Abstract
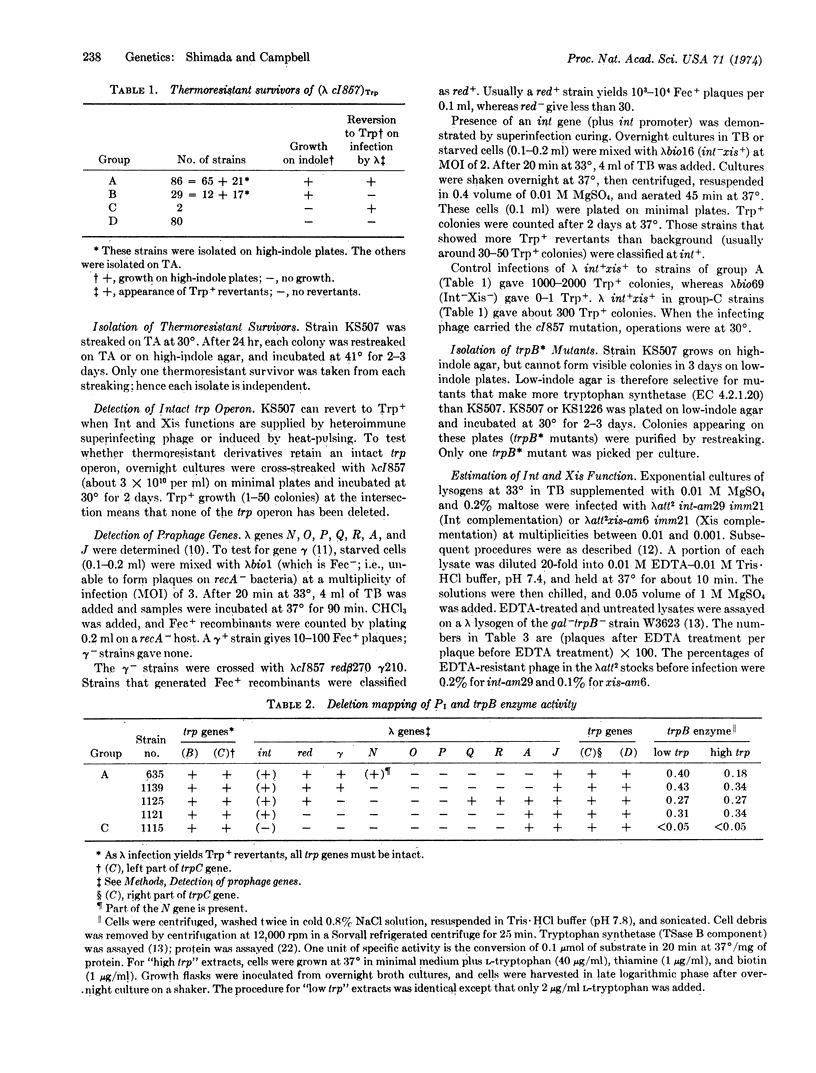
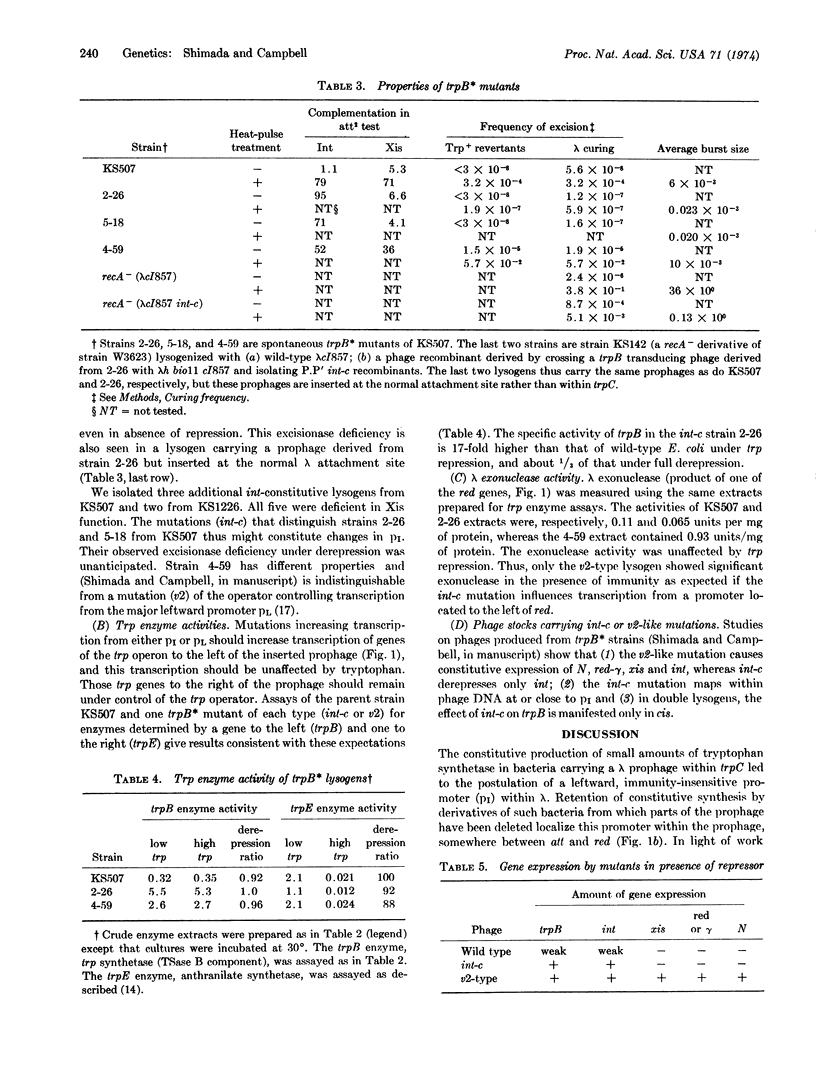
The constitutive production of small amounts of trpB enzyme in an Escherichia coli strain carrying λcI857 prophage within the trpC gene has been examined in derivatives of this strain from which portions of the prophage have been deleted. Enzyme production requires a site (pI) within the prophage close to the left prophage end. Selection for mutants of this lysogen that grow on low concentrations of indole yielded two types of mutations within the prophage: (a) v2-type, in which all phage genes controlled by the major leftward operator are derepressed; and (b) int-c type, in which the only phage gene derepressed is int. The int-c mutations lie in the same part of the prophage as pI. All int-c mutants appear deficient in xis gene function, even when derepressed.
Keywords: lysogenization, regulation, prophage excision, tryptophan synthetase
Full text
PDF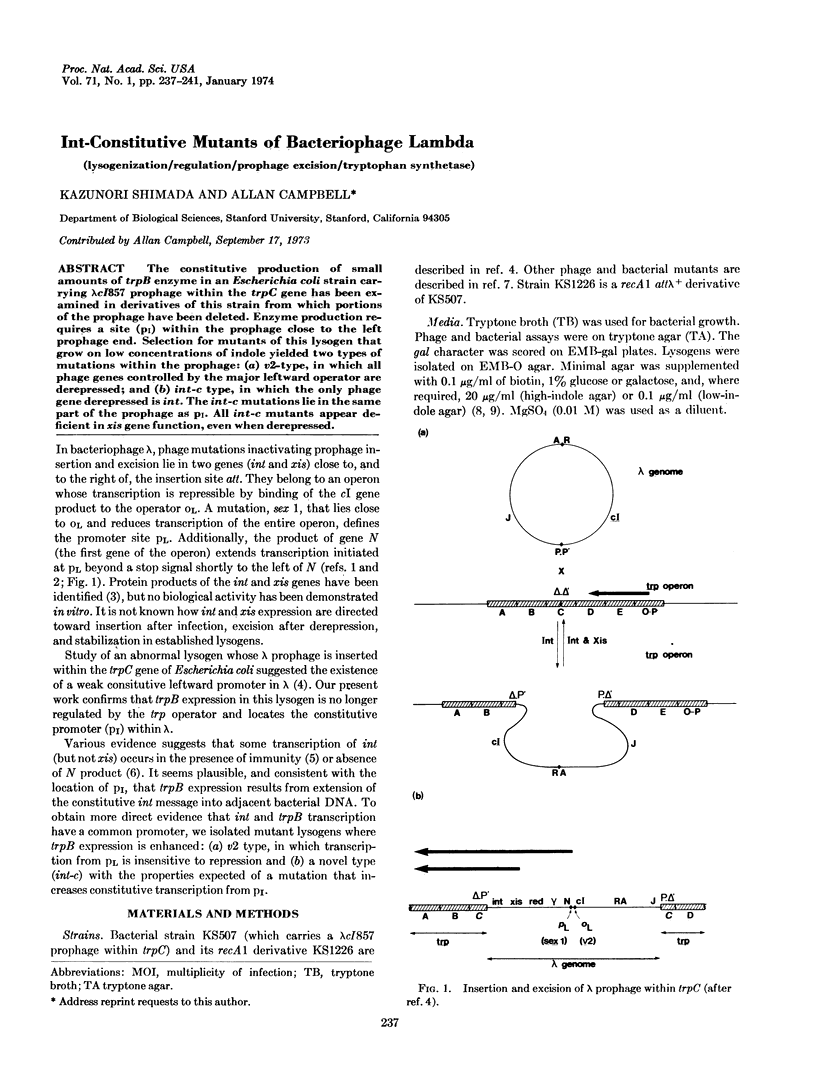


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAMPBELL A. Sensitive mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1961 May;14:22–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Campbell A. Gene regulation in N mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):938–945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.938-945.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Yarmolinsky M. B. Integration-negative mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J., Crawford I. P. Regulation of the enzymes of the tryptophan pathway in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1965 Dec;52(6):1303–1316. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.6.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., WOLLMAN E. L. Etude génétique d'un bactériophage tempéré d'Escherichia coli. l. Le système genétique du bactériophage. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1954 Dec;87(6):653–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser A. D., Masuda T. Evidence for a prophage excision gene in lambda. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Weisberg R. A., Gottesman M. E. Prophage lambda at unusual chromosomal locations. I. Location of the secondary attachment sites and the properties of the lysogens. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):483–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E. R. On the control of lysogeny in phage lambda. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):624–633. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90207-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. Control of development in temperate bacteriophages. 3. Which prophage genes are and which are not trans-activable in the presence of immunity? J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg R. A. Requirements for curing of lambda lysogens. Virology. 1970 May;41(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissler J., Campbell A. The steric effect in lysogenization by bacteriophage lambda. IV. Superinfection of nonimmune lysogens. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):318–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90215-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



