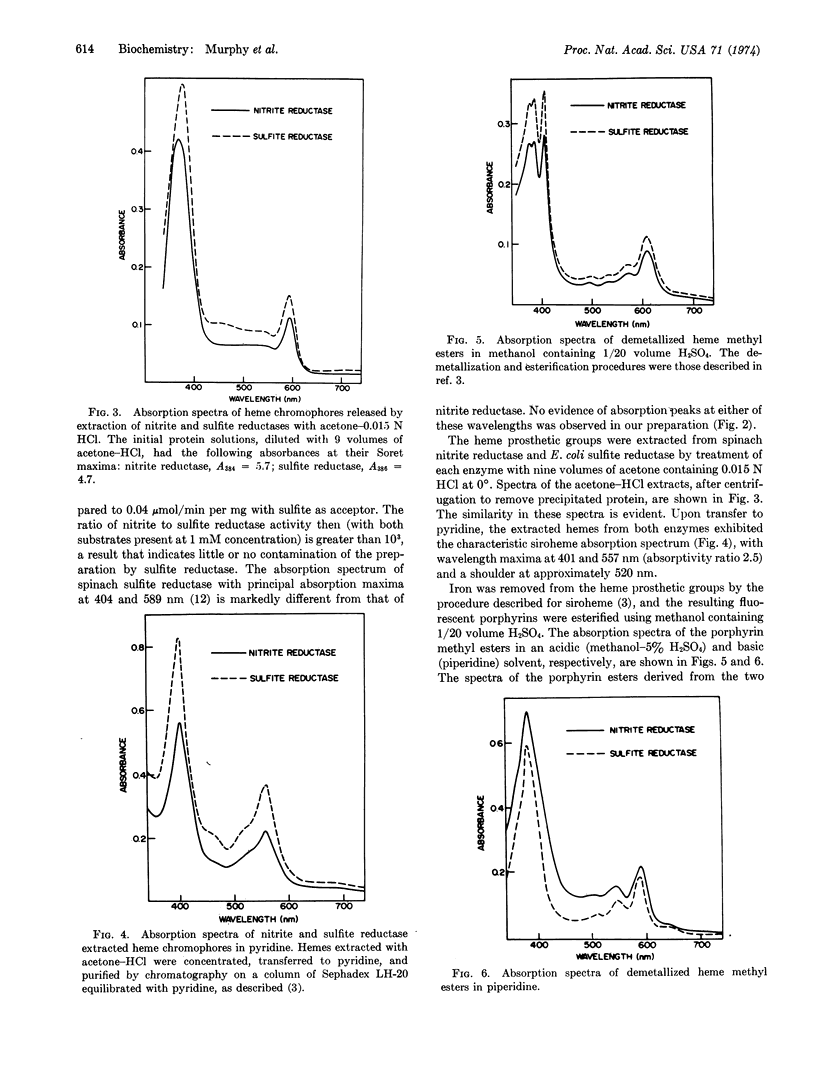
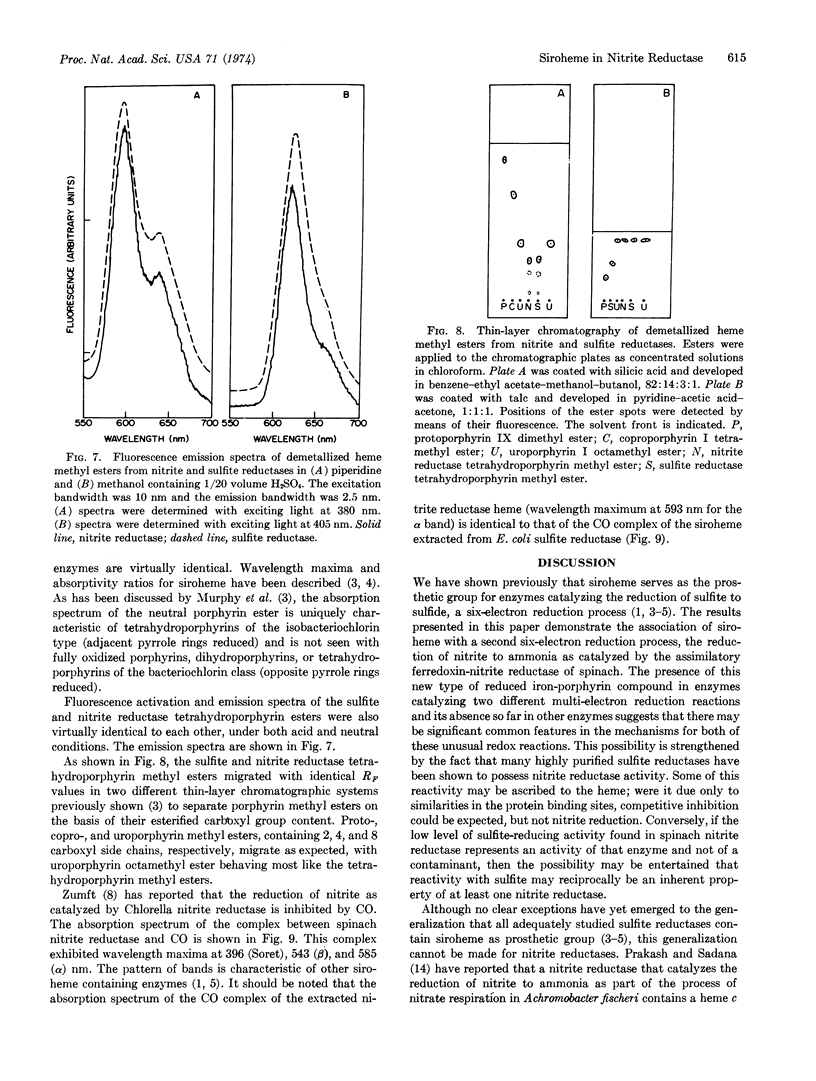
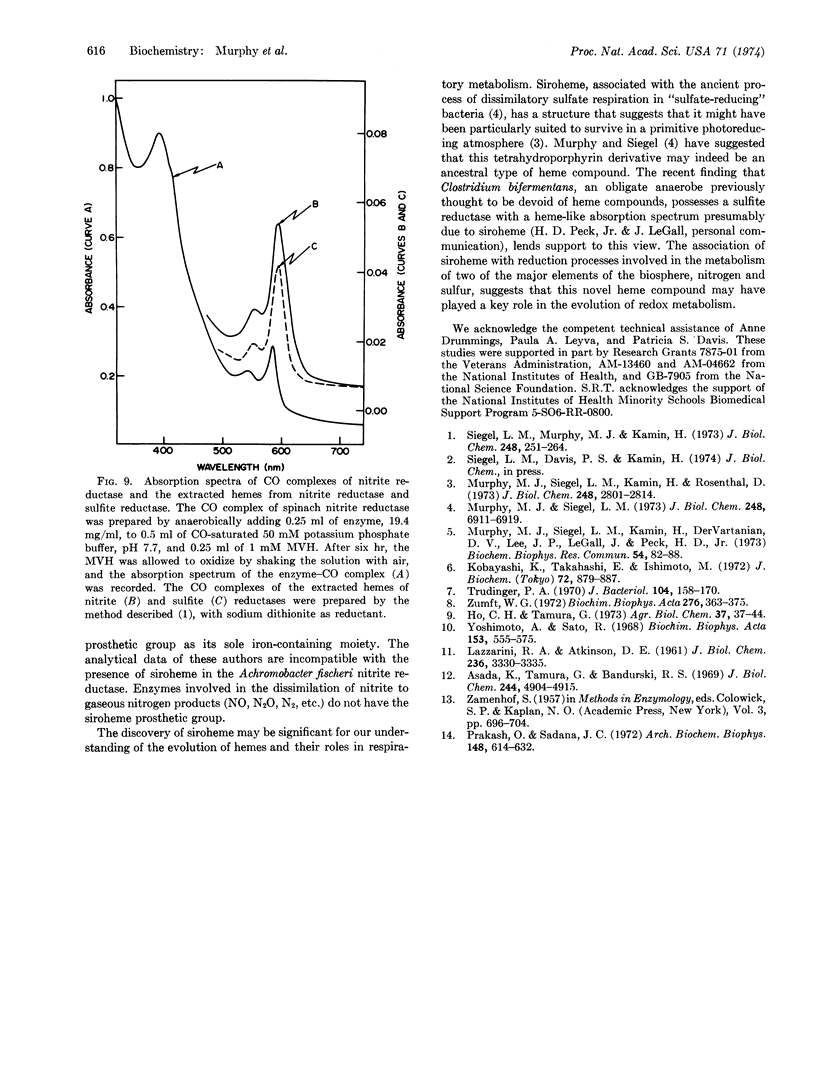
Abstract
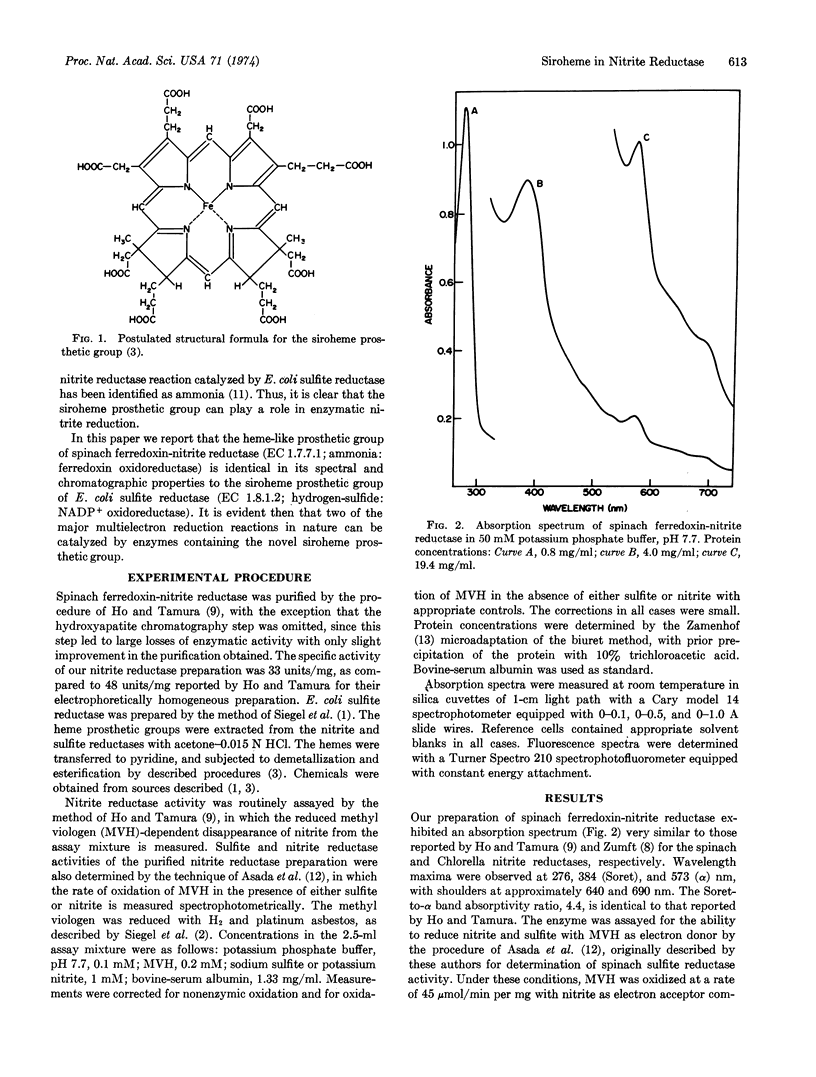
Ferredoxin-nitrite reductase (EC 1.7.7.1) of spinach, an enzyme that catalyzes the six-electron reduction of nitrite to ammonia, contains siroheme, the new type of prosthetic group recently found in several sulfite reductases (both assimilatory and dissimilatory) that can catalyze the reduction of sulfite to sulfide, also a six-electron reduction. The prosthetic group of sulfite reductase had previously been shown to be an iron-tetrahydroporphyrin of the isobacteriochlorin type (adjacent pyrrole rings reduced) with eight carboxylate side chains. This finding suggests that both types of “multi-electron” reduction processes may share common mechanistic features.
Keywords: heme proteins, biochemical evolution, spinach ferredoxin-nitrite reductase, E. coli NADPH-sulfate reductase
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asada K., Tamura G., Bandurski R. S. Methyl viologen-linked sulfite reductase from spinach leaves. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):4904–4915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Takahashi E., Ishimoto M. Biochemical studies on sulfate-reducing bacteria. XI. Purification and some properties of sulfite reductase, desulfoviridin. J Biochem. 1972 Oct;72(4):879–887. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAZZARINI R. A., ATKINSON D. E. A triphosphopyridine nucleotide-specific nitrite reductase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3330–3335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. J., Siegel L. M., Kamin H., DerVartanian D. V., Lee J. P., LeGall J., Peck H. D., Jr An iron tetrahydroporphyrin prosthetic group common to both assimilatory and dissimilatory sulfite reductases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 5;54(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90891-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. J., Siegel L. M., Kamin H., Rosenthal D. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. II. Identification of a new class of heme prosthetic group: an iron-tetrahydroporphyrin (isobacteriochlorin type) with eight carboxylic acid groups. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2801–2814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. J., Siegel L. M. Siroheme and sirohydrochlorin. The basis for a new type of porphyrin-related prosthetic group common to both assimilatory and dissimilatory sulfite reductases. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6911–6919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash O. M., Sadana J. C. Purification, characterization and properties of nitrite reductase of Achromobacter fischeri. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):614–632. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Murphy M. J., Kamin H. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. I. The Escherichia coli hemoflavoprotein: molecular parameters and prosthetic groups. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):251–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudinger P. A. Carbon monoxide-reacting pigment from Desulfotomaculum nigrificans and its possible relevance to sulfite reduction. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):158–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.158-170.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto A., Sato R. Studies on yeast sulfite reductase. I. Purification and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 2;153(3):555–575. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G. Ferredoxin:nitrite oxidoreductase from Chlorella. Purification and properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 28;276(2):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90996-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


