Abstract
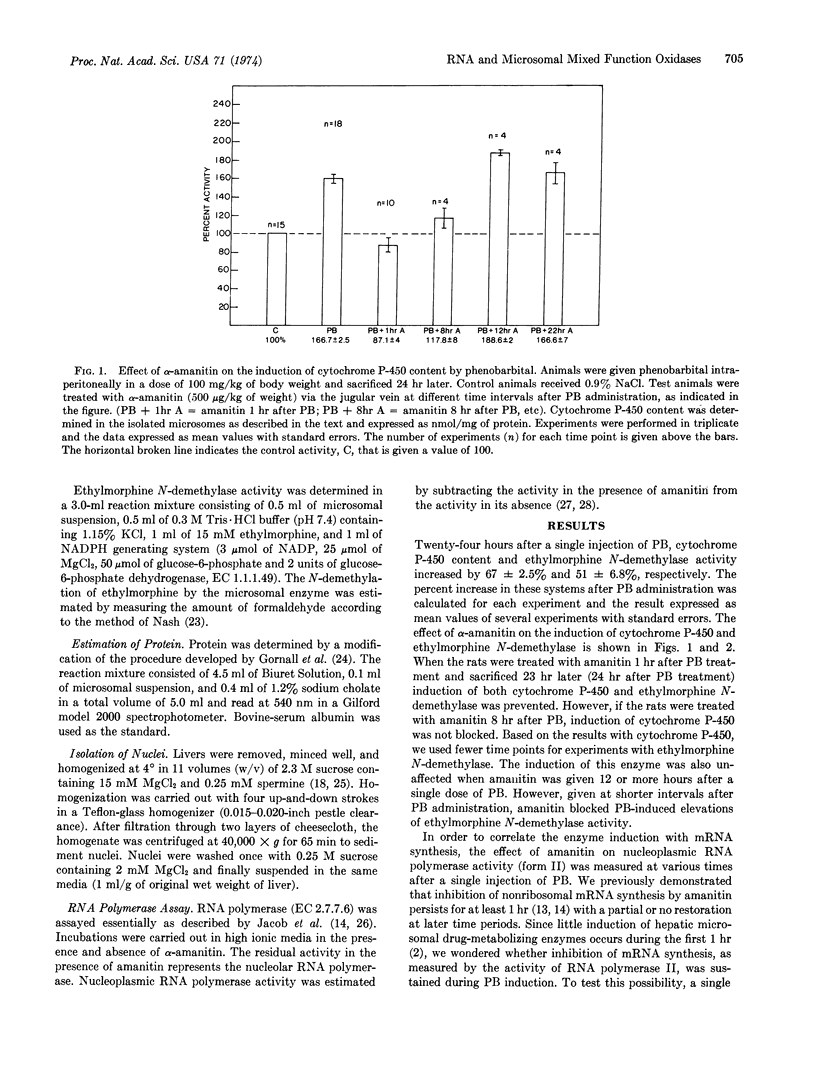
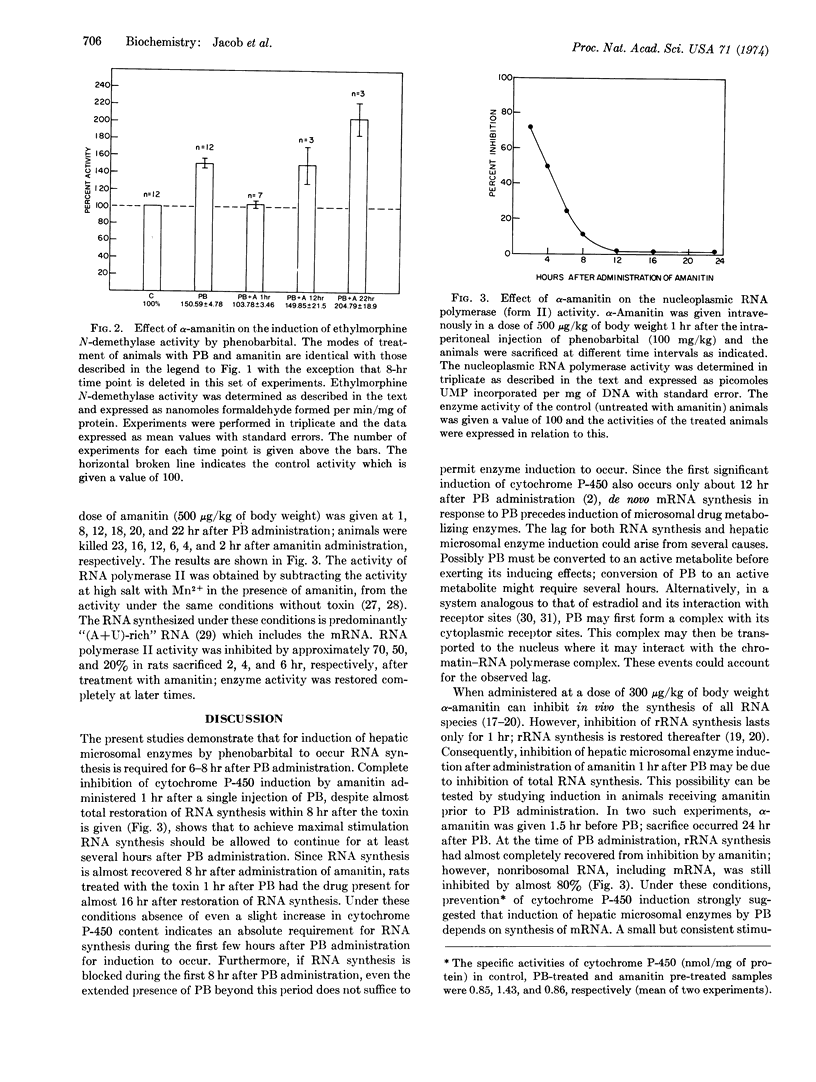
Induction of hepatic microsomal cytochrome P-450 and ethylmorphine N-demethylase activity by phenobarbital requires de novo synthesis of mRNA. Inhibition of RNA synthesis by α-amanitin given up to 8 hr after phenobarbital administration substantially inhibits this induction. However, beyond 8 hr after phenobarbital administration, RNA synthesis is not required for induction of these hepatic microsomal systems. Thus, mRNAs for cytochrome P-450 and ethylmorphine N-demethylase appear to be stable. Furthermore, these experiments reveal that the lag period for RNA synthesis approximates the length of the lag period for induction of the hepatic microsomal enzyme systems.
Keywords: α-amanitin, RNA polymerase, phenobarbital, microsomal enzymes
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busch H., Narayan K. S., Hamilton J. Isolation of nucleoli in a medium containing spermine and magnesium acetate. Exp Cell Res. 1967 Aug;47(1):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Baxter L., Lodish H. F. Actinomycin D and the regulation of enzyme biosynthesis during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):315–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARREN L. D., HOWELL R. R., TOMKINS G. M., CROCCO R. M. A PARADOXICAL EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D: THE MECHANISM OF REGULATION OF ENZYME SYNTHESIS BY HYDROCORTISONE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1121–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Muecke W., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Evidence for extranucleolar control of RNA synthesis in the nucleolus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 27;40(2):334–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Different responses of soluble whole nuclear RNA polymerase and soluble nucleolar RNA polymerase to divalent cations and to inhibition by alpha-amanitin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Feb 20;38(4):765–770. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90647-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Regulation of nucleolar RNA metabolism by hydrocortisone. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):449–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob S. T., Sajdel E. M., Munro H. N. Specific action of alpha-amanitin on mammalian RNA polymerase protein. Nature. 1970 Jan 3;225(5227):60–62. doi: 10.1038/225060b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Mohla S., Gorell T., Tanaka S., DeSombre E. R. Estrophile to nucleophile in two easy steps. J Steroid Biochem. 1972 Apr;3(3):445–458. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(72)90091-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur Paul, Labrie Fernand. Induction of rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase by dibutyryl cyclic AMP and its inhibition by actinomycin D and alpha-Amanitin. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 15;17(1):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80583-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gniazdowski M., Mandel J. L., Jr, Gissinger F., Chambon P. Alpha-amanitin: a specific inhibitor of one of two DNA-pendent RNA polymerase activities from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellermann G., Luyten-Kellermann M., Shaw C. R. Genetic variation of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in human lymphocytes. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 May;25(3):327–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohla S., DeSombre E. R., Jensen E. V. Tissue-specific stimulation of RNA synthesis by transformed estradiol-receptor complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):661–667. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):416–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0550416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niessing J., Schnieders B., Kunz W., Seifart K. H., Sekeris C. E. Inhibition of RNA synthesis by alpha-amanitin in vivo. Z Naturforsch B. 1970 Oct;25(10):1119–1125. doi: 10.1515/znb-1970-1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novello F., Stirpe F. Simultaneous assay of RNA polymerase I and II in nuclei isolated from resting and growing rat liver with the use of alpha-amanitin. FEBS Lett. 1970 May 11;8(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMURA T., SATO R. THE CARBON MONOXIDE-BINDING PIGMENT OF LIVER MICROSOMES. I. EVIDENCE FOR ITS HEMOPROTEIN NATURE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2370–2378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P. THE CELLULAR SITES OF SYNTHESIS OF RIBOSOMAL AND 4S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec;48(12):2179–2186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Tomkins G. M. Effect of inhibitors of nucleic acid synthesis on steroid-mediated induction of tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. S., Garofalo M. Degradation of RNA in liver of rats treated with actinomycin D. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 Jan;3(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz H. S., Sodergren J. E., Sternberg S. S., Philips F. S. Actinomycin D: effects on Ridgway osteogenic sarcoma in mice. Cancer Res. 1966 Sep;26(9):1873–1879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekeris C. E., Niessing J., Seifart K. H. Inhibition by alpha-amanitin of induction of tyrosine transaminase in rat liver by cortisol. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jul 29;9(2):103–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80324-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R. H., Penman S. Messenger RNA in HeLa cells: kinetics of formation and decay. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 5;78(2):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Hill R. N., Gleeson R. A., Vesell E. S. Evidence for post-transcriptional stabilization of ribosomal precursor ribonucleic acid by phenobarbital. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Nov;8(6):691–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. A., Farber E. The rapid acceleration of hepatic nuclear ribonucleic acid breakdown by actinomycin but not by ethionine. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4479–4485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stripp B., Greene F. E., Gillette J. R. Disulfiram impairment of drug metabolism by rat liver microsomes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Dec;170(2):347–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R., Hamilton M. J., Shields D. Effects of alpha-amanitin in vivo on RNA polymerase and nuclear RNA synthesis. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 9;238(84):161–164. doi: 10.1038/newbio238161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesell E. S., Page J. G. Genetic control of the phenobarbital-induced shortening of plasma antipyrine half-lives in man. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2202–2209. doi: 10.1172/JCI106186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. G., Wortham J. S., Gelboin H. V. The effect of methylcholanthrene, phenobarbital and aflatoxin on RNA polymerase of rat liver. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1967;5:385–395. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(67)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber E. A., Penman S. Products of RNA polymerases in HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2861–2865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


