Abstract
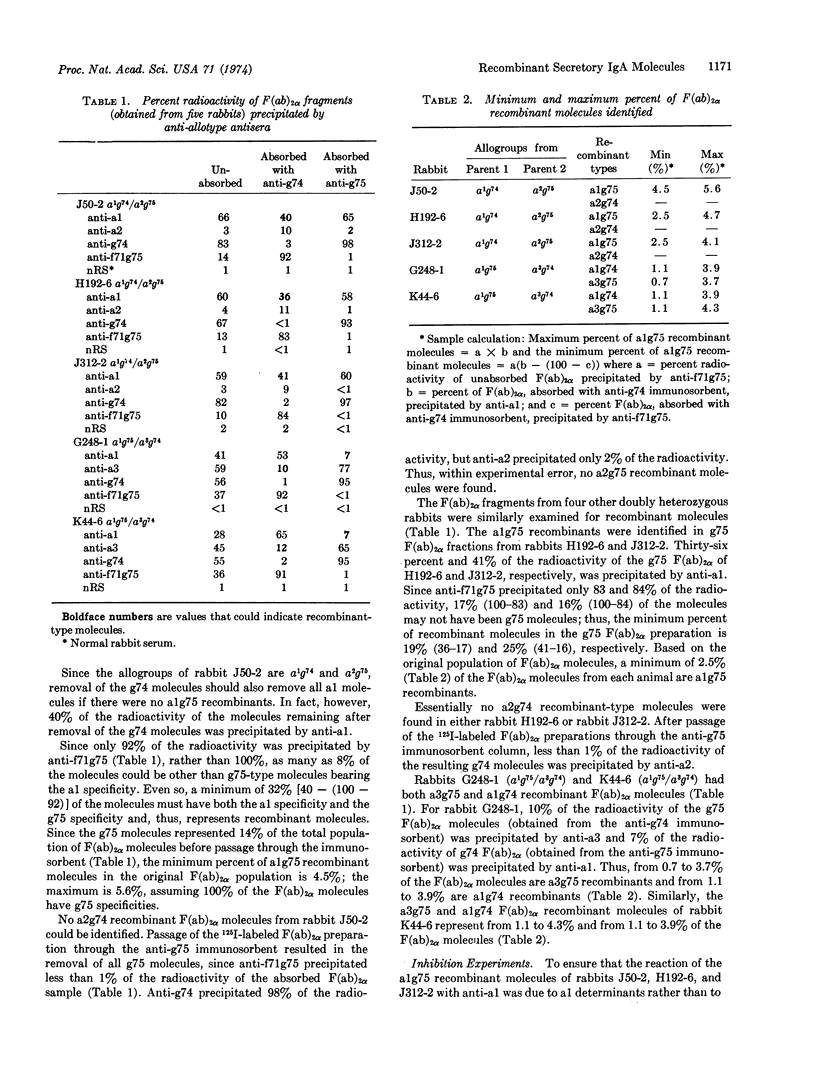
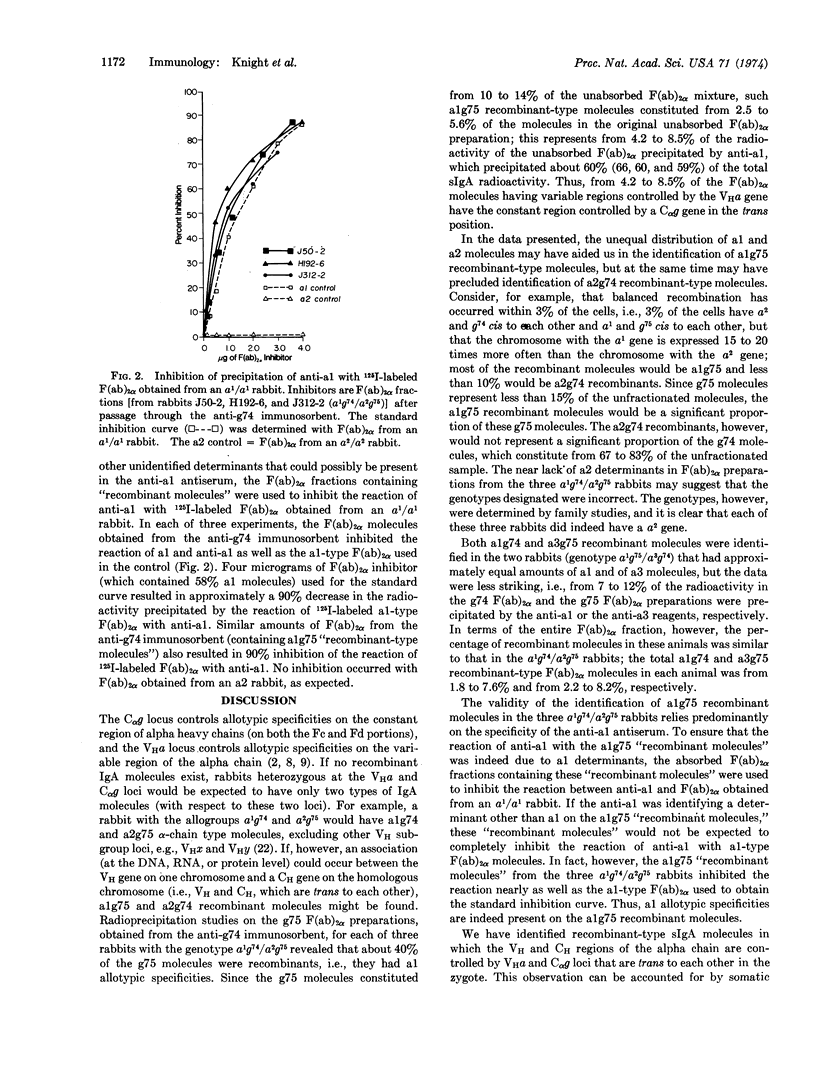
A population of IgA molecules having heavy chains coded by two parental chromosomes in trans position has been identified in rabbits heterozygous at both the VHa locus, which controls allotypic specificities on the variable part of heavy chains, and the Cαg locus, which controls allotypic specificities on the constant part of alpha chains. These recombinant molecules have alpha-chain allotypic specificities controlled by both the maternal VHa gene and the paternal Cαg gene or conversely, the paternal VHa gene and the maternal Cαg gene. These recombinant molecules were found in F(ab)2α fractions obtained after passage of F(ab)2α preparations through immunosorbent columns designed to remove one population of F(ab)2α molecules, i.e., g74- or g75-type molecules. The effluent F(ab)2α fractions were then examined by radioprecipitation methods for allotypic specificities controlled by the VHa and Cαg loci. About 40% of the g75 F(ab)2α molecules from each of three rabbits with the a1g74 and a2g75 allogroups were alg75 recombinants. These alg75 recombinant molecules represented from 2.5-5.6% of the total unfractionated F(ab)2α sample. The F(ab)2α fractions from two rabbits with the a1g75 and a3g74 allogroups had from 1.8-8.2% recombinant molecules: some were alg74 recombinants and some were a3g75 recombinants. Somatic recombination as a mechanism responsible for the synthesis of polypeptide chains in which part of the information is obtained from one chromosome and part from the homologous chromosome is discussed.
Keywords: somatic recombination, immunosorbents, F(ab)2α fragments
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apte B. N., Zipser D. In vivo splicing of protein: one continuous polypeptide from two independently functioning operons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2969–2973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axén R., Porath J., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of peptides and proteins to polysaccharides by means of cyanogen halides. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1302–1304. doi: 10.1038/2141302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Colberg J. E., Dray S. Rabbit lymphoid cells differentiated with respect to alpha-, gamma-, and mu- heavy polypeptide chains and to allotypic markers Aa1 and Aa2. J Exp Med. 1966 Mar 1;123(3):547–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway T. P., Dray S., Lichter E. A. Identification and genetic control of the f4 and f5 rabbit gamma-A immunoglobulin allotypes. Phenogroups at the f locus. J Immunol. 1969 Oct;103(4):662–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRAY S., YOUNG G. O., GERALD L. IMMUNOCHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION AND GENETICS OF RABBIT GAMMA-GLOBULIN ALLOTYPES. J Immunol. 1963 Sep;91:403–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubiski S. Immunochemistry and genetics of a "new" allotypic specificity Ae14 of rabbit gamma-G immunoglobulins: recombination in somatic cells. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):120–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. The genetic control of immunoglobulin synthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:1–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly W. C., Knight K. L., Gilman-Sachs A., Dray S., Lichter E. A. Close linkage of the genes for rabbit IgA allotypes, Af71 to Af75, to the chromosomal region controlling immunoglobulin heavy chain allotypes. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1723–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly W. C., Lichter E. A., Dray S., Knight K. L. Rabbit immunoglobulin A allotypic specificities. Localization to two papain fragments, fab 2 and fc 2 , of secretory immunoglobulin A. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):733–741. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heneen W. K., Nichols W. W. Nonrandom arrangement of metaphase chromosomes in cultured cells of the Indian deer, Muntiacus muntjak. Cytogenetics. 1972;11(3):153–164. doi: 10.1159/000130185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim B. S., Dray S. Identification and genetic control of allotypic specificities on two variable region subgroups of rabbit immunoglobulin heavy chains. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Dec;2(6):509–514. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J., Mandy W. J., Todd C. W. Association of allotypic specificities of group a with allotypic specificities A11 and A12 in rabbit immunoglobulin. Biochemistry. 1970 Apr 28;9(9):2028–2032. doi: 10.1021/bi00811a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindt T. J., Todd C. W. Heavy and light chain allotypic markers on rabbit homocytotropic antibody. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):859–866. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Lichter E. A., Hanly W. C. Papain cleavage of rabbit secretory immunoglobulins A. Differential sensitivity of f and g subclasses. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3197–3203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton A. R., 3rd, Mage R. G. The synthesis of secretory IgA in the rabbit. I. Evidence for synthesis as an 11 S dimer. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):693–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis B., Chiappino G., Kelus A. S., Gell P. G. Cellular localization of immunoglobulins with different allotypic specificities in rabbit lymphoid tissues. J Exp Med. 1965 Nov 1;122(5):853–876. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.5.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernis B., Forni L., Dubiski S., Kelus A. S., Mandy W. J., Todd C. W. Heavy chain variable and constant region allotypes in single rabbit plasma cells. Immunochemistry. 1973 May;10(5):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl J. W., Mandy W. J., Todd C. W. The molecular determinants of the A11 and A12 allotypic specificities in rabbit immunoglobulin. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4935–4940. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. GAMMA-GLOBULIN VARIABILITY: A GENETIC HYPOTHESIS. Nature. 1963 Sep 28;199:1231–1236. doi: 10.1038/1991231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern C. Somatic Crossing over and Segregation in Drosophila Melanogaster. Genetics. 1936 Nov;21(6):625–730. doi: 10.1093/genetics/21.6.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD C. W. Allotypy in rabbit 19S protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 May 3;11:170–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi S. L., Dubiski S., Mage R. G. Distribution of allotypic specificities A1, A2, A14, and A15 among immunoglobulin G molecules. J Immunol. 1970 Mar;104(3):641–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi S. L., Tosi R. M. Recombinant IgG molecules in rabbits doubly heterozygous for group a and group e allotypic specificities. Immunochemistry. 1973 Feb;10(2):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



