Abstract
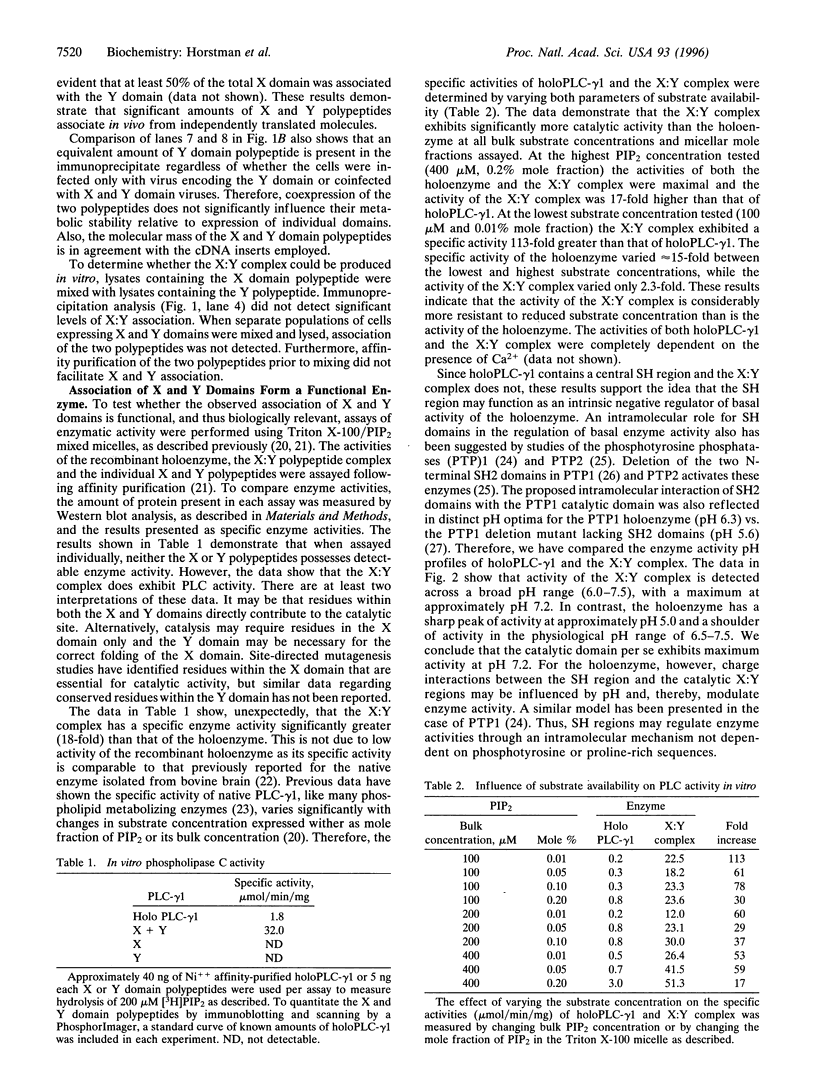
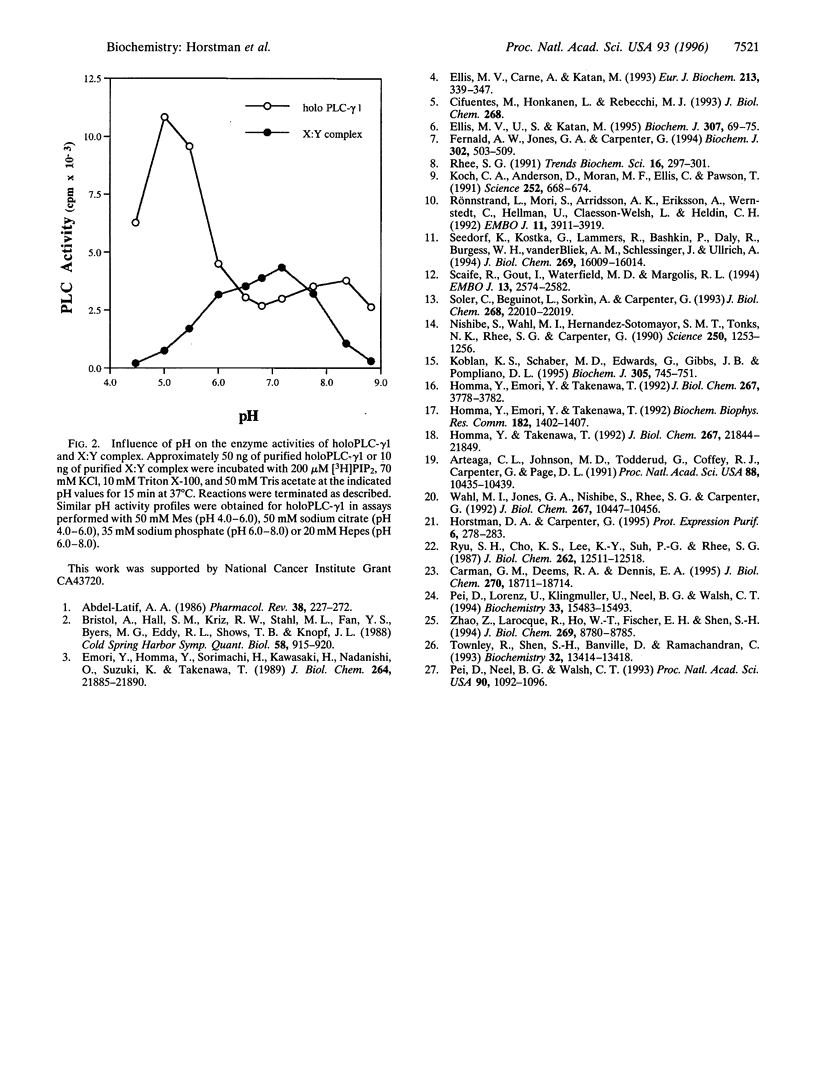
The X and Y domains of phospholipase C (PLC)-gamma1, which are conserved in all mammalian phosphoinositide-specific PLC isoforms and are proposed to interact to form the catalytic site, have been expressed as individual hexahistidine-tagged fusion proteins in the baculovirus system. Following coinfection of insect cells with recombinant viruses, association of X and Y polypeptides was demonstrated in coprecipitation assays. When enzyme activity was examined, neither domain possessed catalytic activity when expressed alone; however, coexpression of the X and Y polypeptides produced a functional enzyme. This reconstituted phospholipase activity remained completely dependent on the presence of free Ca2+. The specific activity of the X:Y complex was significantly greater (20- to 100-fold) than that of holoPLC-gamma1 and was only moderately influenced by varying the concentration of substrate. The enzyme activities of holoPLC-gamma1 and the X:Y complex exhibited distinct pH optima. For holoPLC-gamma1 maximal activity was detected at pH 5.0, while activity of the X:Y complex was maximal at pH 7.2.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Latif A. A. Calcium-mobilizing receptors, polyphosphoinositides, and the generation of second messengers. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Sep;38(3):227–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Latif A. A. Calcium-mobilizing receptors, polyphosphoinositides, and the generation of second messengers. Pharmacol Rev. 1986 Sep;38(3):227–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arteaga C. L., Johnson M. D., Todderud G., Coffey R. J., Carpenter G., Page D. L. Elevated content of the tyrosine kinase substrate phospholipase C-gamma 1 in primary human breast carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10435–10439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristol A., Hall S. M., Kriz R. W., Stahl M. L., Fan Y. S., Byers M. G., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B., Knopf J. L. Phospholipase C-148: chromosomal location and deletion mapping of functional domains. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):915–920. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman G. M., Deems R. A., Dennis E. A. Lipid signaling enzymes and surface dilution kinetics. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 11;270(32):18711–18714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.32.18711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. V., Carne A., Katan M. Structural requirements of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C delta 1 for enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):339–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. V., U S., Katan M. Mutations within a highly conserved sequence present in the X region of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C-delta 1. Biochem J. 1995 Apr 1;307(Pt 1):69–75. doi: 10.1042/bj3070069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Homma Y., Sorimachi H., Kawasaki H., Nakanishi O., Suzuki K., Takenawa T. A second type of rat phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C containing a src-related sequence not essential for phosphoinositide-hydrolyzing activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21885–21890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald A. W., Jones G. A., Carpenter G. Limited proteolysis of phospholipase C-gamma 1 indicates stable association of X and Y domains with enhanced catalytic activity. Biochem J. 1994 Sep 1;302(Pt 2):503–509. doi: 10.1042/bj3020503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Emori Y., Takenawa T. Isolation and characterization of rat 3Y1 fibroblast clones overexpressing the src homology region of phospholipase C-gamma 2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3778–3782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Takenawa T. Inhibitory effect of src homology (SH) 2/SH3 fragments of phospholipase C-gamma on the catalytic activity of phospholipase C isoforms. Identification of a novel phospholipase C inhibitor region. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21844–21849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horstman D. A., Ball R., Carpenter G. Baculovirus expression and purification of the second messenger enzyme phospholipase C-gamma 1, a tyrosine kinase substrate. Protein Expr Purif. 1995 Jun;6(3):278–283. doi: 10.1006/prep.1995.1036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
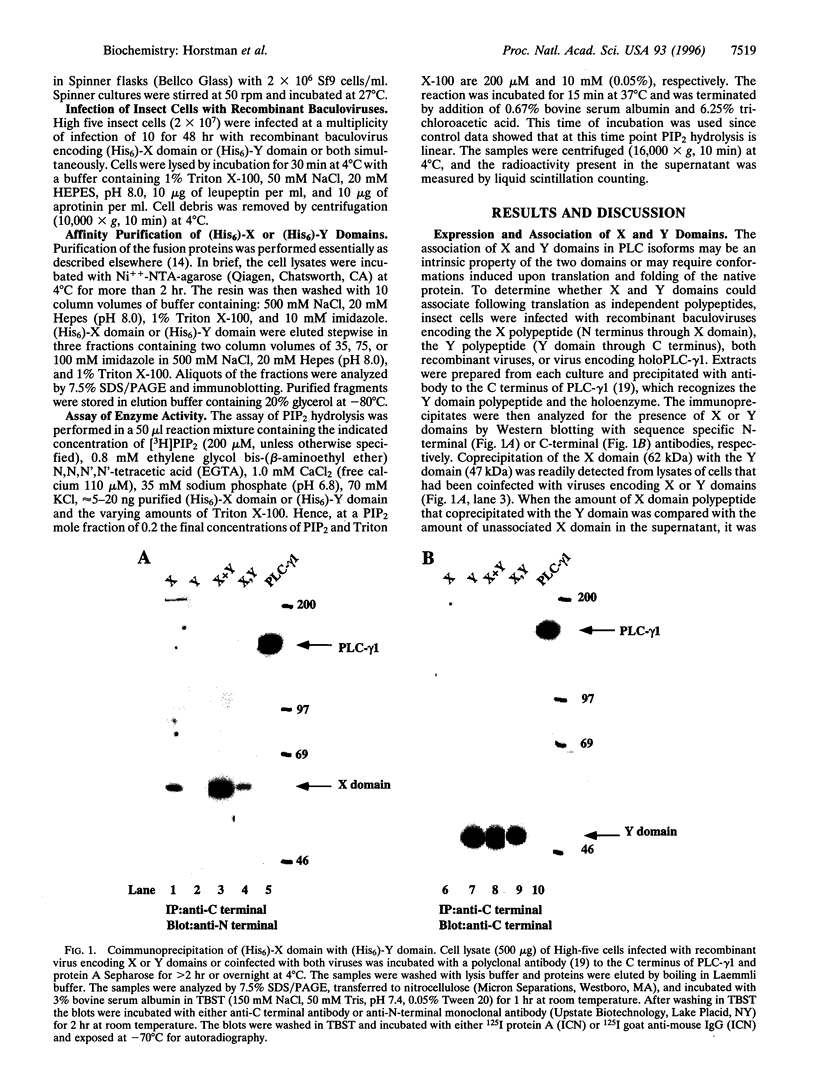
- Koblan K. S., Schaber M. D., Edwards G., Gibbs J. B., Pompliano D. L. src-homology 2 (SH2) domain ligation as an allosteric regulator: modulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C gamma 1 structure and activity. Biochem J. 1995 Feb 1;305(Pt 3):745–751. doi: 10.1042/bj3050745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D., Lorenz U., Klingmüller U., Neel B. G., Walsh C. T. Intramolecular regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP1: a new function for Src homology 2 domains. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 27;33(51):15483–15493. doi: 10.1021/bi00255a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D., Neel B. G., Walsh C. T. Overexpression, purification, and characterization of SHPTP1, a Src homology 2-containing protein-tyrosine-phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1092–1096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipids-specific phospholipase C: interaction of the gamma 1 isoform with tyrosine kinase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Aug;16(8):297–301. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90122-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Purification and characterization of two immunologically distinct phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12511–12518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnstrand L., Mori S., Arridsson A. K., Eriksson A., Wernstedt C., Hellman U., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. Identification of two C-terminal autophosphorylation sites in the PDGF beta-receptor: involvement in the interaction with phospholipase C-gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3911–3919. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaife R., Gout I., Waterfield M. D., Margolis R. L. Growth factor-induced binding of dynamin to signal transduction proteins involves sorting to distinct and separate proline-rich dynamin sequences. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2574–2582. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Kostka G., Lammers R., Bashkin P., Daly R., Burgess W. H., van der Bliek A. M., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Dynamin binds to SH3 domains of phospholipase C gamma and GRB-2. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 10;269(23):16009–16014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler C., Beguinot L., Sorkin A., Carpenter G. Tyrosine phosphorylation of ras GTPase-activating protein does not require association with the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):22010–22019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townley R., Shen S. H., Banville D., Ramachandran C. Inhibition of the activity of protein tyrosine phosphate 1C by its SH2 domains. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 14;32(49):13414–13418. doi: 10.1021/bi00212a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Jones G. A., Nishibe S., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Growth factor stimulation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 activity. Comparative properties of control and activated enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10447–10456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Z., Larocque R., Ho W. T., Fischer E. H., Shen S. H. Purification and characterization of PTP2C, a widely distributed protein tyrosine phosphatase containing two SH2 domains. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):8780–8785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]