Abstract
CD4+ T cells provide help to enhance and sustain cytotoxic CD8+ T cell responses. A direct lytic role for this cell population in mouse models further supports the use of tumor-reactive CD4+ T cells for cancer immunotherapy. CTLA-4 blockade has been shown to expand antigen-specific cytotoxic CD4+ T cells in mouse models. We took advantage of spontaneous immunity to the NY-ESO-1 cancer-testis antigen to investigate quantitative and qualitative changes in antigen-specific CD4+ T cell responses after ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody) treatment in advanced melanoma patients. Four NY-ESO-1 seropositive melanoma patients were chosen upon the availability of suitable blood specimens for characterizing the functions of NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cell response by enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT), intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) and cytotoxicity assays. Multiple NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cell responses with Th1 dominance were induced or enhanced after ipilimumab treatment in peripheral blood in all four patients. NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cell lines established from all 4 patients after ipilimumab treatment recognized naturally processed NY-ESO-1 protein in antigen-presenting cells, expressed master transcription factor Eomesodermin (Eomes) and secreted perforin and Granzyme B. Finally, we demonstrated that these NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cell lines directly lysed autologous melanoma cell lines expressing NY-ESO-1 in an MHC class II restricted manner. Our results show that antigen specific cytotoxic CD4+ T cell responses are induced after ipilimumab therapy in human cancer patients. Ipilimumab may induce the expression of lytic granules on antigen specific cytotoxic CD4+ T cells via Eomes, revealing a novel consequence of immunologic checkpoint blockade.
Keywords: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4, ipilimumab, NY-ESO-1, antibody, melanoma, cytotoxic CD4+ T cell
INTRODUCTION
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) is a co-inhibitory molecule expressed on activated T cells and regulatory T cells (Treg). CTLA-4 is essential in maintaining immune homeostasis and contributes to immune tolerance by down-regulating T cell activation [1,2,3]. Ipilimumab is a fully humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that blocks CTLA-4. Two pivotal phase III trials in patients with advanced melanoma demonstrated a survival benefit for ipilimumab as monotherapy or when added to chemotherapy [4,5], leading to its approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in March 2011, marking a milestone in the field of immunotherapy. Immunotherapeutic strategies have also focused on targeting antigens expressed exclusively on melanoma cells, e.g. melanoma differentiation antigens (such as gp100 or Melan-A) or cancer/testis (CT) antigens. CT antigens are expressed in a variety of human malignancies but not in normal adult tissues except for the testis and placenta [6]. To date, the best characterized CT antigen is NY-ESO-1, which is highly immunogenic and elicits spontaneous antibody (Ab) and T cell responses in cancer patients whose tumors express NY-ESO-1 [7]. Prior studies by our group and others have shown that ipilimumab treatment of advanced melanoma patients induces polyfunctional NY-ESO-1- and Melan-A-specific CD8+ T cell responses [8,9]. We have also correlated the induction of polyfunctional NY-ESO-1 CD4+ T cell responses with the development of integrated Ab and CD8+ T cell responses in patients, who experience clinical benefit [10].
The essential role of CD4+T helper (Th) cells in enhancing and sustaining CD8+ T cell responses is well-established [11]. Recent evidence in mouse models, however, suggests more direct roles for tumor-reactive CD4+ T cells for cancer immunotherapy [12,13]. Specifically, CTLA-4 blockade has the capacity to expand antigen-specific cytotoxic CD4+ T cells in vivo in mice [12]. Furthermore, adoptive transfer of CD4+ T cells expanded from a single tumor-reactive T cell clone resulted in a durable complete response in a melanoma patient [14]. However, the cytotoxic function of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells during ipilimumab treatment and its intracellular mechanism has not been characterized. We hypothesized that CTLA-4 blockade could result in expansion and/or enhancement of cytotoxic CD4+ T cell responses in human cancer patients through the modulation of Th1 transcription factors. To address this, we performed in-depth immune monitoring of four NY-ESO-1 seropositive melanoma patients who received ipilimumab and had availability of properly annotated specimens. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were analyzed by ICS using multiparametric flow cytometry. Samples were analyzed following in vitro stimulation with NY-ESO-1 overlapping or single peptides. Interferon (IFN)-γ ELISPOT was performed to define specific CD4+ T cell peptide responses. Transcription factors T-bet and Eomesodermin (Eomes) as well as cytotoxic degranulation markers perforin and granzyme B were analyzed on NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cells. NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell lines were established to confirm their ability to recognize NY-ESO-1 positive tumor cell lines and to induce tumor lysis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
Blood and tissue samples were analyzed from four patients (09-079-1, 09-079-7, 09-079-10 and 09-079-17) treated on a clinical trial at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) evaluating the pharmacokinetics of two different biosynthetic formulations of ipilimumab (CA184-087, NCT00920907). All patients received four doses of antibody at a dose of 10 mg/kg intravenously administered every 3 weeks for 4 doses during induction therapy. Patients without dose-limiting toxicity and with evidence of clinical benefit (in this case, 09-079-1, 09-079-10 and 09-079-17) then received maintenance ipilimumab at the same dose every 12 weeks starting at week 24. Responses were adjudicated by the recently proposed immune-related response criteria [15]. Toxicity was assessed using National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 3.0. All patients provided informed consent for the clinical studies and additional consent for the collection of blood and tumor tissue for investigational purposes on a separate MSKCC biospecimen utilization protocol. All studies were approved by the MSKCC Institutional Review Board.
Peptides and cell lines
NY-ESO-1 overlapping peptides (17 peptides with ~20-mer length and 10 aa overlap) [16] and NY-ESO-192-100 peptide (LAMPFATPM), NY-ESO-194-102 peptide (MPFATPMEA), NY-ESO-194-104 peptide (MPFATPMEAEL), NY-ESO-196-104 peptide (FATPMEAEL), and NY-ESO-1157-165 peptide (SLLMWITQC) were purchased from JPT Peptide Technologies (Berlin, Germany). Peptides were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide at a concentration of 1 mg/ml and stored in aliquots at −80 °C before use. The following autologous or MHC-matched melanoma cell lines were used as target cells: SK-MEL-381 (from patient 09-079-7), and SK-MEL-351 (from patient 09-079-10, NY-ESO-1 negative). Autologous B-lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL) were generated in our laboratory from the patients’ PBMCs, using EBV-containing supernatants and also used as target cells.
Preparation of PHA-stimulated CD4+ T cells (T-APC)
Phytohemagglutinin (PHA)-stimulated CD4+ T cells (T-antigen presenting cells or T-APCs) were prepared as described previously [17,18,19]. CD4+ T cells were separated from PBMCs using Dynabeads (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instruction and seeded into 48-well plates (NUNC, Roskilde, Denmark) at a density of 1–2×106 cells/well in 1 ml RPMI1640 medium supplemented with 25 μM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1- piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), 10% heat-inactivated human AB serum (Gemini Bio-Products), 2 μM L-glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin (complete medium). 10 μg/mL of PHA (REMEL, Lenexa, KS) was added to the culture at day 0. Half of the medium was replaced with complete medium containing interleukin (IL)-2 (20 IU/ml, Roche, Mannheim, Germany) and IL-7 (40 ng/ml) (R&D systems, Minneapolis, MN) at day 3, which was then repeated twice weekly. The activated CD4+ T-APCs were pulsed with peptides and used as target cells in various assays.
In vitro sensitization for monitoring T cell immune responses
In vitro sensitization was performed as described previously [17,18,19,20]. After separating CD8+ T cells or CD4+ T cells from PBMCs using Dynabeads, CD4+ T cells (5×105 cells/well) were cultured with antigen peptide-pulsed and irradiated (30 Gy) autologous CD4− CD8− PBMCs (5×105 cells/well) in 96 round bottom-well plates in complete medium. From day 4 onwards, half of the medium was replaced with complete medium containing IL-2 and IL-7 twice a week. These CD4+ T cells in the culture wells were the used as effector cells in various assays on day 20.
Generation of NY-ESO-1–specific CD4+ T cell lines
NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cells were isolated by using CD154 (CD40L) expression sorting as described with some modification [21,22]. Pre-sensitized CD4+ T cells were restimulated for 6 hours in 500 μl X-VIVO15 (BioWhittaker -Lonza, Basel, Switzerland) with T-APCs that were pulsed overnight with NY-ESO-1 peptide (1 μM) and labeled with carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) (Invitrogen-Molecular Probes, Grand Island, NY) in the presence of 20 μl of PE conjugated anti-CD154 mAb and 0.3 μl GolgiStop (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). CFSE−CD154+ NY-ESO-1-specific effector T cells were sorted using a FACSAria instrument and FACS Diva software (BD Biosciences). Sorted cells were stimulated with plate-bound anti-CD3 (0.5 μg/mL) and CD28 mAbs (0.5 μg/mL) (eBioscience, San Diego, CA) in the presence of irradiated allogeneic PBMCs and were expanded for about 20 days in the presence of 20 IU/ml of IL-2 and 20 ng/ml of IL-7 in complete medium as described with some modification [23]. Reactivity of the CD4+ T cell lines was tested against autologous melanoma cell lines or autologous LCL pulsed with peptides.
ELISPOT assay
The IFN-γ ELISPOT assay was performed as described previously [18,19,20]. Briefly, 96-well nitrocellulose ELISPOT plates (MAHA S4510; Millipore) were coated overnight at 4°C with 2 μg/ml anti-human IFN-γ mAb (1-D1K) and blocked with 10% human AB serum-containing RPMI 1640 for 2 hours at 37°C. 2×104 sensitized CD4+ T cells and 2×104 peptide-pulsed T-APCs were placed in each well of the ELISPOT plate at a final volume of 200 μl RPMI 1640 medium without serum. After incubation for 22 hours at 37°C in a CO2 incubator, the plate was developed using 0.2 μg/ml biotinylated anti-human IFN-γ mAb (7-B6-1, Mabtech), 1 μg/mL streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase conjugate(Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, Indiana) and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate/NBT (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). The number of spots was evaluated using a C.T.L. Immunospot analyzer and software (Cellular Technology, Shaker Heights, OH). Results were shown as the number of spot-forming cells (SFC) without subtracting the number of background spots, since the number of SFC in negative control was < 3 spots/well in all assays. A positive response with more than 10 spot counts/well as well as spot counts ≥3-fold more than background spots obtained with non-pulsed target cells was considered to be significant.
Intracellular cytokine staining (ICS)
For surface staining, APC-Cy7-CD8, PE-Cy7-CD3, Pacific Blue-CD3 (BD Bioscience), ECD-CD4, ECD-CD45RA, ECD-CD45RO (Beckman Coulter Inc. Brea, CA) and FITC-CCR7 (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) were used. For ICS, in vitro stimulated and cultured CD4+ T cells were harvested as effector cells. 2 × 105 effector CD4+ T cells were co-cultured for 6 hours in 500 μL 10% human AB serum RPMI in the presence of 0.35 μL GolgiStop and with PE-Cy5-CD107a (20 μl/ml, BD Bioscience) with 2 × 105 autologous T-APCs that had been pulsed overnight with each antigen peptide pool and labeled with CFSE. Cytoplasmic cytokines were stained using a BD Cytofix/Cytoperm kit (BD Biosciences) according to manufacturer’s instructions with FITC, Alexa Fluor 647, PE-Cy7, or Horizon-V450-IFN-γ, PE-Macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1β, APC-IL-2, PE or FITC-IL-4, APC-IL-5, Horizon-V450 or APC-IL-13, Alexa Fluor 700-granzyme B, PerCP-Cy5.5-T-bet (BD Bioscience), PE-Cy7-Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, PE-IL-10, Alexa Fluor 647-IL-17A, Alexa Fluor 647-Eomesodermin (Eomes)(eBioscience), PE-perforin (Cell sciences, Canton, MA).
CFSE-negative effector CD4+ T cells were analyzed using a CyAn flow cytometer with Summit software (Dako Cytomation Inc., Carpinteria, CA) or a LSR Fortessa with FACS Diva software (BD Biosciences). All analyses were carried out using FlowJo software (TreeStar, Inc., Ashland, OR). Results were shown as a frequency (%) of antigen-specific cytokine responses and CD107a mobilization (functions+) in CD4+ T cells after subtracting the frequency of background function+ cells. A positive response ≥3-fold more than the negative control obtained with non-pulsed target cells (% function+ cells/sample in all assays) was considered to be significant. All background intracellular responses (function+) were <0.1%, except for the transcription factors T-bet and Eomesodermin (Eomes), which were <0.5%.
Cytotoxicity assay
A cytotoxicity assay was performed as described previously with some modifications [12]. To determine the in vitro killing of tumor targets, target cells were labeled with 0.5 μM CFSE, whereas control target cells were labeled with 5 μM CFSE. NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell lines were co-cultured at different ratios [24] with a 50:50 mixture of target cells and control target cells for 6 hours. Then, cells were acquired on a CyAn flow cytometer with Summit software and analyzed by FlowJo software. 20 μg/mL of anti-human HLA-DR, DP, or DQ antibody (BD Bioscience) and mouse IgG2a, κ antibody (BD Bioscience) as a control were used for blocking of MHC class II on target cells. Cytotoxicity was calculated using the following formula: .
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using Prism 5.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc. La Jolla, CA). All the experiments were repeated two or three times. Statistical significance was determined by a Student’s t test. For real-time PCR, the mean of the relative gene expression (2− ΔCt) of the triplicates was used to determine statistical differences between each group. P < 0.05 was considered a statistically significant difference.
RESULTS
Patients
Patient profiles and clinical demographics are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
Patient profiles
| Patient ID | 09-079-1 | 09-079-7 | 09-079-10 | 09-079-17 |
| Age (years) | 63 | 49 | 39 | 54 |
| Gender | Male | Male | Female | Female |
| PS (Karnofsky) | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Stage | IV | IV | IV | IV |
| Metastatic lesions | adrenal grand, liver, peritoneal | lung, lymph nodes, pancreas, retro eritoneum, bone, soft tissue, thoracic nodes, spleen | lung, thoracic nodes, spleen, liver | skin, axillary lymph node and mesenteric mass |
| WBC (×103/mm2) | 7.0 | 8.2 | 3.9 | 7.7 |
| ALC (×103/mm2) | 1.6 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.8 |
| Adverse event (Grade) | Fatigue(G1) Neuropathy(G1) Tinnitus(G1) Myalgia(G1) |
Diarrhea(G1) Rash(G1) |
Fatigue(G2) Pruritus(G1) Rash(G1) |
Pruritus(G1) Rash(G1) |
| Prior therapy | Temozolomide IMC-1121B+DTIC CVT | None | CVT | Gp100 DNA, High- dose IL-2, Oncovex |
| Total # of dose | 12 | 3 | 11 | 12 |
PS: performance status; CVT: cisplatin + vinblastine + temozolomide; DTIC: dacarbazine; IMC-1121B: ramucirumab.
Case 1 – Patient 09-079-1
Patient 09-079-1 is a 63 year-old man with metastatic melanoma to soft tissue, liver, lymph nodes, bone and left adrenal gland. He had experienced progressive disease (PD) on multiple chemotherapy regimens. In August 2009, he initiated ipilimumab therapy. After completing induction therapy, imaging at week 12 revealed PD but repeat imaging at week 24 demonstrated a partial response (PR), although the adrenal lesion was noted to have increased in size. He initiated maintenance ipilimumab and subsequently underwent resection of the adrenal metastasis during week 27, as a presumed immunologic ‘escape’ lesion. Since that time, he has maintained a durable PR.
Case 2 – Patient 09-079-7
Patient 09-079-7 is a 49 year-old man who was diagnosed with metastatic melanoma to lung, lymph nodes, pancreas, retroperitoneum, bone, soft tissue, thoracic nodes and spleen in April 2009. He received first-line therapy with ipilimumab. Imaging after induction therapy revealed PD. Further imaging at week 16 indicated further significant PD. He was taken off the study protocol, transitioned to supportive care and died in March 2010.
Case 3 – Patient 09-079-10
Patient 09-079-10 is a 39 year-old woman with stage IV melanoma to lung, liver, lymph nodes, spleen and bone, with prior PD on a cisplatin/vinblastine/temozolomide. She initiated ipilimumab therapy in September 2009. Imaging after completing induction therapy revealed PD at week 12 but stable disease (SD) at week 24. She then received maintenance ipilimumab, with her last treatment in July 2011. She continues to have SD.
Case 4 - Patient 09-079-17
Patient 09-079-17 is a 54 year-old woman with recurrent melanoma to the back, abdomen and pelvis. This patient has a history of melanoma dating back to 1990, when she had a 2.4 mm melanoma with deep dermal invasion removed from her left lower back. She was disease free for ~15 years. She was noted to have a recurrence in 2005 and underwent multiple resections, including dermal, axillary node and mesenteric masses. She previously experienced progression of disease on temozolomide, a gp100 DNA vaccine, talimogene laherparepvec (recombinant attenuated herpes simplex virus expressing GM-CSF) and high-dose IL-2. She then initiated protocol therapy with ipilimumab in October 2009. CT imaging revealed PD at week 12 and SD at week 24. She received maintenance ipilimumab and approximately two-and-a-half years into this treatment, she continues to have SD.
Ipilimumab therapy induces Th1 dominant CD4+ T cell responses against multiple NY-ESO-1-specific epitopes in all four patients
Sera collected from these four patients were analyzed for NY-ESO-1 antibody responses. All four patients were seropositive at baseline (Patients 09-079-7, -10 and -17) or following ipilimumab treatment (Patient 09-079-1). NY-ESO-1 Ab titers increased in all four patients, especially in patient 09-079-1, with subsequent ipilimumab treatments (Supplemental Table 1) as we have reported previously [10]. We confirmed baseline NY-ESO-1 antigen expression in tumor tissue from all four patients by immunohistochemistry and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction.
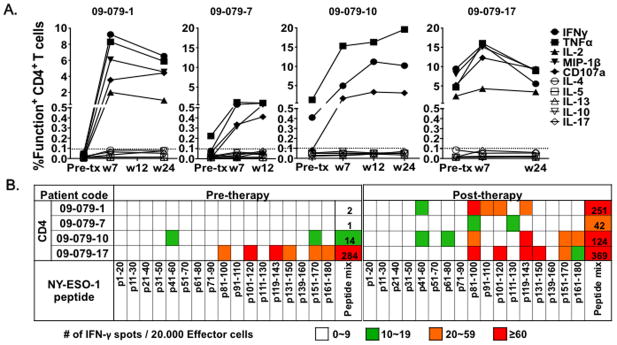
Purified CD4+ T cells isolated from PBMCs were stimulated in vitro with NY-ESO-1 overlapping peptides and cultured for 20 days. Reactivity against NY-ESO-1 overlapping peptides and the individual NY-ESO-1 peptides was then determined for these cultured CD4+ T cells by ICS and IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. In the 3 patients, who were seropositive at baseline (Patients 09-079-7, -10 and -17), pre-treatment NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell responses were detected (TNF-α in pt.09-079-7; IFN-γ and TNF-α in pt. 09-079-10; IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-2, MIP-1β and CD107a in pt.09-079-17). In the patient seronegative at baseline (09-079-1), baseline NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell responses were not detected. After ipilimumab treatment, NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell responses (IFN-γ, TNF-α and CD107a with/without IL-2) were detected in all 4 patients. These cells did not secrete Th2 cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, or IL-13) or Th17 cytokine (IL-17A) by ICS, suggesting that that they are Th1 cells. (Figure 1A)
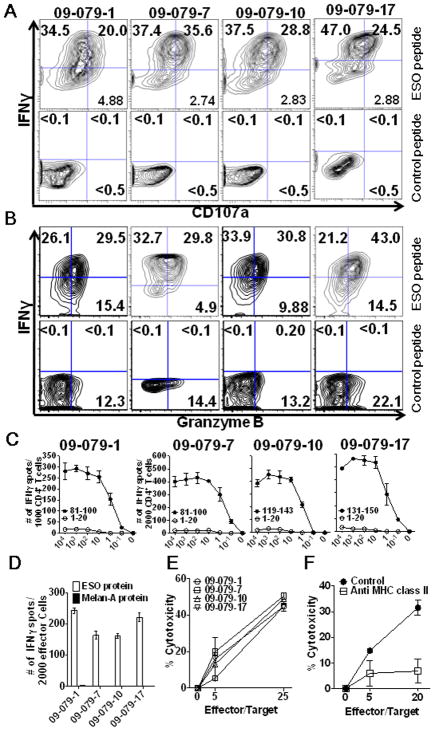
Figure 1. Broad Th1 dominant NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cell responses were detected in peripheral blood from melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab.
Purified CD4+ T cells from patients were cultured for 20 days after pre-sensitization with NY-ESO-1 overlapping peptides. (A) NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific cytokine secretion and CD107a mobilization of CD4+ T cells were assessed against NY-ESO-1 overlapping peptides by ICS assay. Autologous T-APCs were used as target cells for ICS assay. Representative data from two or three independent experiments for each patient are shown. (B) The specificity of CD4+ T cells was tested using autologous T-APCs pulsed with each individual peptide or overlapping peptides by IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. Experiments were repeated twice to confirm the peptide reactivity. *Peptide mix; all of NY-ESO-1 overlapping peptides mixture, with number of spots indicated.
Due to the low frequency of NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in peripheral blood in these four patients, we did not detect NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cell response using ex vivo ICS staining. After 20 days of in vitro cell culture, we were able to obtain ~5 × 106 CD4+ T cells with an approximately 1 log expansion of CD4+ T cells from the initial 5 × 105 CD4+ T cells per well. The yield of detectable NY-ESO-1 peptide-specific CD4+ T cell ranged from 2,500 to 92,250 per well. Using these parameters, a peptide-specific CD4+ T cell response with 10 IFN-γ spots per 20,000 effector cells in an ELISPOT assay after in vitro stimulation is estimated to yield 2,500 NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cells after one 20-day in vitro culture. We studied the breadth and frequency of each peptide-specific T cell response by IFN-γ ELISPOT. Baseline spontaneous CD4+ T cell responses to two individual peptides (10–19 spots, 2,500–4,750 cells/well after stimulation) were detected in patient 09-079-10 and to six peptides: 2 peptides, >60 spots (>15,000 cells/well after stimulation); 4 peptides, 20–59 spots (5,000–14,750 cells/well after stimulation) in patient 09-079-17. Following ipilimumab therapy, a broader spectrum of CD4+ T cell peptide responses was observed with new peptides recognized by 3 patients (all except 09-079-17). The number of peptide-specific responses did not change following ipilimumab therapy (6 peptides) in patient 09-079-17; however, 5 (p81–100, p101–120, p119–143, p131–150, p151–170) of 6 individual T cell peptides (which were positive at baseline) were increased significantly in IFN-γ spot number (p<0.05) (Figure 1B).
After ipilimumab treatment, the majority of peptides recognized by CD4+ T cells included sequences located in four immunodominant distinct regions of the protein, corresponding to peptides NY-ESO-141-60 (2/4 patients), NY-ESO-181–100 (4/4 patients), NY-ESO-1119-143 (3/4 patients) and NY-ESO-1151-170 (2/4 patients) as previously reported in patients with spontaneous responses as well as those immunized with NY-ESO-1 vaccines [25–29] (Figure 1B). In summary, polyfunctional NY-ESO-1 CD4+ T cell responses were detected at baseline or post-therapy samples in all 4 patients.
High avidity CD4+ T cell responses with cytotoxicity to naturally processed antigen are detected in peripheral blood after ipilimumab treatment
We sought to determine whether the NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cells detected after ipilimumab treatment had high affinity T cell receptors capable of recognizing naturally processed tumor antigen. NY-ESO-1 single peptide-specific CD4+ T cell lines were generated from PBMCs from patients 09-079-1 and -17 before and after the treatment at weeks 7 and 24 or from patients 09-079-7 and -10 at weeks 12 and 24 by a CD154 (CD40L) sorting method (Supplemental Figure 1A) after stimulation with individual, dominant NY-ESO-1 peptides. We confirmed that there were no contaminating CD8+ T cells in CD40L sorted NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cells (Supplemental Figure 1B). These cells were then co-cultured with autologous melanoma cell lines and autologous APC (EBV- infected B cell lines; LCLs) with each corresponding peptide or MAGE-A4 overlapping peptides as the negative control. The NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell lines established from 4 patients expressed intracellular IFN-γ, granzyme B and surface CD107a, as compared to the CD4+ T cell response to the negative control (Figure 2, A and B).
Figure 2. High avidity NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cell responses with naturally processed protein recognition were detected in PBMCs after ipilimumab treatment.
Purified CD4+ T cells from patients after ipilimumab treatment (week 7; 09-079-1, -17, week 12; 09-079-7, -10) were cultured for 20 days after pre-sensitization with NY-ESO-1 overlapping peptides. NY-ESO-1 single epitope-specific CD4+ T cell lines were isolated by CD40L sorting after 6 hours in vitro restimulation. After expansion, these cell lines were tested by ICS assay using autologous APCs pulsed with low concentration NY-ESO-1 peptide or control peptide (10 nM). (A, B) Intracellular IFN-γ and surface CD107a (A), and IFN-γ and granzyme B (B) were analyzed in ICS assay. Representative plots are shown from two independent experiments, therefore the gate for patient 09-079-17 was different from the other three patients. Nonspecific staining by isotype control antibodies was <0.1% in all samples (data not shown). (C) Avidity of these CD4+ T cell lines in the recognition of the cognate peptide was tested by ELISPOT assay using autologous APCs pulsed with graded doses of peptide in ELISPOT assay. (D) Recognition of recombinant NY-ESO-1 protein or control Melan-A protein naturally processed in autologous APCs (LCLs) by CD4+ T cell line was tested by ELISPOT assay. (E) Cytotoxicity against autologous LCL pulsed with each cognate peptide (100 nM) by CD4+ T cell line was determined at 5:1 and 25:1 Effector:Target ratio. (F) NY-ESO-181-100-specific CD4+ T cell line from 09-079-7 was co-cultured for 6 hours at different ratios with target cells (labeled with 0.5 μM CFSE) and control target cells (5 μM CFSE) in the presence or absence of MHC class II blocking antibodies. Target cell (T); autologous melanoma cell line (SK-MEL-381; NY-ESO-1 positive) treated with IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) for 24 hours prior cytotoxic assay. Control target cell; melanoma cell line (SK-MEL-351 from patient 09-079-10; NY-ESO-1 negative). Cytotoxicity (%) was calculated with the formula as described in the materials and methods. Each experiment was repeated independently twice or three times with similar results. Data are presented as mean ± SD.
All NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell lines before and after the treatment were of high avidity to recognize 10–100 nM peptide (data not shown). Furthermore, they recognized recombinant NY-ESO-1 protein naturally processed in autologous APCs (LCLs) by ELISPOT assay (Figure 2C) and lysed autologous LCL pulsed with corresponding NY-ESO-1 protein (100 nM) (Figure 2D) using the cytotoxicity assay described above. NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell lines lysed the autologous LCL pulsed with each cognate peptides (100 nM) at 5:1 and 25:1 Effector:Target ratio (Figure 2E). Among the autologous melanoma cell lines derived from these patients, SK-MEL-381 (from patient 09-079-7) expresses both NY-ESO-1 and MHC class II. The NY-ESO-181-100-specific CD4+ T cell line from patient 09-079-7 lysed the autologous tumor cell line (SK-MEL-381) and cytotoxicity was inhibited with by MHC class II antibody blocking of the target cells (Figure 2F). The NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell lines do not co-express CD8 markers before and after re-stimulation in the ICS assay (Supplemental Figure 1C).
Serial changes in cytotoxic NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cells after ipilimumab treatment
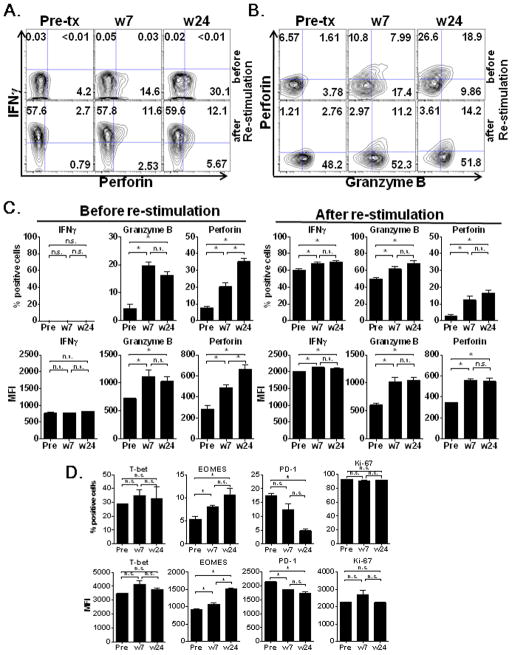
From patient 09-079-17, we were able to establish NY-ESO-1131-150 peptide-specific CD4+ T cell lines at the pre-treatment time point as well as at weeks 7 and 24 by the CD154 (CD40L) sorting method and subsequently analyzed serial changes in cytotoxic function. These cell lines recognized autologous APCs (LCLs) pulsed with NY-ESO-1131-150 peptide (100 nM) in the ICS assay. In contrast to IFN-γ which was consistently produced before and after the therapy, accumulation of granzyme B and perforin was observed only after ipilimumab treatment (Figure 3, A, B, and C). In addition, in vitro peptide re-stimulation induced granzyme B synthesis only in CD4+ T cells after the therapy (Figure 3C). In accordance with the expression of cytotoxic molecules, higher expression of the transcription factor Eomes previously reported as the master regulator of cytotoxic CD8+ T cell [30], were observed after ipilimumab treatment at weeks 7 and 24 when compared to those present pre-treatment (Figure 3D, *p <0.05). In contrast, expression of T-bet was not increased (Figure 3D). Expression of PD-1 became lower at week 24 after treatment when compared to pre-treatment and at week 7 (Figure 3D, *p <0.05).
Figure 3. NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific cytotoxic CD4+ T cell responses were enhanced during ipilimumab treatment in patient 09-079-17.
Purified CD4+ T cells from patient 09-079-17 before (Pre-tx), and after treatment with ipilimumab at weeks 7 (w 7) and 24 (w 24) were cultured for 20 days after pre-sensitization with NY-ESO-1 overlapping peptides. NY-ESO-1131-150 epitope-specific CD4+ T cells from each time point were isolated by CD40L sorting after 6 hours in vitro restimulation with NY-ESO-1131-150 peptide and expanded. (A, B) IFN-γ, perforin and granzyme B expression of these cell lines were tested after 6 hour restimulation with autologous APCs (LCLs) pulsed with NY-ESO-1131-150 peptide (10 nM) or without restimulation in ICS assay. Nonspecific staining by isotype control antibodies was <0.1% in all samples (data not shown). (C–D) Expression of cytotoxic molecules (C), transcription factors and activation and exhaustion makers (D) in CD4+ T cell line from patient 09-079-17 at Pre-treatment, at weeks 7 and 24 are shown (*; P <0.05, n.s.; not significant).
We next assessed whether the ipilimumab-related changes in expression of lytic markers described above in the NY-ESO-1131-150-specific CD4+ T cell lines from patient 09-079-17 affected their ability to lyse autologous LCL pulsed with NY-ESO-1131-150 peptides (100 nM) at 5:1 and 25:1 E/T ratio. The degree of cytotoxicity (%) was significantly increased after ipilimumab treatment (peak at week 7), when compared to that of cells obtained pre-treatment (*P<0.05). This cytotoxicity was inhibited with the use of an MHC class II blocking antibody on target cells (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Enhancement of cytotoxicity of NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell lines during ipilimumab treatment in patient 09-079-17.
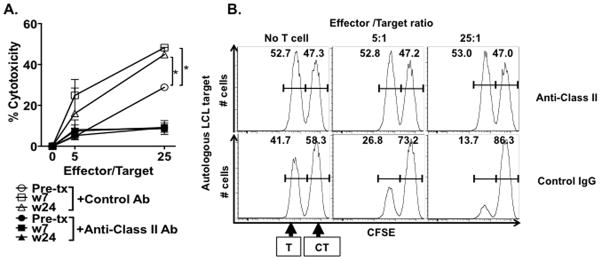
The NY-ESO-1131-150-specific CD4+ T cell lines from patient 09-079-17 were co-cultured for 6 hours at different ratio with target cells (labeled with 0.5 μM CFSE) and control target cells (5 μM CFSE). Target cell (T); autologous APCs (LCLs) pulsed with NY-ESO-1131-150 peptide. Control target cell (CT); autologous LCL pulsed with MAGE-A1 peptide mix as a control antigen. (A) % Cytotoxicity was calculated with the formula as described in the materials and methods. To determine MHC class II-restriction of the cytotoxicity, anti-MHC class II antibodies or control IgG was added during the assay. (*P <0.05) Each experiment was repeated twice with similar results. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. (B) Representative histograms of NY-ESO-1-specific killing are shown at different effector/target ratio.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we performed in-depth immune monitoring on four NY-ESO-1 seropositive melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab, based upon the availability of suitable PBMCs. We found that NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific Th1 responses against multiple epitopes were induced or expanded after ipilimumab treatment in all four patients. NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cell lines established from all four patients were of high avidity and recognized naturally processed NY-ESO-1 protein in APCs, as indicated by the production of perforin, granzyme B and the upregulation of CD107a. Finally, we demonstrated that one of these NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cell lines directly lysed autologous melanoma cells in an MHC class II-restricted manner. We believe this is the first demonstration of the induction or enhancement of tumor-reactive cytotoxic CD4+ T cells after ipilimumab treatment and is therefore a novel property of CTLA-4 blockade.
Induction of antigen-specific T cells against NY-ESO-1 has previously been accomplished in many ways. NY-ESO-1-specific CD8+ T cells could be induced in HLA-A2+ cancer patients vaccinated with NY-ESO-1 peptides p157–165/p157–167 [31]. These T-cells were highly reactive with the peptides used for vaccination, but only rarely recognized HLA-matched, NY-ESO-1-expressing tumor cell lines. Vaccine-induced antigen-specific T-cells were heterogeneous in functional activity, especially in terms of natural tumor recognition. The frequency of antigen-specific T cells does not always equate with functional tumor reactivity. Therefore, precise and multiparametric immune monitoring assays are critical to identify the proportion of tumor-reactive T cells within the population of vaccine-induced antigen-specific effector cells. A NY-ESO-1 helper peptide vaccine has been reported to induce NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cells with lower avidity (>1 μM) compared with NY-ESO-1-specific pre-existing naive CD4+CD25− T cell precursors or spontaneously induced CD4+ T cell effectors in NY-ESO-1 seropositive cancer patients. These cells were only able to recognize NY-ESO-1 helper peptide, but not naturally processed NY-ESO-1 protein in APCs from patients with NY-ESO-1-expressing epithelial ovarian cancer [32]. Our analysis demonstrated that most of the NY-ESO-1 specific CD4+ T cells (lines) generated after ipilimumab treatment were of high avidity and recognized naturally processed NY-ESO-1 protein in APCs in specimens of the 4 patients analyzed, distinguishing these results from those of exogenous vaccination strategies. Our observation in this study was based upon the results collected from either in vitro culture of CD4+ T cells or CD40L sorted NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell lines. Due to the limited PBMC availability and low frequency of NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in peripheral blood from these patients, we were not able to characterize directly these NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in ex vivo assays.
The optimal TCR affinity threshold for natural tumor recognition and maximal anti-tumor T cell response has been measured using human CD8+ T cells transduced with TCR variants [33]. Thus, the relative lack of high affinity/avidity TCRs for CD8+ T cells is considered to be one reason why immune responses toward self-tumor antigens have not been protective. It is possible that the cytotoxic capacity of CD4+ T cells might be subject to an optimal TCR affinity threshold as well. In this study, NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell lines were directly sorted from bulk CD4+ T cell cultures after one round of in vitro pre-sensitization. Therefore, these CD4+ T cell lines, not ‘clones’, reflect a spectrum of the NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cell population in the immune repertoire induced after ipilimumab treatment. The clinical activity of CTLA-4 blockade may mechanistically involve expansion of naturally occurring antigen-specific T cells (NY-ESO-1 cells, as an example) with high avidity. The ability to recognize antigenic epitopes naturally processed endogenously in tumor cells and to lyse tumors are logical characteristics to expect from an effective T cell response.
Cytotoxic effector cells kill tumor cells through FAS, TRAIL or granzyme-perforin-dependent mechanisms [34]. The T-box transcription factor Eomes is critical for inducing the expression of granzyme B and other lytic granules [30]. Dual costimulation of OX40 plus 4-1BB was shown to induce Eomes in HA-specific CD4+ T cells toward cytotoxic Th1 differentiation [35]. Recently our group showed that OX40 agonist antibody in combination with cyclophosphamide treatment and adoptive transfer of tumor specific CD4+ T cells could produce cytotoxic CD4+ T cells through Eomes and T-bet [36]. We analyzed Eomes and T-bet by flow cytometric staining and found higher expression of Eomes on NY-ESO-1 antigen-specific CD4+ T cells after ipilimumab treatment; however, no change was noted for T-bet. Higher secretion of IFN-γ, granzyme B, and perforin were detected consistently after ipilimumab treatment at weeks 7 and 24 when compared to those present pre-treatment. These findings suggests that CTLA-4 blockade may induce the expression of lytic granules on NY-ESO-1-specific cytotoxic CD4+ T cells via Eomes, but further detailed mechanistic studies are needed to conclusively demonstrate this.
In summary, previous studies from several groups have shown the following important points: 1. CTLA-4 blockade enhances regression of spontaneous mouse tumors by expansion of transferred effector CD4+ T cells [12]; 2. Adoptive transfer of autologous CD4+ T cells directed against NY-ESO-1 has resulted in tumor regression in humans [14]; 3. Ipilimumab promotes the expansion of infused CD8+ CTLs as memory CTLs [37]. Our data now bring these observations together by revealing that CTLA-4 blockade with ipilimumab induces the expression of Eomes as well as markers of lytic degranulation on high-affinity cytotoxic-CD4+ T cells. These cytotoxic NY-ESO-1-specific CD4+ T cells are able to lyse autologous tumor cells, which naturally express the cognate NY-ESO-1 antigen. It brings forth a potentially novel therapeutic mechanism in which CTLA-4 blockade or inhibition with other immunomodulatory antibodies might be combined with CD4+ T cells to enhance cytolytic function in cancer immunotherapy clinical trials.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (RC2CA148468, to Dr. Wolchok), the Melanoma Research Alliance (to Drs. Gnjatic and Wolchok), Swim Across America (to Dr. Wolchok), the Cancer Research Institute (to Drs. Gnjatic and Wolchok), the Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research (to Dr. Allison), the Lita Annenberg Hazen Foundation (to Dr. Wolchok), and the Commonwealth Foundation for Cancer Research (to Dr. Wolchok). We thank Teresa Rasalan and Sapna Tandon for their excellent technical assistance. Dedicated to the memory of Dr. Lloyd Old, our mentor and friend and one of the true leaders in investigational cancer medicine. His contributions to tumor immunology inspired much of this work.
References
- 1.Brunner MC, Chambers CA, Chan FK, Hanke J, Winoto A, et al. CTLA-4-Mediated inhibition of early events of T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1999;162:5813–5820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Krummel MF, Allison JP. Cd28 and Ctla-4 Have Opposing Effects on the Response of T-Cells to Stimulation. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 1995;182:459–465. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Karandikar NJ, Vanderlugt CL, Walunas TL, Miller SD, Bluestone JA. CTLA-4: a negative regulator of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1996;184:783–788. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:711–723. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1003466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Robert C, Thomas L, Bondarenko I, O’Day S, MDJ, et al. Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2517–2526. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1104621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Simpson AJ, Caballero OL, Jungbluth A, Chen YT, Old LJ. Cancer/testis antigens, gametogenesis and cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2005;5:615–625. doi: 10.1038/nrc1669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gnjatic S, Nishikawa H, Jungbluth AA, Gure AO, Ritter G, et al. NY-ESO-1: Review of an immunogenic tumor antigen. Advances in Cancer Research. 2006;95:1–30. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)95001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Klein O, Ebert LM, Nicholaou T, Browning J, Russell SE, et al. Melan-A-specific cytotoxic T cells are associated with tumor regression and autoimmunity following treatment with anti-CTLA-4. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:2507–2513. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yuan J, Gnjatic S, Li H, Powel S, Gallardo HF, et al. CTLA-4 blockade enhances polyfunctional NY-ESO-1 specific T cell responses in metastatic melanoma patients with clinical benefit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:20410–20415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810114105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yuan J, Adamow M, Ginsberg BA, Rasalan TS, Ritter E, et al. Integrated NY-ESO-1 antibody and CD8+ T-cell responses correlate with clinical benefit in advanced melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:16723–16728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1110814108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pardoll DM, Topalian SL. The role of CD4+ T cell responses in antitumor immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998;10:588–594. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(98)80228-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Quezada SA, Simpson TR, Peggs KS, Merghoub T, Vider J, et al. Tumor-reactive CD4(+) T cells develop cytotoxic activity and eradicate large established melanoma after transfer into lymphopenic hosts. J Exp Med. 2010;207:637–650. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Xie Y, Akpinarli A, Maris C, Hipkiss EL, Lane M, et al. Naive tumor-specific CD4(+) T cells differentiated in vivo eradicate established melanoma. J Exp Med. 2010;207:651–667. doi: 10.1084/jem.20091921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hunder NN, Wallen H, Cao JH, Hendricks DW, Reilly JZ, et al. Treatment of metastatic melanoma with autologous CD4+ T cells against NY-ESO-1. New England Journal of Medicine. 2008;358:2698–2703. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0800251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wolchok JD, Hoos A, O’Day S, Weber JS, Hamid O, et al. Guidelines for the evaluation of immune therapy activity in solid tumors: immune-related response criteria. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:7412–7420. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tsuji T, Matsuzaki J, Kelly MP, Ramakrishna V, Vitale L, et al. Antibody-targeted NY-ESO-1 to mannose receptor or DEC-205 in vitro elicits dual human CD8+ and CD4+ T cell responses with broad antigen specificity. J Immunol. 2011;186:1218–1227. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Atanackovic D, Matsuo M, Ritter E, Mazzara G, Ritter G, et al. Monitoring CD4(+) T cell responses against viral and tumor antigens using T cells as novel target APC. Journal of Immunological Methods. 2003;278:57–66. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(03)00209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kitano S, Kageyama S, Nagata Y, Miyahara Y, Hiasa A, et al. HER2-specific T-cell immune responses in patients vaccinated with truncated HER2 protein complexed with nanogels of cholesteryl pullulan. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:7397–7405. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Miyahara Y, Naota H, Wang L, Hiasa A, Goto M, et al. Determination of cellularly processed HLA-A2402-restricted novel CTL epitopes derived from two cancer germ line genes, MAGE-A4 and SAGE. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:5581–5589. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Naota H, Miyahara Y, Okumura S, Kuzushima K, Akatsuka Y, et al. Generation of peptide-specific CD8+ T cells by phytohemagglutinin-stimulated antigen-mRNA-transduced CD4+ T cells. J Immunol Methods. 2006;314:54–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2006.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chattopadhyay PK, Yu J, Roederer M. A live-cell assay to detect antigen-specific CD4+ T cells with diverse cytokine profiles. Nat Med. 2005;11:1113–1117. doi: 10.1038/nm1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tsuji T, Altorki NK, Ritter G, Old LJ, Gnjatic S. Characterization of Preexisting MAGE-A3-Specific CD4(+) T Cells in Cancer Patients and Healthy Individuals and Their Activation by Protein Vaccination. Journal of Immunology. 2009;183:4800–4808. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Riddell SR, Greenberg PD. The use of anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies to clone and expand human antigen-specific T cells. J Immunol Methods. 1990;128:189–201. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90210-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Atanackovic D, Altorki NK, Cao Y, Ritter E, Ferrara CA, et al. Booster vaccination of cancer patients with MAGE-A3 protein reveals long-term immunological memory or tolerance depending on priming. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:1650–1655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707140104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Uenaka A, Wada H, Isobe M, Saika T, Tsuji K, et al. T cell immunomonitoring and tumor responses in patients immunized with a complex of cholesterol-bearing hydrophobized pullulan (CHP) and NY-ESO-1 protein. Cancer Immun. 2007;7:9. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Karbach J, Pauligk C, Bender A, Gnjatic S, Franzmann K, et al. Identification of new NY-ESO-1 epitopes recognized by CD4+ T cells and presented by HLA-DQ B1 03011. Int J Cancer. 2006;118:668–674. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Karbach J, Neumann A, Atmaca A, Wahle C, Brand K, et al. Efficient in vivo priming by vaccination with recombinant NY-ESO-1 protein and CpG in antigen naive prostate cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:861–870. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Valmori D, Souleimanian NE, Tosello V, Bhardwaj N, Adams S, et al. Vaccination with NY-ESO-1 protein and CpG in Montanide induces integrated antibody/Th1 responses and CD8 T cells through cross-priming. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:8947–8952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703395104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jager E, Karbach J, Gnjatic S, Neumann A, Bender A, et al. Recombinant vaccinia/fowlpox NY-ESO-1 vaccines induce both humoral and cellular NY-ESO-1-specific immune responses in cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:14453–14458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606512103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pearce EL, Mullen AC, Martins GA, Krawczyk CM, Hutchins AS, et al. Control of effector CD8+ T cell function by the transcription factor Eomesodermin. Science. 2003;302:1041–1043. doi: 10.1126/science.1090148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Karbach J, Gnjatic S, Pauligk C, Bender A, Maeurer M, et al. Tumor-reactive CD8(+) T-cell clones in patients after NY-ESO-1 peptide vaccination. International Journal of Cancer. 2007;121:2042–2048. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nishikawa H, Qian F, Tsuji T, Ritter G, Old LJ, et al. Influence of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells on low/high-avidity CD4(+) T cells following peptide vaccination. Journal of Immunology. 2006;176:6340–6346. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.10.6340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schmid DA, Irving MB, Posevitz V, Hebeisen M, Posevitz-Fejfar A, et al. Evidence for a TCR affinity threshold delimiting maximal CD8 T cell function. J Immunol. 2010;184:4936–4946. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Trapani JA, Smyth MJ. Functional significance of the perforin/granzyme cell death pathway. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:735–747. doi: 10.1038/nri911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Qui HZ, Hagymasi AT, Bandyopadhyay S, St Rose MC, Ramanarasimhaiah R, et al. CD134 plus CD137 dual costimulation induces Eomesodermin in CD4 T cells to program cytotoxic Th1 differentiation. J Immunol. 2011;187:3555–3564. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hirschhorn-Cymerman D, Budhu S, Kitano S, Liu C, Zhao F, et al. Induction of tumoricidal function in CD4+ T cells is associated with concomitant memory and terminally differentiated phenotype. J Exp Med. 2012;209:2113–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.20120532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Butler MO, Friedlander P, Milstein MI, Mooney MM, Metzler G, et al. Establishment of antitumor memory in humans using in vitro-educated CD8+ T cells. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:80ra34. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.