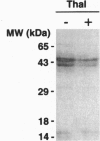
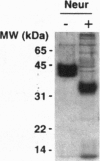
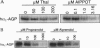Abstract
In addition to its well known sedative and teratogenic effects, thalidomide also possesses potent immunomodulatory and antiinflammatory activities, being most effective against leprosy and chronic graft-versus-host disease. The immunomodulatory activity of thalidomide has been ascribed to the selective inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha from monocytes. The molecular mechanism for the immunomodulatory effect of thalidomide remains unknown. To elucidate this mechanism, we synthesized an active photoaffinity label of thalidomide as a probe to identify the molecular target of the drug. Using the probe, we specifically labeled a pair of proteins of 43-45 kDa with high acidity from bovine thymus extract. Purification of these proteins and partial peptide sequence determination revealed them to be alpha1-acid glycoprotein (AGP). We show that the binding of thalidomide photoaffinity label to authentic human AGP is competed with both thalidomide and the nonradioactive photoaffinity label at concentrations comparable to those required for inhibition of production of tumor necrosis factor alpha from human monocytes, suggesting that AGP may be involved in the immunomodulatory activity of thalidomide.
Full text
PDF
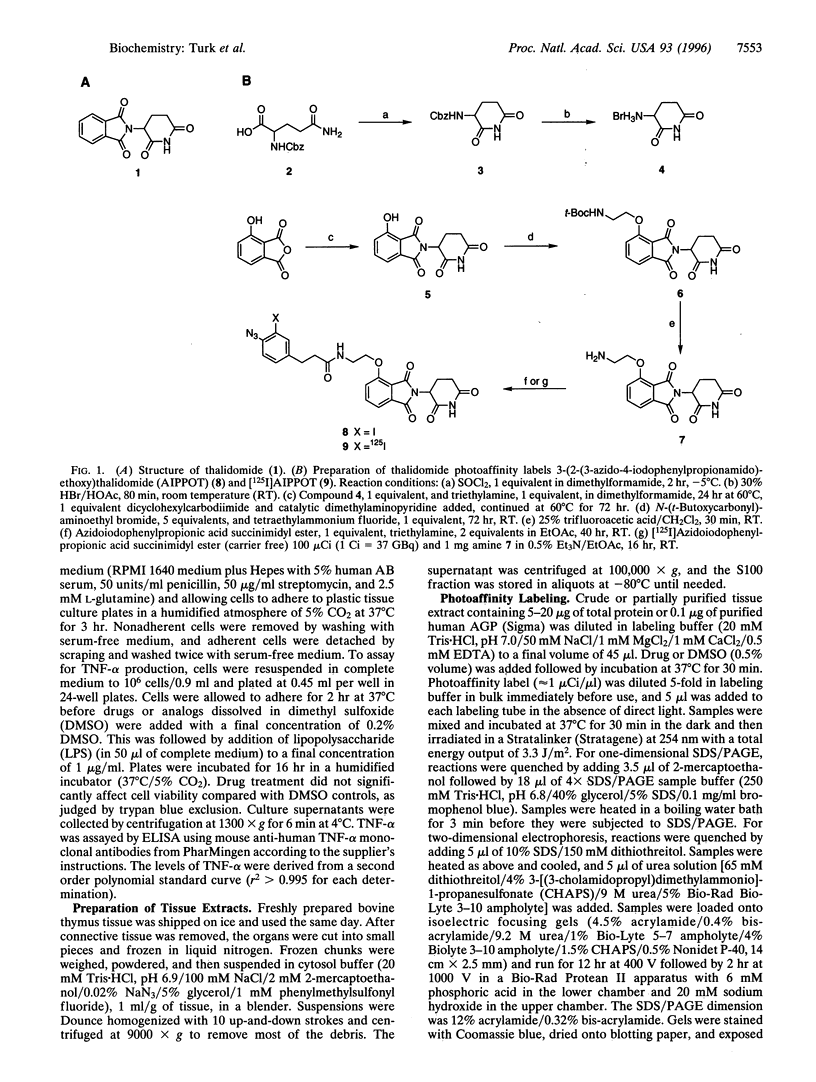
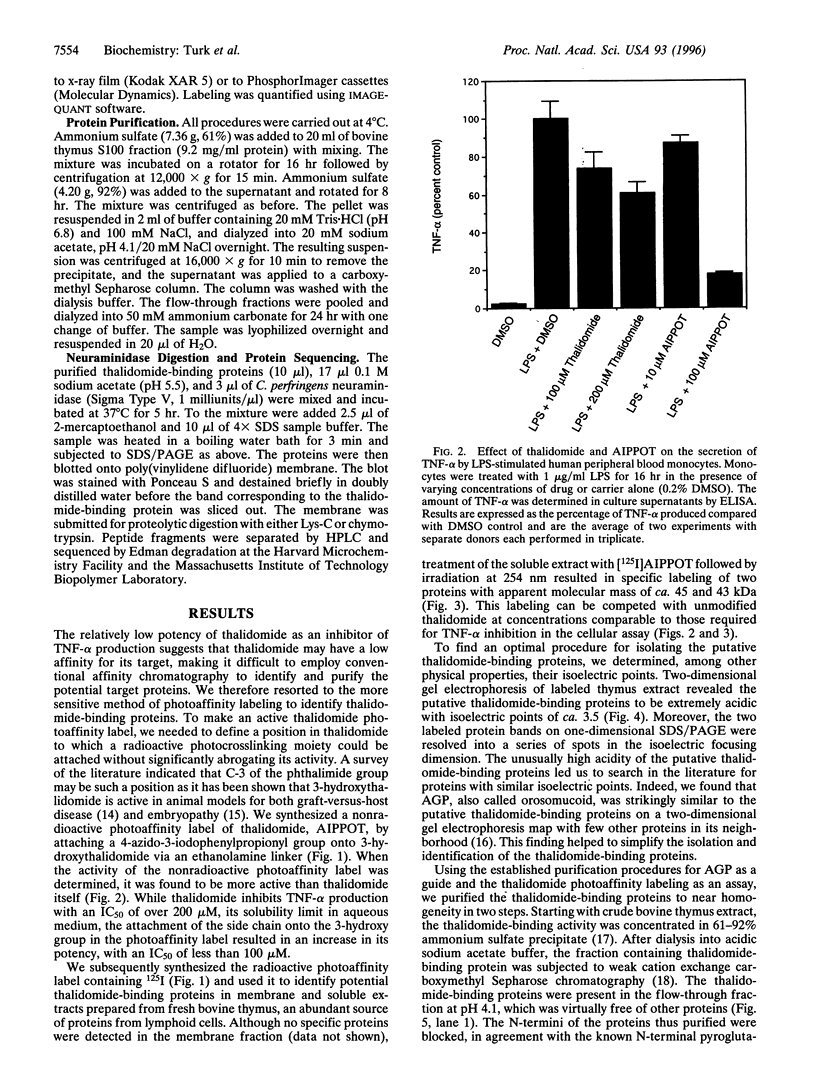


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnaud P., Miribel L., Roux A. F. Alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Methods Enzymol. 1988;163:418–430. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)63040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M., Schmid K. Immunosuppression by human plasma alpha 1-acid glycoprotein: importance of the carbohydrate moiety. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6109–6113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezkorovainy A. Comparative study of the acid glycoproteins isolated from bovine serum, colostrum, and milk whey. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Jun;110(3):558–567. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90450-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutten A., Dehoux M., Deschenes M., Rouzeau J. D., Bories P. N., Durand G. Alpha 1-acid glycoprotein potentiates lipopolysaccharide-induced secretion of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by human monocytes and alveolar and peritoneal macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Oct;22(10):2687–2695. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello M., Fiedel B. A., Gewurz H. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by native and desialised alpha-1 acid glycoprotein. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):677–678. doi: 10.1038/281677a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato R. J., Loughnan M. S., Flynn E., Folkman J. Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):4082–4085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.4082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Andersson L. C. Leukocyte surface origin of human alpha1-acid glycoprotein (orosomucoid). J Exp Med. 1978 Aug 1;148(2):507–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golaz O., Hughes G. J., Frutiger S., Paquet N., Bairoch A., Pasquali C., Sanchez J. C., Tissot J. D., Appel R. D., Walzer C. Plasma and red blood cell protein maps: update 1993. Electrophoresis. 1993 Nov;14(11):1223–1231. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501401183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günzler V. Thalidomide in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) patients. A review of safety considerations. Drug Saf. 1992 Mar-Apr;7(2):116–134. doi: 10.2165/00002018-199207020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaka T., Bammerlin H., Kaufmann H., Schmid K. The amino-terminal peptide of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5560–5563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson J. C., Ashton F. E. Studies on acute phase proteins of rat serum. 3. Site of synthesis of albumin and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and the contents of these proteins in liver microsome fractions from rats suffering from induced inflammation. Can J Biochem. 1973 Jul;51(7):1034–1045. doi: 10.1139/o73-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keenan R. J., Eiras G., Burckart G. J., Stuart R. S., Hardesty R. L., Vogelsang G., Griffith B. P., Zeevi A. Immunosuppressive properties of thalidomide. Inhibition of in vitro lymphocyte proliferation alone and in combination with cyclosporine or FK506. Transplantation. 1991 Nov;52(5):908–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremer J. M., Wilting J., Janssen L. H. Drug binding to human alpha-1-acid glycoprotein in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Mar;40(1):1–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert C., Brouckaert P., Fiers W. Protection by alpha 1-acid glycoprotein against tumor necrosis factor-induced lethality. J Exp Med. 1994 Oct 1;180(4):1571–1575. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.4.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makonkawkeyoon S., Limson-Pobre R. N., Moreira A. L., Schauf V., Kaplan G. Thalidomide inhibits the replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreira A. L., Sampaio E. P., Zmuidzinas A., Frindt P., Smith K. A., Kaplan G. Thalidomide exerts its inhibitory action on tumor necrosis factor alpha by enhancing mRNA degradation. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1675–1680. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Board P. G., Matsushita K., Tanaka H., Matsuyama T., Matsuda T. Alpha 1-acid glycoprotein expression in human leukocytes: possible correlation between alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation. 1993 Feb;17(1):33–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00916390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira A. C., Neubert R., Helge H., Neubert D. Thalidomide and the immune system. 3. Simultaneous up- and down-regulation of different integrin receptors on human white blood cells. Life Sci. 1994;55(2):77–92. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHESKIN J. THALIDOMIDE IN THE TREATMENT OF LEPRA REACTIONS. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1965 May-Jun;6:303–306. doi: 10.1002/cpt196563303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio E. P., Kaplan G., Miranda A., Nery J. A., Miguel C. P., Viana S. M., Sarno E. N. The influence of thalidomide on the clinical and immunologic manifestation of erythema nodosum leprosum. J Infect Dis. 1993 Aug;168(2):408–414. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.2.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio E. P., Sarno E. N., Galilly R., Cohn Z. A., Kaplan G. Thalidomide selectively inhibits tumor necrosis factor alpha production by stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):699–703. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Kaufmann H., Isemura S., Bauer F., Emura J., Motoyama T., Ishiguro M., Nanno S. Structure of 1 -acid glycoprotein. The complete amino acid sequence, multiple amino acid substitutions, and homology with the immunoglobulins. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2711–2724. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Shibata Y., Matsuda Y., Ishida N. Isolation and characterization of an immunosuppressive acidic protein from ascitic fluids of cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1981 Aug;41(8):3244–3252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelsang G. B., Hess A. D., Gordon G., Brundrette R., Santos G. W. Thalidomide induction of bone marrow transplantation tolerance. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 3):2658–2661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIMER H. E., MEHL J. W., WINZLER R. J. Studies on the mucoproteins of human plasma. V. Isolation and characterization of a homogeneous mucoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):561–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]