Abstract
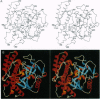
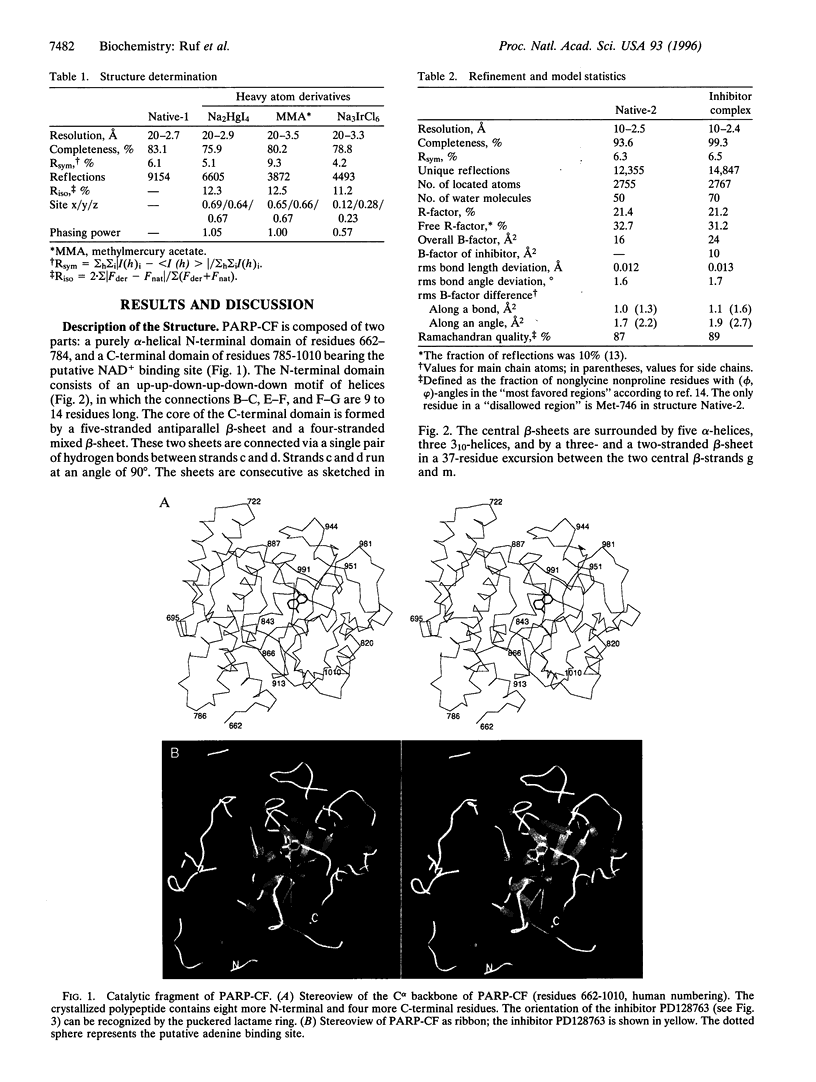
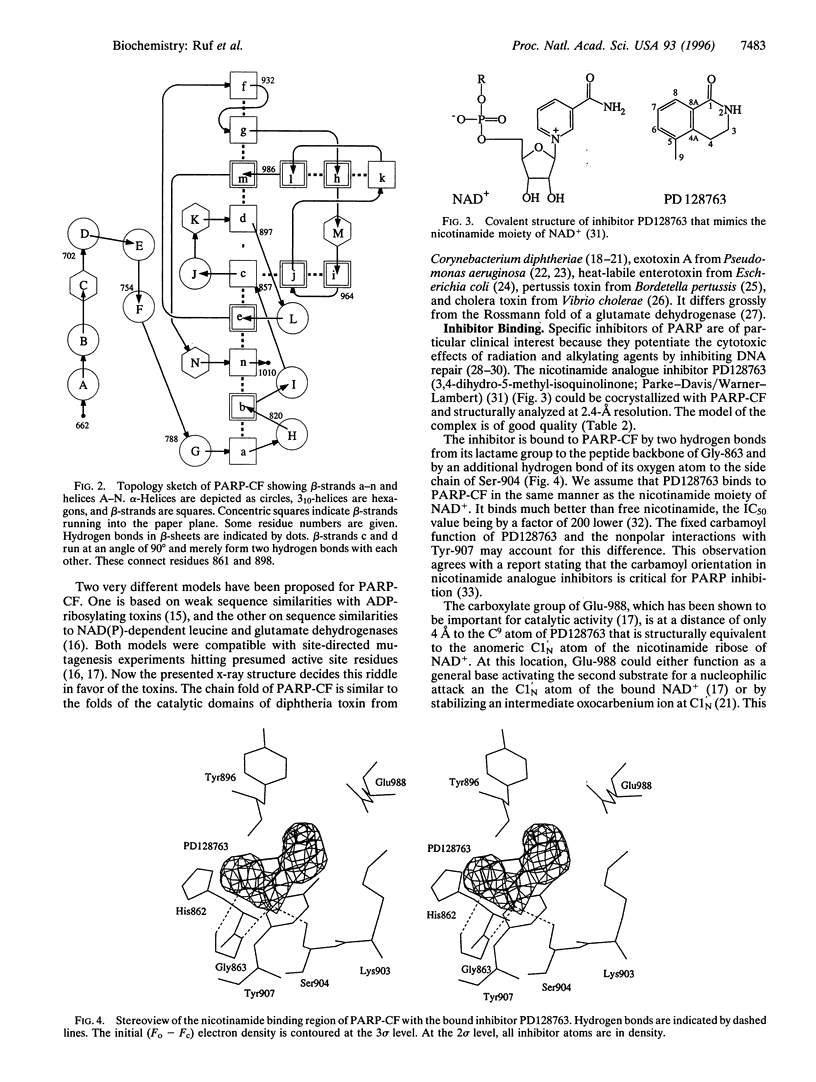
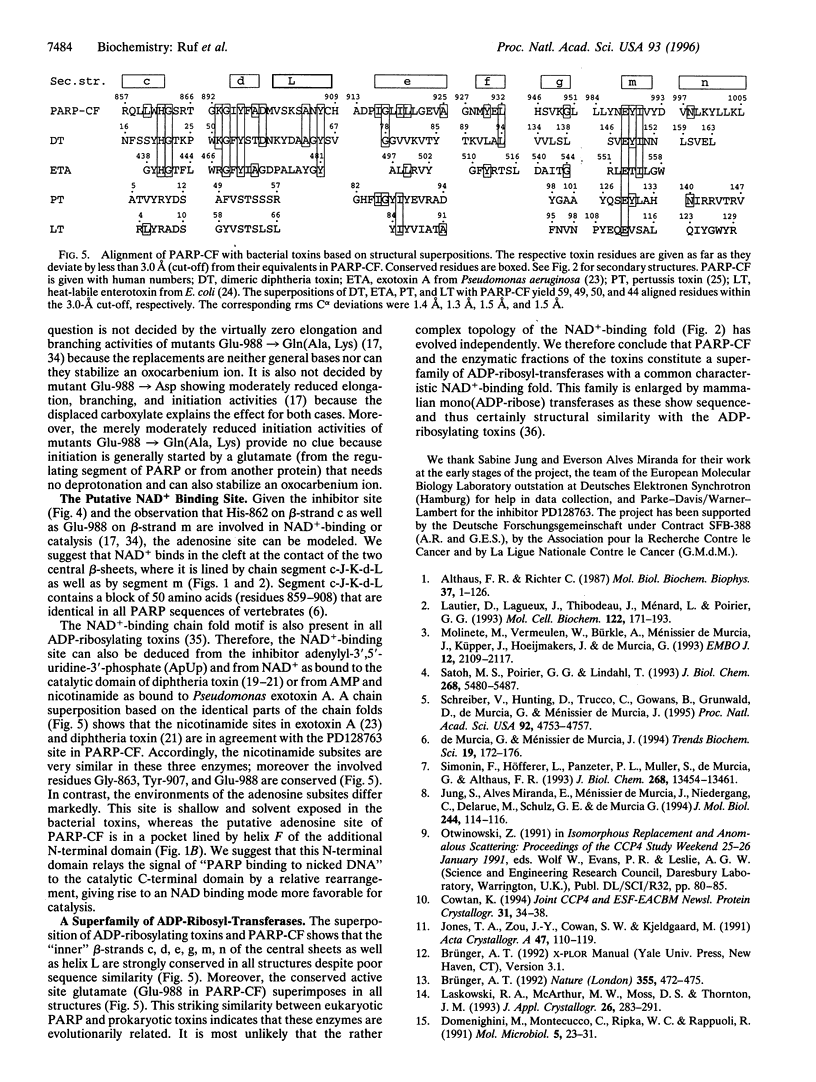
The crystal structures of the catalytic fragment of chicken poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase [NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase; NAD+:poly(adenosine-diphosphate-D-ribosyl)-acceptor ADP-D-ribosyltransferase, EC 2.4.2.30] with and without a nicotinamide-analogue inhibitor have been elucidated. Because this enzyme is involved in the regulation of DNA repair, its inhibitors are of interest for cancer therapy. The inhibitor shows the nicotinamide site and also suggests the adenosine site. The enzyme is structurally related to bacterial ADP-ribosylating toxins but contains an additional alpha-helical domain that is suggested to relay the activation signal issued on binding to damaged DNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allured V. S., Collier R. J., Carroll S. F., McKay D. B. Structure of exotoxin A of Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 3.0-Angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1320–1324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arundel-Suto C. M., Scavone S. V., Turner W. R., Suto M. J., Sebolt-Leopold J. S. Effect of PD 128763, a new potent inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, on X-ray-induced cellular recovery processes in Chinese hamster V79 cells. Radiat Res. 1991 Jun;126(3):367–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Britton K. L., Engel P. C., Farrants G. W., Lilley K. S., Rice D. W., Stillman T. J. Subunit assembly and active site location in the structure of glutamate dehydrogenase. Proteins. 1992 Jan;12(1):75–86. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. E., Eisenberg D. Crystal structure of diphtheria toxin bound to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Biochemistry. 1996 Jan 30;35(4):1137–1149. doi: 10.1021/bi9520848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Hur E., Utsumi H., Elkind M. M. Inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) synthesis enhance X-ray killing of log-phase Chinese hamster cells. Radiat Res. 1984 Mar;97(3):546–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. J., Choe S., Eisenberg D. Refined structure of dimeric diphtheria toxin at 2.0 A resolution. Protein Sci. 1994 Sep;3(9):1444–1463. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe S., Bennett M. J., Fujii G., Curmi P. M., Kantardjieff K. A., Collier R. J., Eisenberg D. The crystal structure of diphtheria toxin. Nature. 1992 May 21;357(6375):216–222. doi: 10.1038/357216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenighini M., Magagnoli C., Pizza M., Rappuoli R. Common features of the NAD-binding and catalytic site of ADP-ribosylating toxins. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Oct;14(1):41–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenighini M., Montecucco C., Ripka W. C., Rappuoli R. Computer modelling of the NAD binding site of ADP-ribosylating toxins: active-site structure and mechanism of NAD binding. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin R. J., Curtin N. J., Newell D. R., Golding B. T., Durkacz B. W., Calvert A. H. The role of inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase as resistance-modifying agents in cancer therapy. Biochimie. 1995;77(6):408–422. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(96)88154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung S., Miranda E. A., de Murcia J. M., Niedergang C., Delarue M., Schulz G. E., de Murcia G. M. Crystallization and X-ray crystallographic analysis of recombinant chicken poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase catalytic domain produced in Sf9 insect cells. J Mol Biol. 1994 Nov 18;244(1):114–116. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautier D., Lagueux J., Thibodeau J., Ménard L., Poirier G. G. Molecular and biochemical features of poly (ADP-ribose) metabolism. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993 May 26;122(2):171–193. doi: 10.1007/BF01076101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., Dyda F., Benhar I., Pastan I., Davies D. R. The crystal structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin domain III with nicotinamide and AMP: conformational differences with the intact exotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9308–9312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsischky G. T., Wilson B. A., Collier R. J. Role of glutamic acid 988 of human poly-ADP-ribose polymerase in polymer formation. Evidence for active site similarities to the ADP-ribosylating toxins. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3247–3254. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson M., Rolli V., Dantzer F., Trucco C., Schreiber V., Fribourg S., Molinete M., Ruf A., Miranda E. A., Niedergang C. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: structure-function relationship. Biochimie. 1995;77(6):456–461. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(96)88160-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinete M., Vermeulen W., Bürkle A., Ménissier-de Murcia J., Küpper J. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., de Murcia G. Overproduction of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase DNA-binding domain blocks alkylation-induced DNA repair synthesis in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2109–2117. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki I. J., Moss J. Common structure of the catalytic sites of mammalian and bacterial toxin ADP-ribosyltransferases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1994 Sep;138(1-2):177–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00928460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M. S., Poirier G. G., Lindahl T. NAD(+)-dependent repair of damaged DNA by human cell extracts. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5480–5487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber V., Hunting D., Trucco C., Gowans B., Grunwald D., De Murcia G., De Murcia J. M. A dominant-negative mutant of human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase affects cell recovery, apoptosis, and sister chromatid exchange following DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):4753–4757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.4753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebolt-Leopold J. S., Scavone S. V. Enhancement of alkylating agent activity in vitro by PD 128763, a potent poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibitor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;22(3):619–621. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(92)90889-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonin F., Höfferer L., Panzeter P. L., Muller S., de Murcia G., Althaus F. R. The carboxyl-terminal domain of human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Overproduction in Escherichia coli, large scale purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13454–13461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonin F., Poch O., Delarue M., de Murcia G. Identification of potential active-site residues in the human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8529–8535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma T. K., Kalk K. H., van Zanten B. A., Dauter Z., Kingma J., Witholt B., Hol W. G. Refined structure of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin, a close relative of cholera toxin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 5;230(3):890–918. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. E., Boodhoo A., Armstrong G. D., Cockle S. A., Klein M. H., Read R. J. The crystal structure of pertussis toxin. Structure. 1994 Jan 15;2(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suto M. J., Turner W. R., Arundel-Suto C. M., Werbel L. M., Sebolt-Leopold J. S. Dihydroisoquinolinones: the design and synthesis of a new series of potent inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Anticancer Drug Des. 1991 May;6(2):107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. S., Blanke S. R., Collier R. J., Eisenberg D. Structure of the isolated catalytic domain of diphtheria toxin. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 24;34(3):773–781. doi: 10.1021/bi00003a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang R. G., Scott D. L., Westbrook M. L., Nance S., Spangler B. D., Shipley G. G., Westbrook E. M. The three-dimensional crystal structure of cholera toxin. J Mol Biol. 1995 Aug 25;251(4):563–573. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Murcia G., Ménissier de Murcia J. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: a molecular nick-sensor. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Apr;19(4):172–176. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]