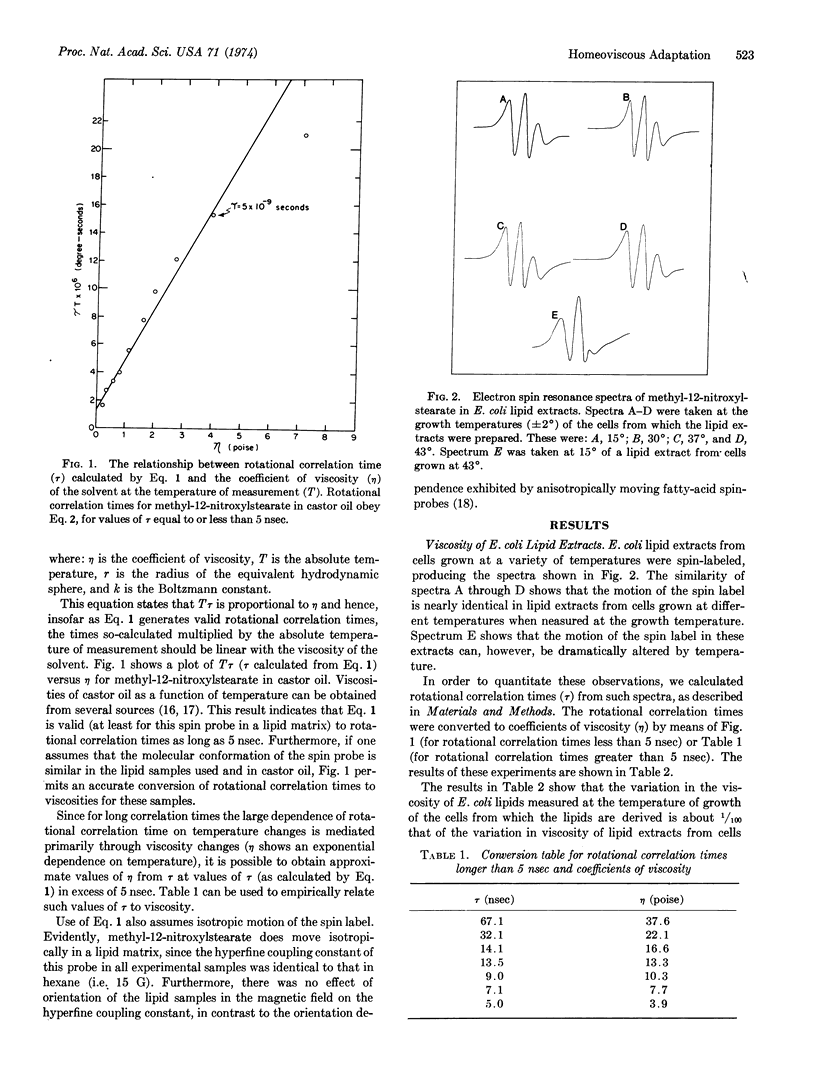
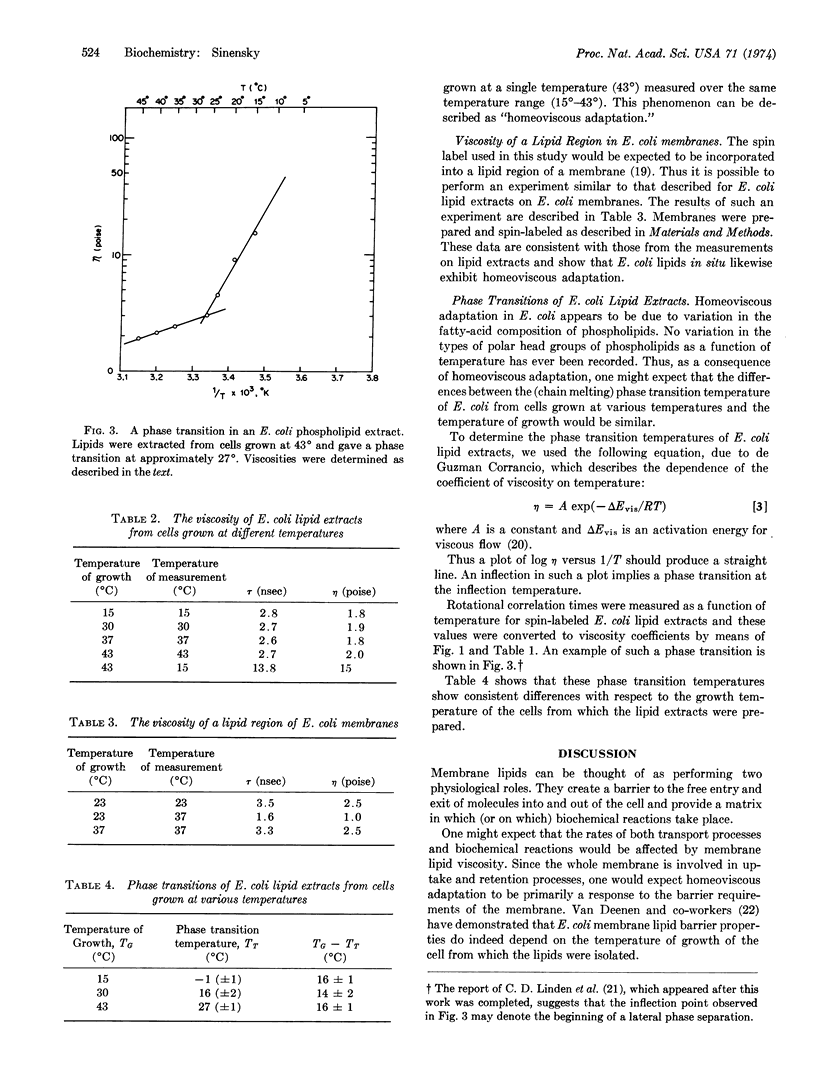
Abstract
E. coli incorporates increasing proportions of saturated and long-chain fatty acids into phospholipids as growth temperature is increased. It was found that this compositional variation results in the biosynthesis of phospholipids that have identical viscosities at the temperature of growth of the cells. This “homeoviscous adaptation” can also be observed in E. coli membrane preparations. Viscosities were determined by use of the electron spin resonance spin-label technique.
Keywords: spin-labeling, phase transitions
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haest C. W., de Gier J., van Deenen L. L. Changes in the chemical and the barrier properties of the membrane lipids of E. coli by variation of the temperature of growth. Chem Phys Lipids. 1969 Dec;3(4):413–417. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(69)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. M., Schofield P., Rich A. Spin-labeled transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1195–1202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P., Libertini L. J., Hebert V. C., Griffith O. H. Lipid spin labels in lecithin multilayers. A study of motion along fatty acid chains. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):77–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., BURROUS J. W. Hybridization between Escherichia coli and Shigella. J Bacteriol. 1957 Oct;74(4):461–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.4.461-476.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden C. D., Wright K. L., McConnell H. M., Fox C. F. Lateral phase separations in membrane lipids and the mechanism of sugar transport in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr A. G., Ingraham J. L. EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE COMPOSITION OF FATTY ACIDS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1260-1267.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Pauli G., Schairer H. U. Fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli. An inducible acyl-CoA synthetase, the mapping of old-mutations, and the isolation of regulatory mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):559–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandermann H., Jr, Strominger J. L. Purification and properties of C 55 -isoprenoid alcohol phosphokinase from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5123–5131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M. Temperature control of phospholipid biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):449–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.449-455.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. J., Buckman T., Nordio P. L., McConnell H. M. Spin-labeled biomolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1010–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. S., Kingzett T. J., Rottschaefer S., Griffith O. H., Keith A. D. A spin-labeled lipid for probing biological membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1969 Sep;3(3):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(69)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



