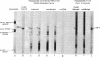
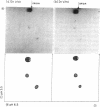
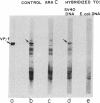
Abstract
Extracts of wheat germ are capable of synthesizing the major capsid protein of simian virus 40. Poly(A)-containing RNA from BS-C-1 cells infected with simian virus 40 directed the synthesis of a novel polypeptide that migrates in polyacrylamide gels together with the major capsid polypeptide of simian virus 40, VP-1. The patterns of the major tryptic peptides of purified VP-1 and the novel polypeptide synthesized in vitro were identical after two-dimensional paper electrophoresis. The novel polypeptide was not synthesized in response to poly(A)-rich RNA from uninfected cells or from virus-infected cells treated with cytosine arabinoside. Messenger RNA from infected cells purified by selective hybridization to DNA of simian virus 40 directs the synthesis of a major polypeptide of electrophoretic mobility similar to that of VP-1 of simian virus 40. This approach should prove useful in identifying additional products specified by DNA tumor viruses.
Keywords: wheat-germ extracts, oligo(dT)-cellulose, gel electrophoresis, peptide analysis, RNA·DNA selective hybridization
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Gesteland R. F. Pattern of protein synthesis in monkey cells infected by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):758–765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.758-765.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boime I., Leder P. Protein synthesis directed by encephalomyocarditis virus mRNA. 3. Discrete polypeptides translated from a monocistronic messenger in vitro. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Dec;153(2):706–713. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90389-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butel J. S., Rapp F. The effect of arabinofuranosylcytosine on the growth cycle of simian virus 40. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):490–495. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Gesteland R. F. Synthesis of polyoma proteins in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):627–634. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Huang E. S., Pagano J. S. Structural polypeptides of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):635–641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.635-641.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M., Marty L., Suarez F. Capsid proteins of Simian virus 40. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 13;40(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E., Tovell D. R. Characterization of the polypeptides formed in response to encephalomyocarditis virus ribonucleic acid in a cell-free system from mouse ascites tumor cells. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):73–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.73-81.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S., Winocour E. Acquisition of sequences homologous to host deoxyribonucleic acid by closed circular simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):309–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.309-316.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Biosynthesis of reticulocyte membrane proteins by membrane-free polyribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Osborn M., Lingrel J. B. Translation of globin messenger RNA in a heterologous cell-free system. Nature. 1971 Oct 13;233(5320):206–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Winocour E. Covalently linked cell and SV40-specific sequences in an RNA from productively infected cells. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):558–566. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90407-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J. Transformation by polyoma virus and simian virus 40. Adv Cancer Res. 1972;16:141–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Roblin R., Dulbecco R. Protein synthesis in Simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):921–924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Ben-Ishai Z., Newbold J. E. Poly A associated with SV40 messenger RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 26;238(82):111–113. doi: 10.1038/newbio238111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Warnaar S. O., Winocour E. Isolation and characterization of simian virus 40 ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):193–201. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.193-201.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E. The investigation of oncogeic viral genomes in transformed cells by nucleic acid hybridization. Adv Cancer Res. 1971;14:37–70. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60518-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]