Abstract
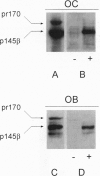
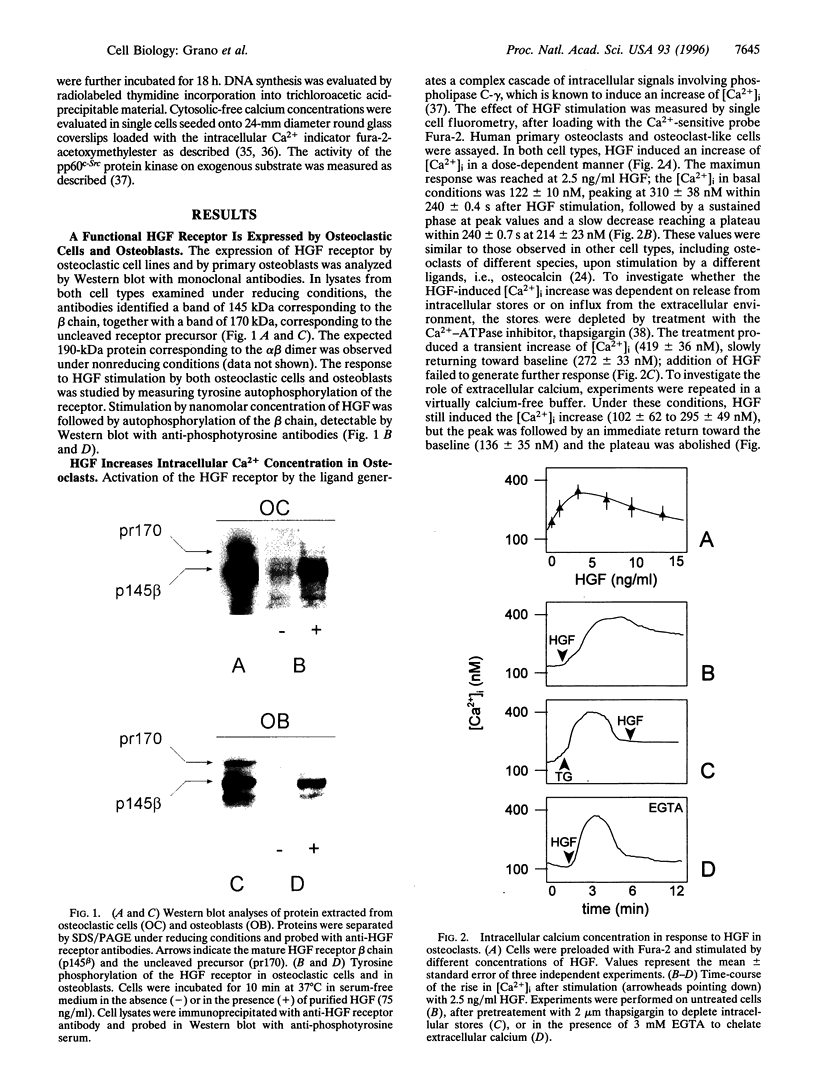
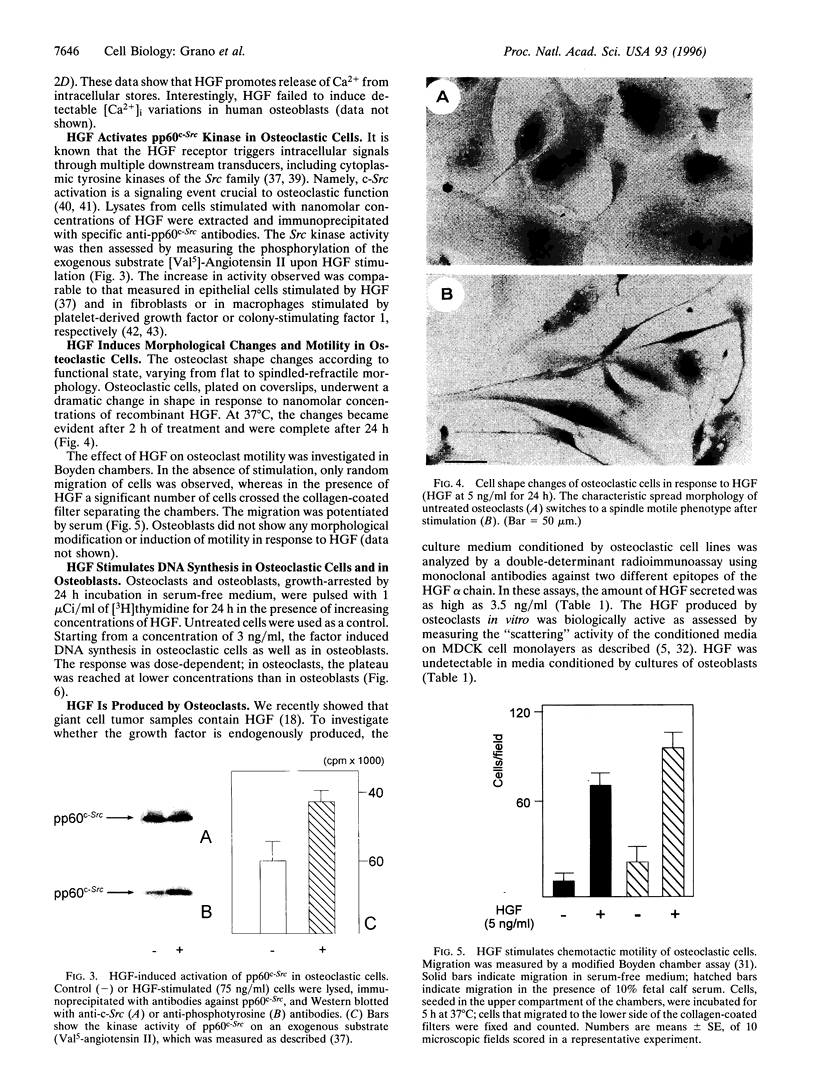
Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), also known as scatter factor, is a powerful motogen, mitogen, and morphogen produced by cells of mesodermal origin, acting on epithelial and endothelial cells. Its receptor is the tyrosine kinase encoded by the c-MET protooncogene. We show that the HGF receptor is expressed by human primary osteoclasts, by osteoclast-like cell lines, and by osteoblasts. In both cell lineages, HGF stimulation triggers the receptor kinase activity and autophosphorylation. In osteoclasts, HGF receptor activation is followed by increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration and by activation of the pp60c-Src kinase. HGF induces changes in osteoclast shape and stimulates chemotactic migration and DNA replication. Osteoblasts respond to HGF by entering the cell cycle, as indicated by stimulation of DNA synthesis. Interestingly, osteoclasts were found to synthesize and secrete biologically active HGF. These data strongly suggest the possibility of an autocrine regulation of the osteoclast by HGF and a paracrine regulation of the osteoblast by the HGF produced by the osteoclast.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardelli A., Maina F., Gout I., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Comoglio P. M., Ponzetto C. Autophosphorylation promotes complex formation of recombinant hepatocyte growth factor receptor with cytoplasmic effectors containing SH2 domains. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):1973–1978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonewald L. F., Mundy G. R. Role of transforming growth factor-beta in bone remodeling. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990 Jan;(250):261–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussolino F., Di Renzo M. F., Ziche M., Bocchietto E., Olivero M., Naldini L., Gaudino G., Tamagnone L., Coffer A., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):629–641. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Magnus C. J. Calcitonin alters behaviour of isolated osteoclasts. J Pathol. 1982 Jan;136(1):27–39. doi: 10.1002/path.1711360104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenu C., Colucci S., Grano M., Zigrino P., Barattolo R., Zambonin G., Baldini N., Vergnaud P., Delmas P. D., Zallone A. Z. Osteocalcin induces chemotaxis, secretion of matrix proteins, and calcium-mediated intracellular signaling in human osteoclast-like cells. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(4):1149–1158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comoglio P. M., Di Renzo M. F., Tarone G., Giancotti F. G., Naldini L., Marchisio P. C. Detection of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins in the detergent-insoluble fraction of RSV-transformed fibroblasts by azobenzene phosphonate antibodies. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):483–489. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01834.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Dhand R., Pilat D., Twamley G. M., Waterfield M. D., Roussel M. F. Activation of Src family kinases by colony stimulating factor-1, and their association with its receptor. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):943–950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Renzo M. F., Bertolotto A., Olivero M., Putzolu P., Crepaldi T., Schiffer D., Pagni C. A., Comoglio P. M. Selective expression of the Met/HGF receptor in human central nervous system microglia. Oncogene. 1993 Jan;8(1):219–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Renzo M. F., Narsimhan R. P., Olivero M., Bretti S., Giordano S., Medico E., Gaglia P., Zara P., Comoglio P. M. Expression of the Met/HGF receptor in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):1997–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J. R., Tarbaux N., Murphy L. A., Masuda T., Baylink D. J. In vitro evidence that bone formation may be coupled to resorption by release of mitogen(s) from resorbing bone. Metabolism. 1987 Apr;36(4):314–321. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(87)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferracini R., Di Renzo M. F., Scotlandi K., Baldini N., Olivero M., Lollini P., Cremona O., Campanacci M., Comoglio P. M. The Met/HGF receptor is over-expressed in human osteosarcomas and is activated by either a paracrine or an autocrine circuit. Oncogene. 1995 Feb 16;10(4):739–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galimi F., Bagnara G. P., Bonsi L., Cottone E., Follenzi A., Simeone A., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor induces proliferation and differentiation of multipotent and erythroid hemopoietic progenitors. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1743–1754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandino L., Longati P., Medico E., Prat M., Comoglio P. M. Phosphorylation of serine 985 negatively regulates the hepatocyte growth factor receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1815–1820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandino L., Munaron L., Naldini L., Ferracini R., Magni M., Comoglio P. M. Intracellular calcium regulates the tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the MET oncogene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16098–16104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi E., Gray J., Stoker M., Perryman M., Furlong R. Purification of scatter factor, a fibroblast-derived basic protein that modulates epithelial interactions and movement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5844–5848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi E., Stoker M. Hepatocyte growth factor--scatter factor: mitogen, motogen, and met. Cancer Cells. 1991 Jun;3(6):227–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Ponzetto C., Di Renzo M. F., Cooper C. S., Comoglio P. M. Tyrosine kinase receptor indistinguishable from the c-met protein. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):155–156. doi: 10.1038/339155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano S., Zhen Z., Medico E., Gaudino G., Galimi F., Comoglio P. M. Transfer of motogenic and invasive response to scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor by transfection of human MET protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):649–653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard S., Clapham D. Acceleration of intracellular calcium waves in Xenopus oocytes by calcium influx. Science. 1993 Apr 9;260(5105):229–232. doi: 10.1126/science.8385801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grano M., Colucci S., De Bellis M., Zigrino P., Argentino L., Zambonin G., Serra M., Scotlandi K., Teti A., Zambonin Zallone A. New model for bone resorption study in vitro: human osteoclast-like cells from giant cell tumors of bone. J Bone Miner Res. 1994 Jul;9(7):1013–1020. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650090708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grano M., Faccio R., Colucci S., Paniccia R., Baldini N., Zallone A. Z., Teti A. Extracellular Ca2+ sensing is modulated by pH in human osteoclast-like cells in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 1):C961–C968. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.267.4.C961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. C., Neff L., Chatterjee D., Lomri A., Levy J. B., Baron R. Osteoclasts express high levels of pp60c-src in association with intracellular membranes. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):1003–1013. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski Z. F. Coupling of bone formation to bone resorption: a broader view. Calcif Tissue Int. 1984 Sep;36(5):531–535. doi: 10.1007/BF02405360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Hayashi N., Tsubouchi H., Tanaka Y., Ito T., Sasaki Y., Fusamoto H., Daikuhara Y., Kamada T. Intracellular calcium as a second messenger for human hepatocyte growth factor in hepatocytes. Hepatology. 1992 Jun;15(6):1173–1178. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Miyazawa K., Uehara Y., Komada M., Okajima A., Okigaki M., Kitamura A. Gene expression and regulation of HGF-SF. EXS. 1993;65:49–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longati P., Bardelli A., Ponzetto C., Naldini L., Comoglio P. M. Tyrosines1234-1235 are critical for activation of the tyrosine kinase encoded by the MET proto-oncogene (HGF receptor). Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C., Yoneda T., Boyce B. F., Chen H., Mundy G. R., Soriano P. Osteopetrosis in Src-deficient mice is due to an autonomous defect of osteoclasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4485–4489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malgaroli A., Meldolesi J., Zallone A. Z., Teti A. Control of cytosolic free calcium in rat and chicken osteoclasts. The role of extracellular calcium and calcitonin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14342–14347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medico E., Mongiovi A. M., Huff J., Jelinek M. A., Follenzi A., Gaudino G., Parsons J. T., Comoglio P. M. The tyrosine kinase receptors Ron and Sea control "scattering" and morphogenesis of liver progenitor cells in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Apr;7(4):495–504. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos G., Cianciulli H. D., Novotny A. R., Kligerman A. D., Strom S. C., Jirtle R. L. Liver regeneration studies with rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Cancer Res. 1982 Nov;42(11):4673–4682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos G., Houck K. A., Dolan M. L., Leutteke N. C. Control of hepatocyte replication by two serum factors. Cancer Res. 1984 Oct;44(10):4414–4419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa K., Shimomura T., Kitamura A., Kondo J., Morimoto Y., Kitamura N. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA for a human serine protease reponsible for activation of hepatocyte growth factor. Structural similarity of the protease precursor to blood coagulation factor XII. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10024–10028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nawa K., Ichihara A. Partial purification and characterization of hepatocyte growth factor from serum of hepatectomized rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1450–1459. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91253-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nishizawa T., Hagiya M., Seki T., Shimonishi M., Sugimura A., Tashiro K., Shimizu S. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):440–443. doi: 10.1038/342440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Tamagnone L., Vigna E., Sachs M., Hartmann G., Birchmeier W., Daikuhara Y., Tsubouchi H., Blasi F., Comoglio P. M. Extracellular proteolytic cleavage by urokinase is required for activation of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4825–4833. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Bardelli A., Follenzi A., Galimi F., Comoglio P. M. Biological activation of pro-HGF (hepatocyte growth factor) by urokinase is controlled by a stoichiometric reaction. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):603–611. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Ferracini R., Longati P., Gandino L., Prat M., Comoglio P. M. The tyrosine kinase encoded by the MET proto-oncogene is activated by autophosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1793–1803. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Weidner K. M., Vigna E., Gaudino G., Bardelli A., Ponzetto C., Narsimhan R. P., Hartmann G., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K. Scatter factor and hepatocyte growth factor are indistinguishable ligands for the MET receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2867–2878. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oreffo R. O., Mundy G. R., Seyedin S. M., Bonewald L. F. Activation of the bone-derived latent TGF beta complex by isolated osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 15;158(3):817–823. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92795-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paniccia R., Colucci S., Grano M., Serra M., Zallone A. Z., Teti A. Immediate cell signal by bone-related peptides in human osteoclast-like cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 1):C1289–C1297. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.5.C1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paniccia R., Riccioni T., Zani B. M., Zigrino P., Scotlandi K., Teti A. Calcitonin down-regulates immediate cell signals induced in human osteoclast-like cells by the bone sialoprotein-IIA fragment through a postintegrin receptor mechanism. Endocrinology. 1995 Mar;136(3):1177–1186. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.3.7867571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Bardelli A., Zhen Z., Maina F., dalla Zonca P., Giordano S., Graziani A., Panayotou G., Comoglio P. M. A multifunctional docking site mediates signaling and transformation by the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor family. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey P. G., Young M. F., Flanders K. C., Roche N. S., Kondaiah P., Reddi A. H., Termine J. D., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Osteoblasts synthesize and respond to transforming growth factor-type beta (TGF-beta) in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):457–463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodan G. A., Martin T. J. Role of osteoblasts in hormonal control of bone resorption--a hypothesis. Calcif Tissue Int. 1981;33(4):349–351. doi: 10.1007/BF02409454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Montgomery C., Geske R., Bradley A. Targeted disruption of the c-src proto-oncogene leads to osteopetrosis in mice. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):693–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90499-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker M., Gherardi E., Perryman M., Gray J. Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial cell mobility. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):239–242. doi: 10.1038/327239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Takahashi N., Martin T. J. Modulation of osteoclast differentiation. Endocr Rev. 1992 Feb;13(1):66–80. doi: 10.1210/edrv-13-1-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura H., Hughes A. R., Thastrup O., Putney J. W., Jr Activation of calcium entry by the tumor promoter thapsigargin in parotid acinar cells. Evidence that an intracellular calcium pool and not an inositol phosphate regulates calcium fluxes at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12266–12271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner K. M., Behrens J., Vandekerckhove J., Birchmeier W. Scatter factor: molecular characteristics and effect on the invasiveness of epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2097–2108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambonin G., Grano M. Biomaterials in orthopaedic surgery: effects of different hydroxyapatites and demineralized bone matrix on proliferation rate and bone matrix synthesis by human osteoblasts. Biomaterials. 1995 Mar;16(5):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(95)98857-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]