Abstract
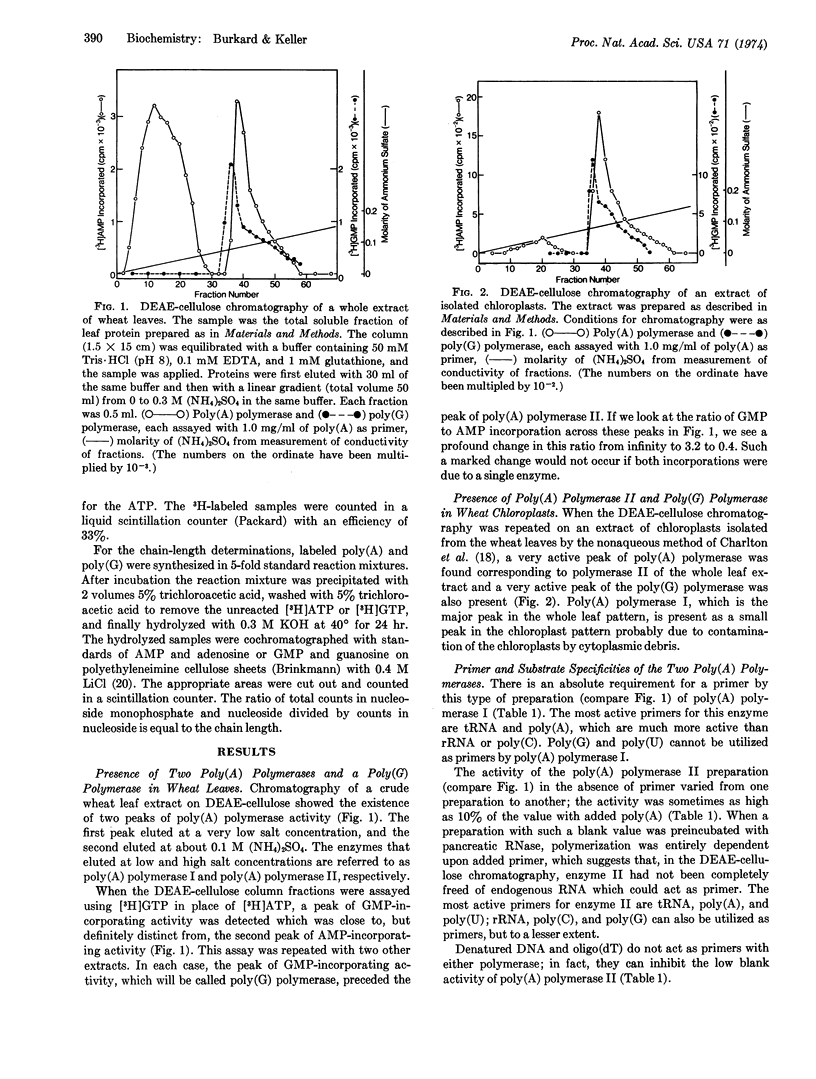
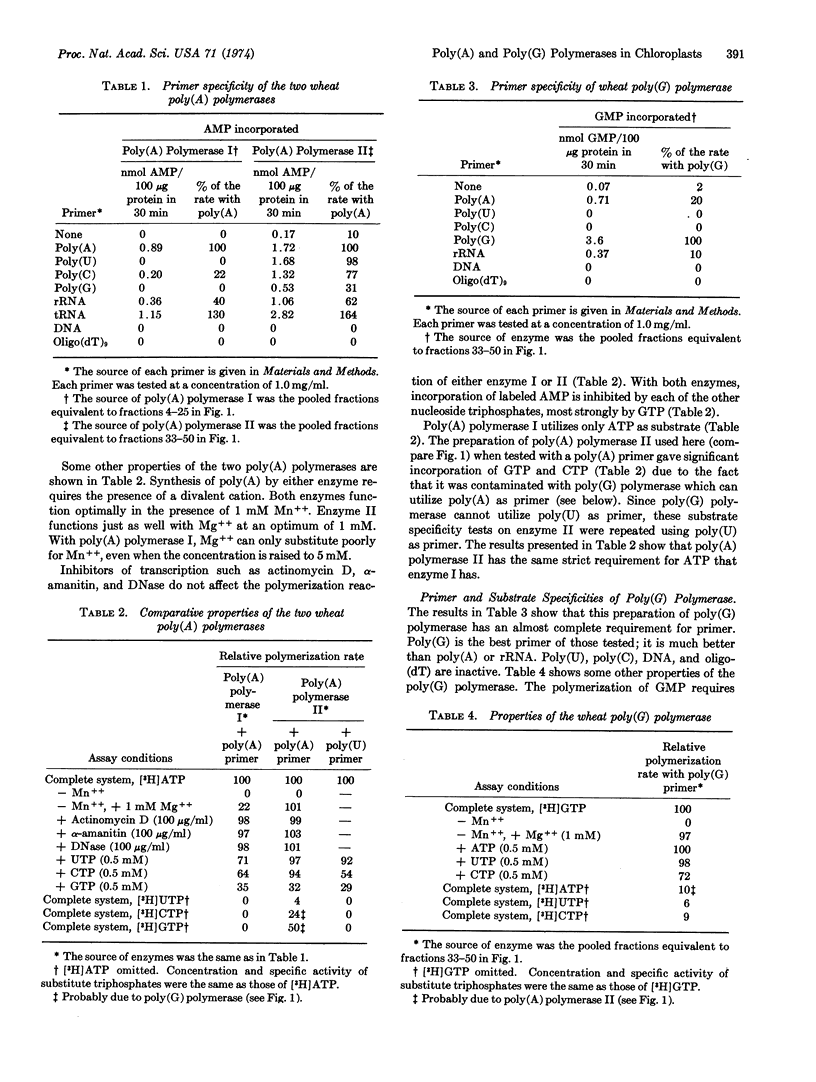
Extracts of wheat chloroplasts contain a poly(A) polymerase which can polymerize AMP residues from ATP onto an RNA primer. Whole extracts of wheat leaves also contain another poly(A) polymerase which is present in much larger amount and is probably derived from the nuclei. Both polymerases can utilize as primer poly(A), poly(C), transfer RNA, and ribosomal RNA, but only the chloroplast polymerase can utilize poly(U) and poly(G). Both enzymes have a specific requirement for ATP. Extracts of wheat chloroplasts contain, in addition to the poly(A) polymerase, a poly(G) polymerase which can polymerize GMP residues from GTP onto primers such as poly(G), poly(A), or ribosomal RNA. The poly(G) polymerase cannot utilize ATP but can slowly polymerize CMP from CTP. When the two chloroplast polymerases are present together in an in vitro incubation with ATP plus GTP and poly(A), the polymerization product is a mixed poly(A,G) tract.
Keywords: ATP and GTP polymerization, RNA primers
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charlton J. M., Treharne K. J., Goodwin T. W. Incorporation of 2-[14C]mevalonic acid into phytoene by isolated chloroplasts. Biochem J. 1967 Oct;105(1):205–212. doi: 10.1042/bj1050205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Wall R., Tushinski R. J. An adenylic acid-rich sequence in messenger RNA of HeLa cells and its possible relationship to reiterated sites in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1321–1325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMONDS M., ABRAMS R. Nature of a polynucleotide required for polyribonucleotide formation from adenosine triphosphate with an enzyme from thymus nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2636–2642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMONDS M., ABRAMS R. Polynucleotide biosynthesis: formation of a sequence of adenylate units from adenosine triphosphate by an enzyme from thymus nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1960 Apr;235:1142–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Kopp D. W. The occurrence of polyadenylate sequences in bacteria and yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1531–1537. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90561-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Vaughan M. H., Jr, Nakazato H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the heterogeneous nuclear RNA and rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA of HeLa cells: possible evidence for a precursor relationship. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1336–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haff L. A., Keller E. B. Two distinct poly(A) polymerases in yeast nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 2;51(3):704–710. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyatt E. A. Polyriboadenylate synthesis by nuclei from developing sea urchin embryos. I. Characterization of the ATP polymerase reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90532-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Schindler D. G. Polyriboadenylate polymerase solubilized from rat liver mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 11;48(1):126–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Mendecki J., Brawerman G. A polynucleotide segment rich in adenylic acid in the rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA component of mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1331–1335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Canellakis E. S. Adenine-rich polymer associated with rabbit reticulocyte messenger RNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):710–712. doi: 10.1038/227710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy G. R., Darnell J. E. Characterization of the poly(adenylic acid) regions and the adjacent nucleotides in heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleic acid and messenger ribonucleic acid from HeLa cells. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2324–2330. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessing J., Sekeris C. E. A homoribopolynucleotide synthetase in rat liver nuclei associated with ribonucleoprotein particles containing DNA-like RNA. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 15;22(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman S., Abelson H. T., Penman S. Mitochondrial protein synthesis: RNA with the properties of Eukaryotic messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):350–353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., LaTorre J. Lack of polyadenylic acid sequences in the messenger RNA of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1593–1600. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90896-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachar R. C. Biosynthesis of ribonucleic and polyadenylic acid in tobacco leaf homogenates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 20;169(1):58–66. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Bretthauer R. K. Properties of a polyriboadenylate polymerase isolated from yeast ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1576–1582. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter T. J., Mans R. J. Transfer RNA-primed oligoadenylate synthesis in maize seedlings. I. Requirements of the reaction and nature of the product with crude enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 17;217(1):72–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters M. A., Edmonds M. A poly(A) polymerase from calf thymus. Purification and properities of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4756–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


