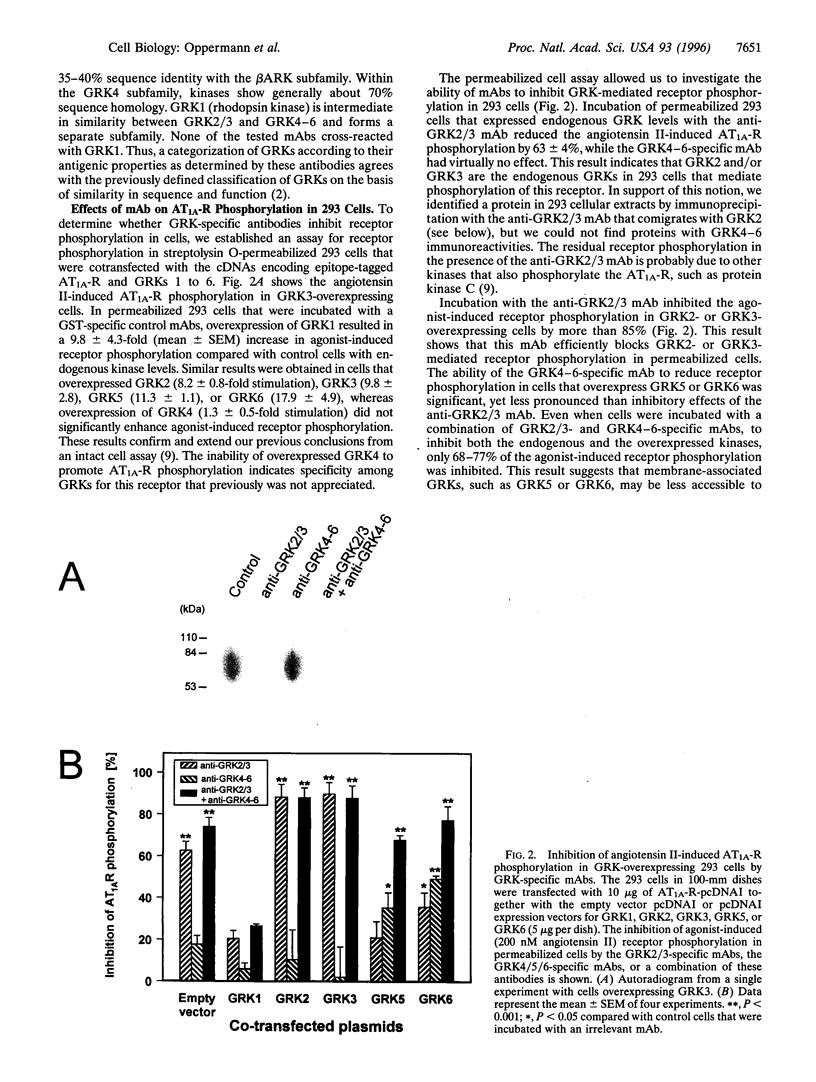
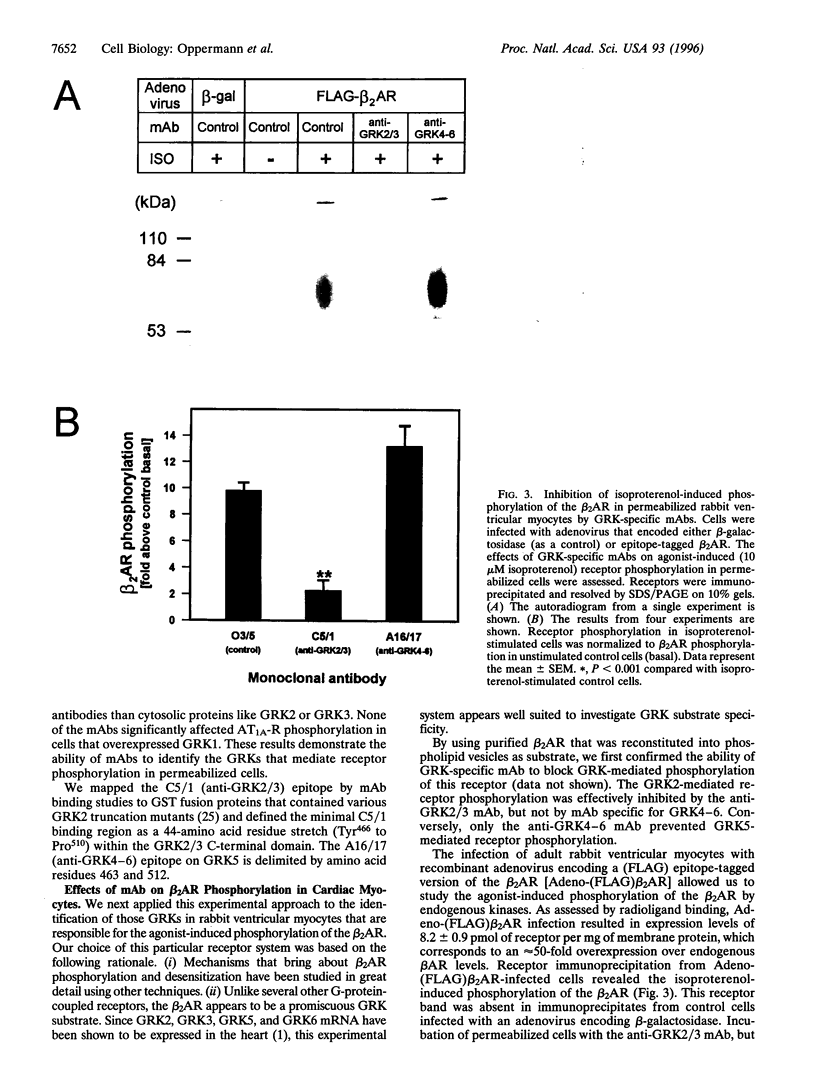
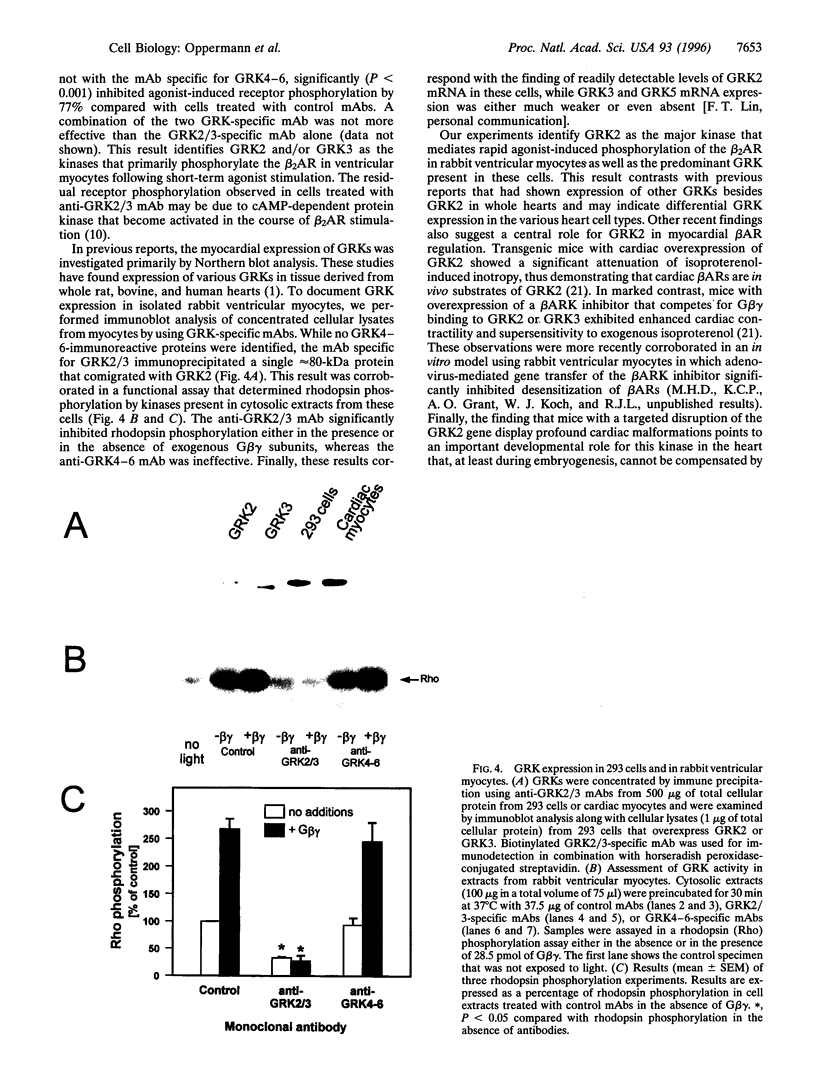
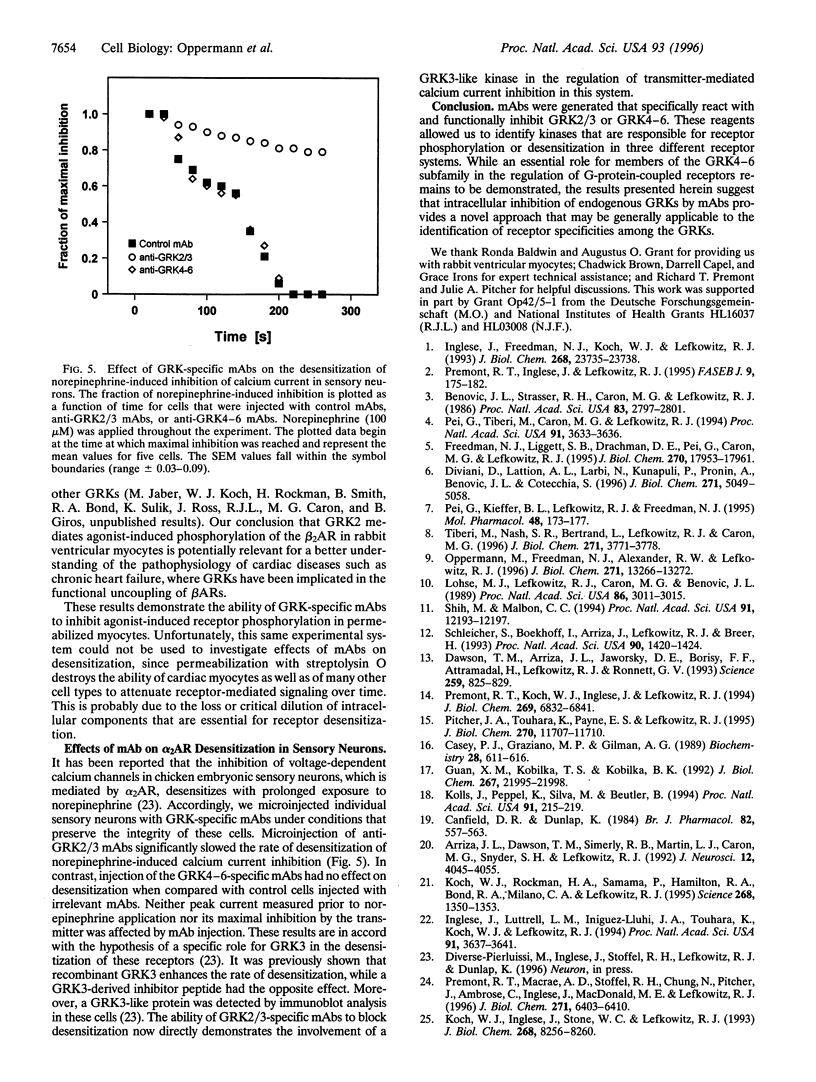
Abstract
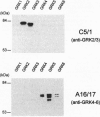
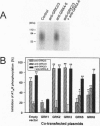
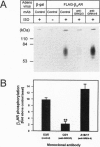
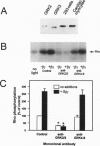
Guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein (G protein)-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) constitute a family of serine/threonine kinases that play a major role in the agonist-induced phosphorylation and desensitization of G-protein-coupled receptors. Herein we describe the generation of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that specifically react with GRK2 and GRK3 or with GRK4, GRK5, and GRK6. They are used in several different receptor systems to identify the kinases that are responsible for receptor phosphorylation and desensitization. The ability of these reagents to inhibit GRK- mediated receptor phosphorylation is demonstrated in permeabilized 293 cells that overexpress individual GRKs and the type 1A angiotensin II receptor. We also use this approach to identify the endogenous GRKs that are responsible for the agonist-induced phosphorylation of epitope-tagged beta2- adrenergic receptors (beta2ARs) overexpressed in rabbit ventricular myocytes that are infected with a recombinant adenovirus. In these myocytes, anti-GRK2/3 mAbs inhibit isoproterenol-induced receptor phosphorylation by 77%, while GRK4-6-specific mAbs have no effect. Consistent with the operation of a betaAR kinase-mediated mechanism, GRK2 is identified by immunoblot analysis as well as in a functional assay as the predominant GRK expressed in these cells. Microinjection of GRK2/3-specific mAbs into chicken sensory neurons, which have been shown to express a GRK3-like protein, abolishes desensitization of the alpha2AR-mediated calcium current inhibition. The intracellular inhibition of endogenous GRKs by mAbs represents a novel approach to the study of receptor specificities among GRKs that should be widely applicable to many G-protein-coupled receptors.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arriza J. L., Dawson T. M., Simerly R. B., Martin L. J., Caron M. G., Snyder S. H., Lefkowitz R. J. The G-protein-coupled receptor kinases beta ARK1 and beta ARK2 are widely distributed at synapses in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):4045–4055. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-04045.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2797–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield D. R., Dunlap K. Pharmacological characterization of amine receptors on embryonic chick sensory neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul;82(3):557–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10794.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Graziano M. P., Gilman A. G. G protein beta gamma subunits from bovine brain and retina: equivalent catalytic support of ADP-ribosylation of alpha subunits by pertussis toxin but differential interactions with Gs alpha. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):611–616. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. M., Arriza J. L., Jaworsky D. E., Borisy F. F., Attramadal H., Lefkowitz R. J., Ronnett G. V. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase-2 and beta-arrestin-2 as mediators of odorant-induced desensitization. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):825–829. doi: 10.1126/science.8381559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diviani D., Lattion A. L., Larbi N., Kunapuli P., Pronin A., Benovic J. L., Cotecchia S. Effect of different G protein-coupled receptor kinases on phosphorylation and desensitization of the alpha1B-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 1;271(9):5049–5058. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.5049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman N. J., Liggett S. B., Drachman D. E., Pei G., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation and desensitization of the human beta 1-adrenergic receptor. Involvement of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):17953–17961. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.30.17953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan X. M., Kobilka T. S., Kobilka B. K. Enhancement of membrane insertion and function in a type IIIb membrane protein following introduction of a cleavable signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):21995–21998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglese J., Freedman N. J., Koch W. J., Lefkowitz R. J. Structure and mechanism of the G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):23735–23738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inglese J., Luttrell L. M., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Touhara K., Koch W. J., Lefkowitz R. J. Functionally active targeting domain of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: an inhibitor of G beta gamma-mediated stimulation of type II adenylyl cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Inglese J., Stone W. C., Lefkowitz R. J. The binding site for the beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins on the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8256–8260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Rockman H. A., Samama P., Hamilton R. A., Bond R. A., Milano C. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Cardiac function in mice overexpressing the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase or a beta ARK inhibitor. Science. 1995 Jun 2;268(5215):1350–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.7761854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolls J., Peppel K., Silva M., Beutler B. Prolonged and effective blockade of tumor necrosis factor activity through adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):215–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Benovic J. L. Inhibition of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase prevents rapid homologous desensitization of beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3011–3015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann M., Freedman N. J., Alexander R. W., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation of the type 1A angiotensin II receptor by G protein-coupled receptor kinases and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 31;271(22):13266–13272. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.22.13266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei G., Kieffer B. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Freedman N. J. Agonist-dependent phosphorylation of the mouse delta-opioid receptor: involvement of G protein-coupled receptor kinases but not protein kinase C. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Aug;48(2):173–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei G., Tiberi M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. An approach to the study of G-protein-coupled receptor kinases: an in vitro-purified membrane assay reveals differential receptor specificity and regulation by G beta gamma subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3633–3636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher J. A., Touhara K., Payne E. S., Lefkowitz R. J. Pleckstrin homology domain-mediated membrane association and activation of the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase requires coordinate interaction with G beta gamma subunits and lipid. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):11707–11710. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.11707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premont R. T., Inglese J., Lefkowitz R. J. Protein kinases that phosphorylate activated G protein-coupled receptors. FASEB J. 1995 Feb;9(2):175–182. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.2.7781920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premont R. T., Koch W. J., Inglese J., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification, purification, and characterization of GRK5, a member of the family of G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6832–6841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premont R. T., Macrae A. D., Stoffel R. H., Chung N., Pitcher J. A., Ambrose C., Inglese J., MacDonald M. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Characterization of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK4. Identification of four splice variants. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 15;271(11):6403–6410. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.11.6403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher S., Boekhoff I., Arriza J., Lefkowitz R. J., Breer H. A beta-adrenergic receptor kinase-like enzyme is involved in olfactory signal termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1420–1424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M., Malbon C. C. Oligodeoxynucleotides antisense to mRNA encoding protein kinase A, protein kinase C, and beta-adrenergic receptor kinase reveal distinctive cell-type-specific roles in agonist-induced desensitization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12193–12197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiberi M., Nash S. R., Bertrand L., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Differential regulation of dopamine D1A receptor responsiveness by various G protein-coupled receptor kinases. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 16;271(7):3771–3778. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.7.3771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]