Abstract
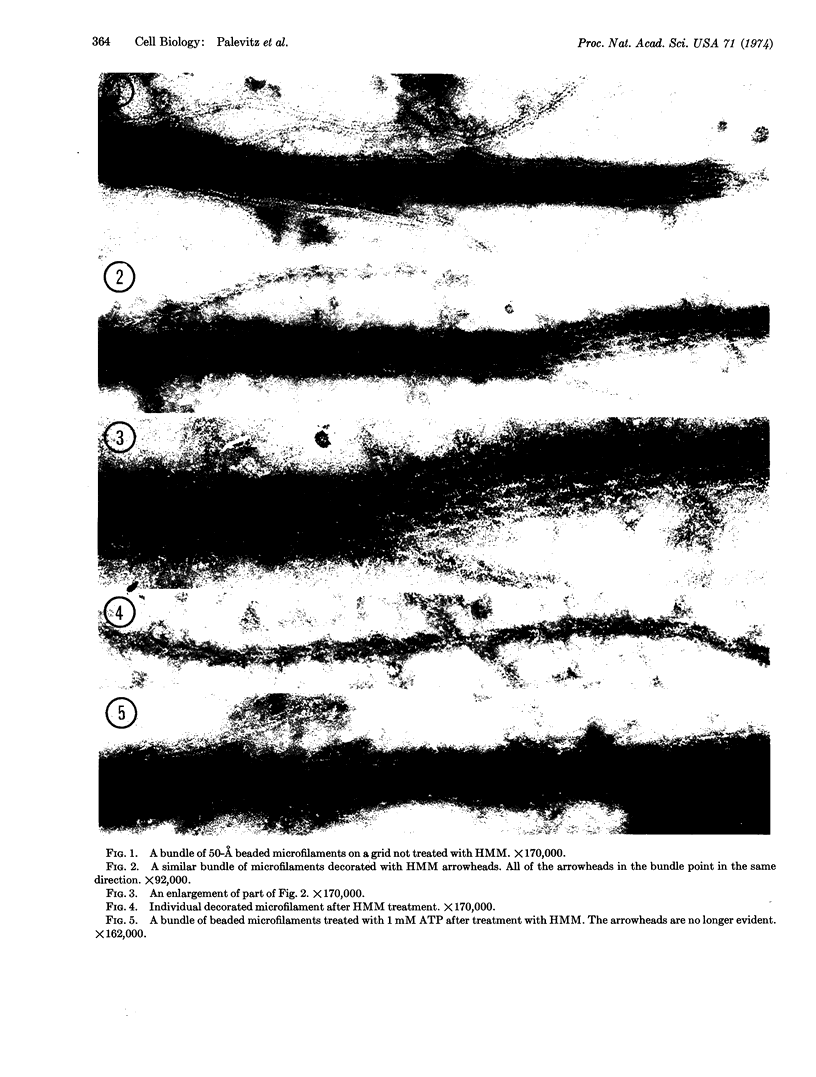
Bundles of microfilaments very similar in appearance to actin are present in cytoplasmic suspensions obtained from Nitella flexilis. The microfilaments bind rabbit heavy meromyosin in arrowhead arrays similar to those produced on muscle actin. The arrowheads are removed with ATP. The results provide evidence that actin is present in green plants, probably in the form of microfilaments thought to be involved in cytoplasmic streaming.
Keywords: heavy meromyosin, microfilaments, electron microscopy, cytoplasmic streaming, plants
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman M. R., Taylor E. W. Further purification and characterization of slime mold myosin and slime mold actin. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4976–4988. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comly L. T. Microfilaments in Chaos carolinensis. Membrane association, distribution, and heavy meromyosin binding in the glycerinated cell. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jul;58(1):230–237. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatano S., Oosawa F. Isolation and characterization of plasmodium actin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90402-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmias V. T., Huxley H. E. Electron microscope observations on actomyosin and actin preparations from Physarum polycephalum, and on their interaction with heavy meromyosin subfragment I from muscle myosin. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90105-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai R., Rebhun L. I. Cytoplasmic microfilaments in streaming Nitella cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Mar;14(5):571–589. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy M. V., Mühlethaler K. Cytoplasmic microfilaments in plant cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Jan;38(1):46–62. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Korn E. D. Filaments of Amoeba proteus. II. Binding of heavy meromyosin by thin filaments in motile cytoplasmic extracts. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jan;48(1):216–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.48.1.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Shelton E., Weihing R. R., Korn E. D. Ultrastructural characterization of F-actin isolated from Acanthamoeba castellanii and identification of cytoplasmic filaments as F-actin by reaction with rabbit heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):91–97. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonomura Y., Appel P., Morales M. On the molecular weight of myosin. II. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):515–521. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOROBEVA Ia, POGLAZOV B. F. VYDELENIE SOKRATITEL'NOGO BELKA IZ VODOROSLI NITELLA FLEXILIS. Biofizika. 1963;8:427–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihing R. R., Korn E. D. Acanthamoeba actin. Isolation and properties. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 16;10(4):590–600. doi: 10.1021/bi00780a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessells N. K., Spooner B. S., Ludueña M. A. Surface movements, microfilaments and cell locomotion. Ciba Found Symp. 1973;14:53–82. doi: 10.1002/9780470719978.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley D. E. An actin-like protein from amoebae of dictyostelium discoideum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jun;150(2):519–530. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]