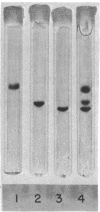
Abstract
A comparison has been made of the electrophoretic behavior, chemical composition, amino-terminal sequence, and immunological properties of bovine prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), and factor X (Stuart factor). Some immunological crossreactivity was found between the antibody to prothrombin and factor X although prothrombin and factor X differ substantially in amino-acid and carbohydrate composition. Considerable amino-acid sequence homology was found in the amino-terminal portion of prothrombin, factor IX, and the light chain of factor X. These data provide further evidence to support the hypothesis that at least three of the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors have evolved from a common ancestral gene.
Keywords: blood coagulation, glycoprotein, homology, immunology
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARONSON D. L. N-Terminal amino-acids formed during the activation of prothrombin. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:475–476. doi: 10.1038/194475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. C., Hanahan D. J. The isolation of undegraded bovine prothrombin and its partial characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 28;207(1):49–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M., Krull L. H., Cavins J. F. The chromatographic determination of cystine and cysteine residues in proteins as s-beta-(4-pyridylethyl)cysteine. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3868–3871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. Bovine factors X 1 and X 2 (Stuart factor). Isolation and characterization. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4882–4891. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Thompson A. R., Legaz M. E., Meyer R. G., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor). Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4938–4945. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDELL S. Determination of hexosamines. Methods Biochem Anal. 1958;6:289–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldebrant C. M., Noyes C., Kingdon H. S., Mann K. G. The activation of prothrombin. 3. The partial amino acid sequences at the amino terminal of prothrombin and the intermediates of activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 5;54(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90902-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Ericsson L. H., Titani K., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Application of sequenator analyses to the study of proteins. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4493–4502. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M. Characterization of two glycoprotein variants of bovine factor X and demonstration that the factor X zymogen contains two polypeptide chains. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4873–4882. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Hanahan D. J. Studies on bovine factor X. II. Characterization of purified factor X. Observations on some alterations in zone electrophoretic and chromatographic behavior occurring during purification. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4506–4517. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER K. D. Chromatographic isolation of plasma prothrombin and t trans-alpha-glucosylase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Apr;231(2):987–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattock P., Esnouf M. P. A form of bovine factor X with a single polypeptide chain. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 21;242(116):90–92. doi: 10.1038/newbio242090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Hermodson M. A., Fujikawa K., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Davie E. W. Bovine factor X 1a (activated Stuart factor). Evidence of homology with mammalian serine proteases. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4899–4903. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS D. E., REISFELD R. A. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS IN POLYACRYLAMIDE GELS: EXTENSION TO NEW CONDITIONS OF PH AND BUFFER. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]