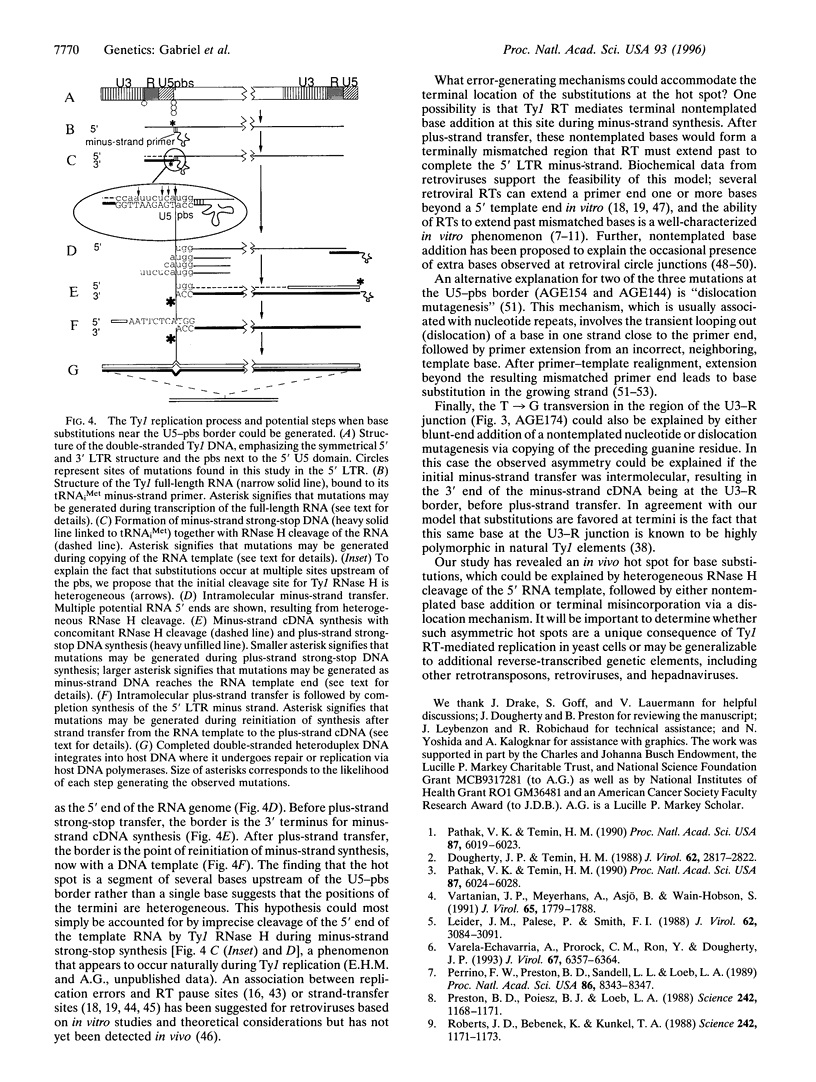
Abstract
Retroviruses undergo a high frequency of genetic alterations during the process of copying their RNA genomes. However, little is known about the replication fidelity of other elements that transpose via reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. The complete sequence of 29 independently integrated copies of the yeast retrotransposon Ty1 (173,043 nt) was determined, and the mutation rate during a single cycle of replication was calculated. The observed base substitution rate of 2.5 x 10(-5) bp per replication cycle suggests that this intracellular element can mutate as rapidly as retroviruses. The pattern and distribution of errors in the Ty1 genome is nonrandom and provides clues to potential in vivo molecular mechanisms of reverse transcriptase-mediated error generation, including heterogeneous RNase H cleavage of Ty1 RNA, addition of terminal nontemplated bases, and transient dislocation and realignment of primer-templates. Overall, analysis of errors generated during Ty1 replication underscores the utility of a genetically tractable model system for the study of reverse transcriptase fidelity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battula N., Loeb L. A. On the fidelity of DNA replication. Lack of exodeoxyribonuclease activity and error-correcting function in avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):982–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebenek K., Abbotts J., Roberts J. D., Wilson S. H., Kunkel T. A. Specificity and mechanism of error-prone replication by human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16948–16956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bebenek K., Abbotts J., Wilson S. H., Kunkel T. A. Error-prone polymerization by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Contribution of template-primer misalignment, miscoding, and termination probability to mutational hot spots. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10324–10334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Eichinger D., Castrillon D., Fink G. R. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome contains functional and nonfunctional copies of transposon Ty1. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1432–1442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SPT3 gene is required for transposition and transpositional recombination of chromosomal Ty elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3575–3581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Xu H., Fink G. R. A general method for the chromosomal amplification of genes in yeast. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):280–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2827308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casacuberta J. M., Vernhettes S., Grandbastien M. A. Sequence variability within the tobacco retrotransposon Tnt1 population. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2670–2678. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M. Novel non-templated nucleotide addition reactions catalyzed by procaryotic and eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9677–9686. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curcio M. J., Garfinkel D. J. Single-step selection for Ty1 element retrotransposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):936–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., McClure M. A. Origins and evolutionary relationships of retroviruses. Q Rev Biol. 1989 Mar;64(1):1–30. doi: 10.1086/416128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. P., Temin H. M. Determination of the rate of base-pair substitution and insertion mutations in retrovirus replication. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2817–2822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2817-2822.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake J. W. A constant rate of spontaneous mutation in DNA-based microbes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7160–7164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake J. W. Rates of spontaneous mutation among RNA viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4171–4175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler R. G., Degnen G. E., Cox E. C. Mutational specificity of a conditional Escherichia coli mutator, mutD5. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;133(3):179–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00267667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresco J. R., Alberts B. M. THE ACCOMMODATION OF NONCOMPLEMENTARY BASES IN HELICAL POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACIDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):311–321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarmann G. J., Schauber C. A., Preston B. D. Template-directed pausing of DNA synthesis by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase during polymerization of HIV-1 sequences in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9793–9802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Alexander P. S. The base substitution fidelity of eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Mispairing frequencies, site preferences, insertion preferences, and base substitution by dislocation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):160–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leider J. M., Palese P., Smith F. I. Determination of the mutation rate of a retrovirus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3084–3091. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3084-3091.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin H. L. A novel mechanism of self-primed reverse transcription defines a new family of retroelements. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):3310–3317. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.3310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luan D. D., Korman M. H., Jakubczak J. L., Eickbush T. H. Reverse transcription of R2Bm RNA is primed by a nick at the chromosomal target site: a mechanism for non-LTR retrotransposition. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansky L. M., Temin H. M. Lower mutation rate of bovine leukemia virus relative to that of spleen necrosis virus. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):494–499. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.494-499.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelman L. V., Boosalis M. S., Petruska J., Goodman M. F. Nearest neighbor influences on DNA polymerase insertion fidelity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14415–14423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelman L. V., Petruska J., Goodman M. F. Base mispair extension kinetics. Comparison of DNA polymerase alpha and reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2338–2346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk R. J., Malik F. G., Stokesberry D., Evans L. H. Direct determination of the point mutation rate of a murine retrovirus. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3683–3689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3683-3689.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J. C., Swanstrom R. A new pathway in the generation of defective retrovirus DNA. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.779-789.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. H., Preston B. D. Marked infidelity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase at RNA and DNA template ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):549–553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak V. K., Temin H. M. Broad spectrum of in vivo forward mutations, hypermutations, and mutational hotspots in a retroviral shuttle vector after a single replication cycle: deletions and deletions with insertions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6024–6028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak V. K., Temin H. M. Broad spectrum of in vivo forward mutations, hypermutations, and mutational hotspots in a retroviral shuttle vector after a single replication cycle: substitutions, frameshifts, and hypermutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6019–6023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peliska J. A., Benkovic S. J. Fidelity of in vitro DNA strand transfer reactions catalyzed by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 5;33(13):3890–3895. doi: 10.1021/bi00179a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peliska J. A., Benkovic S. J. Mechanism of DNA strand transfer reactions catalyzed by HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1112–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.1279806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrino F. W., Preston B. D., Sandell L. L., Loeb L. A. Extension of mismatched 3' termini of DNA is a major determinant of the infidelity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8343–8347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston B. D., Poiesz B. J., Loeb L. A. Fidelity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1168–1171. doi: 10.1126/science.2460924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricchetti M., Buc H. Reverse transcriptases and genomic variability: the accuracy of DNA replication is enzyme specific and sequence dependent. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1583–1593. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. D., Bebenek K., Kunkel T. A. The accuracy of reverse transcriptase from HIV-1. Science. 1988 Nov 25;242(4882):1171–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.2460925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Kim S. Y., Roth M. J. Analysis of long terminal repeat circle junctions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6286–6290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6286-6290.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhauer D. A., Holland J. J. Rapid evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:409–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavis J. E., Ganem D. Expression of functional hepatitis B virus polymerase in yeast reveals it to be the sole viral protein required for correct initiation of reverse transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4107–4111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Retrovirus variation and reverse transcription: abnormal strand transfers result in retrovirus genetic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6900–6903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Echavarría A., Garvey N., Preston B. D., Dougherty J. P. Comparison of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutation rate with the fidelity of its reverse transcriptase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24681–24688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Echavarría A., Prorock C. M., Ron Y., Dougherty J. P. High rate of genetic rearrangement during replication of a Moloney murine leukemia virus-based vector. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6357–6364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6357-6364.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartanian J. P., Meyerhans A., Asjö B., Wain-Hobson S. Selection, recombination, and G----A hypermutation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genomes. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1779–1788. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1779-1788.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. H., Seeger C. The reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus acts as a protein primer for viral DNA synthesis. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):663–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90599-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb J. M., Kumar R., Hughes S. H. Sequence of the circle junction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: implications for reverse transcription and integration. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4903–4906. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4903-4906.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Durbin K. J., Fink G. R. The SPT3 gene is required for normal transcription of Ty elements in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):675–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90474-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Minehart P. L. Analysis of the yeast SPT3 gene and identification of its product, a positive regulator of Ty transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6885–6900. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Goodman M. F. Comparison of HIV-1 and avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase fidelity on RNA and DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10888–10896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Temin H. M. Retrovirus recombination depends on the length of sequence identity and is not error prone. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2409–2414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2409-2414.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerly S., Guo H., Perlman P. S., Lambowitz A. M. Group II intron mobility occurs by target DNA-primed reverse transcription. Cell. 1995 Aug 25;82(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinnen S., Hsieh J. C., Modrich P. Misincorporation and mispaired primer extension by human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24195–24202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]