Abstract
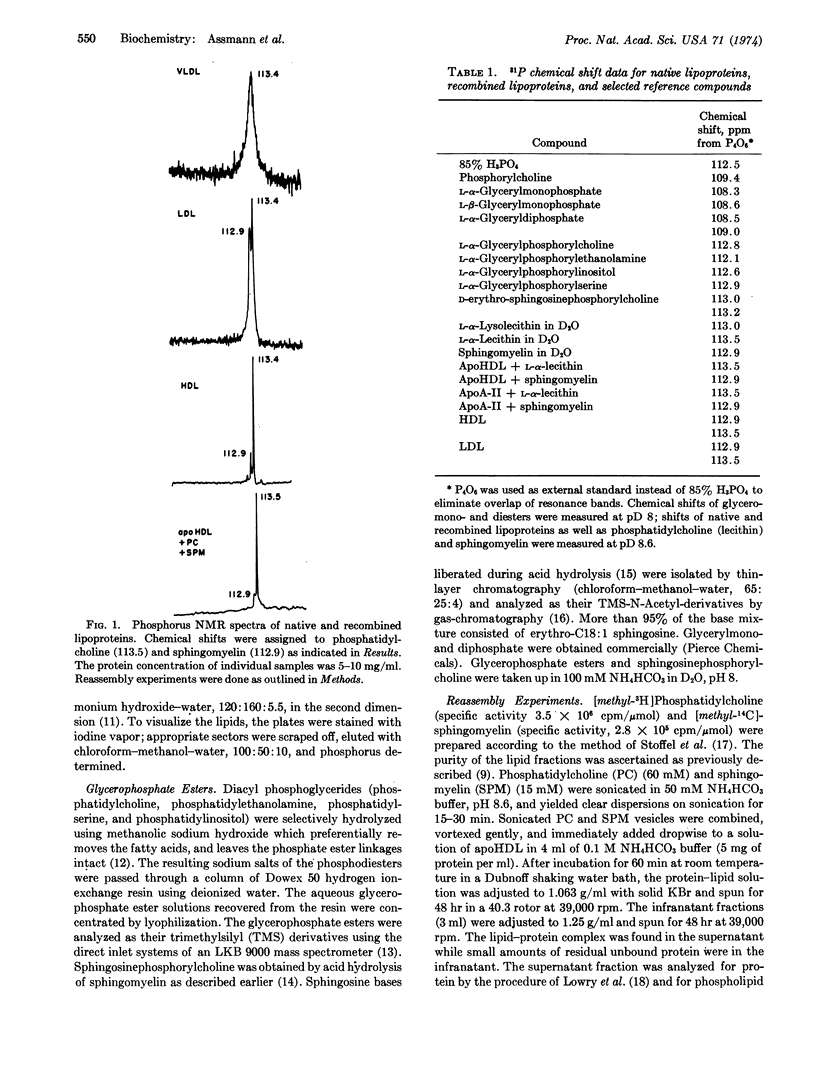
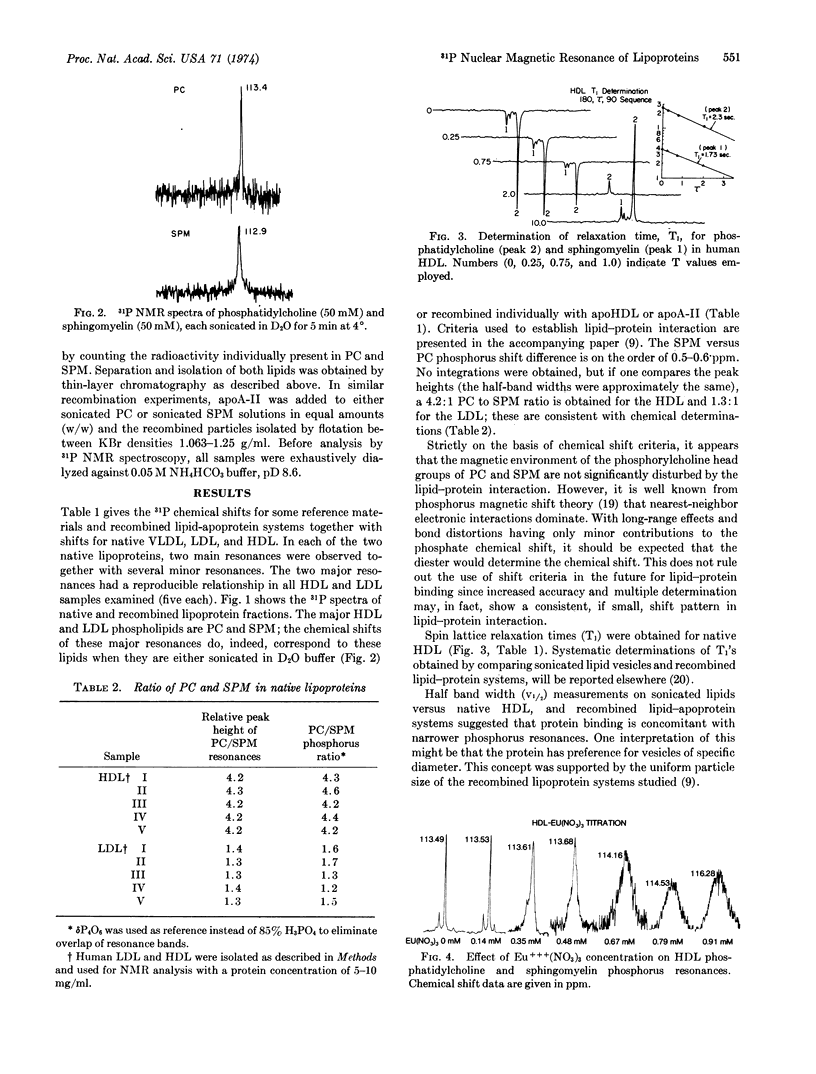
Native and recombined lipoproteins have been studied by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Very low-, low-, and high-density lipoproteins exhibited characteristic spectra. The main resonances were assigned to phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin. Relaxation times for these phospholipids were separately measured in low-density lipoproteins and high-density lipoproteins. The effect of paramagnetic ions (Eu+++) on the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of high-density lipoproteins is reported.
Keywords: lipid-protein binding, high- and low-density lipoproteins, europium-lipoprotein interactions, sphingomyelin-phosphorus ratio of lipoproteins, chemical shift and relaxation times of lipoprotein constituents
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHWORTH L. A., GREEN C. THE ACTION OF ENZYMES OF HUMAN ALPHA-LIPOPROTEIN. Biochem J. 1963 Dec;89:561–564. doi: 10.1042/bj0890561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews S. B., Faller J. W., Gilliam J. M., Barrnett R. J. Lanthanide ion-induced isotropic shifts and broadening for nuclear magnetic resonance structural analysis of model membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G. The structure of human density lipoprotein: a study of the effect of phospholipase A and trypsin on its components and of the behavior of the lipid and protein moieties at the air-water interphase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar;175(2):290–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter H. E., Gaver R. C. Improved reagent for trimethylsilylation of sphingolipid bases. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jul;8(4):391–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Leslie R. B., Hirz R., Scanu A. M. 220 MHz nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of high density serum lipoproteins. Nature. 1969 Jan 18;221(5177):260–261. doi: 10.1038/221260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D., Leslie R. B., Hirz R., Scanu A. M. High-resolution NMR spectra of high-density serum lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 29;176(3):524–536. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. H., Lennarz W. J., Fenselau C. C. Mass spectral analysis glycerophospholipids. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):927–932. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Sloan H. R., Hansen C. T. Lipid abnormalities in foam cell reticulosis of mice, an analogue of human sphingomyelin lipidosis. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):288–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAVER R. C., SWEELEY C. C. METHODS FOR METHANOLYSIS OF SPHINGOLIPIDS AND DIRECT DETERMINATION OF LONG-CHAIN BASES BY GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Apr;42:294–298. doi: 10.1007/BF02540132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Jr Recent studies on the structure of human serum low-and high-density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1119–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Kon H. Application of electron spin resonance to the study of the structure of human serum lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 22;37(3):444–450. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90935-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Kon H., Birnbaumer M. E. Electron spin resonance studies of lipid-protein interaction in human serum lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):145–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Kon H. Observations on the conformation of human serum high-density lipoproteins using infrared spectroscopy, circular dichroism, and electron spin resonance. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4276–4283. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Shore B. Conformation of human serum high density lipoprotein and its peptide components. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):69–70. doi: 10.1038/224069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. A., Talkowski C., Williams E., Avila E. M., Allerhand A., Cordes E. H., Camejo G. Natural abundance carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of human serum lipoproteins. Science. 1973 Apr 15;180(4082):193–195. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4082.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C., Leslie R. B., Scanu M. Fluorescence studies of a high density serum lipoprotein. Chem Phys Lipids. 1970 Aug;4(3):367–374. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(70)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie R. B., Chapman D., Scanu A. M. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies on serum low density lipoproteins (LDL2). Chem Phys Lipids. 1969 Apr;3(2):152–158. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(69)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Brewer H. B., Jr Isolation and characterization of apoLp-Gln-II (apoA-II), a plasma high density apolipoprotein containing two identical polypeptide chains. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7510–7518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Horwitz A. F., Klein M. P. Transbilayer asymmetry and surface homogeneity of mixed phospholipids in cosonicated vesicles. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2637–2645. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M. The effect of reduction and carboxymethylation on the circular dichroic spectra of two polypeptide classes of serum high density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 31;200(3):570–572. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A., Hirz R. On the structure of human serum high-density lipoprotein: studies by the technique of circular dichroism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):890–894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. Studies on the conformation of human serum high-density lipoproteins HDL2 and HDL3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1699–1705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. G., Atkinson D., Scanu A. M. Small-angle x-ray scattering of human serum high-density lipoproteins. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(2):98–104. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore B., Shore V. Isolation and characterization of polypeptides of human serum lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4510–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steim J. M., Edner O. J., Bargoot F. G. Structure of human serum lipoproteins: nuclear magnetic resonance supports a micellar model. Science. 1968 Nov 22;162(3856):909–911. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3856.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Assmann G. On the metabolism of sphinganyl- and sphingenyl-1-phosphorylcholine. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Jan;353(1):65–74. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., LeKim D., Tschung T. S. A simple chemical method for labelling phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin in the choline moiety. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Aug;352(8):1058–1064. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.2.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



