Abstract
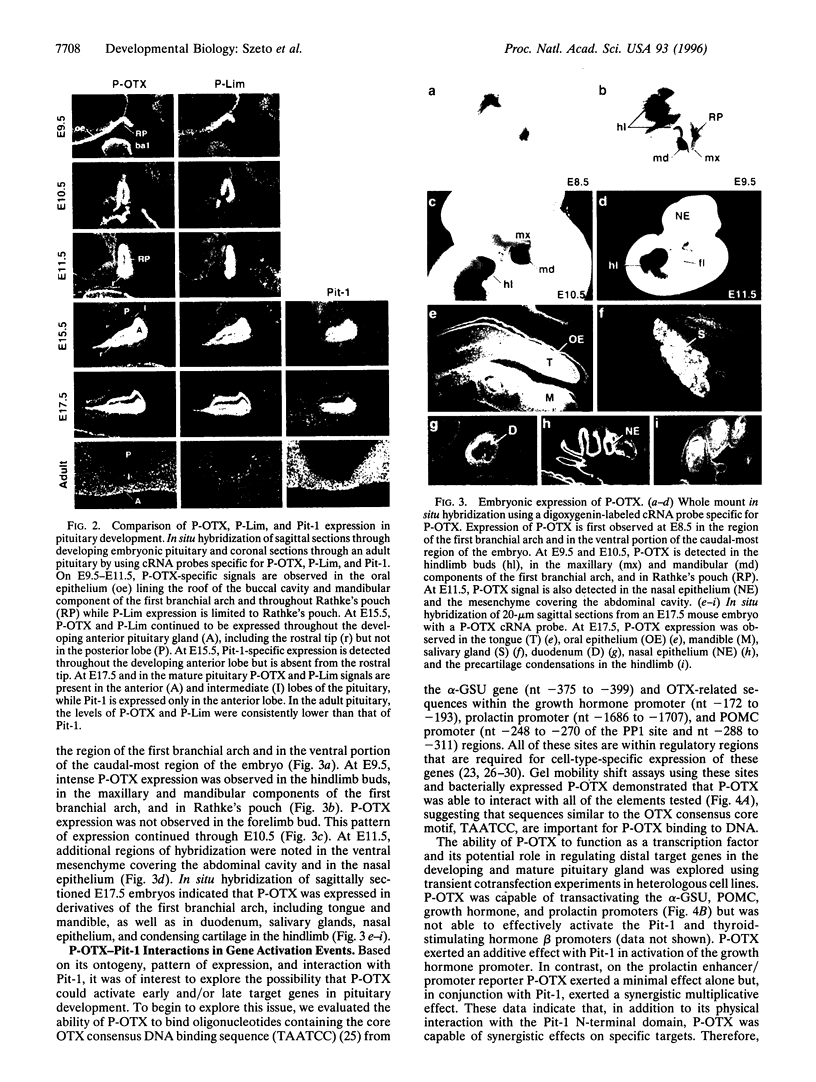
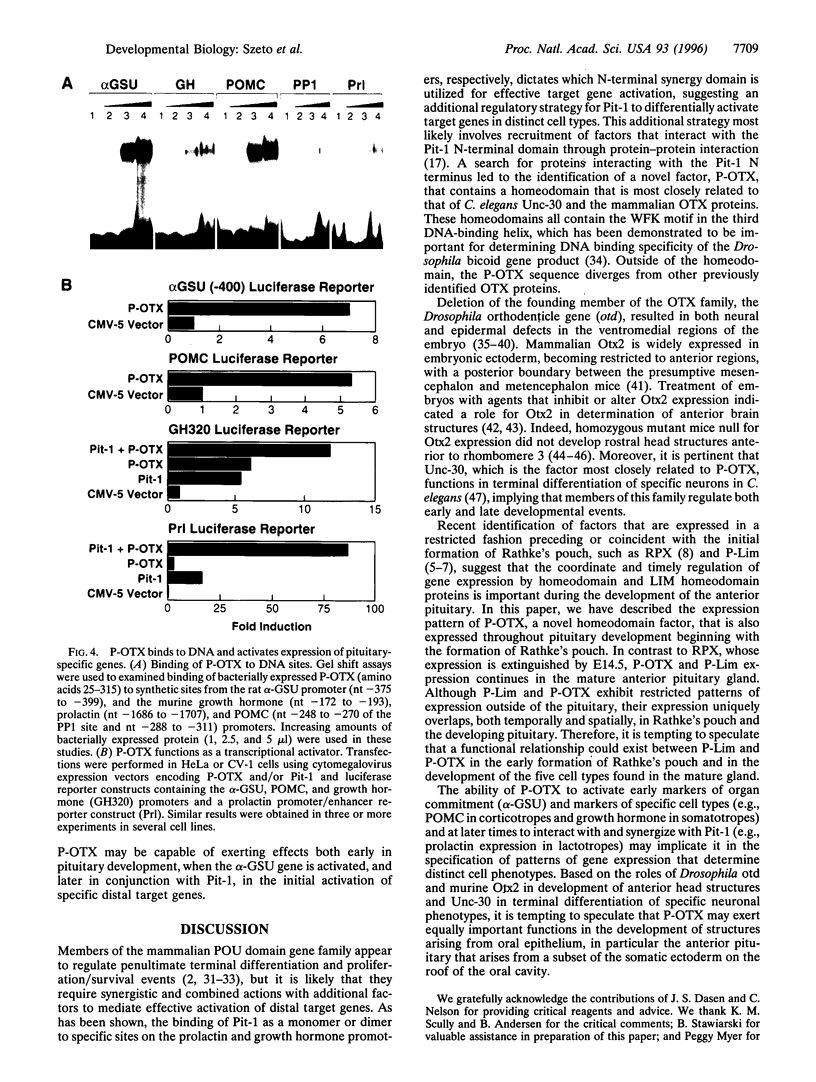
A novel OTX-related homeodomain transcription factor has been identified on the basis of its ability to interact with the transactivation domain of the pituitary-specific POU domain protein, Pit-1. This factor, referred to as P-OTX (pituitary OTX-related factor), is expressed in primordial Rathke's pouch, oral epithelium, first bronchial arch, duodenum, and hindlimb. In the developing anterior pituitary, it is expressed in all regions from which cells with distinct phenotypes will emerge in the mature gland. P-OTX is able to independently activate and to synergize with Pit-1 on pituitary-specific target gene promoters. Therefore, P-OTX may subserve functions in generating both precursor and specific cell phenotypes in the anterior pituitary gland and in several other organs.
Full text
PDF
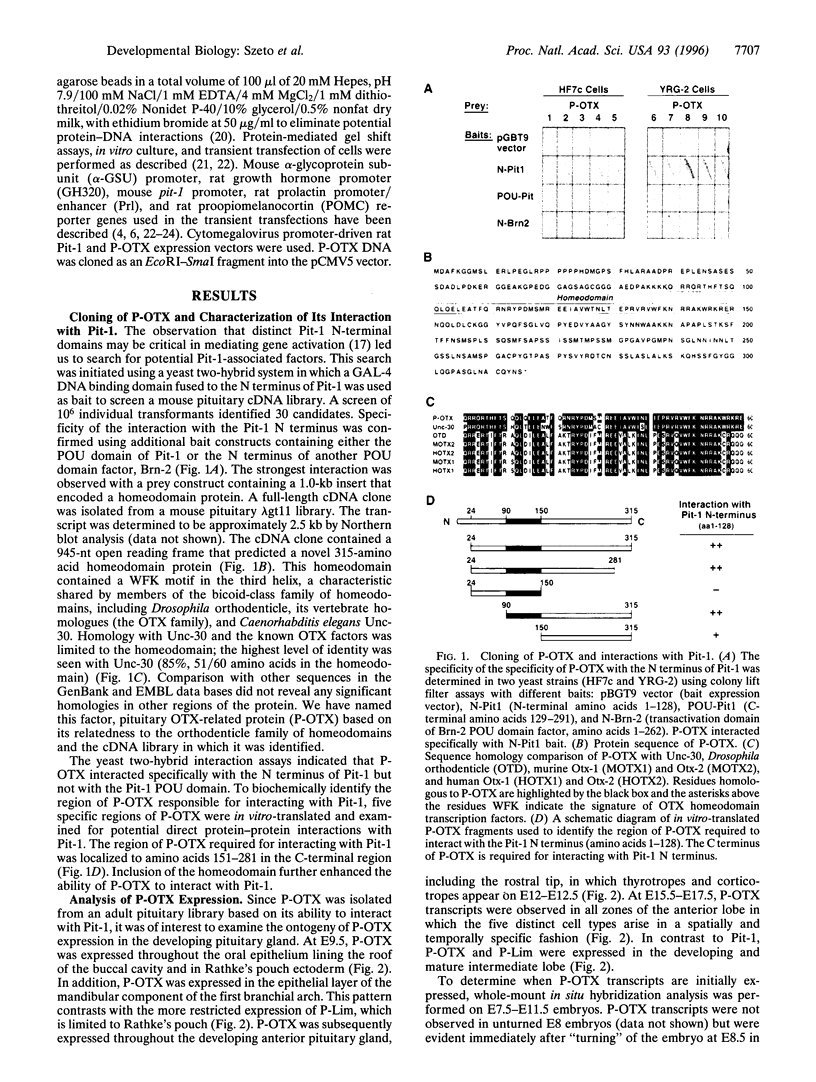

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acampora D., Mazan S., Lallemand Y., Avantaggiato V., Maury M., Simeone A., Brûlet P. Forebrain and midbrain regions are deleted in Otx2-/- mutants due to a defective anterior neuroectoderm specification during gastrulation. Development. 1995 Oct;121(10):3279–3290. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.10.3279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen B., Rosenfeld M. G. Pit-1 determines cell types during development of the anterior pituitary gland. A model for transcriptional regulation of cell phenotypes in mammalian organogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29335–29338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ang S. L., Jin O., Rhinn M., Daigle N., Stevenson L., Rossant J. A targeted mouse Otx2 mutation leads to severe defects in gastrulation and formation of axial mesoderm and to deletion of rostral brain. Development. 1996 Jan;122(1):243–252. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach I., Rhodes S. J., Pearse R. V., 2nd, Heinzel T., Gloss B., Scully K. M., Sawchenko P. E., Rosenfeld M. G. P-Lim, a LIM homeodomain factor, is expressed during pituitary organ and cell commitment and synergizes with Pit-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2720–2724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camper S. A., Saunders T. L., Katz R. W., Reeves R. H. The Pit-1 transcription factor gene is a candidate for the murine Snell dwarf mutation. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):586–590. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Karvelas M., Nossal G. J., Ye Z. S., Jacks T., Baltimore D. Oct-2, although not required for early B-cell development, is critical for later B-cell maturation and for postnatal survival. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):570–582. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Kalla K., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Cell-specific expression of the prolactin gene in transgenic mice is controlled by synergistic interactions between promoter and enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):959–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R., Perrimon N. The orthodenticle gene is regulated by bicoid and torso and specifies Drosophila head development. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):485–488. doi: 10.1038/346485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R., Smouse D., Capaci T. M., Spradling A. C., Perrimon N. The orthodenticle gene encodes a novel homeo domain protein involved in the development of the Drosophila nervous system and ocellar visual structures. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1516–1527. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrero M. R., McEvilly R. J., Turner E., Lin C. R., O'Connell S., Jenne K. J., Hobbs M. V., Rosenfeld M. G. Brn-3.0: a POU-domain protein expressed in the sensory, immune, and endocrine systems that functions on elements distinct from known octamer motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10841–10845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey P., Rahal J. O., Beamer W. G., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Mayo K. E. GHRH receptor of little mice contains a missense mutation in the extracellular domain that disrupts receptor function. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):227–232. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanes S. D., Brent R. DNA specificity of the bicoid activator protein is determined by homeodomain recognition helix residue 9. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1275–1283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermesz E., Mackem S., Mahon K. A. Rpx: a novel anterior-restricted homeobox gene progressively activated in the prechordal plate, anterior neural plate and Rathke's pouch of the mouse embryo. Development. 1996 Jan;122(1):41–52. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirth F., Therianos S., Loop T., Gehring W. J., Reichert H., Furukubo-Tokunaga K. Developmental defects in brain segmentation caused by mutations of the homeobox genes orthodenticle and empty spiracles in Drosophila. Neuron. 1995 Oct;15(4):769–778. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway J. M., Szeto D. P., Scully K. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. Pit-1 binding to specific DNA sites as a monomer or dimer determines gene-specific use of a tyrosine-dependent synergy domain. Genes Dev. 1995 Aug 15;9(16):1992–2006. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.16.1992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y., Hoskins R., Horvitz H. R. Control of type-D GABAergic neuron differentiation by C. elegans UNC-30 homeodomain protein. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):780–783. doi: 10.1038/372780a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klämbt C., Jacobs J. R., Goodman C. S. The midline of the Drosophila central nervous system: a model for the genetic analysis of cell fate, cell migration, and growth cone guidance. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):801–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90509-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J. S., Herr W. Ethidium bromide provides a simple tool for identifying genuine DNA-independent protein associations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6958–6962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Rawson E. J., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Dwarf locus mutants lacking three pituitary cell types result from mutations in the POU-domain gene pit-1. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):528–533. doi: 10.1038/347528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. C., Li S., Drolet D. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Pituitary ontogeny of the Snell dwarf mouse reveals Pit-1-independent and Pit-1-dependent origins of the thyrotrope. Development. 1994 Mar;120(3):515–522. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.3.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lira S. A., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Glass C. K., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Identification of rat growth hormone genomic sequences targeting pituitary expression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4755–4759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu B., Mortrud M., Low M. J. DNA elements with AT-rich core sequences direct pituitary cell-specific expression of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene in transgenic mice. Biochem J. 1995 Dec 15;312(Pt 3):827–832. doi: 10.1042/bj3120827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie A., Ferguson M. W., Sharpe P. T. Hox-7 expression during murine craniofacial development. Development. 1991 Oct;113(2):601–611. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.2.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangalam H. J., Albert V. R., Ingraham H. A., Kapiloff M., Wilson L., Nelson C., Elsholtz H., Rosenfeld M. G. A pituitary POU domain protein, Pit-1, activates both growth hormone and prolactin promoters transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):946–958. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C. A., Gan L., Klein W. H. Multiple Otx binding sites required for expression of the Strongylocentrotus purpuratus Spec2a gene. Dev Biol. 1994 Sep;165(1):229–242. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo I., Kuratani S., Kimura C., Takeda N., Aizawa S. Mouse Otx2 functions in the formation and patterning of rostral head. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 1;9(21):2646–2658. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai S., Kawano H., Yudate T., Nishi M., Kuno J., Nagata A., Jishage K., Hamada H., Fujii H., Kawamura K. The POU domain transcription factor Brn-2 is required for the determination of specific neuronal lineages in the hypothalamus of the mouse. Genes Dev. 1995 Dec 15;9(24):3109–3121. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.24.3109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver G., Mailhos A., Wehr R., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Gruss P. Six3, a murine homologue of the sine oculis gene, demarcates the most anterior border of the developing neural plate and is expressed during eye development. Development. 1995 Dec;121(12):4045–4055. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.12.4045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannese M., Polo C., Andreazzoli M., Vignali R., Kablar B., Barsacchi G., Boncinelli E. The Xenopus homologue of Otx2 is a maternal homeobox gene that demarcates and specifies anterior body regions. Development. 1995 Mar;121(3):707–720. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.3.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Püschel A. W., Gruss P., Westerfield M. Sequence and expression pattern of pax-6 are highly conserved between zebrafish and mice. Development. 1992 Mar;114(3):643–651. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.3.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Chen R., DiMattia G. E., Scully K. M., Kalla K. A., Lin S. C., Yu V. C., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific enhancer confers Pit-1-dependent morphogen inducibility and autoregulation on the pit-1 gene. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):913–932. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonemann M. D., Ryan A. K., McEvilly R. J., O'Connell S. M., Arias C. A., Kalla K. A., Li P., Sawchenko P. E., Rosenfeld M. G. Development and survival of the endocrine hypothalamus and posterior pituitary gland requires the neuronal POU domain factor Brn-2. Genes Dev. 1995 Dec 15;9(24):3122–3135. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.24.3122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Barale J. C., Marcinkiewicz M., Mattei M. G., Day R., Chrétien M. The mouse homeoprotein mLIM-3 is expressed early in cells derived from the neuroepithelium and persists in adult pituitary. DNA Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;13(12):1163–1180. doi: 10.1089/dna.1994.13.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Gulisano M., Stornaiuolo A., Boncinelli E. Nested expression domains of four homeobox genes in developing rostral brain. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):687–690. doi: 10.1038/358687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Avantaggiato V., Moroni M. C., Mavilio F., Arra C., Cotelli F., Nigro V., Acampora D. Retinoic acid induces stage-specific antero-posterior transformation of rostral central nervous system. Mech Dev. 1995 May;51(1):83–98. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(95)96241-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. M., Voss J. W., Ingraham H. A., Holloway J. M., Broide R. S., Rosenfeld M. G., Swanson L. W. Pituitary cell phenotypes involve cell-specific Pit-1 mRNA translation and synergistic interactions with other classes of transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):695–711. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slabaugh M. B., Lieberman M. E., Rutledge J. J., Gorski J. Growth hormone and prolactin synthesis in normal and homozygous Snell and Ames dwarf mice. Endocrinology. 1981 Oct;109(4):1040–1046. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-4-1040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therrien M., Drouin J. Cell-specific helix-loop-helix factor required for pituitary expression of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2342–2353. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therrien M., Drouin J. Pituitary pro-opiomelanocortin gene expression requires synergistic interactions of several regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3492–3503. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. Q., Johnson B. V., Rathjen J., Rathjen P. D. Sequence, genomic organization, and expression of the novel homeobox gene Hesx1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):3869–3875. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.3869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay Y., Tretjakoff I., Peterson A., Antakly T., Zhang C. X., Drouin J. Pituitary-specific expression and glucocorticoid regulation of a proopiomelanocortin fusion gene in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8890–8894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieschaus E., Perrimon N., Finkelstein R. orthodenticle activity is required for the development of medial structures in the larval and adult epidermis of Drosophila. Development. 1992 Jul;115(3):801–811. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.3.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E. A., Jäckle H., Pfeifle C., Cohen S. M. A Drosophila homologue of human Sp1 is a head-specific segmentation gene. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):690–694. doi: 10.1038/366690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhadanov A. B., Bertuzzi S., Taira M., Dawid I. B., Westphal H. Expression pattern of the murine LIM class homeobox gene Lhx3 in subsets of neural and neuroendocrine tissues. Dev Dyn. 1995 Apr;202(4):354–364. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002020405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]