Abstract
Glutamate decarboxylase (L-glutamate l-carboxylase; EC 4.1.1.15), the enzyme in brain that forms γ-aminobutyric acid, was made visible on sections of rat cerebellum by use of rabbit antiserum to purified mouse-brain glutamate decarboxylase. Cerebellar sections obtained from rats that were perfused with 4% paraformaldehyde were treated with antiserum against the enzyme or with serum from unimmunized rabbits, washed, and then incubated with peroxidase-labeled goat antibody against rabbit immunoglobulin. The glutamate decarboxylase was made visible on sections by means of the product formed by the action of peroxidase on 3,3′-diaminobenzidine and H2O2. A weak and diffuse reaction was observed in Purkinje cell bodies, suggesting the occurrence of the enzyme within these cells. In addition, an intense, punctate deposition of reaction product was located around the Purkinje cells and around the neurons of the deep cerebellar nuclei, suggesting the impingement of many nerve terminals containing the enzyme upon these neuronal surfaces. No specific reaction product was observed in sections treated with serum from unimmunized rabbits. The distribution of glutamate decarboxylase observed in our preparations is consistent with a large body of indirect biochemical, physiological, and morphological data dealing with the synaptic role of γ-aminobutyric acid neurons in the cerebellum.
Keywords: Purkinje cells, γ-aminobutyric acid, synapse
Full text
PDF
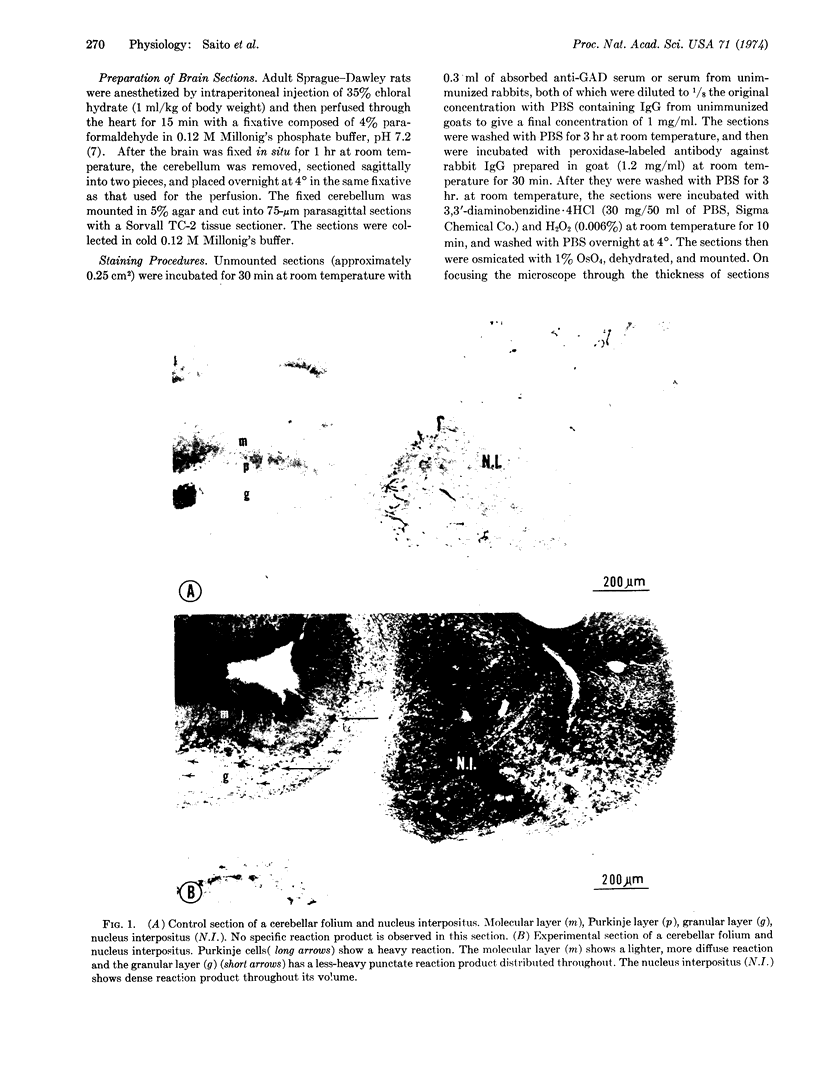



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan-Palay V. The recurrent collaterals of Purkinje cell axons: a correlated study of the rat's cerebellar cortex with electron microscopy and the Golgi method. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1971;134(2):200–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00519300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakane P. K., Pierce G. B., Jr Enzyme-labeled antibodies for the light and electron microscopic localization of tissue antigens. J Cell Biol. 1967 May;33(2):307–318. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts E., Kuriyama K. Biochemical-physiological correlations in studies of the gamma-aminobutyric acid system. Brain Res. 1968 Apr;8(1):1–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. Y., Matsuda T., Roberts E. Purification and characterization of glutamate decarboxylase from mouse brain. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3029–3034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






