancer (2005) 5(4):311–21 10.1038/nrc1592 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kavalerchik E, Goff D, Jamieson CH. Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. J Clin Oncol (2008) 26(17):2911–5 10.1200/JCO.2008.17.5745 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Garcia-Manero G, Faderl S, O’Brien S, Cortes J, Talpaz M, Kantarjian HM. Chronic myelogenous leukemia: a review and update of therapeutic strategies. Cancer (2003) 98(3):437–57 10.1002/cncr.11520 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin (2013) 63(1):11–30 10.3322/caac.21166 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.SEER Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results. Bethesda, MD: US National Cancer Institute & National Institutes of Health; (2010). [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sokal JE, Baccarani M, Russo D, Tura S. Staging and prognosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Semin Hematol (1988) 25(1):49–61 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Calabretta B, Perrotti D. The biology of CML blast crisis. Blood (2004) 103(11):4010–22 10.1182/blood-2003-12-4111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wong S, Witte ON. The BCR-ABL story: bench to bedside and back. Annu Rev Immunol (2004) 22:247–306 10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104753 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F, et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med (2003) 348(11):994–1004 10.1056/NEJMoa022457 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med (2006) 355(23):2408–17 10.1056/NEJMoa062867 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kantarjian H, Shah NP, Hochhaus A, Cortes J, Shah S, Ayala M, et al. Dasatinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med (2010) 362(24):2260–70 10.1056/NEJMoa1002315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Saglio G, Kim DW, Issaragrisil S, le Coutre P, Etienne G, Lobo C, et al. Nilotinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med (2010) 362(24):2251–9 10.1056/NEJMoa0912614 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kantarjian HM, Shah NP, Cortes JE, Baccarani M, Agarwal MB, Undurraga MS, et al. Dasatinib or imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: 2-year follow-up from a randomized phase 3 trial (DASISION). Blood (2012) 119(5):1123–9 10.1182/blood-2011-08-376087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.O’Hare T, Zabriskie MS, Eiring AM, Deininger MW. Pushing the limits of targeted therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer (2012) 12(8):513–26 10.1038/nrc3317 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Negrin RS, Schiffer CA. Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Accelerated Phase. UpToDate: Waltham, MA: (2013). [Google Scholar]
- 22.Druker BJ, O’Brien SG, Cortes J, Radich J. Chronic myelogenous leukemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program (2002) 2002(1):111–35 10.1182/asheducation-2002.1.111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Estey E, Dohner H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet (2006) 368(9550):1894–907 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69780-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Van Etten RA. Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. UpToDate: Waltham, MA: (2013). [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zeisig BB, Kulasekararaj AG, Mufti GJ, So CW. SnapShot: acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell (2012) 22(5):698–e1 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.10.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Larson RA. Induction Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Younger Adults. UpToDate: Waltham, MA: (2013). [Google Scholar]
- 27.Martner A, Thoren FB, Aurelius J, Hellstrand K. Immunotherapeutic strategies for relapse control in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev (2013) 27(5):209–16 10.1016/j.blre.2013.06.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Corbin AS, Agarwal A, Loriaux M, Cortes J, Deininger MW, Druker BJ. Human chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells are insensitive to imatinib despite inhibition of BCR-ABL activity. J Clin Invest (2011) 121(1):396–409 10.1172/JCI35721 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, Murdoch B, Hoang T, Caceres-Cortes J, et al. A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature (1994) 367(6464):645–8 10.1038/367645a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med (1997) 3(7):730–7 10.1038/nm0797-730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Blair A, Hogge DE, Ailles LE, Lansdorp PM, Sutherland HJ. Lack of expression of Thy-1 (CD90) on acute myeloid leukemia cells with long-term proliferative ability in vitro and in vivo. Blood (1997) 89(9):3104–12 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Blair A, Hogge DE, Sutherland HJ. Most acute myeloid leukemia progenitor cells with long-term proliferative ability in vitro and in vivo have the phenotype CD34(+)/CD71(-)/HLA-DR. Blood (1998) 92(11):4325–35 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Blair A, Sutherland HJ. Primitive acute myeloid leukemia cells with long-term proliferative ability in vitro and in vivo lack surface expression of c-kit (CD117). Exp Hematol (2000) 28(6):660–71 10.1016/S0301-472X(00)00155-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jordan CT, Upchurch D, Szilvassy SJ, Guzman ML, Howard DS, Pettigrew AL, et al. The interleukin-3 receptor alpha chain is a unique marker for human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Leukemia (2000) 14(10):1777–84 10.1038/sj.leu.2401903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jaiswal S, Jamieson CH, Pang WW, Park CY, Chao MP, Majeti R, et al. CD47 is upregulated on circulating hematopoietic stem cells and leukemia cells to avoid phagocytosis. Cell (2009) 138(2):271–85 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Majeti R, Chao MP, Alizadeh AA, Pang WW, Jaiswal S, Gibbs KD, Jr, et al. CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and therapeutic antibody target on human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cell (2009) 138(2):286–99 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sarry JE, Murphy K, Perry R, Sanchez PV, Secreto A, Keefer C, et al. Human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells are rare and heterogeneous when assayed in NOD/SCID/IL2Rgammac-deficient mice. J Clin Invest (2011) 121(1):384–95 10.1172/JCI41495 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Taussig DC, Miraki-Moud F, Anjos-Afonso F, Pearce DJ, Allen K, Ridler C, et al. Anti-CD38 antibody-mediated clearance of human repopulating cells masks the heterogeneity of leukemia-initiating cells. Blood (2008) 112(3):568–75 10.1182/blood-2007-10-118331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Buccisano F, Maurillo L, Del Principe MI, Del Poeta G, Sconocchia G, Lo-Coco F, et al. Prognostic and therapeutic implications of minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood (2012) 119(2):332–41 10.1182/blood-2011-08-363291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Paietta E. Minimal residual disease in acute myeloid leukemia: coming of age. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program (2012) 2012:35–42 10.1182/asheducation-2012.1.35 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Feller N, van der Pol MA, van Stijn A, Weijers GW, Westra AH, Evertse BW, et al. MRD parameters using immunophenotypic detection methods are highly reliable in predicting survival in acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia (2004) 18(8):1380–90 10.1038/sj.leu.2403405 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bachas C, Schuurhuis GJ, Hollink IH, Kwidama ZJ, Goemans BF, Zwaan CM, et al. High-frequency type I/II mutational shifts between diagnosis and relapse are associated with outcome in pediatric AML: implications for personalized medicine. Blood (2010) 116(15):2752–8 10.1182/blood-2010-03-276519 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Barrett AJ, Savani BN. Does chemotherapy modify the immune surveillance of hematological malignancies? Leukemia (2009) 23(1):53–8 10.1038/leu.2008.273 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hirano N, Takahashi T, Ohtake S, Hirashima K, Emi N, Saito K, et al. Expression of costimulatory molecules in human leukemias. Leukemia (1996) 10(7):1168–76 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Maeda A, Yamamoto K, Yamashita K, Asagoe K, Nohgawa M, Kita K, et al. The expression of co-stimulatory molecules and their relationship to the prognosis of human acute myeloid leukaemia: poor prognosis of B7-2-positive leukaemia. Br J Haematol (1998) 102(5):1257–62 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1998.00901.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hicks C, Keoshkerian E, Gaudry L, Lindeman R. CD80 (B7-1) expression on human acute myeloid leukaemic cells cultured with GM-CSF, IL-3 and IL-6. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2001) 50(4):173–80 10.1007/PL00006686 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Whiteway A, Corbett T, Anderson R, Macdonald I, Prentice HG. Expression of co-stimulatory molecules on acute myeloid leukaemia blasts may effect duration of first remission. Br J Haematol (2003) 120(3):442–51 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.04085.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tamura H, Dan K, Tamada K, Nakamura K, Shioi Y, Hyodo H, et al. Expression of functional B7-H2 and B7.2 costimulatory molecules and their prognostic implications in de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res (2005) 11(16):5708–17 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2672 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Morecki S, Revel-Vilk S, Nabet C, Pick M, Ackerstein A, Nagler A, et al. Immunological evaluation of patients with hematological malignancies receiving ambulatory cytokine-mediated immunotherapy with recombinant human interferon-alpha 2a and interleukin-2. Cancer Immunol Immunother (1992) 35(6):401–11 10.1007/BF01789019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Salesse S, Verfaillie CM. BCR/ABL: from molecular mechanisms of leukemia induction to treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Oncogene (2002) 21(56):8547–59 10.1038/sj.onc.1206082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Weiden PL, Flournoy N, Thomas ED, Prentice R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, et al. Antileukemic effect of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of allogeneic-marrow grafts. N Engl J Med (1979) 300(19):1068–73 10.1056/NEJM197905103001902 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gale RP, Horowitz MM, Ash RC, Champlin RE, Goldman JM, Rimm AA, et al. Identical-twin bone marrow transplants for leukemia. Ann Intern Med (1994) 120(8):646–52 10.7326/0003-4819-120-8-199404150-00004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Horowitz MM, Gale RP, Sondel PM, Goldman JM, Kersey J, Kolb HJ, et al. Graft-versus-leukemia reactions after bone marrow transplantation. Blood (1990) 75(3):555–62 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kolb HJ, Mittermuller J, Clemm C, Holler E, Ledderose G, Brehm G, et al. Donor leukocyte transfusions for treatment of recurrent chronic myelogenous leukemia in marrow transplant patients. Blood (1990) 76(12):2462–5 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kolb HJ, Schattenberg A, Goldman JM, Hertenstein B, Jacobsen N, Arcese W, et al. Graft-versus-leukemia effect of donor lymphocyte transfusions in marrow grafted patients. Blood (1995) 86(5):2041–50 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sehn LH, Alyea EP, Weller E, Canning C, Lee S, Ritz J, et al. Comparative outcomes of T-cell-depleted and non-T-cell-depleted allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia: impact of donor lymphocyte infusion. J Clin Oncol (1999) 17(2):561–8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Montagna D, Maccario R, Locatelli F, Montini E, Pagani S, Bonetti F, et al. Emergence of antitumor cytolytic T cells is associated with maintenance of hematologic remission in children with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood (2006) 108(12):3843–50 10.1182/blood-2006-05-021535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lim SH, Coleman S. Chronic myeloid leukemia as an immunological target. Am J Hematol (1997) 54(1):61–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Molldrem JJ, Lee PP, Wang C, Felio K, Kantarjian HM, Champlin RE, et al. Evidence that specific T lymphocytes may participate in the elimination of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Nat Med (2000) 6(9):1018–23 10.1038/79526 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Butt NM, Rojas JM, Wang L, Christmas SE, Abu-Eisha HM, Clark RE. Circulating bcr-abl-specific CD8+ T cells in chronic myeloid leukemia patients and healthy subjects. Haematologica (2005) 90(10):1315–23 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Selleri C, Maciejewski JP. The role of FAS-mediated apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma (2000) 37(3-4):283–97 10.3109/10428190009089429 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Scheibenbogen C, Letsch A, Thiel E, Schmittel A, Mailaender V, Baerwolf S, et al. CD8 T-cell responses to Wilms tumor gene product WT1 and proteinase 3 in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood (2002) 100(6):2132–7 10.1182/blood-2002-01-0163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lickliter JD, Kratzke RA, Nguyen PL, Niehans GA, Miller JS. Fas ligand is highly expressed in acute leukemia and during the transformation of chronic myeloid leukemia to blast crisis. Exp Hematol (1999) 27(10):1519–27 10.1016/S0301-472X(99)00091-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mumprecht S, Schurch C, Schwaller J, Solenthaler M, Ochsenbein AF. Programmed death 1 signaling on chronic myeloid leukemia-specific T cells results in T-cell exhaustion and disease progression. Blood (2009) 114(8):1528–36 10.1182/blood-2008-09-179697 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Schürch C, Riether C, Amrein MA, Ochsenbein AF. Cytotoxic T cells induce proliferation of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells by secreting interferon-gamma. J Exp Med (2013) 210(3):605–21 10.1084/jem.20121229 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Schürch C, Riether C, Matter MS, Tzankov A, Ochsenbein AF. CD27 signaling on chronic myelogenous leukemia stem cells activates Wnt target genes and promotes disease progression. J Clin Invest (2012) 122(2):624–38 10.1172/JCI45977 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.de Visser KE, Eichten A, Coussens LM. Paradoxical roles of the immune system during cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer (2006) 6(1):24–37 10.1038/nrc1782 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Mumprecht S. Immunosurveillance of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. PhD Thesis, Bern: University of Bern; (2007). [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bhatia R, McGlave PB. T lymphocytes cultured from chronic myelogenous leukemia bone marrow suppress autologous hematopoietic progenitors. Leukemia (1995) 9(6):1006–12 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Giralt S, Hester J, Huh Y, Hirsch-Ginsberg C, Rondon G, Seong D, et al. CD8-depleted donor lymphocyte infusion as treatment for relapsed chronic myelogenous leukemia after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood (1995) 86(11):4337–43 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kiani A, Habermann I, Schake K, Neubauer A, Rogge L, Ehninger G. Normal intrinsic Th1/Th2 balance in patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia not treated with interferon-alpha or imatinib. Haematologica (2003) 88(7):754–61 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.van Denderen J, Hermans A, Meeuwsen T, Troelstra C, Zegers N, Boersma W, et al. Antibody recognition of the tumor-specific bcr-abl joining region in chronic myeloid leukemia. J Exp Med (1989) 169(1):87–98 10.1084/jem.169.1.87 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Alyea EP, Soiffer RJ, Canning C, Neuberg D, Schlossman R, Pickett C, et al. Toxicity and efficacy of defined doses of CD4(+) donor lymphocytes for treatment of relapse after allogeneic bone marrow transplant. Blood (1998) 91(10):3671–80 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Wu CJ, Yang XF, McLaughlin S, Neuberg D, Canning C, Stein B, et al. Detection of a potent humoral response associated with immune-induced remission of chronic myelogenous leukemia. J Clin Invest (2000) 106(5):705–14 10.1172/JCI10196 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Cervantes F, Pierson BA, McGlave PB, Verfaillie CM, Miller JS. Autologous activated natural killer cells suppress primitive chronic myelogenous leukemia progenitors in long-term culture. Blood (1996) 87(6):2476–85 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Pierson BA, Miller JS. CD56+bright and CD56+dim natural killer cells in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia progressively decrease in number, respond less to stimuli that recruit clonogenic natural killer cells, and exhibit decreased proliferation on a per cell basis. Blood (1996) 88(6):2279–87 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Pierson BA, Miller JS. The role of autologous natural killer cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma (1997) 27(5–6):387–99 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ruggeri L, Capanni M, Urbani E, Perruccio K, Shlomchik WD, Tosti A, et al. Effectiveness of donor natural killer cell alloreactivity in mismatched hematopoietic transplants. Science (2002) 295(5562):2097–100 10.1126/science.1068440 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Mohty M, Isnardon D, Vey N, Briere F, Blaise D, Olive D, et al. Low blood dendritic cells in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients correlates with loss of CD34+/CD38− primitive haematopoietic progenitors. Br J Haematol (2002) 119(1):115–8 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2002.03831.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Boissel N, Rousselot P, Raffoux E, Cayuela JM, Maarek O, Charron D, et al. Defective blood dendritic cells in chronic myeloid leukemia correlate with high plasmatic VEGF and are not normalized by imatinib mesylate. Leukemia (2004) 18(10):1656–61 10.1038/sj.leu.2403474 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Orsini E, Calabrese E, Maggio R, Pasquale A, Nanni M, Trasarti S, et al. Circulating myeloid dendritic cell directly isolated from patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia are functional and carry the bcr-abl translocation. Leuk Res (2006) 30(7):785–94 10.1016/j.leukres.2005.11.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Dong R, Cwynarski K, Entwistle A, Marelli-Berg F, Dazzi F, Simpson E, et al. Dendritic cells from CML patients have altered actin organization, reduced antigen processing, and impaired migration. Blood (2003) 101(9):3560–7 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1841 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Heinzinger M, Waller CF, von den Berg A, Rosenstiel A, Lange W. Generation of dendritic cells from patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Ann Hematol (1999) 78(4):181–6 10.1007/s002770050497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Smit WM, Rijnbeek M, van Bergen CA, de Paus RA, Vervenne HA, van de Keur M, et al. Generation of dendritic cells expressing bcr-abl from CD34-positive chronic myeloid leukemia precursor cells. Hum Immunol (1997) 53(2):216–23 10.1016/S0198-8859(96)00285-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Eibl B, Ebner S, Duba C, Bock G, Romani N, Erdel M, et al. Dendritic cells generated from blood precursors of chronic myelogenous leukemia patients carry the Philadelphia translocation and can induce a CML-specific primary cytotoxic T-cell response. Genes Chromosomes Cancer (1997) 20(3):215–23 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Eisendle K, Lang A, Eibl B, Nachbaur D, Glassl H, Fiegl M, et al. Phenotypic and functional deficiencies of leukaemic dendritic cells from patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol (2003) 120(1):63–73 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.03979.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Mohty M, Jarrossay D, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Zandotti C, Briere F, de Lamballeri XN, et al. Circulating blood dendritic cells from myeloid leukemia patients display quantitative and cytogenetic abnormalities as well as functional impairment. Blood (2001) 98(13):3750–6 10.1182/blood.V98.13.3750 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Mumprecht S, Claus C, Schurch C, Pavelic V, Matter MS, Ochsenbein AF. Defective homing and impaired induction of cytotoxic T cells by BCR/ABL-expressing dendritic cells. Blood (2009) 113(19):4681–9 10.1182/blood-2008-05-156471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Narita M, Takahashi M, Liu A, Nikkuni K, Furukawa T, Toba K, et al. Leukemia blast-induced T-cell anergy demonstrated by leukemia-derived dendritic cells in acute myelogenous leukemia. Exp Hematol (2001) 29(6):709–19 10.1016/S0301-472X(01)00636-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Ge W, Ma X, Li X, Wang Y, Li C, Meng H, et al. B7-H1 up-regulation on dendritic-like leukemia cells suppresses T cell immune function through modulation of IL-10/IL-12 production and generation of Treg cells. Leuk Res (2009) 33(7):948–57 10.1016/j.leukres.2009.01.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Curti A, Trabanelli S, Onofri C, Aluigi M, Salvestrini V, Ocadlikova D, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-expressing leukemic dendritic cells impair a leukemia-specific immune response by inducing potent T regulatory cells. Haematologica (2010) 95(12):2022–30 10.3324/haematol.2010.025924 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Wang X, Zheng J, Liu J, Yao J, He Y, Li X, et al. Increased population of CD4(+)CD25(high), regulatory T cells with their higher apoptotic and proliferating status in peripheral blood of acute myeloid leukemia patients. Eur J Haematol (2005) 75(6):468–76 10.1111/j.1600-0609.2005.00537.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Szczepanski MJ, Szajnik M, Czystowska M, Mandapathil M, Strauss L, Welsh A, et al. Increased frequency and suppression by regulatory T cells in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res (2009) 15(10):3325–32 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-3010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Shenghui Z, Yixiang H, Jianbo W, Kang Y, Laixi B, Yan Z, et al. Elevated frequencies of CD4(+) CD25(+) CD127lo regulatory T cells is associated to poor prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Cancer (2011) 129(6):1373–81 10.1002/ijc.25791 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Nadal E, Garin M, Kaeda J, Apperley J, Lechler R, Dazzi F. Increased frequencies of CD4(+)CD25(high) T(regs) correlate with disease relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia (2007) 21(3):472–9 10.1038/sj.leu.2404522 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Zhou Q, Munger ME, Highfill SL, Tolar J, Weigel BJ, Riddle M, et al. Program death-1 signaling and regulatory T cells collaborate to resist the function of adoptively transferred cytotoxic T lymphocytes in advanced acute myeloid leukemia. Blood (2010) 116(14):2484–93 10.1182/blood-2010-03-275446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Le Dieu R, Taussig DC, Ramsay AG, Mitter R, Miraki-Moud F, Fatah R, et al. Peripheral blood T cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients at diagnosis have abnormal phenotype and genotype and form defective immune synapses with AML blasts. Blood (2009) 114(18):3909–16 10.1182/blood-2009-02-206946 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.van Luijn MM, van den Ancker W, Chamuleau ME, Ossenkoppele GJ, van Ham SM, van de Loosdrecht AA. Impaired antigen presentation in neoplasia: basic mechanisms and implications for acute myeloid leukemia. Immunotherapy (2010) 2(1):85–97 10.2217/imt.09.84 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Saudemont A, Quesnel B. In a model of tumor dormancy, long-term persistent leukemic cells have increased B7-H1 and B7.1 expression and resist CTL-mediated lysis. Blood (2004) 104(7):2124–33 10.1182/blood-2004-01-0064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Dolen Y, Esendagli G. Myeloid leukemia cells with a B7-2(+) subpopulation provoke Th-cell responses and become immuno-suppressive through the modulation of B7 ligands. Eur J Immunol (2013) 43(3):747–57 10.1002/eji.201242814 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Chamuleau ME, Souwer Y, Van Ham SM, Zevenbergen A, Westers TM, Berkhof J, et al. Class II-associated invariant chain peptide expression on myeloid leukemic blasts predicts poor clinical outcome. Cancer Res (2004) 64(16):5546–50 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1350 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.van Luijn MM, van den Ancker W, Chamuleau ME, Zevenbergen A, Westers TM, Ossenkoppele GJ, et al. Absence of class II-associated invariant chain peptide on leukemic blasts of patients promotes activation of autologous leukemia-reactive CD4+ T cells. Cancer Res (2011) 71(7):2507–17 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3689 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.van Luijn MM, Chamuleau ME, Ossenkoppele GJ, van de Loosdrecht AA, Marieke van Ham S. Tumor immune escape in acute myeloid leukemia: class II-associated invariant chain peptide expression as result of deficient antigen presentation. Oncoimmunology (2012) 1(2):211–3 10.4161/onci.1.2.18100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.van Luijn MM, van de Loosdrecht AA, Lampen MH, van Veelen PA, Zevenbergen A, Kester MG, et al. Promiscuous binding of invariant chain-derived CLIP peptide to distinct HLA-I molecules revealed in leukemic cells. PLoS One (2012) 7(4):e34649. 10.1371/journal.pone.0034649 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Baessler T, Krusch M, Schmiedel BJ, Kloss M, Baltz KM, Wacker A, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein ligand subverts immunosurveillance of acute myeloid leukemia in humans. Cancer Res (2009) 69(3):1037–45 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2650 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Baessler T, Charton JE, Schmiedel BJ, Grunebach F, Krusch M, Wacker A, et al. CD137 ligand mediates opposite effects in human and mouse NK cells and impairs NK-cell reactivity against human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood (2010) 115(15):3058–69 10.1182/blood-2009-06-227934 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Schmiedel BJ, Nuebling T, Steinbacher J, Malinovska A, Wende CM, Azuma M, et al. Receptor activator for NF-kappaB ligand in acute myeloid leukemia: expression, function, and modulation of NK cell immunosurveillance. J Immunol (2013) 190(2):821–31 10.4049/jimmunol.1201792 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Theocharides AP, Jin L, Cheng PY, Prasolava TK, Malko AV, Ho JM, et al. Disruption of SIRPalpha signaling in macrophages eliminates human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells in xenografts. J Exp Med (2012) 209(10):1883–99 10.1084/jem.20120502 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Chao MP, Majeti R, Weissman IL. Programmed cell removal: a new obstacle in the road to developing cancer. Nat Rev Cancer (2012) 12(1):58–67 10.1038/nrc3171 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Shen L, Evel-Kabler K, Strube R, Chen SY. Silencing of SOCS1 enhances antigen presentation by dendritic cells and antigen-specific anti-tumor immunity. Nat Biotechnol (2004) 22(12):1546–53 10.1038/nbt1035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Evel-Kabler K, Song XT, Aldrich M, Huang XF, Chen SY. SOCS1 restricts dendritic cells’ ability to break self tolerance and induce antitumor immunity by regulating IL-12 production and signaling. J Clin Invest (2006) 116(1):90–100 10.1172/JCI26169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Liu G, Ng H, Akasaki Y, Yuan X, Ehtesham M, Yin D, et al. Small interference RNA modulation of IL-10 in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells enhances the Th1 response. Eur J Immunol (2004) 34(6):1680–7 10.1002/eji.200425081 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ochsenbein AF, Sierro S, Odermatt B, Pericin M, Karrer U, Hermans J, et al. Roles of tumour localization, second signals and cross priming in cytotoxic T-cell induction. Nature (2001) 411(6841):1058–64 10.1038/35082583 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Zinkernagel RM. On cross-priming of MHC class I-specific CTL: rule or exception? Eur J Immunol (2002) 32(9):2385–92 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Bevan MJ. Cross-priming. Nat Immunol (2006) 7(4):363–5 10.1038/ni0406-363 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Alvarez D, Vollmann EH, von Andrian UH. Mechanisms and consequences of dendritic cell migration. Immunity (2008) 29(3):325–42 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Allan RS, Waithman J, Bedoui S, Jones CM, Villadangos JA, Zhan Y, et al. Migratory dendritic cells transfer antigen to a lymph node-resident dendritic cell population for efficient CTL priming. Immunity (2006) 25(1):153–62 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.04.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Steinman RM, Hawiger D, Liu K, Bonifaz L, Bonnyay D, Mahnke K, et al. Dendritic cell function in vivo during the steady state: a role in peripheral tolerance. Ann N Y Acad Sci (2003) 987:15–25 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb06029.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Hernandez J, Aung S, Marquardt K, Sherman LA. Uncoupling of proliferative potential and gain of effector function by CD8(+) T cells responding to self-antigens. J Exp Med (2002) 196(3):323–33 10.1084/jem.20011612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Redmond WL, Sherman LA. Peripheral tolerance of CD8 T lymphocytes. Immunity (2005) 22(3):275–84 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.01.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Melief CJ. Cancer immunotherapy by dendritic cells. Immunity (2008) 29(3):372–83 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.08.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Dhodapkar MV, Dhodapkar KM, Palucka AK. Interactions of tumor cells with dendritic cells: balancing immunity and tolerance. Cell Death Differ (2008) 15(1):39–50 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402247 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Gabrilovich D. Mechanisms and functional significance of tumour-induced dendritic-cell defects. Nat Rev Immunol (2004) 4(12):941–52 10.1038/nri1498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Mussai F, De Santo C, Abu-Dayyeh I, Booth S, Quek L, McEwen-Smith RM, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia creates an arginase-dependent immunosuppressive microenvironment. Blood (2013) 122(5):749–58 10.1182/blood-2013-01-480129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Lion E, Willemen Y, Berneman ZN, Van Tendeloo VF, Smits EL. Natural killer cell immune escape in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia (2012) 26(9):2019–26 10.1038/leu.2012.87 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Zhou Q, Munger ME, Veenstra RG, Weigel BJ, Hirashima M, Munn DH, et al. Coexpression of Tim-3 and PD-1 identifies a CD8+ T-cell exhaustion phenotype in mice with disseminated acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood (2011) 117(17):4501–10 10.1182/blood-2010-10-310425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Buggins AG, Milojkovic D, Arno MJ, Lea NC, Mufti GJ, Thomas NS, et al. Microenvironment produced by acute myeloid leukemia cells prevents T cell activation and proliferation by inhibition of NF-kappaB, c-Myc, and pRb pathways. J Immunol (2001) 167(10):6021–30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Alatrash G, Ono Y, Sergeeva A, Sukhumalchandra P, Zhang M, St John LS, et al. The role of antigen cross-presentation from leukemia blasts on immunity to the leukemia-associated antigen PR1. J Immunother (2012) 35(4):309–20 10.1097/CJI.0b013e31824b3b14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Zitvogel L, Galluzzi L, Smyth MJ, Kroemer G. Mechanism of action of conventional and targeted anticancer therapies: reinstating immunosurveillance. Immunity (2013) 39(1):74–88 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.06.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Swann JB, Smyth MJ. Immune surveillance of tumors. J Clin Invest (2007) 117(5):1137–46 10.1172/JCI31405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Schwartzentruber DJ, Hwu P, Marincola FM, Topalian SL, et al. Immunologic and therapeutic evaluation of a synthetic peptide vaccine for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma. Nat Med (1998) 4(3):321–7 10.1038/nm0398-321 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Amoscato AA, Prenovitz DA, Lotze MT. Rapid extracellular degradation of synthetic class I peptides by human dendritic cells. J Immunol (1998) 161(8):4023–32 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Anguille S, Van Tendeloo VF, Berneman ZN. Leukemia-associated antigens and their relevance to the immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia (2012) 26(10):2186–96 10.1038/leu.2012.145 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Makita M, Azuma T, Hamaguchi H, Niiya H, Kojima K, Fujita S, et al. Leukemia-associated fusion proteins, dek-can and bcr-abl, represent immunogenic HLA-DR-restricted epitopes recognized by fusion peptide-specific CD4+ T lymphocytes. Leukemia (2002) 16(12):2400–7 10.1038/sj.leu.2402742 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Osman Y, Takahashi M, Zheng Z, Toba K, Liu A, Furukawa T, et al. Dendritic cells stimulate the expansion of PML-RAR alpha specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes: its applicability for antileukemia immunotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res (1999) 18(4):485–92 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Scholl S, Salzmann S, Kaufmann AM, Hoffken K. Flt3-ITD mutations can generate leukaemia specific neoepitopes: potential role for immunotherapeutic approaches. Leuk Lymphoma (2006) 47(2):307–12 10.1080/10428190500301306 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Greiner J, Ono Y, Hofmann S, Schmitt A, Mehring E, Gotz M, et al. Mutated regions of nucleophosmin 1 elicit both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell responses in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood (2012) 120(6):1282–9 10.1182/blood-2011-11-394395 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Oka Y, Tsuboi A, Taguchi T, Osaki T, Kyo T, Nakajima H, et al. Induction of WT1 (Wilms’ tumor gene)-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes by WT1 peptide vaccine and the resultant cancer regression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2004) 101(38):13885–90 10.1073/pnas.0405884101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Rezvani K, Yong AS, Mielke S, Savani BN, Musse L, Superata J, et al. Leukemia-associated antigen-specific T-cell responses following combined PR1 and WT1 peptide vaccination in patients with myeloid malignancies. Blood (2008) 111(1):236–42 10.1182/blood-2007-08-108241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Rezvani K, Yong AS, Tawab A, Jafarpour B, Eniafe R, Mielke S, et al. Ex vivo characterization of polyclonal memory CD8+ T-cell responses to PRAME-specific peptides in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and acute and chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood (2009) 113(10):2245–55 10.1182/blood-2008-03-144071 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Van Tendeloo VF, Van de Velde A, Van Driessche A, Cools N, Anguille S, Ladell K, et al. Induction of complete and molecular remissions in acute myeloid leukemia by Wilms’ tumor 1 antigen-targeted dendritic cell vaccination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2010) 107(31):13824–9 10.1073/pnas.1008051107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Snauwaert S, Vanhee S, Goetgeluk G, Verstichel G, Van Caeneghem Y, Velghe I, et al. RHAMM/HMMR (CD168) is not an ideal target antigen for immunotherapy of acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica (2012) 97(10):1539–47 10.3324/haematol.2012.065581 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Arai J, Yasukawa M, Ohminami H, Kakimoto M, Hasegawa A, Fujita S. Identification of human telomerase reverse transcriptase-derived peptides that induce HLA-A24-restricted antileukemia cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Blood (2001) 97(9):2903–7 10.1182/blood.V97.9.2903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Oehler VG, Guthrie KA, Cummings CL, Sabo K, Wood BL, Gooley T, et al. The preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma (PRAME) inhibits myeloid differentiation in normal hematopoietic and leukemic progenitor cells. Blood (2009) 114(15):3299–308 10.1182/blood-2008-07-170282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.van den Ancker W, Ruben JM, Westers TM, Wulandari D, Bontkes HJ, Hooijberg E, et al. Priming of PRAME- and WT1-specific CD8 T cells in healthy donors but not in AML patients in complete remission: implications for immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology (2013) 2(4):e23971. 10.4161/onci.23971 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Yang J, Ikezoe T, Nishioka C, Nobumoto A, Udaka K, Yokoyama A. CD34(+)/CD38(-) acute myelogenous leukemia cells aberrantly express Aurora kinase A. Int J Cancer (2013) 133(11):2706–19 10.1002/ijc.28277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Inoue K, Tamaki H, Ogawa H, Oka Y, Soma T, Tatekawa T, et al. Wilms’ tumor gene (WT1) competes with differentiation-inducing signal in hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood (1998) 91(8):2969–76 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Gaiger A, Carter L, Greinix H, Carter D, McNeill PD, Houghton RL, et al. WT1-specific serum antibodies in patients with leukemia. Clin Cancer Res (2001) 7(3 Suppl):761s–5s [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Elisseeva OA, Oka Y, Tsuboi A, Ogata K, Wu F, Kim EH, et al. Humoral immune responses against Wilms tumor gene WT1 product in patients with hematopoietic malignancies. Blood (2002) 99(9):3272–9 10.1182/blood.V99.9.3272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Van Driessche A, Berneman ZN, Van Tendeloo VF. Active specific immunotherapy targeting the Wilms’ tumor protein 1 (WT1) for patients with hematological malignancies and solid tumors: lessons from early clinical trials. Oncologist (2012) 17(2):250–9 10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Xue SA, Gao L, Hart D, Gillmore R, Qasim W, Thrasher A, et al. Elimination of human leukemia cells in NOD/SCID mice by WT1-TCR gene-transduced human T cells. Blood (2005) 106(9):3062–7 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Keilholz U, Letsch A, Busse A, Asemissen AM, Bauer S, Blau IW, et al. A clinical and immunologic phase 2 trial of Wilms tumor gene product 1 (WT1) peptide vaccination in patients with AML and MDS. Blood (2009) 113(26):6541–8 10.1182/blood-2009-02-202598 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Ochi T, Fujiwara H, Suemori K, Azuma T, Yakushijin Y, Hato T, et al. Aurora-A kinase: a novel target of cellular immunotherapy for leukemia. Blood (2009) 113(1):66–74 10.1182/blood-2008-06-164889 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Yang J, Ikezoe T, Nishioka C, Udaka K, Yokoyama A. Bcr-Abl activates AURKA and AURKB in chronic myeloid leukemia cells via AKT signaling. Int J Cancer (2014)134(5):1183–94 10.1002/ijc.28434 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Schmidt SM, Schag K, Muller MR, Weck MM, Appel S, Kanz L, et al. Survivin is a shared tumor-associated antigen expressed in a broad variety of malignancies and recognized by specific cytotoxic T cells. Blood (2003) 102(2):571–6 10.1182/blood-2002-08-2554 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Yotnda P, Firat H, Garcia-Pons F, Garcia Z, Gourru G, Vernant JP, et al. Cytotoxic T cell response against the chimeric p210 BCR-ABL protein in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. J Clin Invest (1998) 101(10):2290–6 10.1172/JCI488 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Bocchia M, Korontsvit T, Xu Q, Mackinnon S, Yang SY, Sette A, et al. Specific human cellular immunity to bcr-abl oncogene-derived peptides. Blood (1996) 87(9):3587–92 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Clark RE, Dodi IA, Hill SC, Lill JR, Aubert G, Macintyre AR, et al. Direct evidence that leukemic cells present HLA-associated immunogenic peptides derived from the BCR-ABL b3a2 fusion protein. Blood (2001) 98(10):2887–93 10.1182/blood.V98.10.2887 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, Dhingra K, Estey E, Keating MJ, Ku S, et al. Significance of the P210 versus P190 molecular abnormalities in adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute leukemia. Blood (1991) 78(9):2411–8 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Greiner J, Ringhoffer M, Taniguchi M, Hauser T, Schmitt A, Dohner H, et al. Characterization of several leukemia-associated antigens inducing humoral immune responses in acute and chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Cancer (2003) 106(2):224–31 10.1002/ijc.11200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Ochsenreither S, Majeti R, Schmitt T, Stirewalt D, Keilholz U, Loeb KR, et al. Cyclin-A1 represents a new immunogenic targetable antigen expressed in acute myeloid leukemia stem cells with characteristics of a cancer-testis antigen. Blood (2012) 119(23):5492–501 10.1182/blood-2011-07-365890 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Greiner J, Ringhoffer M, Simikopinko O, Szmaragowska A, Huebsch S, Maurer U, et al. Simultaneous expression of different immunogenic antigens in acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol (2000) 28(12):1413–22 10.1016/S0301-472X(00)00550-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Sergeeva A, Alatrash G, He H, Ruisaard K, Lu S, Wygant J, et al. An anti-PR1/HLA-A2 T-cell receptor-like antibody mediates complement-dependent cytotoxicity against acute myeloid leukemia progenitor cells. Blood (2011) 117(16):4262–72 10.1182/blood-2010-07-299248 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Molldrem J, Dermime S, Parker K, Jiang YZ, Mavroudis D, Hensel N, et al. Targeted T-cell therapy for human leukemia: cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for a peptide derived from proteinase 3 preferentially lyse human myeloid leukemia cells. Blood (1996) 88(7):2450–7 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Rao NV, Wehner NG, Marshall BC, Gray WR, Gray BH, Hoidal JR. Characterization of proteinase-3 (PR-3), a neutrophil serine proteinase. Structural and functional properties. J Biol Chem (1991) 266(15):9540–8 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Weber G, Gerdemann U, Caruana I, Savoldo B, Hensel NF, Rabin KR, et al. Generation of multi-leukemia antigen-specific T cells to enhance the graft-versus-leukemia effect after allogeneic stem cell transplant. Leukemia (2013) 27(7):1538–47 10.1038/leu.2013.66 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Riley CL, Mathieu MG, Clark RE, McArdle SE, Rees RC. Tumour antigen-targeted immunotherapy for chronic myeloid leukaemia: is it still viable? Cancer Immunol Immunother (2009) 58(9):1489–99 10.1007/s00262-009-0675-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Adams SP, Sahota SS, Mijovic A, Czepulkowski B, Padua RA, Mufti GJ, et al. Frequent expression of HAGE in presentation chronic myeloid leukaemias. Leukemia (2002) 16(11):2238–42 10.1038/sj.leu.2402732 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Inoue K, Ogawa H, Sonoda Y, Kimura T, Sakabe H, Oka Y, et al. Aberrant overexpression of the Wilms tumor gene (WT1) in human leukemia. Blood (1997) 89(4):1405–12 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Inoue K, Sugiyama H, Ogawa H, Nakagawa M, Yamagami T, Miwa H, et al. WT1 as a new prognostic factor and a new marker for the detection of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia. Blood (1994) 84(9):3071–9 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Molldrem JJ, Clave E, Jiang YZ, Mavroudis D, Raptis A, Hensel N, et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for a nonpolymorphic proteinase 3 peptide preferentially inhibit chronic myeloid leukemia colony-forming units. Blood (1997) 90(7):2529–34 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Riether C, Schurch C, Ochsenbein AF. From “magic bullets” to specific cancer immunotherapy. Swiss Med Wkly (2013) 143:w13734. 10.4414/smw.2013.13734 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Brandau S, Suttmann H. Thirty years of BCG immunotherapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a success story with room for improvement. Biomed Pharmacother (2007) 61(6):299–305 10.1016/j.biopha.2007.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med (2010) 363(8):711–23 10.1056/NEJMoa1003466 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Baron F, Storb R. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation following nonmyeloablative conditioning as treatment for hematologic malignancies and inherited blood disorders. Mol Ther (2006) 13(1):26–41 10.1016/j.ymthe.2005.09.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, Berger ER, Small EJ, Penson DF, et al. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med (2010) 363(5):411–22 10.1056/NEJMoa1001294 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Palucka K, Banchereau J. Cancer immunotherapy via dendritic cells. Nat Rev Cancer (2012) 12(4):265–77 10.1038/nrc3258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Lee JJ, Kook H, Park MS, Nam JH, Choi BH, Song WH, et al. Immunotherapy using autologous monocyte-derived dendritic cells pulsed with leukemic cell lysates for acute myeloid leukemia relapse after autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. J Clin Apher (2004) 19(2):66–70 10.1002/jca.10080 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Wolchok JD, Kluger H, Callahan MK, Postow MA, Rizvi NA, Lesokhin AM, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med (2013) 369(2):122–33 10.1056/NEJMoa1302369 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Porter DL, Levine BL, Kalos M, Bagg A, June CH. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in chronic lymphoid leukemia. N Engl J Med (2011) 365(8):725–33 10.1056/NEJMoa1103849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Grupp SA, Kalos M, Barrett D, Aplenc R, Porter DL, Rheingold SR, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for acute lymphoid leukemia. N Engl J Med (2013) 368(16):1509–18 10.1056/NEJMoa1215134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Legras S, Gunthert U, Stauder R, Curt F, Oliferenko S, Kluin-Nelemans HC, et al. A strong expression of CD44-6v correlates with shorter survival of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood (1998) 91(9):3401–13 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Neu S, Geiselhart A, Sproll M, Hahn D, Kuci S, Niethammer D, et al. Expression of CD44 isoforms by highly enriched CD34-positive cells in cord blood, bone marrow and leukaphereses. Bone Marrow Transplant (1997) 20(7):593–8 10.1038/sj.bmt.1700940 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Casucci M, Nicolis di Robilant B, Falcone L, Camisa B, Norelli M, Genovese P, et al. CD44v6-targeted T cells mediate potent antitumor effects against acute myeloid leukemia and multiple myeloma. Blood (2013) 122(20):3461–72 10.1182/blood-2013-04-493361 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.van de Loosdrecht AA, van den Ancker W, Houtenbos I, Ossenkoppele GJ, Westers TM. Dendritic cell-based immunotherapy in myeloid leukaemia: translating fundamental mechanisms into clinical applications. Handb Exp Pharmacol (2009) 188:319–48 10.1007/978-3-540-71029-5_15 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Dietz AB, Padley DJ, Butler GW, Maas ML, Greiner CW, Gastineau DA, et al. Clinical-grade manufacturing of DC from CD14+ precursors: experience from phase I clinical trials in CML and malignant melanoma. Cytotherapy (2004) 6(6):563–70 10.1080/14653240410005357-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Bol KF, Tel J, de Vries IJ, Figdor CG. Naturally circulating dendritic cells to vaccinate cancer patients. Oncoimmunology (2013) 2(3):e23431. 10.4161/onci.23431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Zhang J, Raper A, Sugita N, Hingorani R, Salio M, Palmowski MJ, et al. Characterization of Siglec-H as a novel endocytic receptor expressed on murine plasmacytoid dendritic cell precursors. Blood (2006) 107(9):3600–8 10.1182/blood-2005-09-3842 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Houtenbos I, Westers TM, Hess CJ, Waisfisz Q, Ossenkoppele GJ, van de Loosdrecht AA. Flt-3 internal tandem duplication hampers differentiation of AML blasts towards leukemic dendritic cells. Leukemia (2006) 20(10):1892–5 10.1038/sj.leu.2404348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Houtenbos I, Westers TM, Ossenkoppele GJ, van de Loosdrecht AA. Leukemia-derived dendritic cells: towards clinical vaccination protocols in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica (2006) 91(3):348–55 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Anguille S, Willemen Y, Lion E, Smits EL, Berneman ZN. Dendritic cell vaccination in acute myeloid leukemia. Cytotherapy (2012) 14(6):647–56 10.3109/14653249.2012.693744 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Houtenbos I, Westers TM, Ossenkoppele GJ, van de Loosdrecht AA. Leukaemic dendritic cell vaccination for patients with acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol (2006) 134(4):445–6 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06196.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Kremser A, Dressig J, Grabrucker C, Liepert A, Kroell T, Scholl N, et al. Dendritic cells (DCs) can be successfully generated from leukemic blasts in individual patients with AML or MDS: an evaluation of different methods. J Immunother (2010) 33(2):185–99 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181b8f4ce [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Grabrucker C, Liepert A, Dreyig J, Kremser A, Kroell T, Freudenreich M, et al. The quality and quantity of leukemia-derived dendritic cells from patients with acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome are a predictive factor for the lytic potential of dendritic cells-primed leukemia-specific T cells. J Immunother (2010) 33(5):523–37 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181d87ffd [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Liepert A, Grabrucker C, Kremser A, Dreyssig J, Ansprenger C, Freudenreich M, et al. Quality of T-cells after stimulation with leukemia-derived dendritic cells (DC) from patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myeloid dysplastic syndrome (MDS) is predictive for their leukemia cytotoxic potential. Cell Immunol (2010) 265(1):23–30 10.1016/j.cellimm.2010.06.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Klammer M, Waterfall M, Samuel K, Turner ML, Roddie PH. Fusion hybrids of dendritic cells and autologous myeloid blasts as a potential cellular vaccine for acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol (2005) 129(3):340–9 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05477.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Herr W, Ranieri E, Olson W, Zarour H, Gesualdo L, Storkus WJ. Mature dendritic cells pulsed with freeze-thaw cell lysates define an effective in vitro vaccine designed to elicit EBV-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocyte responses. Blood (2000) 96(5):1857–64 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science (2011) 331(6024):1565–70 10.1126/science.1203486 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Ponsaerts P, Van Tendeloo VF, Berneman ZN. Cancer immunotherapy using RNA-loaded dendritic cells. Clin Exp Immunol (2003) 134(3):378–84 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Decker WK, Xing D, Li S, Robinson SN, Yang H, Yao X, et al. Double loading of dendritic cell MHC class I and MHC class II with an AML antigen repertoire enhances correlates of T-cell immunity in vitro via amplification of T-cell help. Vaccine (2006) 24(16):3203–16 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.01.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Tel J, Aarntzen EH, Baba T, Schreibelt G, Schulte BM, Benitez-Ribas D, et al. Natural human plasmacytoid dendritic cells induce antigen-specific T-cell responses in melanoma patients. Cancer Res (2013) 73(3):1063–75 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2583 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Anguille S, Lion E, Smits E, Berneman ZN, van Tendeloo VF. Dendritic cell vaccine therapy for acute myeloid leukemia: questions and answers. Hum Vaccin (2011) 7(5):579–84 10.4161/hv.7.5.14652 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Choudhury A, Gajewski JL, Liang JC, Popat U, Claxton DF, Kliche KO, et al. Use of leukemic dendritic cells for the generation of antileukemic cellular cytotoxicity against Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood (1997) 89(4):1133–42 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Charbonnier A, Gaugler B, Sainty D, Lafage-Pochitaloff M, Olive D. Human acute myeloblastic leukemia cells differentiate in vitro into mature dendritic cells and induce the differentiation of cytotoxic T cells against autologous leukemias. Eur J Immunol (1999) 29(8):2567–78 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Brouwer RE, van der Hoorn M, Kluin-Nelemans HC, van Zelderen-Bhola S, Willemze R, Falkenburg JH. The generation of dendritic-like cells with increased allostimulatory function from acute myeloid leukemia cells of various FAB subclasses. Hum Immunol (2000) 61(6):565–74 10.1016/S0198-8859(00)00111-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Cignetti A, Vallario A, Roato I, Circosta P, Allione B, Casorzo L, et al. Leukemia-derived immature dendritic cells differentiate into functionally competent mature dendritic cells that efficiently stimulate T cell responses. J Immunol (2004) 173(4):2855–65 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Houtenbos I, Westers TM, de Gruijl TD, Scheper RJ, Ossenkoppele GJ, van de Loosdrecht AA. TNF-alpha receptor 1 expression on acute myeloid leukemic blasts predicts differentiation into leukemic dendritic cells. Leukemia (2004) 18(6):1149–53 10.1038/sj.leu.2403359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Houtenbos I, Westers TM, Ossenkoppele GJ, van de Loosdrecht AA. Employing the immunological synapse in AML: development of leukemic dendritic cells for active specific immunization. Immunobiology (2005) 210(2–4):249–57 10.1016/j.imbio.2005.05.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Westers TM, Houtenbos I, van de Loosdrecht AA, Ossenkoppele GJ. Divergent autologous T cell responses to leukaemic dendritic cells during remission in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Cell Oncol (2005) 27(4):261–6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Westers TM, Houtenbos I, Snoijs NC, van de Loosdrecht AA, Ossenkoppele GJ. Leukemia-derived dendritic cells in acute myeloid leukemia exhibit potent migratory capacity. Leukemia (2005) 19(7):1270–2 10.1038/sj.leu.2403794 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Dubsky P, Saito H, Leogier M, Dantin C, Connolly JE, Banchereau J, et al. IL-15-induced human DC efficiently prime melanoma-specific naive CD8+ T cells to differentiate into CTL. Eur J Immunol (2007) 37(6):1678–90 10.1002/eji.200636329 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Anguille S, Smits EL, Cools N, Goossens H, Berneman ZN, Van Tendeloo VF. Short-term cultured, interleukin-15 differentiated dendritic cells have potent immunostimulatory properties. J Transl Med (2009) 7:109. 10.1186/1479-5876-7-109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Zobywalski A, Javorovic M, Frankenberger B, Pohla H, Kremmer E, Bigalke I, et al. Generation of clinical grade dendritic cells with capacity to produce biologically active IL-12p70. J Transl Med (2007) 5:18. 10.1186/1479-5876-5-18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Boullart AC, Aarntzen EH, Verdijk P, Jacobs JF, Schuurhuis DH, Benitez-Ribas D, et al. Maturation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells with Toll-like receptor 3 and 7/8 ligands combined with prostaglandin E2 results in high interleukin-12 production and cell migration. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2008) 57(11):1589–97 10.1007/s00262-008-0489-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.de Vries IJ, Lesterhuis WJ, Barentsz JO, Verdijk P, van Krieken JH, Boerman OC, et al. Magnetic resonance tracking of dendritic cells in melanoma patients for monitoring of cellular therapy. Nat Biotechnol (2005) 23(11):1407–13 10.1038/nbt1154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Reizis B, Colonna M, Trinchieri G, Barrat F, Gilliet M. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells: one-trick ponies or workhorses of the immune system? Nat Rev Immunol (2011) 11(8):558–65 10.1038/nri3027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Villadangos JA, Young L. Antigen-presentation properties of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Immunity (2008) 29(3):352–61 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.09.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Le Bon A, Etchart N, Rossmann C, Ashton M, Hou S, Gewert D, et al. Cross-priming of CD8+ T cells stimulated by virus-induced type I interferon. Nat Immunol (2003) 4(10):1009–15 10.1038/ni978 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Senti G, Johansen P, Kundig TM. Intralymphatic immunotherapy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol (2009) 9(6):537–43 10.1097/ACI.0b013e3283310ff7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Van Driessche A, Van de Velde AL, Nijs G, Braeckman T, Stein B, De Vries JM, et al. Clinical-grade manufacturing of autologous mature mRNA-electroporated dendritic cells and safety testing in acute myeloid leukemia patients in a phase I dose-escalation clinical trial. Cytotherapy (2009) 11(5):653–68 10.1080/14653240902960411 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]