Abstract
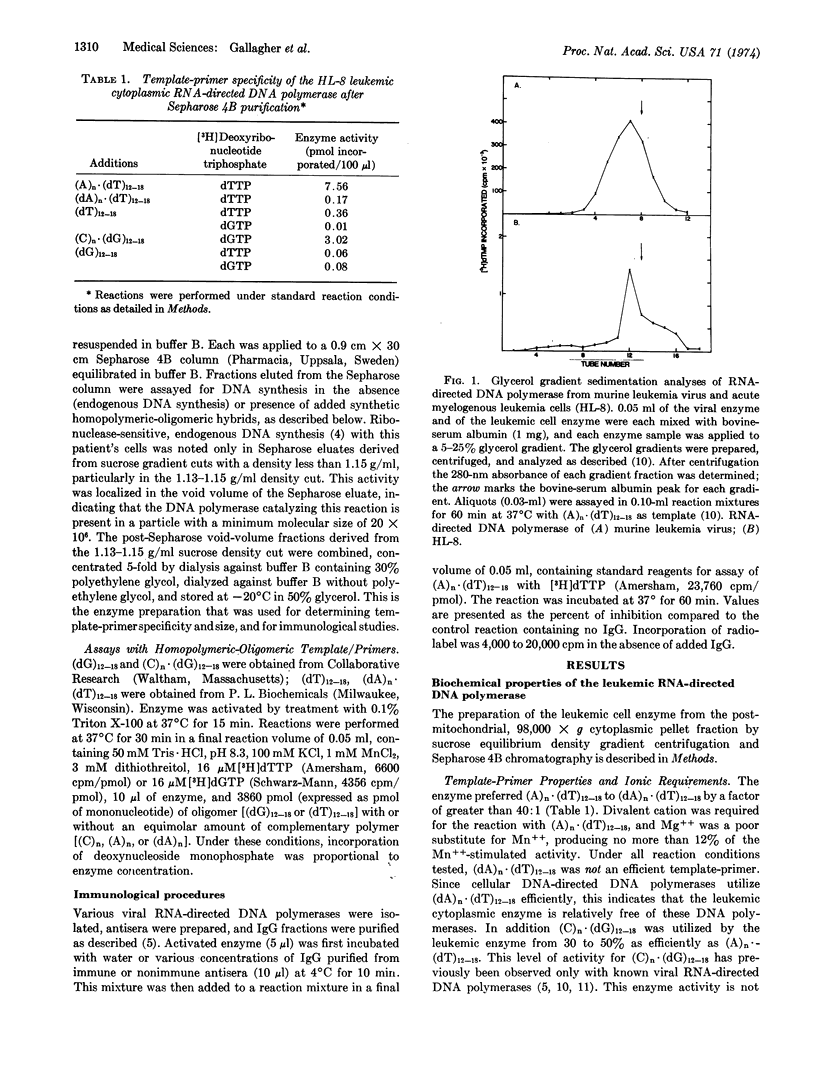
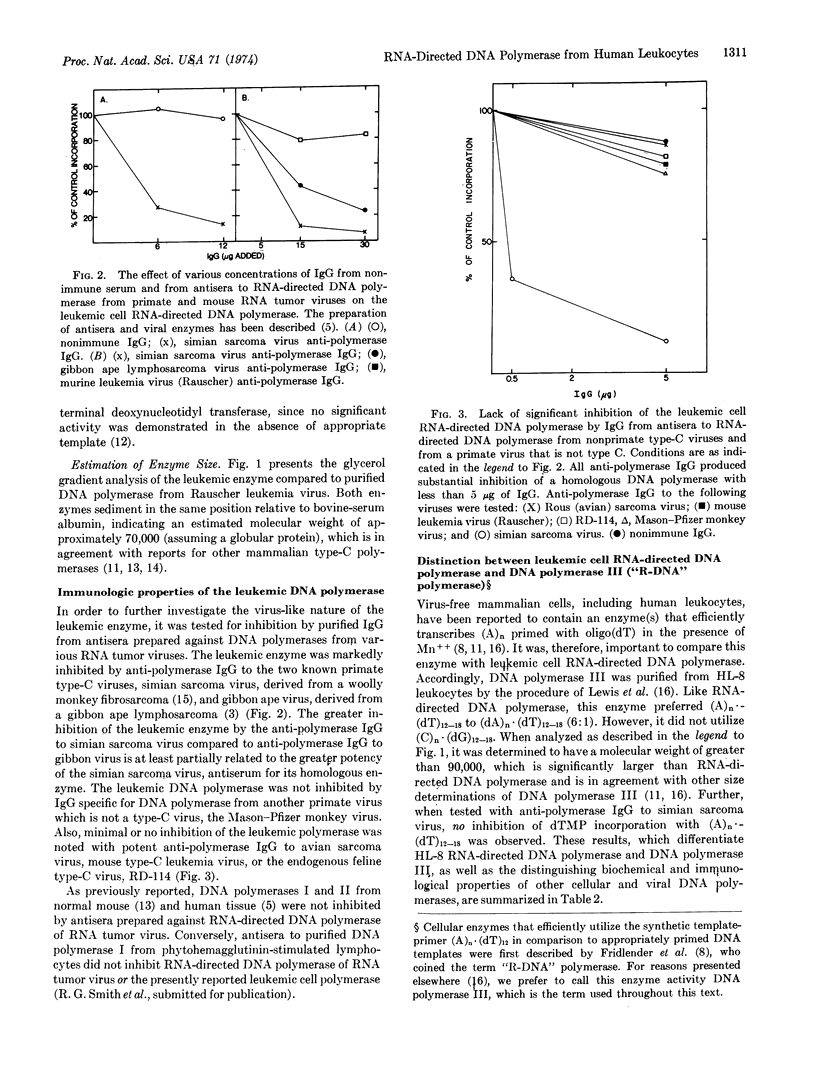
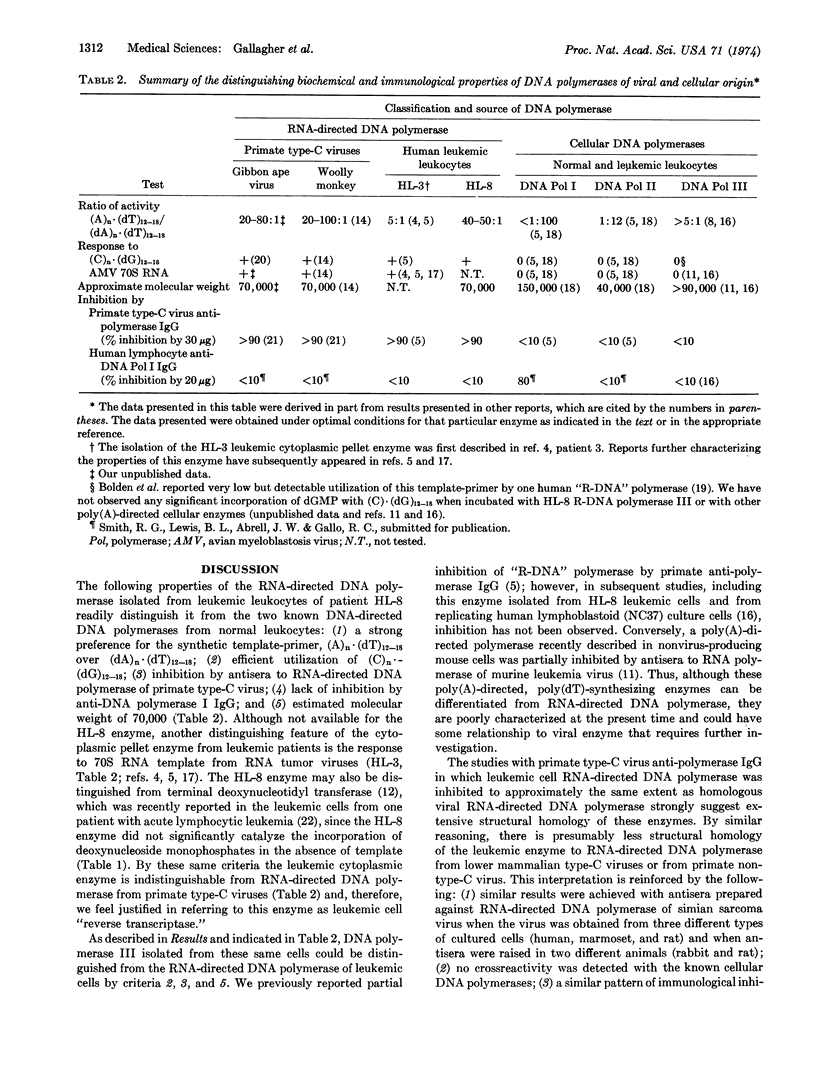
An RNA-directed DNA polymerase was isolated from the peripheral blood leukocytes of a patient with acute myelomonocytic leukemia by successive purification of a particulate cytoplasmic fraction with endogenous, ribonuclease-sensitive DNA polymerase activity. Like RNA-directed DNA polymerase from mammalian type-C virus, the human leukemic cell enzyme efficiently utilized (A)n·(dT)12-18 and (C)n·(dG)12-18 and had an approximate molecular weight of 70,000. Further, the leukemic cell enzyme was strongly inhibited by antisera to RNA-directed DNA polymerase of primate type-C virus in a fashion similar to that noted with an extensively purified RNA-directed DNA polymerase from a person with acute myelogenous leukemia [Todaro, G.J. & Gallo, R.C. (1973), Nature 244, 206]. By these biochemical and immunological results the leukemic cell enzyme could be differentiated from all other known cellular DNA polymerases but could not be distinguished from RNA-directed DNA polymerase of primate type-C virus. We interpret these data, combined with observations published elsewhere, to indicate that human acute myelogenous leukemia cells contain components related to primate type-C virus. The parameters used in this study may provide the specificity and sensitivity required for determining the presence or absence and (if present) the relatedness of RNA-directed DNA polymerase in other cases and types of human leukemia.
Keywords: human leukemia, antibody to virus polymerase
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrell J. W., Gallo R. C. Purification, characterization, and comparison of the DNA polymerases from two primate RNA tumor viruses. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):431–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.431-439.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. Primer requirement and template specificity of the DNA polymerase of RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1507–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt W., Hehlmann R., Spiegelman S. Human leukaemic cells contain reverse transcriptase associated with a high molecular weight virus-related RNA. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 15;240(98):72–75. doi: 10.1038/newbio240072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya J., Xuma M., Reitz M., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C. Utilization of mammalian 70S RNA by a purified reverse transcriptase from human myelocytic leukemic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 5;54(1):324–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90926-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolden A., Fry M., Muller R., Citarella R., Weissbach A. The presence of a polyriboadenylic acid-dependent DNA polymerase in eukaryotic cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Nov;153(1):26–33. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90416-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridlender B., Fry M., Bolden A., Weissbach A. A new synthetic RNA-dependent DNA polymerase from human tissue culture cells (HeLa-fibroblast-synthetic oligonucleotides-template-purified enzymes). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):452–455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Miller N. R., Saxinger W. C., Gillespie D. Primate RNA tumor virus-like DNA synthesized endogenously by RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virus-like particles from fresh human acute leukemic blood cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3219–3224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. D., Jr, Old L. J., Hess P. W., Essex M., Cotter S. Horizontal transmission of feline leukaemia virus. Nature. 1973 Aug 3;244(5414):266–269. doi: 10.1038/244266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K. I., Gonçalves J. M., Houts G. E., Bollum F. J. Deoxynucleotide-polymerizing enzymes of calf thymus gland. II. Properties of the terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2780–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T. G., Huff S. D., Buckley P. M., Dungworth D. L., Synder S. P., Gilden R. V. C-type virus associated with gibbon lymphosarcoma. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 9;235(58):170–171. doi: 10.1038/newbio235170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B. J., Abrell J. W., Smith R. G., Gallo R. C. Human DNA polymerase 3 (R-DNA polymerase): distinction from DNA polymerase I and reverse transcriptase. Science. 1974 Mar 1;183(4127):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4127.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M., Serxner L. E., Howk D. J., Hudson J., Todaro G. J. Characterization of a new murine cellular DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):57–62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey R., Smoler D. F., Baltimore D. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase in a case of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):521–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddick D. H., Gallo R. C. Correlation of transfer RNA methylase activity with growth and differentiation in normal and neoplastic tissues. Cancer Res. 1970 Oct;30(10):2484–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Scolnick E. M., Todaro G. J., Aaronson S. A. Separation of murine cellular and murine leukaemia virus DNA polymerases. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 9;231(23):163–167. doi: 10.1038/newbio231163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarngadharan M. G., Sarin P. S., Reitz M. S., Gallo R. C. Reverse transcriptase activity of human acute leukaemic cells: purification of the enzyme, response to AMV 70S RNA, and characterization of the DNA product. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 15;240(98):67–72. doi: 10.1038/newbio240067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P., Todaro G. J., Aaronson S. A. Immunological characterization of primate C-type virus reverse transcriptases. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 12;235(54):35–40. doi: 10.1038/newbio235035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. G., Gallo R. C. DNA-dependent DNA polymerases I and II from normal human-blood lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2879–2884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilen G. H., Gould D., Fowler M., Dungworth D. L. C-type virus in tumor tissue of a woolly monkey (Lagothrix spp.) with fibrosarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Oct;47(4):881–889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Gallo R. C. Immunological relationship of DNA polymerase from human acute leukaemia cells and primate and mouse leukaemia virus reverse transcriptase. Nature. 1973 Jul 27;244(5413):206–209. doi: 10.1038/244206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Huebner R. J. N.A.S. symposium: new evidence as the basis for increased efforts in cancer research. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):1009–1015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe L. G., Deinhardt F., Theilen G. H., Rabin H., Kawakami T., Bustad L. K. Induction of tumors in marmoset monkeys by simian sarcoma virus, type 1 (Lagothrix): a preliminary report. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Nov;47(5):1115–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


