Abstract
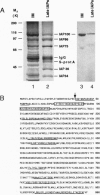
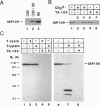
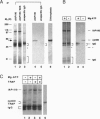
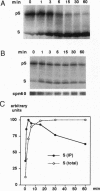
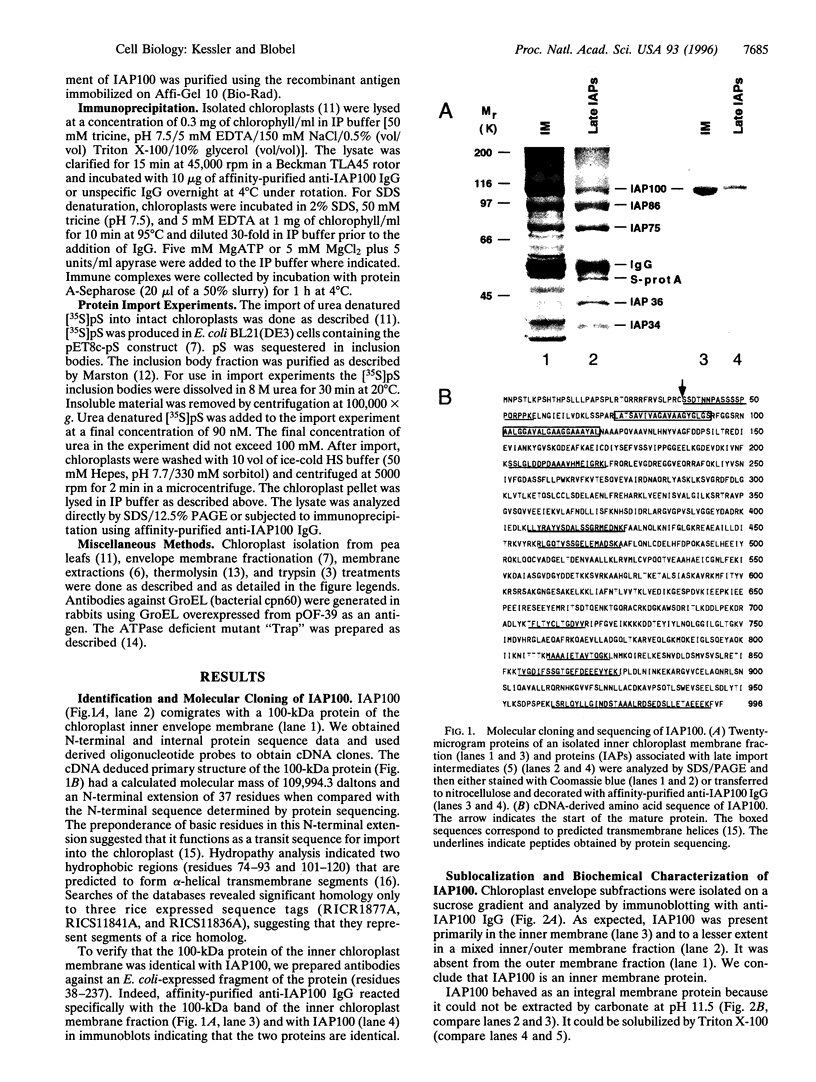
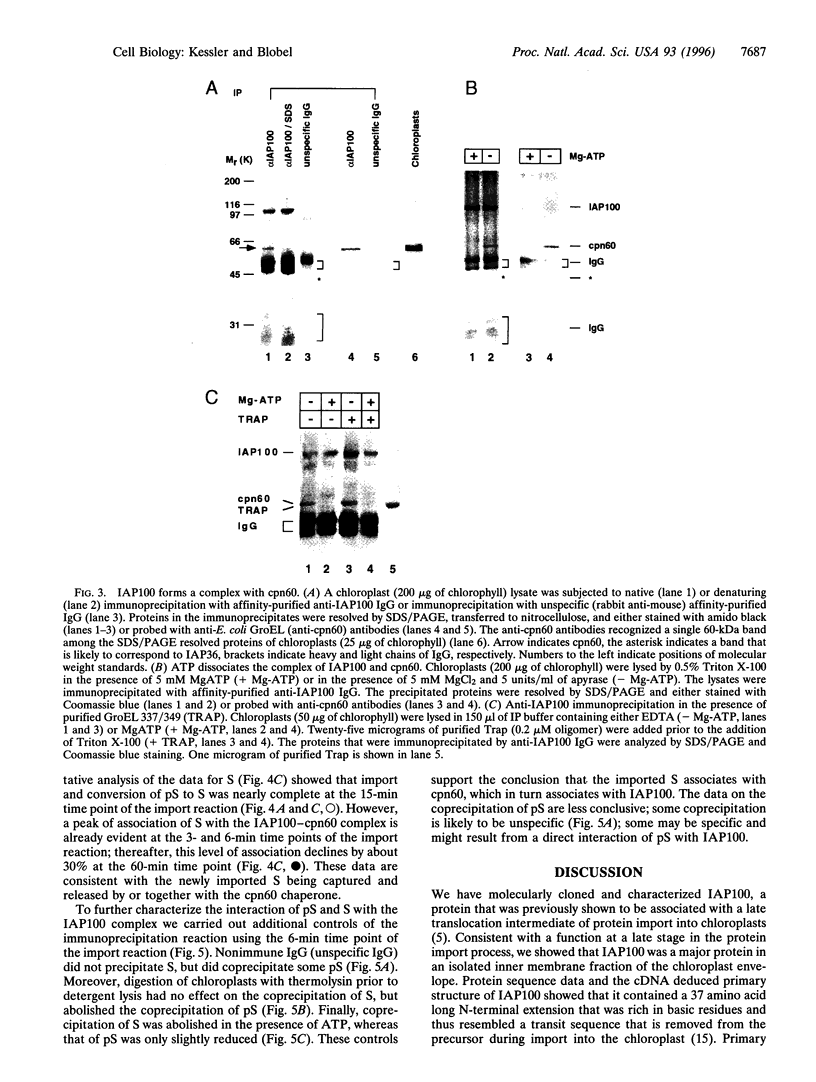
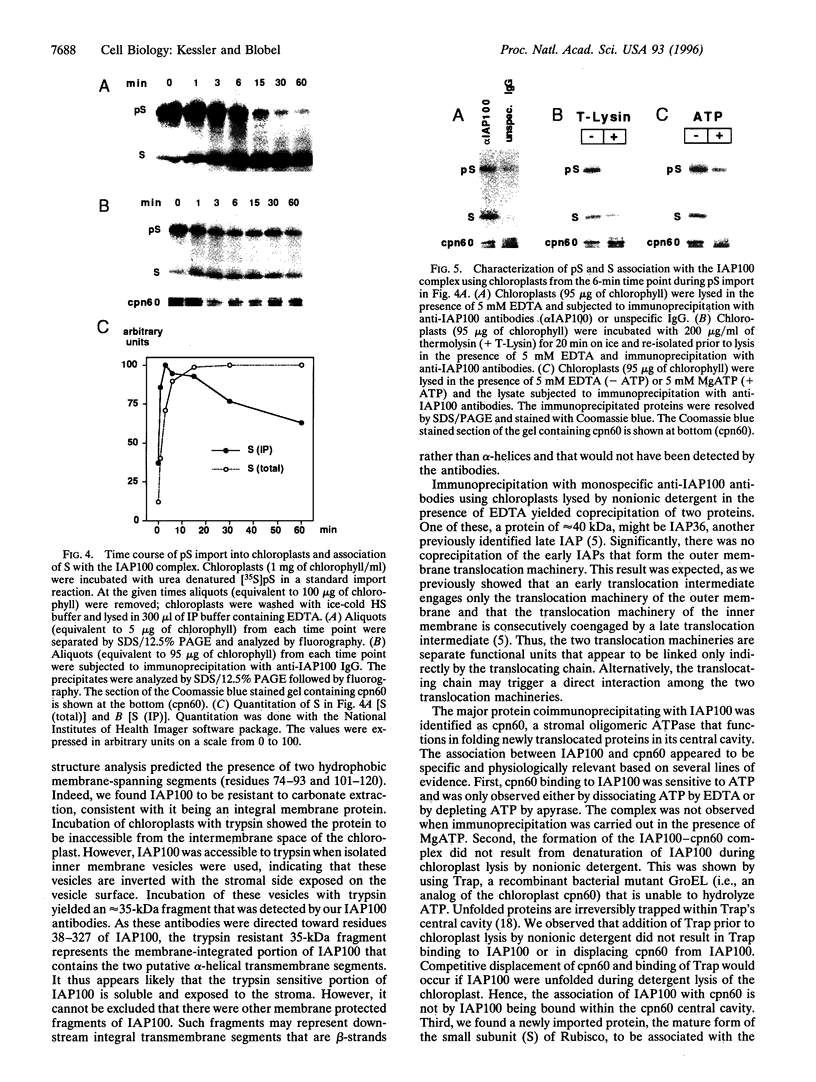
We report the molecular cloning of import intermediate associated protein (IAP) 100, a 100-kDa protein of the chloroplast protein import machinery of peas. IAP100 contains two potential alpha-helical transmembrane segments and also behaves like an integral membrane protein. It was localized to the inner chloroplast envelope membrane. Immunoprecipitation experiments using monospecific anti-IAP100 antibodies and a nonionic detergent-generated chloroplast lysate gave the following results. (i) The four integral membrane proteins of the outer chloroplast import machinery were not coprecipitated with IAP100 indicating that the inner and outer membrane import machineries are not coupled in isolated chloroplasts. (ii) the major protein that coprecipitated with IAP100 was identified as stromal chaperonin 60 (cpn60); the association of IAP100 and cpn60 was specific and was abolished when immunoprecipitation was carried out in the presence of ATP. (iii) In a lysate from chloroplasts that had been preincubated for various lengths of time in an import reaction with radiolabeled precursor (pS) of the small subunit of Rubisco, we detected coimmunoprecipitation of IAP100, cpn60, and the imported mature form (S) of precursor. Relative to the time course of import, coprecipitation of S first increased and then decreased, consistent with a transient association of the newly imported S with the chaperonin bound to IAP100. These data suggest that IAP100 serves in recruiting chaperonin for folding of newly imported proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Werner-Washburne M., Andrews J., Keegstra K. Thermolysin is a suitable protease for probing the surface of intact pea chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):675–678. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., Hemmingsen S. M. Molecular chaperones: proteins essential for the biogenesis of some macromolecular structures. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Aug;14(8):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. C., Row P. E. Protein translocation across chloroplast envelope membranes. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;5(6):243–247. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)89018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Purification and properties of groE, a host protein involved in bacteriophage assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler F., Blobel G., Patel H. A., Schnell D. J. Identification of two GTP-binding proteins in the chloroplast protein import machinery. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1035–1039. doi: 10.1126/science.7973656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayhew M., da Silva A. C., Martin J., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Hartl F. U. Protein folding in the central cavity of the GroEL-GroES chaperonin complex. Nature. 1996 Feb 1;379(6564):420–426. doi: 10.1038/379420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain D., Blobel G. Protein import into chloroplasts requires a chloroplast ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3288–3292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell D. J., Blobel G. Identification of intermediates in the pathway of protein import into chloroplasts and their localization to envelope contact sites. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):103–115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell D. J., Blobel G., Pain D. Signal peptide analogs derived from two chloroplast precursors interact with the signal recognition system of the chloroplast envelope. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3335–3342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell D. J., Blobel G., Pain D. The chloroplast import receptor is an integral membrane protein of chloroplast envelope contact sites. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):1825–1838. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell D. J., Kessler F., Blobel G. Isolation of components of the chloroplast protein import machinery. Science. 1994 Nov 11;266(5187):1007–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.7973649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell D. J. Shedding light on the chloroplast protein import machinery. Cell. 1995 Nov 17;83(4):521–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman J. S., Kashi Y., Fenton W. A., Horwich A. L. GroEL-mediated protein folding proceeds by multiple rounds of binding and release of nonnative forms. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):693–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90533-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Steppuhn J., Herrmann R. G. Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):535–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]