Abstract
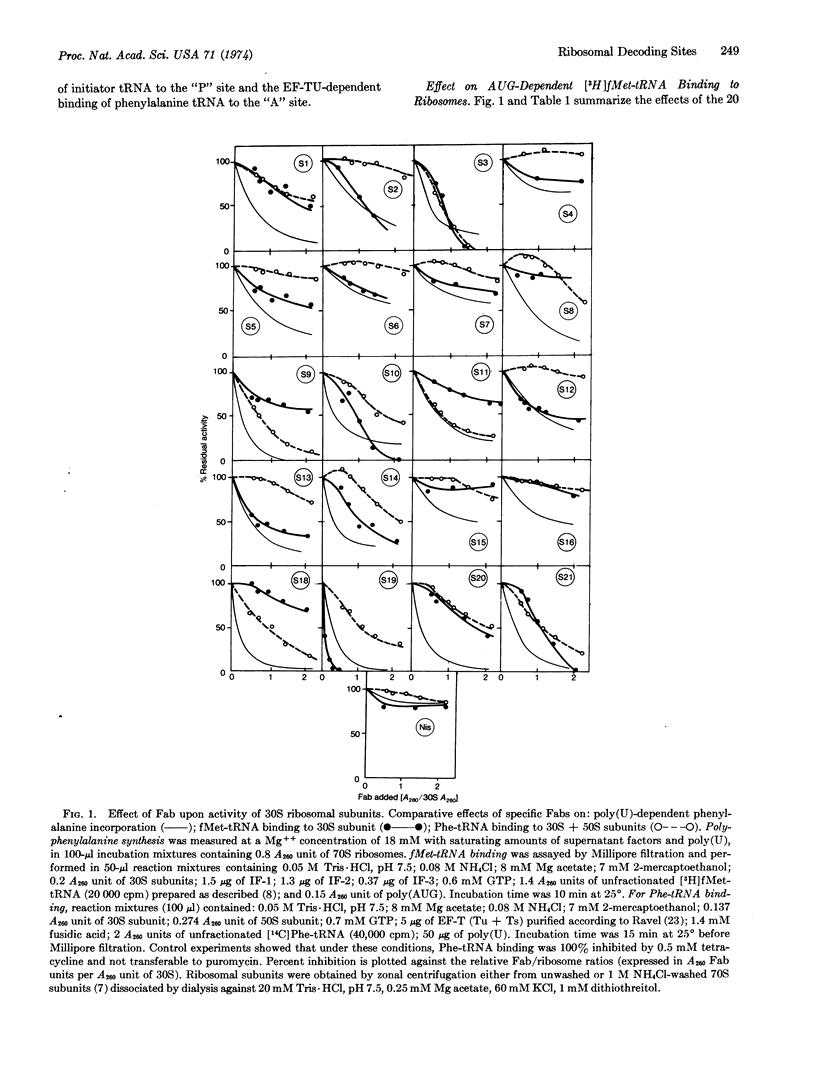
Specific anti-30S protein immunoglobulin G fragments (Fab) were used to determine the contribution of each of the 30S ribosomal proteins to: (1) polyphenylalanine synthesis, (2) initiation factor-dependent binding of fMet-tRNA, (3) T-factor-dependent binding of phenylalanyl-tRNA, and (4) fixation of radioactive dihydrostreptomycin. Twenty of the 21 possible antibodies (antibody against S17 excepted) were used. In conditions where all the 30S proteins were accessible to Fabs, all of these monovalent antibodies strongly inhibited polyphenylalanine synthesis in vitro. Antibodies against S4, S6, S7, S12, S15, and S16, however, showed a weaker effect.
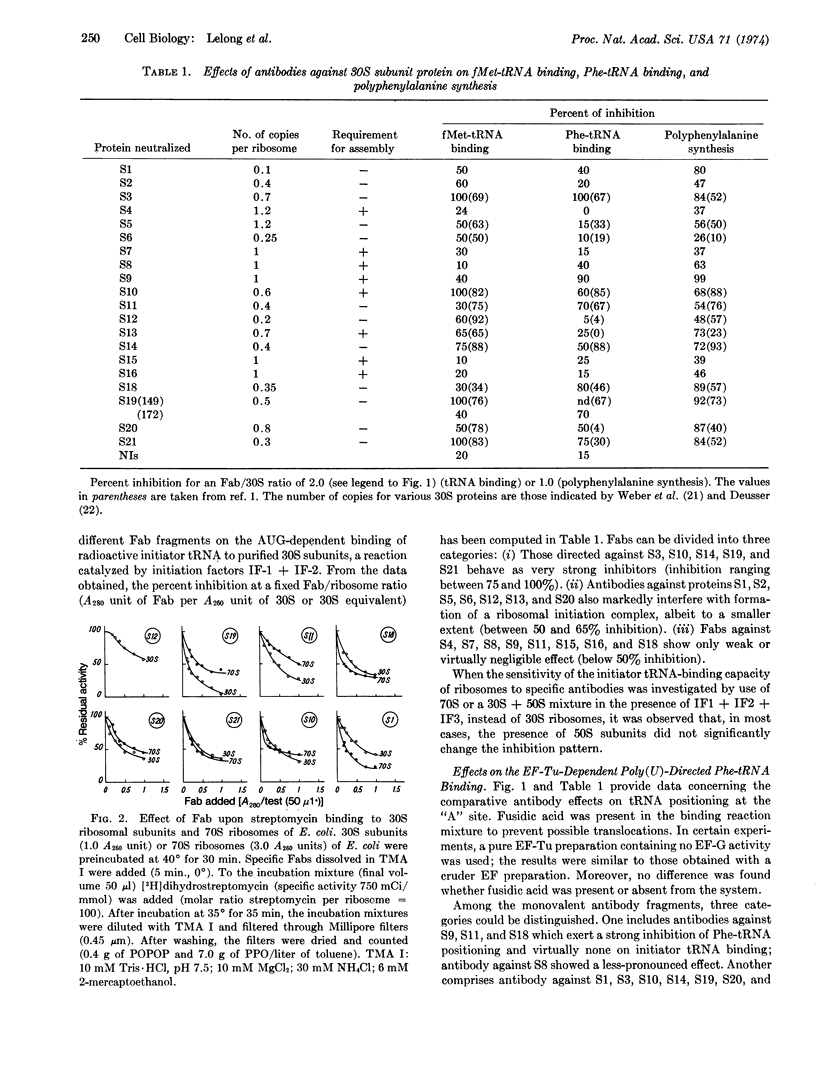
30S proteins can be classified into four categories by their contributions to the function of sites “A” and “P”: class I appears nonessential for tRNA positioning at either site (S4, S7, S15, and S16); class II includes proteins whose role in initiation is critical (S2, S5, S6, S12, and S13); class III (S8, S9, S11, and S18) corresponds to proteins whose blockade prevents internal (elongation factor Tudependent) positioning; and class IV includes entities that are essential for activities of both “A” and “P” sites (S1, S3, S10, S14, S19, S20, and S21). Dihydrostreptomycin fixation to the 30S or 70S ribosomes was inhibited by antibodies against S1, S10, S11, S18, S19, S20, and S21, but only weakly by the anti-S12 (Str A protein) Fab.
The significance of these results is discussed in relation to 30S protein function, heterogeneity, and topography.
Keywords: polyphenylalanine synthesis, streptomycin fixation, IF-fMet-tRNA, EF-Tu-Phe-tRNA
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biswas D. K., Gorini L. The attachment site of streptomycin to the 30S ribosomal subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2141–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrer B., Vázquez D., Modolell J. Inhibition by elongation factor EF G of aminoacyl-tRNA binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):733–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deusser E. Heterogeneity of ribosomal populations in Escherichia coli cells grown in different media. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):249–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00333862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highland J. H., Bodley J. W., Gordon J., Hasenbank R., Stöffler G. Identity of the ribosomal proteins involved in the interaction with elongation factor G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):147–150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G., Voynow P., Hardy S. J., Randall L., Lutter L. Physical and functional heterogeneity of E. coli ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:17–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M., Gros F. Translation initiation defects in ribosomes from streptomycin dependent strains. Biochimie. 1973;55(2):171–181. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80389-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelong J. C., Cousin M. A., Gros F., Miskin R., Vogel Z., Groner Y., Revel M. Protection of Escherichia coli ribosomes against streptomycin by purified initiation factors. Eur J Biochem. 1972 May;27(1):174–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lelong J. C., Gros D., Cousin M. A., Grunberg-Manago M., Gros F. Streptomycin induced release of fMet-tRNA from the ribosomal initiation complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):530–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90403-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Davis B. D. Breakdown by streptomycin of initiation complexes formed on ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1148–1155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momose H., Gorini L. Genetic analysis of streptomycin dependence in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1971 Jan;67(1):19–38. doi: 10.1093/genetics/67.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Mizushima S., Ozaki M., Traub P., Lowry C. V. Structure and function of ribosomes and their molecular components. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:49–61. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUTNAM F. W., TAN M., LYNN L. T., EASLEY C. W., MIGITA S. The cleavage of rabbit gamma-globulin by papain. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:717–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall-Hazelbauer L. L., Kuland C. G. Identification of three 30S proteins contributing to the ribosomal A site. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(3):234–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00268887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revel M., Lelong J. C., Brawerman G., Gros F. Function of three protein factors and ribosomal subunits in the initiation of protein synthesis in E. coli. Nature. 1968 Sep 7;219(5158):1016–1021. doi: 10.1038/2191016a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter D. Inability of E. coli ribosomes to interact simultaneously with the bacterial elongation factors EF Tu and EF G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Mar 10;46(5):1850–1856. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Daya L., Rak K. H., Garrett R. A. Ribosomal proteins. XXVI. The number of specific protein binding sites on 16 s and 23 s RNA of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):411–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90437-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XXV. Immunological studies on Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):407–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöffler G., Wittmann H. G. Sequence differences of Escherichia coli 30S ribosomal proteins as determined by immunochemical methods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duin J., Kurland C. G. Functional heterogeneity of the 30S ribosomal subunit of E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(2):169–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00269653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber H. J. Stoichiometric measurements of 30S and 50S ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):233–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00333861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin J., van Knippenberg P. H., Dieben M. Functional heterogeneity of the 30S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. II. Effect of S21 on initiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;116(2):181–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00582227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



