Abstract
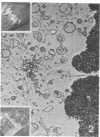
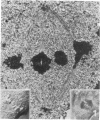
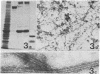
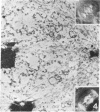
Mitotic cells lysed into solutions of polymerizable microtubule protein contain a spindle which is similar to the living spindle in two respects: it will lose and gain birefringence when cooled and warmed, and it will move anaphase chromosomes to the opposite ends of the cell. Early anaphase cells lysed into buffers containing high molecular weight polyethylene glycol and nucleotide triphosphates will continue chromosome motion and spindle elongation in the absence of exogenous spindle subunits. These results suggest that while spindle growth requires microtubule polymerization, anaphase motions do not.
Keywords: microtubule assembly, motility, anaphase in vitro
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bibring T., Baxandall J. Immunochemical studies of 22S protein from isolated mitotic apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):577–590. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G., Olmsted J. B. Nucleated assembly of microtubules in porcine brain extracts. Science. 1972 Sep 29;177(4055):1196–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4055.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G., Taylor E. W. The mechanism of action of colchicine. Colchicine binding to sea urchin eggs and the mitotic apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):535–548. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley B. R., Murphy P., Richardson L. C. Procedure for embedding in situ selected cells cultured in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):279–283. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley B. R., Stubblefield E., Hsu T. C. The effects of colcemid inhibition and reversal on the fine structure of the mitotic apparatus of Chinese hamster cells in vitro. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Jul;19(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen W. D., Gottlieb T. C-microtubules in isolated mitotic spindles. J Cell Sci. 1971 Nov;9(3):603–619. doi: 10.1242/jcs.9.3.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen W. D., Rebhun L. I. An estimate of the amount of microtubule protein in the isolated mitotic apparatus. J Cell Sci. 1970 Jan;6(1):159–176. doi: 10.1242/jcs.6.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forer A., Behnke O. An actin-like component in spermatocytes of a crane fly (Nephrotoma suturalis Loew). I. The spindle. Chromosoma. 1972;39(2):145–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00319840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons B. H., Gibbons I. R. Flagellar movement and adenosine triphosphatase activity in sea urchin sperm extracted with triton X-100. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jul;54(1):75–97. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Rebhun L. I. The structure and some properties of the isolated mitotic apparatus. J Cell Sci. 1969 Jan;4(1):179–209. doi: 10.1242/jcs.4.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN-BERLING H. Adenosintriphosphat als Betriebsstoff von Zellbewegungen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Jun;14(2):182–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoué S., Sato H. Cell motility by labile association of molecules. The nature of mitotic spindle fibers and their role in chromosome movement. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):259–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANE R. E. The mitotic apparatus. Fine structure of the isolated unit. J Cell Biol. 1962 Nov;15:279–287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.15.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazia D., Petzelt C., Williams R. O., Meza I. A Ca-activated ATPase in the mitotic apparatus of the sea urchin egg (isolated by a new method). Exp Cell Res. 1972 Feb;70(2):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebhun L. I., Sander G. Ultrastructure and birefringence of the isolated mitotic apparatus of marine eggs. J Cell Biol. 1967 Sep;34(3):859–883. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberg R. C. Microtubule formation in vitro in solutions containing low calcium concentrations. Science. 1972 Sep 22;177(4054):1104–1105. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4054.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]