Abstract
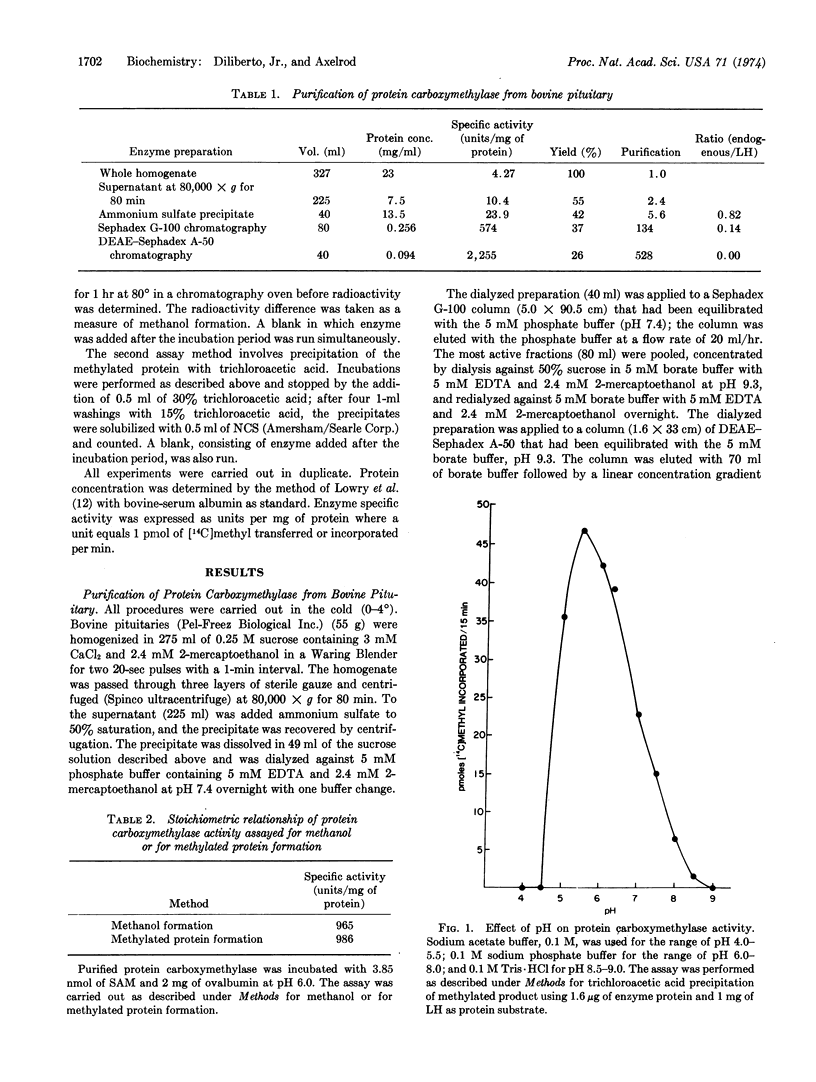
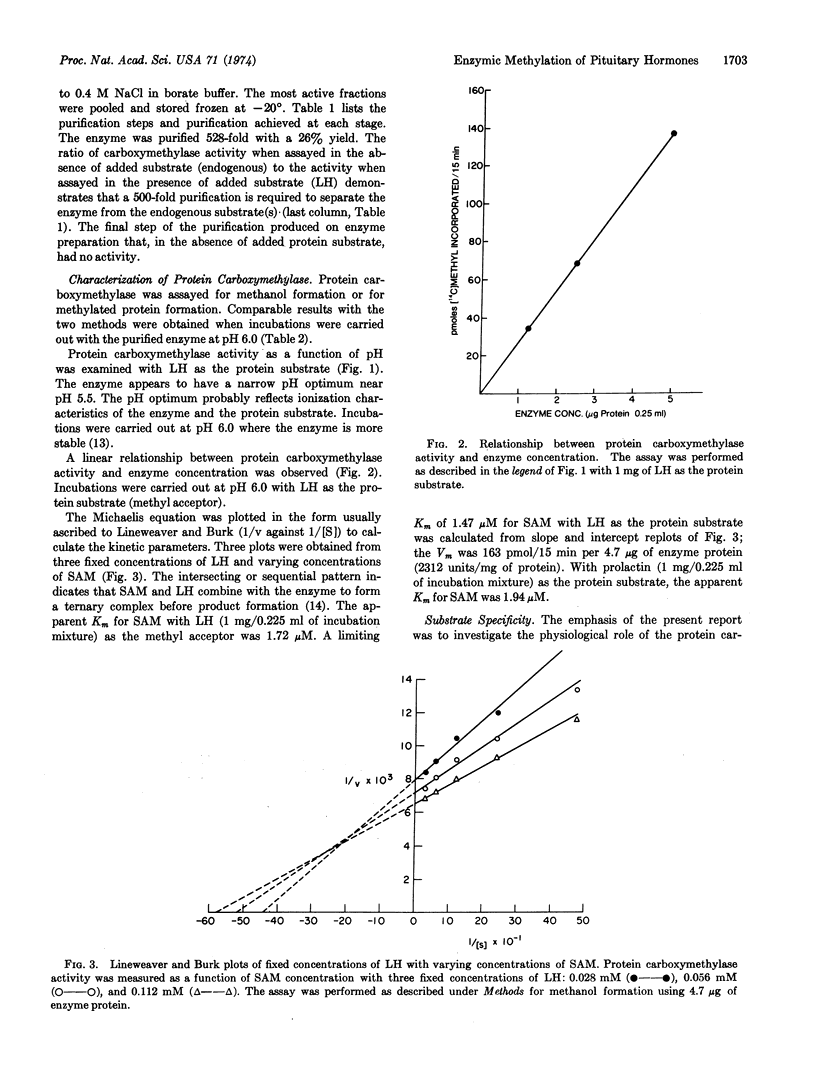
Protein carboxymethylase, an enzyme capable of methylating proteins and polypeptides, was purified from bovine pituitary. The anterior pituitary hormones, luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and prolactin, were found to be substrates for this enzyme. The posterior pituitary hormones, oxytocin and vasopressin, did not serve as substrates. With luteinizing hormone as the substrate, protein carboxymethylase had a pH optimum near pH 5.5. A limiting Km of 1.47 μM for S-adenosyl-L-methionine was obtained with luteinizing hormone as the methyl acceptor. Possible roles of this enzyme in the posterior and anterior pituitary are discussed.
Keywords: protein hormones, S-adenosyl-L-methionine, neuroendocrine, methanol-forming enzyme
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J., Cohn C. K. Methyltransferase enzymes in red blood cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Mar;176(3):650–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod J., Daly J. Pituitary gland: enzymic formation of methanol from S-adenosylmethionine. Science. 1965 Nov 12;150(3698):892–893. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3698.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaranello R. D., Dankers H. J., Barchas J. D. The enzymatic formation of methanol from S-adenosylmethionine by various tissues of the rat. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 May;8(3):311–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb D. G., Sarkar N., Pinzino C. J. The methylation of lysine residues in protein. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1857–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T., Barchas J. Inhibition of transmethylations of biogenic amines by S-adenosylhomocysteine. Enhancement of transmethylation by adenosylhomocysteinase. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3175–3181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Paik W. K. Purification and properties of protein methylaase II. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1806–1813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Pail W. K. Studies on the structural requirements of substrate protein for protein methylase II. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 3;10(16):3141–3145. doi: 10.1021/bi00792a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. Purification and properties of protein methylase II. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Aug;157(2):476–484. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90665-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liss M., Maxam A. M., Cuprak L. J. Methylation of protein by calf spleen methylase. A new protein methylation reaction. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 25;244(6):1617–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liss M., Maxam A. M. Methylation of ovalbumin and human serum albumin by a purified enzyme from calf spleen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 15;140(3):555–557. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90536-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin A. M., Liss M. Evidence for a methylated protein intermediate in pituitary methanol formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):373–378. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90721-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik W. K., Kim S. Protein methylase I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 10;243(9):2108–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



