Abstract
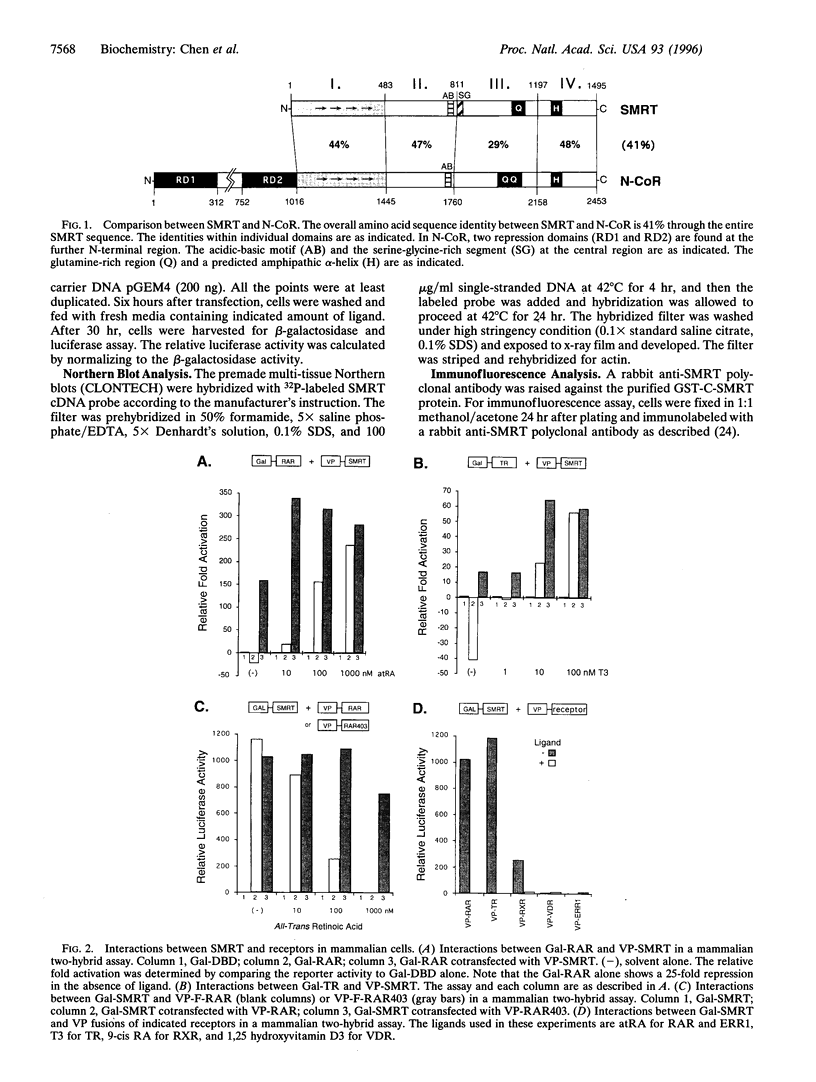
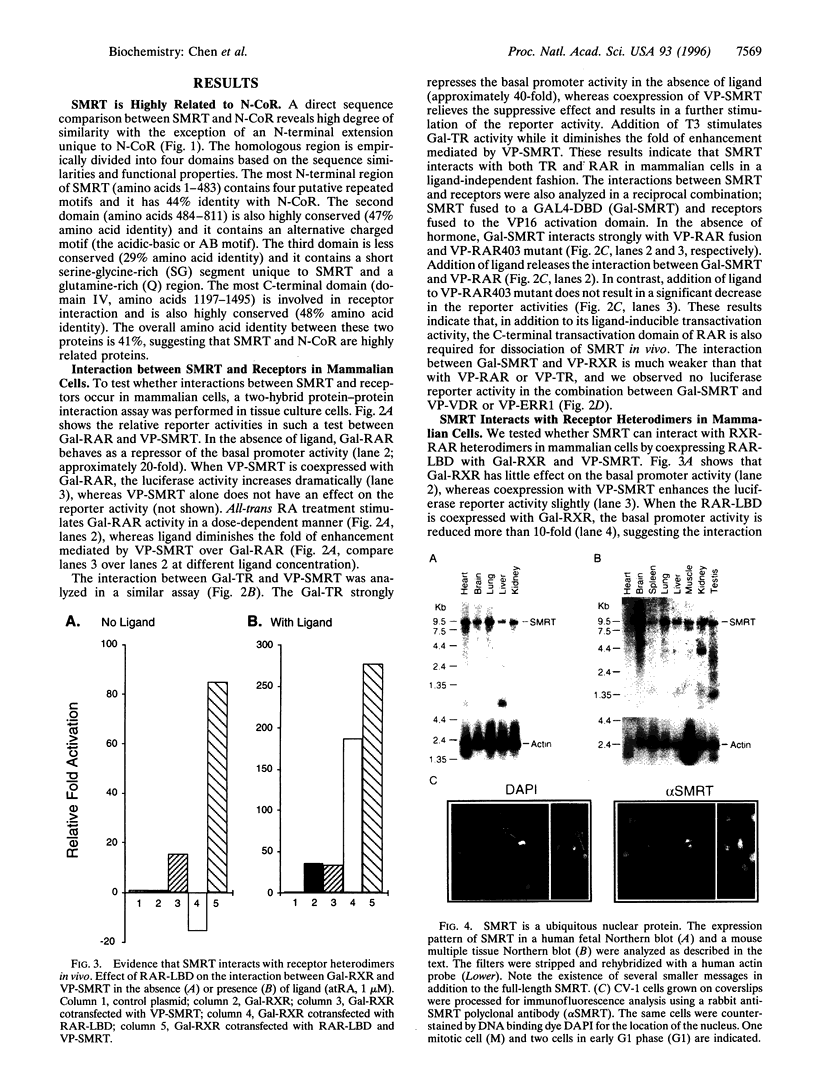
Transcriptional repression represents an important component in the regulation of cell differentiation and oncogenesis mediated by nuclear hormone receptors. Hormones act to relieve repression, thus allowing receptors to function as transcriptional activators. The transcriptional corepressor SMRT was identified as a silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid hormone receptors. SMRT is highly related to another corepressor, N-CoR, suggesting the existence of a new family of receptor-interacting proteins. We demonstrate that SMRT is a ubiquitous nuclear protein that interacts with unliganded receptor heterodimers in mammalian cells. Furthermore, expression of the receptor-interacting domain of SMRT acts as an antirepressor, suggesting the potential importance of splicing variants as modulators of thyroid hormone and retinoic acid signaling.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayer D. E., Lawrence Q. A., Eisenman R. N. Mad-Max transcriptional repression is mediated by ternary complex formation with mammalian homologs of yeast repressor Sin3. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Ha I., Reinberg D., Tsai S., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Interaction of human thyroid hormone receptor beta with transcription factor TFIIB may mediate target gene derepression and activation by thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8832–8836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. A transferable silencing domain is present in the thyroid hormone receptor, in the v-erbA oncogene product and in the retinoic acid receptor. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Steiner C., Köhne A. C., Renkawitz R. Modular structure of a chicken lysozyme silencer: involvement of an unusual thyroid hormone receptor binding site. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90532-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguet W., Ruff M., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H., Moras D. Crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of the human nuclear receptor RXR-alpha. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):377–382. doi: 10.1038/375377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillès V., Dauvois S., L'Horset F., Lopez G., Hoare S., Kushner P. J., Parker M. G. Nuclear factor RIP140 modulates transcriptional activation by the estrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3741–3751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Evans R. M. A transcriptional co-repressor that interacts with nuclear hormone receptors. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):454–457. doi: 10.1038/377454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Beug H., Graf T., Vennström B. A single point mutation in erbA restores the erythroid transforming potential of a mutant avian erythroblastosis virus (AEV) defective in both erbA and erbB oncogenes. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):375–382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04765.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Evans R. M. Identification of a domain required for oncogenic activity and transcriptional suppression by v-erbA and thyroid-hormone receptor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10668–10672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Heyman R. A., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Functional inhibition of retinoic acid response by dominant negative retinoic acid receptor mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2989–2993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielian P. S., White R., Lees J. A., Parker M. G. Identification of a conserved region required for hormone dependent transcriptional activation by steroid hormone receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1025–1033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck J. A., Maul G. G., Miller W. H., Jr, Chen J. D., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. A novel macromolecular structure is a target of the promyelocyte-retinoic acid receptor oncoprotein. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fondell J. D., Brunel F., Hisatake K., Roeder R. G. Unliganded thyroid hormone receptor alpha can target TATA-binding protein for transcriptional repression. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Jan;16(1):281–287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halachmi S., Marden E., Martin G., MacKay H., Abbondanza C., Brown M. Estrogen receptor-associated proteins: possible mediators of hormone-induced transcription. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1455–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.8197458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Adler S., Nelson C. A., Rosenfeld M. G. The C'-terminal interaction domain of the thyroid hormone receptor confers the ability of the DNA site to dictate positive or negative transcriptional activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8160–8164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörlein A. J., När A. M., Heinzel T., Torchia J., Gloss B., Kurokawa R., Ryan A., Kamei Y., Söderström M., Glass C. K. Ligand-independent repression by the thyroid hormone receptor mediated by a nuclear receptor co-repressor. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):397–404. doi: 10.1038/377397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imakado S., Bickenbach J. R., Bundman D. S., Rothnagel J. A., Attar P. S., Wang X. J., Walczak V. R., Wisniewski S., Pote J., Gordon J. S. Targeting expression of a dominant-negative retinoic acid receptor mutant in the epidermis of transgenic mice results in loss of barrier function. Genes Dev. 1995 Feb 1;9(3):317–329. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.3.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Redd M. J., Schultz J., Carlson M., Johnson A. D. Ssn6-Tup1 is a general repressor of transcription in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komachi K., Redd M. J., Johnson A. D. The WD repeats of Tup1 interact with the homeo domain protein alpha 2. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 1;8(23):2857–2867. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.23.2857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa R., DiRenzo J., Boehm M., Sugarman J., Gloss B., Rosenfeld M. G., Heyman R. A., Glass C. K. Regulation of retinoid signalling by receptor polarity and allosteric control of ligand binding. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):528–531. doi: 10.1038/371528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa R., Söderström M., Hörlein A., Halachmi S., Brown M., Rosenfeld M. G., Glass C. K. Polarity-specific activities of retinoic acid receptors determined by a co-repressor. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):451–454. doi: 10.1038/377451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin B., Zechel C., Garnier J. M., Lutz Y., Tora L., Pierrat P., Heery D., Gronemeyer H., Chambon P., Losson R. The N-terminal part of TIF1, a putative mediator of the ligand-dependent activation function (AF-2) of nuclear receptors, is fused to B-raf in the oncogenic protein T18. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):2020–2033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07194.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. W., Ryan F., Swaffield J. C., Johnston S. A., Moore D. D. Interaction of thyroid-hormone receptor with a conserved transcriptional mediator. Nature. 1995 Mar 2;374(6517):91–94. doi: 10.1038/374091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leng X., Blanco J., Tsai S. Y., Ozato K., O'Malley B. W., Tsai M. J. Mouse retinoid X receptor contains a separable ligand-binding and transactivation domain in its E region. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;15(1):255–263. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.1.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Evans R. M. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):841–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Thummel C., Beato M., Herrlich P., Schütz G., Umesono K., Blumberg B., Kastner P., Mark M., Chambon P. The nuclear receptor superfamily: the second decade. Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):835–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90199-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oñate S. A., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Sequence and characterization of a coactivator for the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1995 Nov 24;270(5240):1354–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5240.1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paroush Z., Finley R. L., Jr, Kidd T., Wainwright S. M., Ingham P. W., Brent R., Ish-Horowicz D. Groucho is required for Drosophila neurogenesis, segmentation, and sex determination and interacts directly with hairy-related bHLH proteins. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):805–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaud J. P., Rochel N., Ruff M., Vivat V., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H., Moras D. Crystal structure of the RAR-gamma ligand-binding domain bound to all-trans retinoic acid. Nature. 1995 Dec 14;378(6558):681–689. doi: 10.1038/378681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R. Repression mechanisms of v-ERBA and other members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 11;684:1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb32266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou M., Sugai S., Tanaka T., Shimouchi K., Fuchs E., Narumiya S., Kakizuka A. Inhibition of skin development by targeted expression of a dominant-negative retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):159–162. doi: 10.1038/374159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. Repression of transcription mediated at a thyroid hormone response element by the v-erb-A oncogene product. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):242–244. doi: 10.1038/340242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber-Agus N., Chin L., Chen K., Torres R., Rao G., Guida P., Skoultchi A. I., DePinho R. A. An amino-terminal domain of Mxi1 mediates anti-Myc oncogenic activity and interacts with a homolog of the yeast transcriptional repressor SIN3. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):777–786. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman I. G., Chakravarti D., Juguilon H., Romo A., Evans R. M. Interactions between the retinoid X receptor and a conserved region of the TATA-binding protein mediate hormone-dependent transactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8288–8292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seol W., Choi H. S., Moore D. D. Isolation of proteins that interact specifically with the retinoid X receptor: two novel orphan receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Jan;9(1):72–85. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.1.7760852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S., Bartelmez S., Heyman R., Damm K., Evans R., Collins S. J. A mutated retinoic acid receptor-alpha exhibiting dominant-negative activity alters the lineage development of a multipotent hematopoietic cell line. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2258–2269. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzamarias D., Struhl K. Functional dissection of the yeast Cyc8-Tup1 transcriptional co-repressor complex. Nature. 1994 Jun 30;369(6483):758–761. doi: 10.1038/369758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. L., Apriletti J. W., McGrath M. E., West B. L., Baxter J. D., Fletterick R. J. A structural role for hormone in the thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1995 Dec 14;378(6558):690–697. doi: 10.1038/378690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]