Abstract
Context:
Osteosarcoma is a rare malignant bone tumor, commonly occurring in the age group of 10 to 24 years. Recent reports have indicated that there is a link between fluoride exposure and osteosarcoma.
Aims:
The present study was planned to analyze serum levels of fluoride in patients of osteosarcoma and fluoride content of their drinking water.
Settings and Design:
The present study was carried out comparing 10 patients of osteosarcoma and 10 healthy volunteers (who served as controls).
Materials and Methods:
Serum and drinking water fluoride levels were estimated by ion selective electrode.
Statistical analysis used:
The data were computed as mean ± SD and Student’s t test was applied.
Results:
Both, the serum and drinking water fluoride levels, were significant by higher in patients with osteosarcoma as compared to controls (P > 0.05, P > 0.001, respectively).
Conclusions:
These results suggest a link between fluoride exposure and osteosarcoma.
Keywords: Fluoride, osteosarcoma, serum, water
Introduction
Osteosarcoma is a rare malignant bone tumor, commonly occurring in the age group of 10 to-24 years. Bone is the principal site of fluoride accumulation.[1,2] In several parts of India, particularly Haryana, incidence of fluorosis is high in certain areas.[3] Recent reports have indicated that there is a direct link between fluoride exposure and osteosarcoma.[4,5] Studies have also linked high incidence of bone cancer to fluoridation in drinking water.[5,6,7] On the other hand, a few reports have also indicated that fluoride exposure has no role in osteosarcoma.[2,8,9]
To the best of our knowledge, we could not come across any study where fluoride levels have been estimated in serum and drinking water of osteosarcoma patients. Hence, the present study was planned to analyze serum levels of fluoride in patients of osteosarcoma and fluoride content of their drinking water.
Materials and Methods
The present study was conducted in 10 patients of osteosarcoma and 10 healthy volunteers, who served as controls. 2 ml venous blood was collected aseptically from antecubital vein, and serum was separated by centrifugation. Also, 10 ml drinking water samples brought by these subjects from their home were also evaluated. Serum and fluoride levels were estimated by ion selective electrode.[11] The data were computed as mean ± SD and Student’s t test was applied.
Results
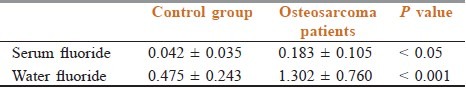
Serum fluoride levels were significant by higher in patients with osteosarcoma as compared to controls (P > 0.05, Table 1). Also, drinking water fluoride levels were significantly higher in osteosarcoma group as compared to controls (P > 0.001, Table 1). There was also a positive correlation between drinking water fluoride and serum fluoride levels in the osteosarcoma group patients (r = 0.855, P > 0.01).
Table 1.
Fluoride levels in two groups (mean ± SD, mg/L)
Discussion
Fluoride influences bone growth by acting as mitogenic agent for Osteoblasts.[12] Recent studies have indicated relationship of high fluoride levels in drinking water with incidence of osteosarcoma.[4] There are no reports available in literature where serum and drinking water fluoride levels have been correlated in osteosarcoma. We have recently reported on serum fluoride and sialic acid levels in osteosarcoma.[13]
In the present study, significantly higher serum fluoride levels were documented in osteosarcoma patients as compared to healthy controls (Table 1, P > 0.05). Also, samples of drinking water from the homes of these patients also showed a higher fluoride content.
Fluoride gets incorporated into bone lattice by forming fluoroapatite, which is more stable than hydroxyapatite. During periods of rapid skeleton growth, fluoride uptakes in bone increases since hydroxyapatite crystal are extremely small in young age. Also, fluoride has been reported to increase calcium absorption in intestine,[14] and this property is exploited in treatment of osteoporosis.
We showed a correlation between drinking water fluoride and serum fluoride in osteosarcoma patients. However, a Chinese report documented no correlation between drinking water fluoride and serum fluoride (correlation coefficient was 0.855) where fluoride in drinking water is safe and reasonable.[15]
In vitro studies have shown that exposure to fluoride causes osteoblast proliferation and malignant transformation.[16] Optimal dose of between 10-100 μmol/L is required to stimulate bone cell proliferation and differentiation.[16] Also, a link between p53 mutations and fluoride bone content has been reported in tissue samples from osteosarcoma patients.[17]
Finding of high serum fluoride levels in osteosarcoma patients along with high drinking water fluoride level in our patients suggest a link between fluoride and osteosarcoma.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.Lav KH, Baylink DJ. Molecular mechanism of action of fluoride on bone cells. J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13:1660–7. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1998.13.11.1660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Operskalski EA, Martin SP, Henderson B, Vischer BR. A case control study of osteosarcoma in young persons. Am J Epidemiol. 1987;126:118–9. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Susheela AK. UNICEF 2003. Delhi-India: Fluorosis Research and Rural Development Foundation; 2001. A treatise on fluorosis; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bassin EB, Wypij D, Davis RB, Mittleman MA. Age specific fluoride exposure in drinking water and osteosarcoma. Cancer Causes Control. 2006;17:421–8. doi: 10.1007/s10552-005-0500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hoover RN, Devsa SS, Cantor KP, Lubin JH, Fraumani JF. National Cancer Institute. DHHS review of fluoride benefits and risks. US Public Health Service; 1990. Time trends for bone and joint cancers and osteosarcomas in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results (SEER) program; pp. F1–7. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cohn PD. A brief report on the association of drinking water fluoridation and the incidence of osteosarcoma among young males. New Jersey: Department of Health: Environmental Health Service; 1992. pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yiamouyiannis JA. Fluoridation and cancer. The biology and epidemiology of bone and oral cancer related to fluoridation. Fluoride. 1993;26:83–96. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mcguire SM, Vanable ED, Mcguire MH, Buckwalter JA, Douglass CW. Is there a link between fluoridated water and osteosarcoma? J Am Dent Assoc. 1991;122:39–45. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1991.0149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gelberg KH, Fitzgerald EF, Synian H, Robert D. Fluoride exposure and childhood osteosarcoma: A Case Control Study. Am J Public Health. 1995;85:1678–83. doi: 10.2105/ajph.85.12.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Freni SC, Gaylor DW. International trends in the incidence of bone cancer are not related to drinking water fluoridation. Cancer. 1992;70:611–8. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920801)70:3<611::aid-cncr2820700312>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Venkateswarlu P. Evaluation of analytical method for fluorine in biological and related materials. J Dent Res. 1990;69:514–21. doi: 10.1177/00220345900690S105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Caverzasio J, Palmer G, Suzuki A, Bonjour JP. Mechanism of the mitogenic effect of fluoride on osteoblast-like cells; evidence for a G-protein dependent tyrosine phosphorylation process. J Bone Miner Res. 1997;12:1975–83. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1997.12.12.1975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sandhu R, Lal H, Kundu ZS, Kharb S. Serum fluoride and sialic acid levels in osteosarcoma. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2011;144:1–5 (accepted). doi: 10.1007/s12011-009-8382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pasquini GM, Davey RA, Michelangeli VP, Grill V, Kaczmarczyk SJ, Zajac JD. Local secretion of parathyroid hormone related protein by an osteoblastic osteosarcoma (UMR 106-01) cell line results in growth inhibition. Bone. 2002;31:598–605. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(02)00872-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xiang QY, Liang YX, Chen BH, Wang CS, Zhen LQ, Chan LS, et al. Study on the application of benchmark dose and biological monitoring indexes of fluoride in drinking water. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2004;38:261–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wergedal JE, Lau K-HW, Baylink DJ. Fluoride and bovine bone extract influence cell proliferation and phosphatase activities in human bone cell cultures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;233:274–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ramesh N, Vuayaraghavan AS, Desai BS, Natarajan M, Murthy PB, Pillai KS. Low levels of p53 mutations in Indian patients with osteosarcoma and the correlation with fluoride levels in bone. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 2001;20:237–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


