Abstract
Prior exercise has the potential to enhance subsequent performance by accelerating the oxygen uptake (VO2) kinetics. The present study investigated the effects of two different intensities of prior exercise on pulmonary VO2 kinetics and exercise time during subsequent exhaustive rowing exercise. It was hypothesized that in prior heavy, but not prior moderate exercise condition, overall VO2 kinetics would be faster and the VO2 primary amplitude would be higher, leading to longer exercise time at VO2max. Six subjects (mean ± SD; age: 22.9±4.5 yr; height: 181.2±7.1 cm and body mass: 75.5±3.4 kg) completed square-wave transitions to 100% of VO2max from three different conditions: without prior exercise, with prior moderate and heavy exercise. VO2 was measured using a telemetric portable gas analyser (K4b2, Cosmed, Rome, Italy) and the data were modelled using either mono or double exponential fittings. The use of prior moderate exercise resulted in a faster VO2 pulmonary kinetics response (τ1 = 13.41±3.96 s), an improved performance in the time to exhaustion (238.8±50.2 s) and similar blood lactate concentrations ([La−]) values (11.8±1.7 mmol.L−1) compared to the condition without prior exercise (16.0±5.56 s, 215.3±60.1 s and 10.7±1.2 mmol.L−1, for τ1, time sustained at VO2max and [La−], respectively). Performance of prior heavy exercise, although useful in accelerating the VO2 pulmonary kinetics response during a subsequent time to exhaustion exercise (τ1 = 9.18±1.60 s), resulted in a shorter time sustained at VO2max (155.5±46.0 s), while [La−] was similar (13.5±1.7 mmol.L−1) compared to the other two conditions. Although both prior moderate and heavy exercise resulted in a faster pulmonary VO2 kinetics response, only prior moderate exercise lead to improved rowing performance.
Introduction
Prior exercise is traditionally accepted as indispensable before participation in a subsequent vigorous exercise. Enhancing the cardiorespiratory and neuromuscular systems, “priming exercise” has been used extensively as an intervention to investigate the limitations of pulmonary oxygen consumption (VO2) following the onset of a subsequent exercise bout. These limitations may be due to central (O2 delivery and transportation to the working muscles) or peripheral factors (from convective O2 transport, to its diffusion and utilization in the muscles). Measurement of pulmonary VO2 at the mouth is accepted to reflect muscle VO2 during exercise [5], thus studying the VO2 kinetics at the onset of exercise may provide a valid insight into the factors that regulate oxidative metabolism at the muscle [6].
Previously, the kinetics of pulmonary VO2 response to exercise has been studied in three different intensity domains: moderate, heavy and severe [7]. For moderate exercise (at intensities below the lactate threshold), a steady-state VO2 is normally reached within 2–3 min of exercise onset [8]; in the heavy domain (at exercise intensities higher than the lactate threshold but below critical power), an additional complexity (VO2 slow component) delays the achievement of a VO2 steady-state [9]. During severe intensity exercise (above critical power), VO2 does not achieve a steady state, but continues to increase until the point of exhaustion, as VO2max is reached.
It has previously been shown that the magnitude and nature of VO2 responses are profoundly altered by prior exercise. The increases in bulk O2 delivery to the exercising muscle has dramatic effects on the response to subsequence exercise. In fact, the renewed interest on this VO2 kinetics area was generated by the report of Gerbino et al. [10], who demonstrated that prior heavy exercise could speed the overall VO2 kinetics during a second bout of heavy exercise performed 6 min after the first. Typically, studies conducted on VO2 kinetics have involved different prior exercise intensities [10], [11], [12], group ages [6], durations of recovery time [13], [14], body positions [4], [15], [16], baseline pulmonary VO2 values [17], [18], [19], [20], pedal rates [21], type of exercises [2], [22], [23], [24], [25], combinations of prior warm-up [3], [26], [27], [28] and types of subsequent bouts of exercise [29], [30]. The studies that analysed specific prior intensities have shown that the subsequent exercise performance can benefited by prior heavy exercise, as a result of an increased amplitude of the primary component and a reduced amplitude of the slow component, with no change in the primary component time constant ([11], [13], [31]). While the aforementioned alterations in VO2 kinetics might be expected to enhance exercise tolerance, the appropriate combination of prior exercise intensity and recovery time duration can be even more important than the prior exercise intensity per se [14].
We are only aware of one previous study conducted at perimaximal intensities (100%, 110% and 120% of VO2max) [32], that demonstrated that the time sustained at VO2max was higher when prior heavy exercise was performed. Nonetheless, the effects of prior exercise have not been addressed in rowing exercise in trained athletes. Given the widespread interest in the use of prior exercise, both for training and scientific purposes, it is surprising that research focused mainly on the VO2 pulmonary kinetics response in cycling exercise using heavy intensity prior exercise. Thus, it is unclear whether the prior exercise regimes that are ergogenic during cycle ergometry are also ergogenic during rowing ergometry. The purpose of the present study was to examine the influence of prior moderate and heavy intensity exercise on pulmonary VO2 kinetics and rowing performance. On the basis of cycling data from previous studies performed at the same exercise intensity used in the present study (100% VO2max) [3], [32], it was hypothesized that in prior heavy, but not prior moderate exercise condition, overall VO2 kinetics would be faster and the VO2 primary amplitude would be higher, leading to longer exercise time at VO2max.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statement
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Faculty of Sport from the University of Porto. All of the participants (or parent/guardian when subjects were under 18yrs) provided informed written consent before data collection. The procedures were performed according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Subjects
Six nationally ranked highly trained male subjects (mean ± SD; age: 22.9±4.5 yr, height: 181.2±7.1 cm and body mass: 75.5±3.4 kg) volunteered to participate in the current study. Subjects were familiar with the laboratory testing procedures, as they were involved in previous similar evaluations. All participants avoided strenuous exercise in the 24 hrs before each testing session, and were well hydrated and abstained from food, alcohol and caffeine intake. The protocols were conducted at the same time of the day for each subject and were separated by, at least, 24 h.
Experimental design
Subjects visited the laboratory on four different occasions over a two week period to perform the rowing ergometer exercises (Concept II, Model D, CTS, Inc.). In their first visit, VO2max and the lactate threshold were determined. During each of the subsequent visits, all subjects completed exhaustive exercise at 100% of VO2max with prior moderate and heavy intensity exercises and without prior exercise. All exhaustive exercise bouts were performed at the same cadence on the rowing ergometer (ranging between 30 and 40 rpm) and encouragement was given to motivate the subjects to perform their best effort.
Incremental exercise and exhaustive bouts
An intermittent incremental protocol of 2-min step durations, with increments of 40 W per step and 30-sec intervals between each step, until volitional exhaustion, was used to assess VO2max and the corresponding minimal power that elicited VO2max. VO2max was considered to be reached according to primary and secondary criteria [33] and the VO2 mean value was measured over the last 60-sec of the exercise.
A total of three experimental exhaustive conditions were investigated, conducted in randomized order. In the control condition (without prior exercise), subjects performed 2-min of rowing at 20% of maximal power (previously determined in the incremental exercise), followed by 7-min of passive recovery, and an abrupt step increment to the intensity of 100% of the minimal power that elicits VO2max. The subjects' then sustained their individual intensity until voluntary exhaustion. Voluntary exhaustion was defined as when the subjects' could no longer sustained the previously determined power In the other two conditions, after the initial 2-min period of rowing at 20% of corresponding minimal power that elicits VO2max, 6-min bouts of prior exercise were performed at moderate or heavy intensity. After the prior exercise, they had 7-min of passive recovery, which was followed by the abrupt step increment to the minimal power that elicits VO2max, and they maintained this for as long as possible (cf. Figure 1). VO2peak and HRpeak were deterred as the average VO2 and HR values measured over the last 60-sec of the exercise in the exhaustive exercise bouts.
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the experimental protocol.
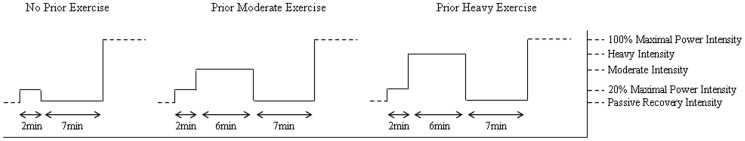
Without prior (2-min of rowing at 20% of maximal power, 7-min of passive recovery and a transition to 100% of maximal power), prior moderate (2-min of rowing at 20% of maximal power, 6-min of rowing at the moderate intensity, 7-min of passive recovery and a transition to 100% of maximal power), prior heavy (2-min of rowing at 20% of maximal power, 6-min of rowing at the heavy intensity, 7-min of passive recovery and a transition to 100% of maximal power).
Experimental measurements
VO2 was measured using a telemetric portable gas analyzer (K4b2, Cosmed, Rome, Italy), with the subjects breathing through a facemask with a low-dead-space. The gas analysers were calibrated before each test with gases of known concentration (16% O2 and 5% CO2) and the turbine volume transducer was calibrated by using a 3-L syringe. Heart rate (HR) was monitored and registered continuously by a Polar Vantage NV (Polar electro Oy, Kempele, Finland) that telemetrically emitted the data to the K4b2 portable unit. Capillary blood samples (25 µl) for determination of lactate concentrations ([La−]) were collected from the earlobe at 30-sec intervals immediately at the end of exercise, and during the 1st, 3rd, 5th and 7th-min of the recovery period in the intermittent incremental protocol (Lactate Pro, Arkay, Inc, Kyoto, Japan). In the exhaustive exercise bouts, capillary blood samples were collected just before the exercise, after the prior exercise (in the 6-min of the passive recovery), and during the 1st, 3rd, 5th and 7th-min of recovery.
Data analysis
Firstly, occasional VO2 breath values were omitted from the analysis by including only those in-between VO2 mean ±4 standard deviation. After verification of the data, individual breath-by-breath VO2 responses were smoothed by using a 3-breath moving average and time-average of 5-sec [34].
VO2 kinetics during exhaustive exercises was assessed using 5-sec average VO2 data. The first 20-sec of data after the onset of exercise (cardio-dynamic phase) were not considered for model analysis with both a mono-exponential (Equation 1) or double-exponential (Equation 2) equations. For both model fits, a nonlinear least squares method was implemented in the MatLab Software to fit the VO2 data with each model. To allow the comparison of the VO2 response, data were modeled using both mono and double exponential approaches to isolate the VO2 fast component response. An F-Test (p>0.05) was used to evaluate whether the mono-exponential or double-exponential models provided the best fit to each data set. A T-Test (p<0.05) was employed to compare the difference between mono-exponential and double-exponential mean values.
| (1) |
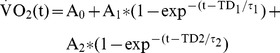 |
(2) |
where 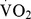 (t) represents the relative VO2 at the time t, A0 is the
(t) represents the relative VO2 at the time t, A0 is the 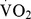 at rest (ml.kg−1.min−1) and A1 and A2 (ml.kg−1.min−1), TD1 and TD2 (s), and τ1 and τ2 (s) are the amplitudes, the corresponding time delays and time constants of the fast and slow
at rest (ml.kg−1.min−1) and A1 and A2 (ml.kg−1.min−1), TD1 and TD2 (s), and τ1 and τ2 (s) are the amplitudes, the corresponding time delays and time constants of the fast and slow 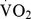 components, respectively. The mean response time (MRT) was used to represent the overall pulmonary VO2 kinetics response and was calculated as the sum of TD1 and τ1.
components, respectively. The mean response time (MRT) was used to represent the overall pulmonary VO2 kinetics response and was calculated as the sum of TD1 and τ1.
The lactate threshold was determined by visual inspection of the data as the disproportionate increase in [La−] as a function of work rate. In addition, to confirm the lactate threshold, it was also determined by the [La−]/velocity curve mathematically modelling method (least squares) [35], allowing the exact point of exponential rise in [La−] to be determined. Having determined the individual minimal power that elicits VO2max and the lactate threshold, the work rates equivalent to 90% of the work rate at lactate threshold and to 50% of difference between the work rate at lactate threshold and at VO2max were estimated and assumed to represent the moderate and heavy intensities, respectively.
Statistics
Individual, mean and standard deviations (SD) are used for descriptive analysis for all studied variables. Measures of skewness, kurtosis and the Shapiro-Wilk test were used to assess the normality and homogeneity of the data. The differences between [La−] and HR mean values before and after performing the exhaustive bouts were tested using the unpaired T-Test. The differences in pulmonary VO2 kinetics parameters and time sustained between the exhaustive bouts preceded by moderate intensity and heavy intensity exercise and without prior exercise were tested for statistical significance using ANOVA for repeated measures. When a significant F value was achieved, the Bonferroni post hoc procedures were performed to locate the pairwise differences between the averages. Simple linear regression and Pearson's correlation coefficient were also used.All statistical procedures were conducted with SPSS 10.05 and the significance level was set at 5%.
Results
The mean (± SD) VO2max values of the subjects were 67.4±4.1 ml.kg−1.min−1, with the lactate threshold taking place at 298.3±25.6 W (corresponding to 74.9±5.7% of VO2max). The work rates corresponding to moderate and heavy prior exercise intensity bouts conditions were 268.5±23.1 and 348.3±16.1 W, respectively.
The basal [La−], baseline VO2 and HR mean values, just before and after the prior exercises were: 1.1±0.2 mmol.L−1, 6.1±1.2 ml.kg−1.min−1 and 74.6±8.4 bpm, increasing to 1.23±0.1 mmol.L−1, 7.3±2.2 ml.kg−1.min−1 and 83.3±7.5 bpm (p<0.05) for the without prior exercise condition, 1.14±0.3 mmol.L−1, 6.7±1.2 ml.kg−1.min−1 and 73.1±6.1 bpm, increasing to 2.8±0.8 mmol.L−1(p<0.01), 9.8±2.7 ml.kg−1.min−1 (p<0.05) and to 97.1±4.5 bpm (p<0.01), for the moderate prior exercise condition and 1.38±0.3 mmol.L−1, 6.3±1.5 ml.kg−1.min−1 and 73.4±4.1 bpm, increasing to 5.9±1.2 mmol.L−1 (p<0.01), 12.3±2.2 ml.kg−1.min−1 (p<0.01) and to 114.2±5.3 bpm (p<0.01), for the heavy prior exercise condition.
Table 1 shows the pulmonary VO2 kinetic parameters in the exhaustive exercise bouts, without prior exercise and with prior moderate and prior heavy exercises.
Table 1. Mean (± SD) values for the VO2 kinetics, ventilatory and metabolic parameters in the time to exhaustion bouts performed without prior exercise, with prior moderate and with prior heavy exercises.
| Parameters | Without prior exercise | Prior moderate exercise | Prior heavy exercise |
| A0 (ml.kg−1.min−1) | 20.48±3.49 | 20.91±3.48 | 21.61±5.28 |
| A1 (ml.kg−1.min−1) | 44.07±2.13 | 43.74±6.52 | 40.76±5.83 |
| TD1 (s) | 4.04±3.46 | 8.67±4.66 | 7.49±2.73 |
| τ1 (s) | 16.0±5.56 a | 13.41±3.96 b | 9.18±1.60 |
| MRT (s) | 20.05±5.44 | 22.08±7.46 | 17.24±3.29 |
| Time sustained at VO2max (s) | 215.30±60.10 a | 238.83±50.22 b | 155.50±46.05 |
| VO2peak (ml.kg−1.min−1) | 66.64±1.85 | 66.96±3.53 | 63.08±6.02 |
| HRpeak (bpm) | 179.0±15.12 | 182.80±9.51 | 182.80±14.09 |
| [La−] | 10.71±1.20 | 11.76±1.69 | 13.46±1.72 |
A0 = VO2 at rest, A1 = amplitude of the fast component, TD1 = time delay of the fast component, τ1 = time constant of the fast component, MRT = mean response time (TD1 + τ1); VO2peak = peak oxygen consumption, HRpeak = peak heart rate, [La−] = blood lactate concentrations. a significant different from prior moderate and prior heavy exercises; b significant different from prior heavy exercise.
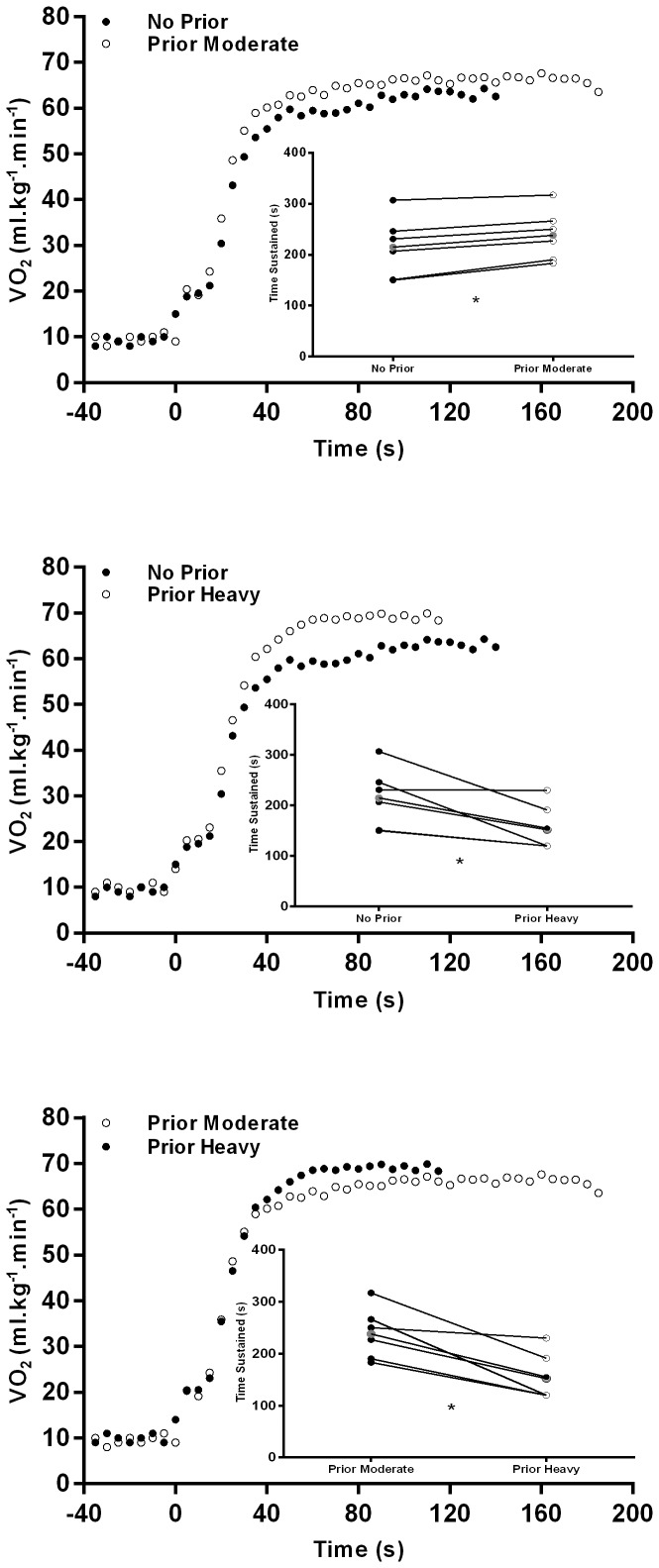
There were no significant differences regarding A0, A1, TD1 and VO2peak values between all three studied conditions. The overall pulmonary VO2 kinetics response in the fast phase was not significantly different when performing prior exercise, independently of its intensity, comparing to the condition where no previous exercise was conducted. However, τ1 was higher when no prior exercise was performed, comparing to the other two conditions. No significant differences were found between MRT, HRpeak and [La−]. A representative pulmonary VO2 kinetics and the individual and mean values of the time sustained responses at each studied condition are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. VO2 dynamic response of one subject performing time to exhaustion exercise bouts.
After no prior exercise (closed circles) and after prior moderate exercise (open circles) (upper panel); after no prior exercise (closed circles) and after prior heavy exercise (open circles) (middle panel); after prior moderate exercise (closed circles) and after prior heavy exercise (open circles) (lower panel). The insets in the respective VO2 graphs represent the individual (full black and full white) and mean (full grey) values in the time sustained at the correspondent exercise bout released. *significant differences between the two studied conditions (p<0.05).
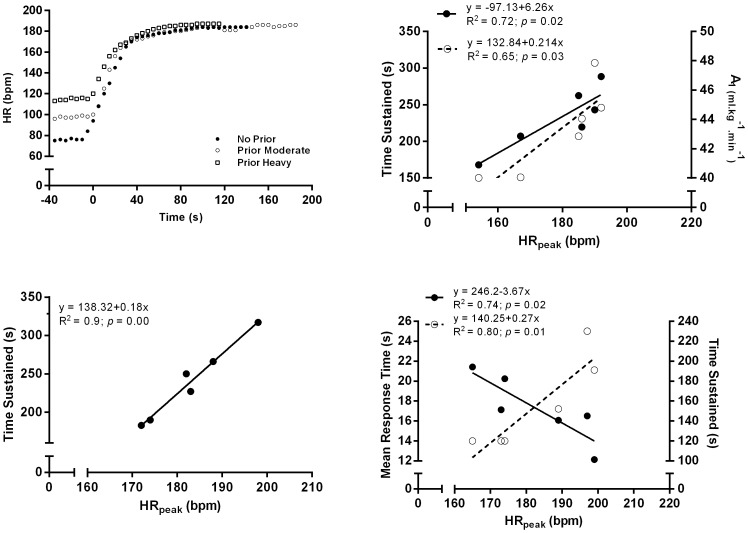
The time sustained in the exhaustive exercise bouts was longer when prior moderate exercise was performed compared to the other two studied conditions. Moreover, when a prior heavy exercise bout was implemented, the time to exhaustion was significantly shorter when compared to the without prior exercise condition. Figure 3 shows the positive relationships between HRpeak and the time sustained in the exhaustive bouts (all conditions). In addition, the subjects who had higher values of HRpeak were the ones with higher A1 values when no prior exercise was performed. However, in the prior heavy exercise condition, subjects who presented lower HRpeak values, had an enhanced fast component of VO2 kinetics (given by the MRT value). No significant relationships were found between VO2peak and VO2max and all other kinetic parameters.
Figure 3. HR dynamic response of one subject performing time to exhaustion exercise bouts.
After no prior exercise (closed circles), after prior moderate exercise (open circles) and after prior heavy exercise (open squares) (upper left panel); relationships between peak heart rate and time sustained (filled circles) and between peak heart rate and amplitude of the fast component (unfilled circles) when no prior exercise was performed (upper right panel), between peak heart rate and time sustained when prior moderate exercise was performed (lower left panel) and between peak heart rate and mean response time (filled circles) and between peak heart rate and time sustained (unfilled circles) when prior heavy exercise was performed (lower right panel). The regression equations, determination coefficients and significance level values are identified.
Discussion
Studies regarding the effect of “priming exercise” on VO2 pulmonary kinetics have been conducted mainly in cycle ergometry and using heavy intensity prior exercise domain. Only one study examined VO2 kinetics during rowing [36], but this study did not address the influence of “priming exercise”. The current study is the first to examine the influence of prior moderate and heavy exercises on subsequent pulmonary exhaustive rowing exercise compare to the absence of prior exercise (warm up). The main findings were that both prior moderate and heavy exercises significantly altered the pulmonary VO2 kinetics response to subsequent exhaustive exercise performed at 100%VO2max. In these two conditions, the τ1 was significantly shorter compared to the condition without prior exercise, in opposition to our hypothesis that prior heavy, but not moderate exercise condition, would reduce τ1 phase II pulmonary VO2 kinetics. In addition, there were significant differences among all studied conditions regarding the time sustained at VO2max, with higher values when prior moderate exercise was performed, again not supporting our hypothesis that time sustained at VO2max would be increased when prior heavy, but not moderate, exercise would be performed.
There were significant differences in VO2 kinetics (τ1) between all studied conditions, with the values being 16.2% and 42.6% longer when no prior exercise was performed, compared to the conditions with prior moderate and heavy exercise conditions, respectively. These results for rowing are not consistent with previous studies conducted in cycling [11], [12], [13], [14], [17] or running exercise. These differences suggest that in rowing exercise, pulmonary VO2 steady-state is achieved faster than in cycling. It has been suggested that similarities and differences in VO2 kinetics between exercise sports provide insight into the physiological mechanisms responsible for the control of, and the limitations to, VO2 kinetics following the onset of exercise [37].
Only one study has been conducted comparing the pulmonary VO2 kinetic responses to step transitions to moderate and heavy intensity exercises during upright cycle and rowing ergometer exercises [38]. These authors showed that VO2 kinetic responses were similar between both types of exercise. This was not an expected outcome since rowing exercise engages a higher percentage of active muscular mass [39], potentially compromising muscle perfusion, particularly during heavy exercise where a larger fraction of the maximal cardiac output is used [40], Under this condition, a slower VO2 kinetics might be expected in rowing compared to cycling, which was not verified This outcome suggests that the greater active muscular mass engaged in rowing exercise is not, per se, an important explanatory factor of the differences between pulmonary VO2 kinetic rowing and cycling responses in moderate and heavy exercise intensities. This may also indicate that VO2 kinetic responses may be strongly influenced not only by metabolic constrains, but also by the muscle contraction regimen and muscle fibre recruitment profile [37]. Due to the higher intensity performed in our study (100%VO2max) it was expectable that bulk muscle blood flow was become even more committed compared to cycling exercise. Moreover, comparison of exercise performed with both arms and the legs reveals that muscle blood flow decreases, compared to the condition when legs or arms are exercised alone, which is explained by the sympathetic control of blood flow (muscle pressor reflex) [41]. However, this possible site of control may have been attenuated by the performance of a prior exercise and eventually resulted in a faster pulmonary VO2 kinetics response, which was not verified in cycling exercise. Moreover, the differences in training status of the subjects, could explain the absence of agreement between our results and the data reported in the literature, particularly for other exercise modes.
In the current study, there were differences in the time exercise was sustained at VO2max between the three studied conditions, with higher values when prior moderate exercise was performed. In fact, in this condition, the time sustained at VO2max was increased in 10.9% and 34.9% compared to the without prior and prior heavy exercise conditions, respectively. However, exercise time was diminished 27.8% compared to the without prior exercise condition. Recent studies have shown that exercise performance could be compromised after 6 min of cycling with a severe exercise [31], [42], enhanced after 6 min of cycling heavy exercise[31], [32] or even have no influence after 6 min of cycling at severe exercise [31]. It has been reported that prior exercise may predispose subjects to increase exercise tolerance in the subsequent bout of exercise, due to the sparing of anaerobic energy as a result of the increase in muscle aerobic energy turnover [10], [43]. This was verified in the present study by shorter τ1 values in the prior moderate exercise condition (compared to the without prior exercise condition), although no significant differences were found in HR kinetics between each studied condition The unexpected result that the time sustained at VO2max in the prior heavy exercise condition was shorter than the other two conditions may be due to the significant higher [La−] values observed before the exhaustive bout was begun, compared to the prior heavy bout exercise and no prior exercise conditions.
As suggested previously, residual acidosis provides a stimulus for an increased O2 availability through facilitation of vasodilatation and a Bohr shift in the O2 dissociation curve [2], [10], [12]. However, the effects of prior heavy exercise lead also to an exaggerated accumulation of metabolites in the vascular beds in the exercised muscles and a decrease in blood pH, although muscle oxygenation was reported to be improved [2], [14]. In order to preserve the effects of prior exercise on VO2 kinetics and provide sufficient time for muscle homeostasis, Bailey et al. [14] reported that prior high intensity exercise can enhance the tolerance to subsequent high intensity exercise if it is coupled with adequate recovery duration (≥9 min) in between bouts. In fact, blood [La−], VO2 baseline and HR mean values were significantly elevated in the baseline period preceding the exhaustive exercise bout (5.9 mmol.L−1, 12.3 ml.kg−1.min−1 and 114.2 bpm), which could indicate that the recovery period may not long enough to allowed sufficient time for restoration of intramuscular high energy phosphates and/or removal of fatiguing metabolites before the beginning of the subsequent exhaustive exercise bout. The elevated [La−], VO2 baseline and HR prior to subsequent exercise could lead to a lower exercise tolerance [23], [32], [44]. This suggests that in the prior heavy exercise condition in the present study that led to the faster pulmonary VO2 kinetics (shown by shorter τ1 mean values in the prior heavy exercise condition compared to the non prior exercise one), was not the single determinant of the duration of the exercise. Instead, might do so through interaction with other physiological parameters, and, in contrast to our hypothesis, the time sustained at VO2max in the prior heavy exercise condition was shorter.
In the current study, based on the positive relationship between HRpeak and exercise time at VO2max, it was shown that the subjects who had higher HRpeak in all three studied conditions, were also the ones who sustained exhaustive exercises time longer. However, since no significant differences were found in HRpeak between all studied conditions, the O2 availability during exercise was similar, and so, once again, this factor is not, per se, the single determinant of the tolerable duration of exercise. Moreover, the subjects who presented higher A1 were the ones that achieved higher HRpeak values when no prior exercise was conducted. When prior heavy exercise was performed, negative relationships were observed between MRT and HRpeak, as these relationships were influenced by significantly shorter τ1 values. In fact, a shorter τ1 in this condition lead to an anticipated steady-state compared to the other conditions; however, this condition has not contributed advantageous, per si, to a longer exercise time at VO2max intensity.
Further studies to define the optimal intensity of prior exercise and subsequent recovery time required to optimise exercise performance are supported by the data from this study. However, the methodologies used to establish the intensities in both prior moderate and heavy exercise conditions (90% of anaerobic threshold and Δ50%, respectively) may have allowed that some subjects had performed them at intensities similar to important physiological boundaries: the anaerobic threshold and the critical power in the prior moderate and heavy exercise conditions, respectively. Consequently, this could have limited the rowers' performance and influenced its VO2 kinetics, and for that, should be construed as a possible limitation of the present study.
Conclusions
Performance of prior moderate exercise resulted in faster VO2 pulmonary kinetics and also improved exercise time rowing at 100% of VO2max. Prior heavy exercise, although effective in accelerating VO2 kinetics in a subsequent exhaustive exercise, it resulted in a shorter exercise time at VO2max compared to no prior exercise and prior moderate exercise. These results may have important implications for the preparation of athletes in training and competition suggesting the use of an optimal warm-up exercise intensity (and duration) with optimal recovery combination to improve performance.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank Professor David Pendergast for his revision of the manuscript.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology - Ref. SFRH/BD/72610/2010. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Jones AM, Koppo K, Burnley M (2003) Effects of prior exercise on metabolic and gas exchange responses to exercise. Sports Med 33: 949–971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Jones AM, DiMenna F, Lothian F, Taylor E, Garland SW, et al. (2008) 'Priming' exercise and O2 uptake kinetics during treadmill running. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 161: 182–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Wilkerson DP, Koppo K, Barstow TJ, Jones AM (2004) Effect of prior multiple-sprint exercise on pulmonary O2 uptake kinetics following the onset of perimaximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 97: 1227–1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Jones AM, Berger NJ, Wilkerson DP, Roberts CL (2006) Effects of “priming” exercise on pulmonary O2 uptake and muscle deoxygenation kinetics during heavy-intensity cycle exercise in the supine and upright positions. J Appl Physiol 101: 1432–1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Grassi B, Poole DC, Richardson RS, Knight DR, Erickson BK, et al. (1996) Muscle O2 uptake kinetics in humans: implications for metabolic control. Journal of Applied Physiology 80: 988–998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Barker AR, Jones AM, Armstrong N (2010) The influence of priming exercise on oxygen uptake, cardiac output, and muscle oxygenation kinetics during very heavy-intensity exercise in 9- to 13-yr-old boys. J Appl Physiol 109: 491–500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Gaesser GA, Poole DC (1996) The slow component of oxygen uptake kinetics in humans. Exercise & Sport Sciences Reviews 24: 35–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Pringle JS, Doust JH, Carter H, Tolfrey K, Campbell IT, et al. (2003) Oxygen uptake kinetics during moderate, heavy and severe intensity “submaximal” exercise in humans: the influence of muscle fibre type and capillarisation. Eur J Appl Physiol 89: 289–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Barstow TJ, Mole PA (1991) Linear and nonlinear characteristics of oxygen uptake kinetics during heavy exercise. Journal of Applied Physiology 71: 2099–2106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Gerbino A, Ward SA, Whipp BJ (1996) Effects of prior exercise on pulmonary gas-exchange kinetics during high-intensity exercise in humans. Journal of Applied Physiology 80: 99–107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Burnley M, Jones AM, Carter H, Doust JH (2000) Effects of prior heavy exercise on phase II pulmonary oxygen uptake kinetics during heavy exercise. J Appl Physiol 89: 1387–1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Burnley M, Doust JH, Ball D, Jones AM (2002) Effects of prior heavy exercise on VO(2) kinetics during heavy exercise are related to changes in muscle activity. J Appl Physiol 93: 167–174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Burnley M, Doust JH, Carter H, Jones AM (2001) Effects of prior exercise and recovery duration on oxygen uptake kinetics during heavy exercise in humans. Exp Physiol 86: 417–425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Bailey SJ, Vanhatalo A, Wilkerson DP, Dimenna FJ, Jones AM (2009) Optimizing the “priming” effect: influence of prior exercise intensity and recovery duration on O2 uptake kinetics and severe-intensity exercise tolerance. J Appl Physiol 107: 1743–1756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. DiMenna FJ, Bailey SJ, Jones AM (2010) Influence of body position on muscle deoxy[Hb+Mb] during ramp cycle exercise. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 173: 138–145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. DiMenna FJ, Wilkerson DP, Burnley M, Bailey SJ, Jones AM (2010) Priming exercise speeds pulmonary O2 uptake kinetics during supine “work-to-work” high-intensity cycle exercise. J Appl Physiol 108: 283–292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. DiMenna FJ, Bailey SJ, Vanhatalo A, Chidnok W, Jones AM (2010) Elevated baseline VO2 per se does not slow O2 uptake kinetics during work-to-work exercise transitions. J Appl Physiol 109: 1148–1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Breese BC, Barker AR, Armstrong N, Jones AM, Williams CA (2012) The effect of baseline metabolic rate on pulmonary O(2) uptake kinetics during very heavy intensity exercise in boys and men. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 180: 223–229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Wilkerson DP, Jones AM (2007) Effects of baseline metabolic rate on pulmonary O2 uptake on-kinetics during heavy-intensity exercise in humans. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 156: 203–211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. DiMenna FJ, Wilkerson DP, Burnley M, Jones AM (2008) Influence of priming exercise on pulmonary O2 uptake kinetics during transitions to high-intensity exercise from an elevated baseline. J Appl Physiol 105: 538–546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Dimenna FJ, Wilkerson DP, Burnley M, Bailey SJ, Jones AM (2009) Influence of extreme pedal rates on pulmonary O(2) uptake kinetics during transitions to high-intensity exercise from an elevated baseline. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 169: 16–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Koppo K, Bouckaert J, Jones AM (2002) Oxygen uptake kinetics during high-intensity arm and leg exercise. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 133: 241–250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Jones AM, Fulford J, Wilkerson DP (2008) Influence of prior exercise on muscle [phosphorylcreatine] and deoxygenation kinetics during high-intensity exercise in men. Exp Physiol 93: 468–478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Dimenna FJ, Fulford J, Bailey SJ, Vanhatalo A, Wilkerson DP, et al. (2010) Influence of priming exercise on muscle [PCr] and pulmonary O2 uptake dynamics during 'work-to-work' knee-extension exercise. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 172: 15–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Jones AM, Wilkerson DP, Fulford J (2008) Muscle [phosphocreatine] dynamics following the onset of exercise in humans: the influence of baseline work-rate. J Physiol 586: 889–898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Burnley M, Doust JH, Jones AM (2002) Effects of prior heavy exercise, prior sprint exercise and passive warming on oxygen uptake kinetics during heavy exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 87: 424–432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Koppo K, Jones AM, Bouckaert J (2003) Effect of prior heavy arm and leg exercise on VO2 kinetics during heavy leg exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 88: 593–600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Burnley M, Doust JH, Jones AM (2005) Effects of prior warm-up regime on severe-intensity cycling performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37: 838–845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Palmer CD, Jones AM, Kennedy GJ, Cotter JD (2009) Effects of prior heavy exercise on energy supply and 4000-m cycling performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41: 221–229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Parker Simpson L, Jones AM, Vanhatalo A, Wilkerson DP (2012) Influence of initial metabolic rate on the power-duration relationship for all-out exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 112: 2467–2473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Burnley M, Davison G, Baker JR (2011) Effects of priming exercise on VO2 kinetics and the power-duration relationship. Medicine and science in sports and Exercise 43: 2171–2179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Jones AM, Wilkerson DP, Burnley M, Koppo K (2003) Prior heavy exercise enhances performance during subsequent perimaximal exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35: 2085–2092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Howley ET, Bassett DR, Welch HG (1995) Criteria for maximal oxygen uptake: review and commentary. Med Sci Sports Exerc 27: 1292–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Fernandes R, de Jesus K, Baldari C, Sousa A, Vilas-Boas J, et al. (2012) Different VO2max Time-Averaging Intervals in Swimming. Int J Sport Med 33: 1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Fernandes RJ, Keskinen KL, Colaco P, Querido AJ, Machado LJ, et al. (2008) Time limit at VO2max velocity in elite crawl swimmers. Int J Sports Med 29: 145–150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Roberts CL, Wilkerson DP, Jones AM (2005) Pulmonary O2 uptake on-kinetics in rowing and cycle ergometer exercise. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 146: 247–258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jones AM, Poole DC (2005) Oxygen uptake kinetics in sport, exercise and medicine: Routledge London.
- 38. Roberts CL, Wilkerson DP, Jones AM (2005) Pulmonary O2 uptake on-kinetics in rowing and cycle ergometer exercise. Respiratory physiology & neurobiology 146: 247–258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Secher NH (1993) Physiological and biomechanical aspects of rowing. Sports Medicine 15: 24–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Secher NH, Clausen JP, Klausen K, Noer I, Trap-Jensen J (1977) Central and regional circulatory effects of adding arm exercise to leg exercise. Acta physiologica scandinavica 100: 288–297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Secher NH, Volianitis S (2006) Are the arms and legs in competition for cardiac output? Medicine and science in sports and Exercise 38: 1797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Ferguson C, Whipp BJ, Cathcart AJ, Rossiter HB, Turner AP, et al. (2007) Effects of prior very-heavy intensity exercise on indices of aerobic function and high-intensity exercise tolerance. Journal of Applied Physiology 103: 812–822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Krustrup P, González-Alonso J, Quistorff B, Bangsbo J (2001) Muscle heat production and anaerobic energy turnover during repeated intense dynamic exercise in humans. The Journal of physiology 536: 947–956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Jones AM, Wilkerson DP, Fulford J (2008) Muscle [phosphocreatine] dynamics following the onset of exercise in humans: the influence of baseline work-rate. The Journal of physiology 586: 889–898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]