Abstract
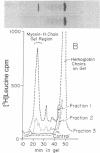
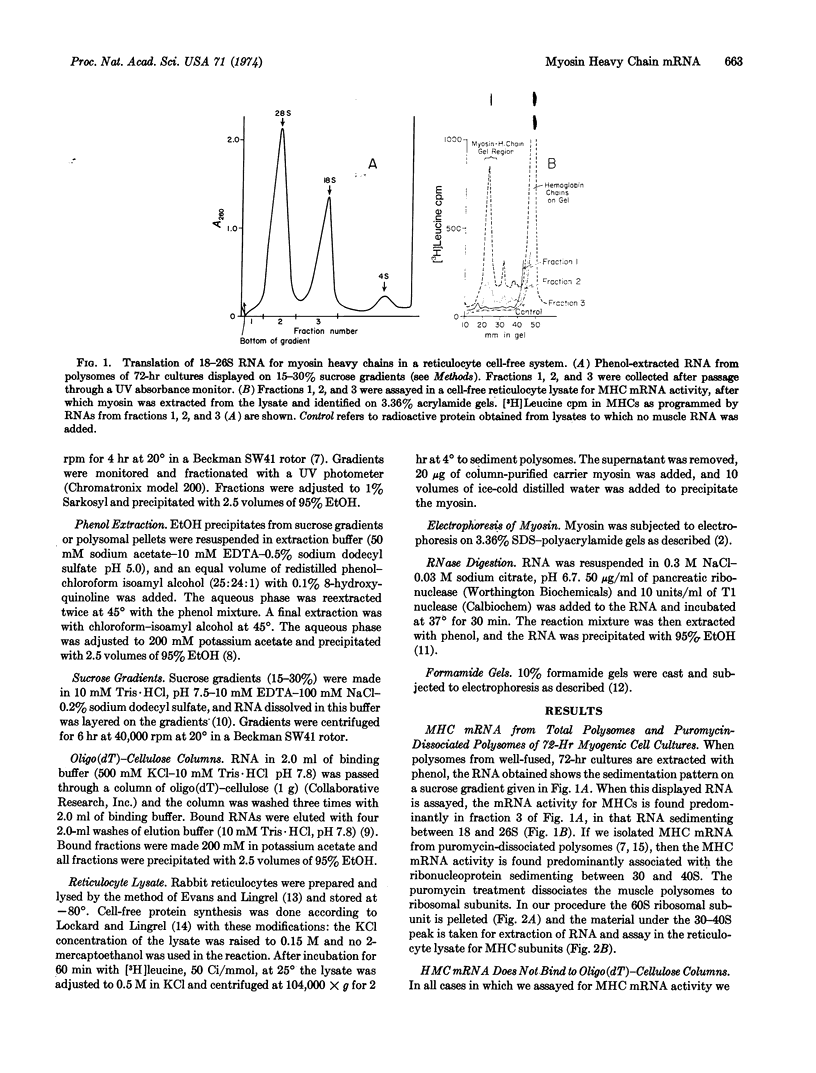
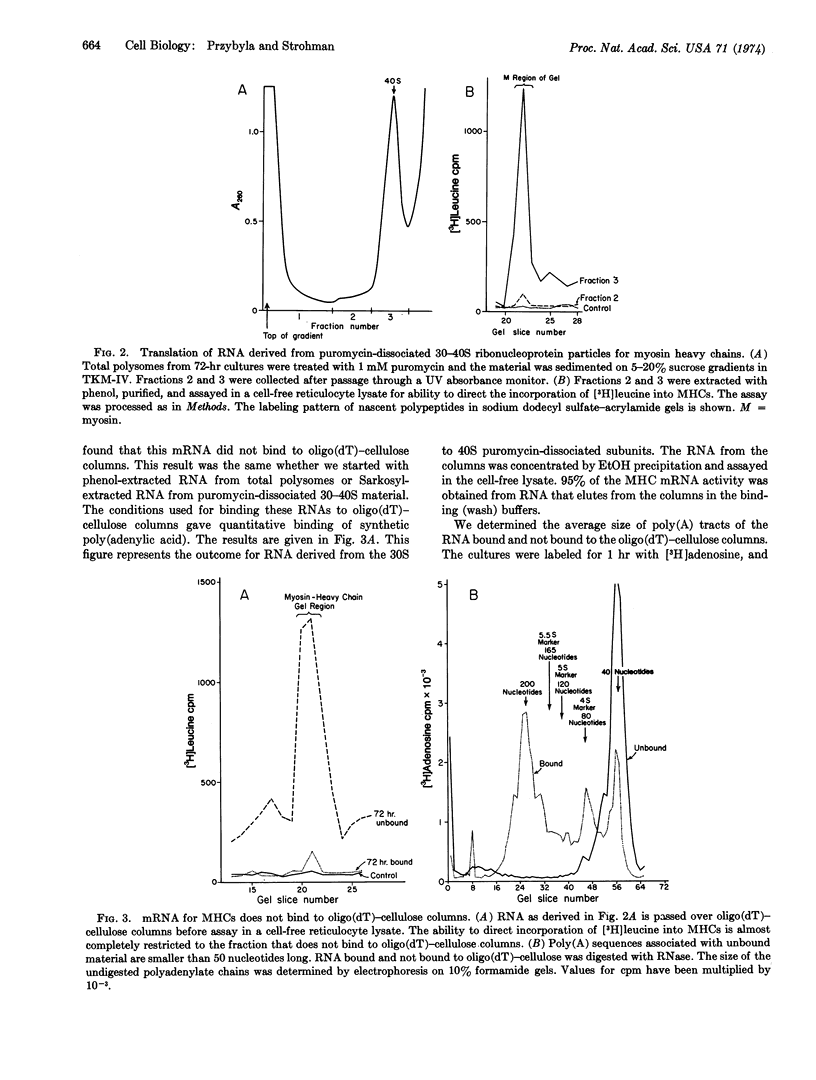
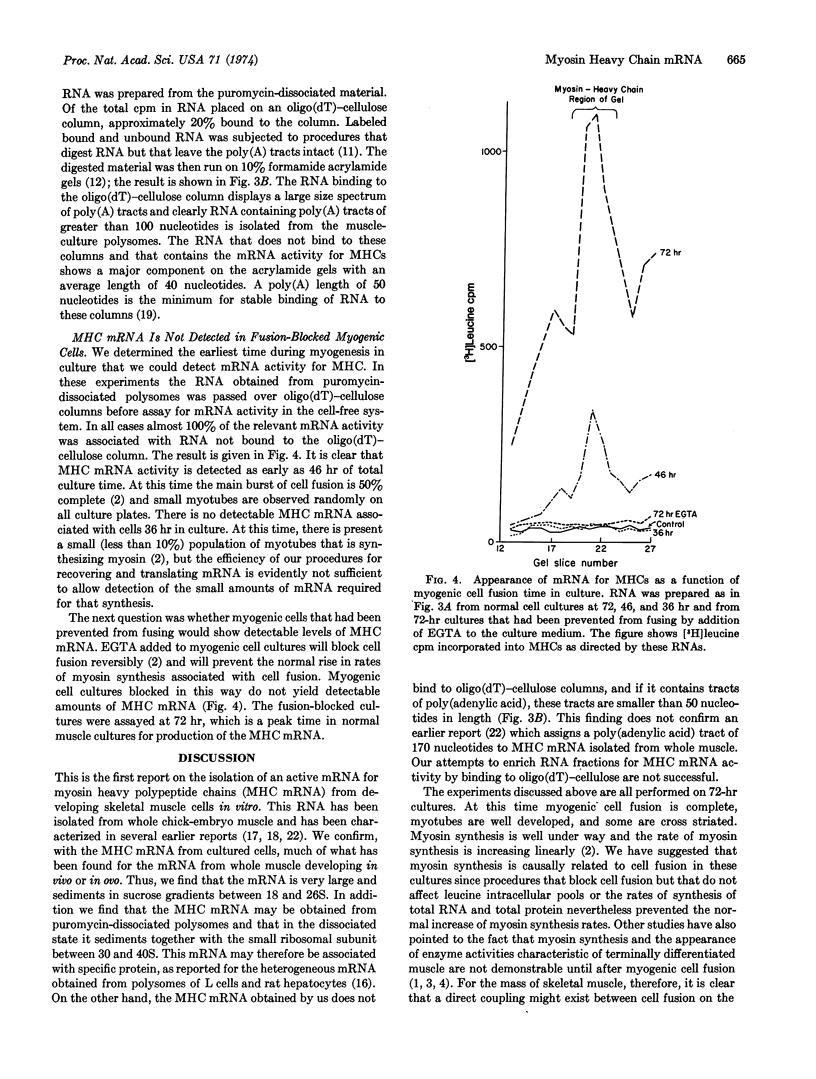
The appearance of messenger RNA for myosin heavy chains in chick-embryo myogenic cell cultures was investigated. Total polyribosomes were isolated from cultures at various times of development and were purified in sucrose step gradients. These polysomes were either extracted with phenol or were treated with puromycin. The ribonucleoprotein particles and ribosomal subunits released by puromycin were fractionated on sucrose gradients. RNA from polysomes or from puromycin-dissociated subunits was fractionated on oligo(dT)-cellulose columns, and the bound and unbound RNA was assayed for activity of myosin heavy chain messenger RNA in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free system. RNA stimulating myosin heavy-chain synthesis was found predominantly in the unbound fractions of the oligo(dT)-cellulose columns. After puromycin treatment of polysomes, the myosin heavy chain messenger RNA, which sediments at 18-26 S, was associated with a ribonucleoprotein particle sedimenting between 30 and 40 S. Myosin heavy chain messenger RNA was obtained from cultures containing well-developed myotubes and from cultures undergoing myogenic cell fusion. This messenger RNA was not detectable in early, unfused cultures, or in later cultures in which myogenic cell fusion had been prevented by treatment with ethyleneglycol bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N′-tetraacetic acid. These experiments demonstrate that messenger RNA for myosin heavy chains becomes associated with ribosomes only after myogenic cell fusion has begun.
Keywords: oligo(dT)-cellulose, poly(A), reticulocyte lysate, chick embryo
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN E. R., PEPE F. A. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF DEVELOPING MUSCLE CELLS IN THE CHICK EMBRYO. Am J Anat. 1965 Jan;116:115–147. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001160107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I., Wilt F. H., Wartiovaara J. Characterization of pulse-labeled nuclear RNA in sea urchin embryos. Exp Cell Res. 1972 May;72(1):309–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90592-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. A protein of molecular weight 78,000 bound to the polyadenylate region of eukaryotic messenger RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):924–928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Release, identification, and isolation of messenger RNA from mammalian ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):832–835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Sabatini D. Dissociation of mammalian polyribosomes into subunits by puromycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):390–394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. R., Coleman A. W. Muscle differentiation and macromolecular synthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2 Suppl):19–34. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Lingrel J. B. Hemoglobin messenger ribonucleic acid. Distribution of the 9S ribonucleic acid in polysomes of different sizes. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):829–831. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood S. M., Nwagwu M. Partial characterization of presumptive myosin messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1969 Sep;8(9):3839–3845. doi: 10.1021/bi00837a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Lingrel J. B. The synthesis of mouse hemoglobin beta-chains in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free system programmed with mouse reticulocyte 9S RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 8;37(2):204–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90720-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M., Strohman R. C. Changes in DNA polymerase activity associated with cell fusion in cultures of embryonic muscle. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Feb;73(1):61–68. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040730109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B., Prives J. Appearance of acetylcholine receptor in differentiating cultures of embryonic chick breast muscle. J Cell Biol. 1973 Oct;59(1):241–245. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B., Strohman R. C. Myosin synthesis in cultures of differentiating chicken embryo skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1972 Oct;29(2):113–138. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainberg A., Yagil G., Yaffe D. Alterations of enzymatic activities during muscle differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1971 May;25(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staynov D. Z., Pinder J. C., Gratzer W. B. Molecular weight determination of nucleic acids by gel electrophoresis in non-aqueous solution. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 26;235(56):108–110. doi: 10.1038/newbio235108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan N., Roberts W. K. Characterization and poly(adenylic acid) content of Ehrlich ascites cell ribonucleic acids fractionated on unmodified cellulose columns. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 19;12(13):2395–2403. doi: 10.1021/bi00737a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilt F. H. Polyadenylation of maternal RNA of sea urchin eggs after fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2345–2349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Developmental changes preceding cell fusion during muscle differentiation in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1971 May;66(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]