Abstract
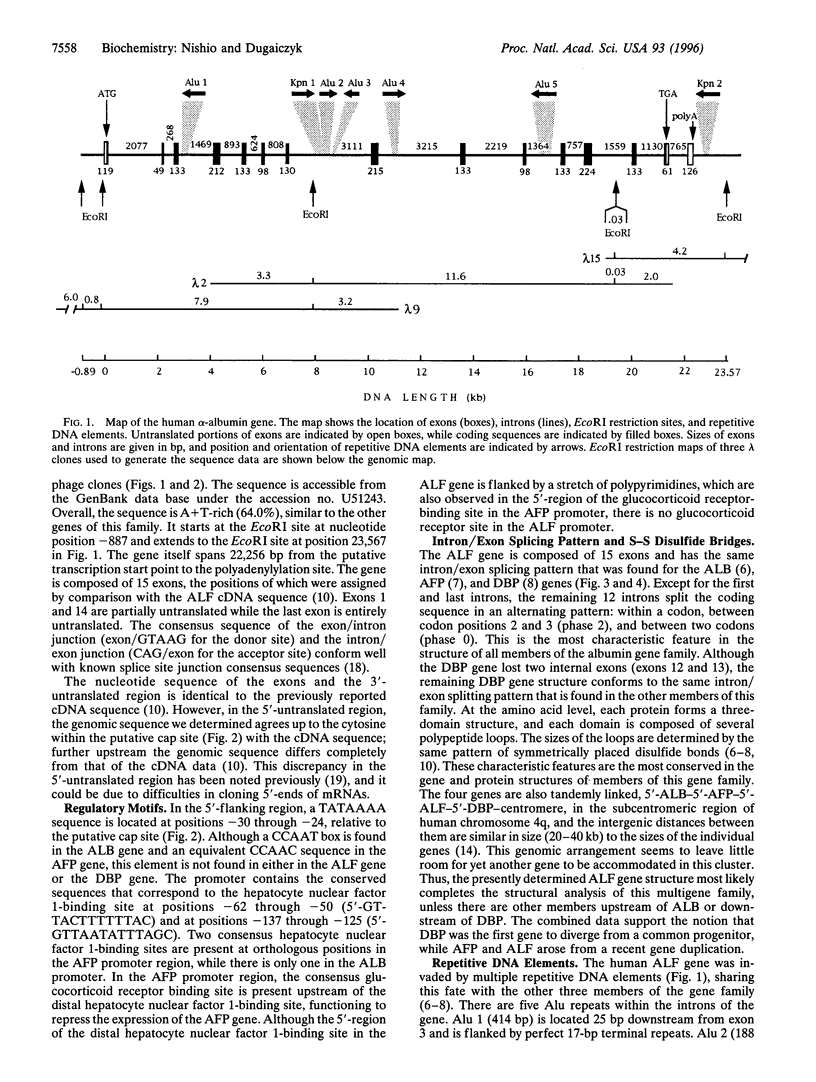
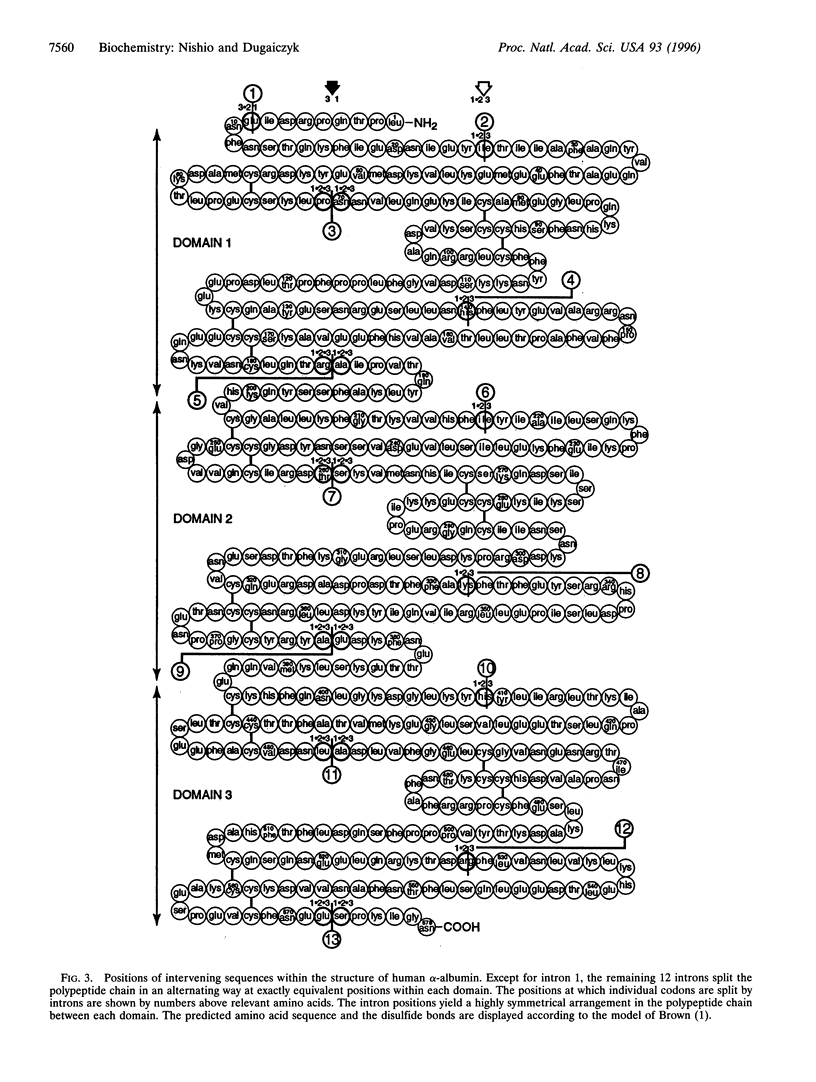
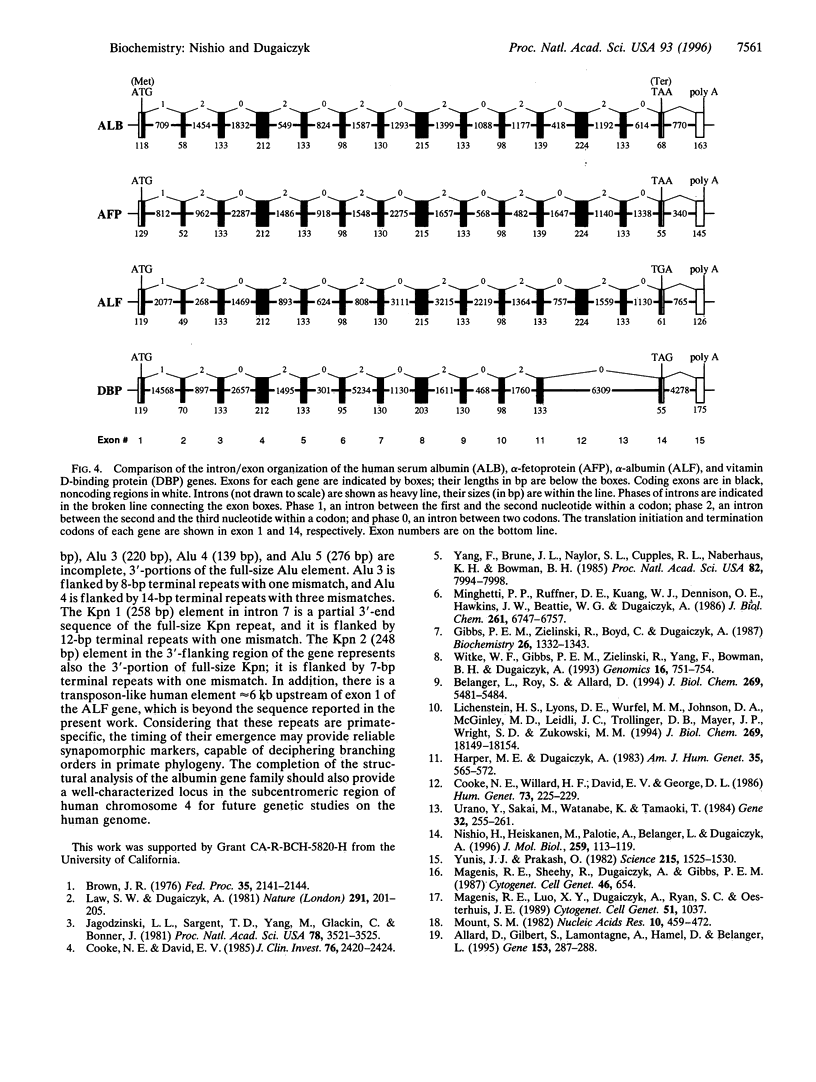
The nucleotide sequence of the human alpha-albumin gene, including 887 bp of the 5'-flanking region and 1311 bp of the 3-flanking region (24,454 in total), was determined from three overlapping lambda phage clones. The sequence spans 22,256 bp from the cap site to the polyadenylylation site, revealing a gene structure of 15 exons separated by 14 introns. The methionine initiation codon ATG is within exon 1; the termination codon TGA is within exon 14. Exon 15 is entirely untranslated and contains the polyadenylylation signal AATAAA. The deduced polypeptide chain is composed of a 21-amino-acid leader peptide, followed by 578 amino acids of the mature protein. There are seven repetitive DNA elements (Alu and Kpn) in the introns and 3-flanking region. The sizes of the 15 alpha-albumin exons match closely those of the albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, and vitamin D-binding protein genes. The exons are symmetrically placed within the three domains of the individual proteins, and they share a characteristic codon splitting pattern that is conserved among members of the gene family. The results provide strong evidence that alpha-albumin belongs to, and most likely completes with, the serum albumin gene family. Based on structural similarity, alpha-albumin appears to be most closely related to alpha-fetoprotein. The complete structure of this family of four tandemly linked genes provides a well-characterized approximately 200 kb locus in the 4q subcentromeric region of the human genome.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allard D., Gilbert S., Lamontagne A., Hamel D., Bélanger L. Identification of rat alpha-albumin and cDNA cloning of its human ortholog. Gene. 1995 Feb 14;153(2):287–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00745-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R. Structural origins of mammalian albumin. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2141–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bélanger L., Roy S., Allard D. New albumin gene 3' adjacent to the alpha 1-fetoprotein locus. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5481–5484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., David E. V. Serum vitamin D-binding protein is a third member of the albumin and alpha fetoprotein gene family. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2420–2424. doi: 10.1172/JCI112256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Willard H. F., David E. V., George D. L. Direct regional assignment of the gene for vitamin D binding protein (Gc-globulin) to human chromosome 4q11-q13 and identification of an associated DNA polymorphism. Hum Genet. 1986 Jul;73(3):225–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00401232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs P. E., Zielinski R., Boyd C., Dugaiczyk A. Structure, polymorphism, and novel repeated DNA elements revealed by a complete sequence of the human alpha-fetoprotein gene. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1332–1343. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Dugaiczyk A. Linkage of the evolutionarily-related serum albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes within q11-22 of human chromosome 4. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Jul;35(4):565–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagodzinski L. L., Sargent T. D., Yang M., Glackin C., Bonner J. Sequence homology between RNAs encoding rat alpha-fetoprotein and rat serum albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3521–3525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. W., Dugaiczyk A. Homology between the primary structure of alpha-fetoprotein, deduced from a complete cDNA sequence, and serum albumin. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):201–205. doi: 10.1038/291201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichenstein H. S., Lyons D. E., Wurfel M. M., Johnson D. A., McGinley M. D., Leidli J. C., Trollinger D. B., Mayer J. P., Wright S. D., Zukowski M. M. Afamin is a new member of the albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, and vitamin D-binding protein gene family. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):18149–18154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minghetti P. P., Ruffner D. E., Kuang W. J., Dennison O. E., Hawkins J. W., Beattie W. G., Dugaiczyk A. Molecular structure of the human albumin gene is revealed by nucleotide sequence within q11-22 of chromosome 4. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6747–6757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishio H., Heiskanen M., Palotie A., Bélanger L., Dugaiczyk A. Tandem arrangement of the human serum albumin multigene family in the sub-centromeric region of 4q: evolution and chromosomal direction of transcription. J Mol Biol. 1996 May 31;259(1):113–119. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urano Y., Sakai M., Watanabe K., Tamaoki T. Tandem arrangement of the albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes in the human genome. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W. F., Gibbs P. E., Zielinski R., Yang F., Bowman B. H., Dugaiczyk A. Complete structure of the human Gc gene: differences and similarities between members of the albumin gene family. Genomics. 1993 Jun;16(3):751–754. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Brune J. L., Naylor S. L., Cupples R. L., Naberhaus K. H., Bowman B. H. Human group-specific component (Gc) is a member of the albumin family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7994–7998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Prakash O. The origin of man: a chromosomal pictorial legacy. Science. 1982 Mar 19;215(4539):1525–1530. doi: 10.1126/science.7063861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




