Abstract
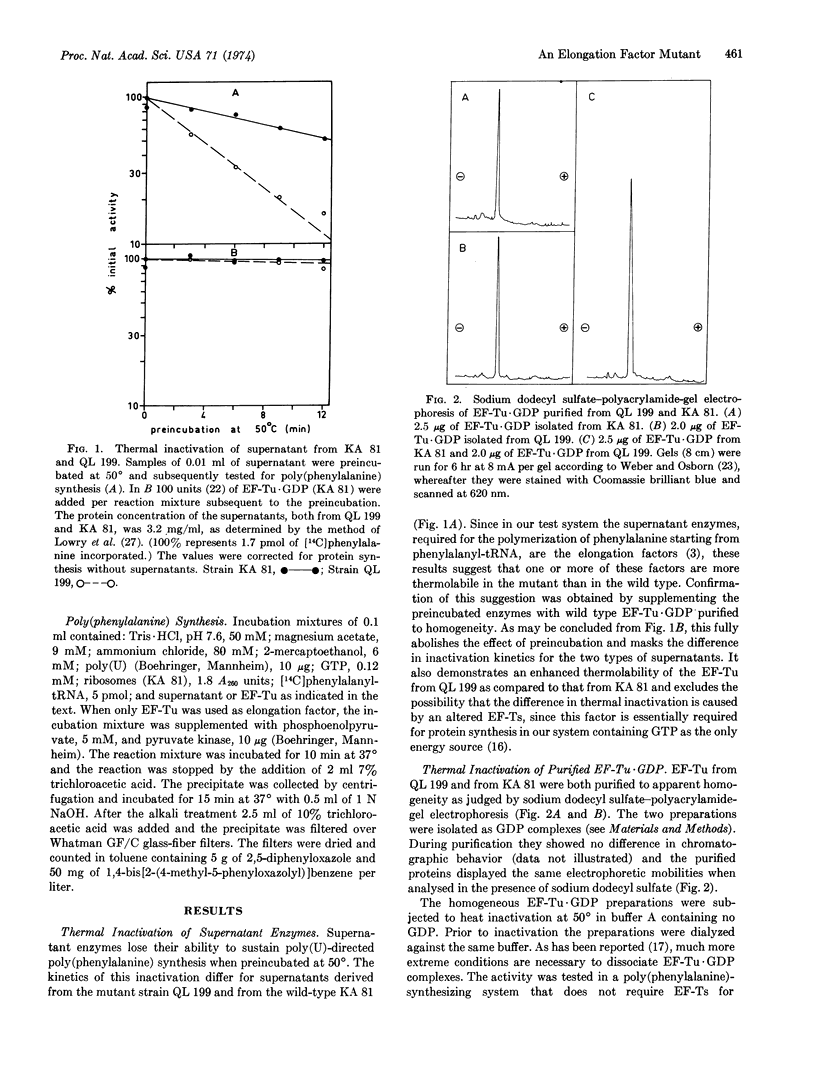
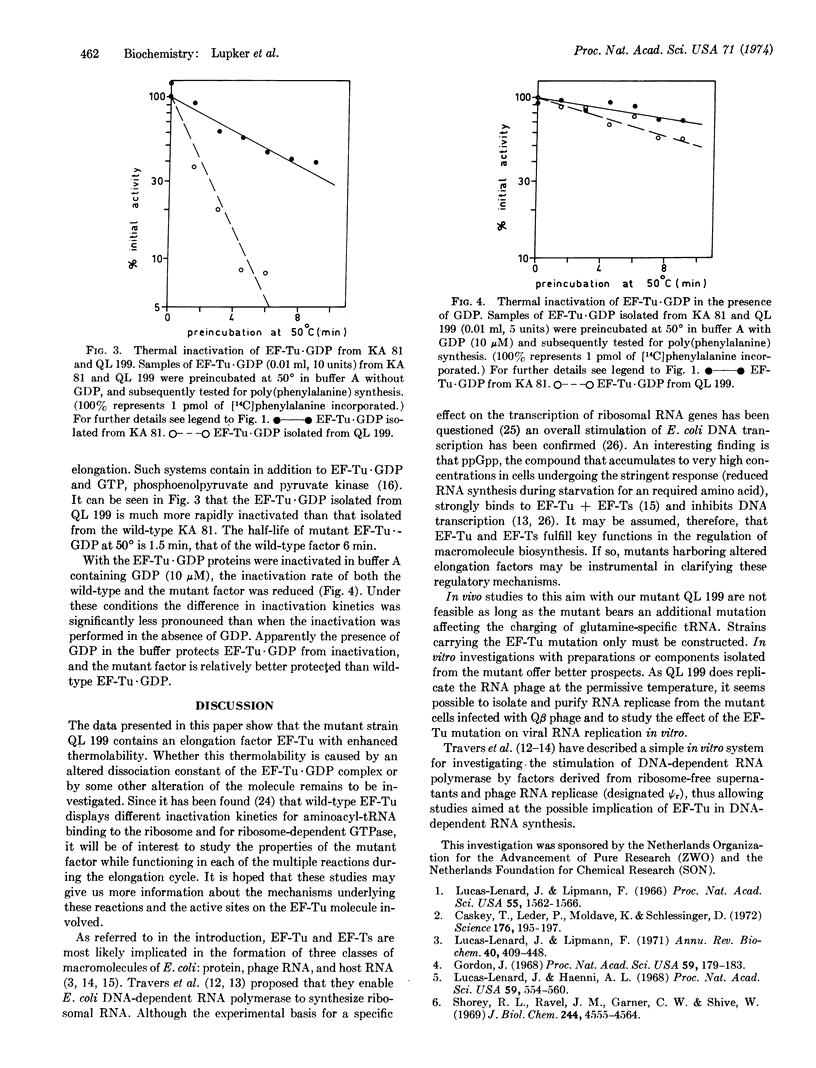
A thermosensitive mutant of Escherichia coli has been isolated that is unable to replicate the bacteriophage MS2 at 42° but permits phage production at 37°. Thermal inactivation studies of the supernatant enzymes show that this mutant contains a factor essential for the polymerization of phenylalanine from phenylalanyl-tRNA that at 50° is more rapidly inactivated than the corresponding wild-type factor. The elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) was isolated and purified to apparent homogeneity as the EF-Tu·GDP complex, both from mutant and wild-type cells.
Addition of purified wild-type EF-Tu·GDP to reaction mixtures fully restored the activity of thermally inactivated mutant supernatants. These experiments excluded EF-Ts as the thermolabile factor involved. Similar inactivation studies, dealing with the purified factors and performed in reaction mixtures that were not supplemented with GDP, revealed that the half-life of mutant EF-Tu·GDP at 50° was 1.5 min, that of the wild-type factor 6 min. Addition of GDP (10μM) to the medium reduced the inactivation rate of both wild-type and mutant factor and also the difference in inactivation kinetics. Besides the altered elongation factor Tu, the mutant skill contains a second mutation affecting the glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase.
Keywords: protein synthesis, heat inactivation kinetics, GDP
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K. I., Kawakita M., Kaziro Y. Studies on polypeptide elongation factors from Escherichia coli. II. Purification of factors Tu-guanosine diphosphate, Ts, and Tu-Ts, and crystallization of Tu-guanosine diphosphate and Tu-Ts. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7029–7037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballesta J. P., Vazquez D. Elongation factor T-dependent hydrolysis of guanosine triphosphate resistant to thiostrepton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3058–3062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Landers T. A., Weber K. Bacteriophage Q replicase contains the protein biosynthesis elongation factors EF Tu and EF Ts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1313–1317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caskey T., Leder P., Moldave K., Schlessinger D. Translation: its mechanism and control. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):195–197. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. A stepwise reaction yielding a complex between a supernatant fraction from E. coli, guanosine 5'-triphosphate, and aminoacyl-sRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):179–183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A. In vitro transcription of Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA genes. Nature. 1972 Feb 11;235(5337):329–333. doi: 10.1038/235329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Kawano G., Tanaka N. Association of fusidic acid sensitivity with G factor in a protein-synthesizing system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Dec 9;33(5):769–773. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Ono M., Yamamoto M., Endo H., Kamiya T. Elongation factor T altered in a temperature-sensitive Escherichia coli mutant. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 25;244(134):107–109. doi: 10.1038/newbio244107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J., Haenni A. L. Requirement of granosine 5'-triphosphate for ribosomal binding of aminoacyl-SRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):554–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J., Lipmann F. Separation of three microbial amino acid polymerization factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1562–1566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:409–448. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Weissbach H. Interactions between the elongation factors: the displacement of GPD from the TU-GDP complex by factor Ts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 27;38(6):1016–1022. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90341-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Weissbach H. Studies on the purification and properties of factor Tu from E. coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):26–37. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettijohn D. E. Ordered and preferential initiation of ribosomal RNA synthesis in vitro. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 16;235(59):204–206. doi: 10.1038/newbio235204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorey R. L., Ravel J. M., Garner C. W., Shive W. Formation and properties of the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid-guanosine triphosphate-protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 10;244(17):4555–4564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tocchini-Valentini G. P., Felicetti L., Rinaldi G. M. Mutants of Escherichia coli blocked in protein synthesis: mutants with an altered G factor. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:463–468. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Kamen R. I., Schleif R. F. Factor necessary for ribosomal RNA synthesis. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):748–751. doi: 10.1038/228748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A., Buckland R. Heterogeneity of E. coli RNA polymerase. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 27;243(130):257–260. doi: 10.1038/newbio243257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef N. J., Bosch L. Chain initiation during polypeptide synthesis in cell-free bacterial systems programmed with a plant viral messenger. Initiation with N-acetylated aminoacyl-tRNAs on adjacent codons. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorma H. O., Benne R., den Hertog T. J. Binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to ribosomes programmed with bacteriophage MS2-RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb;18(4):451–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach H., Miller D. L., Hachmann J. Studies on the role of factor Ts in polypeptide synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Mar;137(1):262–269. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach H., Redfield B., Brot N. Further studies on the role of factors Ts and Tu in protein synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 May;144(1):224–229. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90472-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach H., Redfield B., Hachmann J. Studies on the role of factor Ts in aminoacyl-tRNA binding to ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):384–386. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


