Abstract
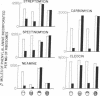
The chloroplast ribosomes from five antibiotic resistant strains of Chlamydomonas, each carrying one mutant gene mapping in chloroplast DNA, have been shown to be resistant to the corresponding antibiotic in a poly(U)-directed amino-acid incorporating assay system. The alteration conferring resistance was localized to the 30S subunit in ribosomes from streptomycin, neamine, and spectinomycin resistant strains, and to the 50S subunit in ribosomes from cleocin and carbomycin resistant strains. Spectinomycin resistant ribosomes showed no cross-resistance to any other drugs, but limited cross-resistance was noted with the other mutant ribosomes. The similarity between these findings and results reported by others with bacterial ribosomes supports our hypothesis that at least some chloroplast ribosomal proteins are coded by genes in chloroplast DNA.
Keywords: chloroplast genes, ribosomal subunit, in vitro polypeptide synthesis
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borst P. Mitochondrial nucleic acids. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:333–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti A., Bogdanov S. Different effects of streptomycin on the ribosomes from sensitive and resistant mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun 15;35(3):482–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque D. P., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Studies on the structure and cellular location of various ribosome and ribosomal RNA species in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardi. J Cell Sci. 1971 Jan;8(1):153–183. doi: 10.1242/jcs.8.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourque D. P., Wildman S. G. Evidence that nuclear genes code for several chloroplast ribosomal proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):532–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90872-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. H., Wildman S. G. Chloroplast DNA codes for the primary structure of the large subunit of fraction I protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 14;277(3):677–680. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Blobel G., Siekevitz P. Isolation of cytoplasmic and chloroplast ribosomes and their dissociation into active subunits from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):798–814. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Nomura M. The genetics of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:203–234. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Schiltz E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XXVII. Localization of the amino acid exchanges in protein S5 from two Escherichia coli mutants resistant to spectinomycin. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(2):106–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00332781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. 33. Location of amino-acid replacements in protein S12 isolated from Escherichia coli mutants resistant to streptomycin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 28;68(3):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E., Burkholder B. Mutations altering chloroplast ribosome phenotype in Chlamydomonas. I. Non-mendelian mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):1026–1033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldthwaite C., Smith I. Genetic mapping of aminoglycoside and fusidic acid resistant mutations in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(3):181–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01788887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grivell L. A., Walg H. L. Subunit homology between Escherichia coli, mitochondrial and chloroplast ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 18;49(6):1452–1458. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90502-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K., Blobel G. Characterization of the chloroplastic and cytoplasmic ribosomes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):121–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloppstech K., Schweiger H. G. Nuclear genome codes for chloroplast ribosomal proteins in Acetabularia. II. Nuclear transplantation experiments. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jul;80(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90276-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R., Tewari K. K. Molecular size and conformation of chloroplast deoxyribonucleic acid from pea leaves. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 10;247(19):6355–6364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnane A. W., Haslam J. M., Lukins H. B., Nagley P. The biogenesis of mitochondria in microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1972;26:163–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.26.100172.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mets L. J., Bogorad L. Mendelian and uniparental alterations in erythromycin binding by plastid ribosomes. Science. 1971 Nov 12;174(4010):707–709. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4010.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mets L., Bogorad L. Altered chlorplast ribosomal proteins associated with erythromycin-resistant mutants in two genetic systems of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3779–3783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Itoh T., Osawa S., Tanaka K., Tamaki M. Peptide analyses of a protein component, 50-8, of 50s ribosomal subunit from erythromycin resistant mutants of Escherichia coli and Escherichia freudii. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(1):14–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00268742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R. Streptomycin as a mutagen for nonchromosomal genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2018–2026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Hamilton M. G. Cytoplasmic and chloroplast ribosomes of Chlamydomonas: ultracentrifugal characterization. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):709–711. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R., Ramanis Z. A genetic map of non-Mandelian genes in Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):593–600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlanger G., Sager R., Ramanis Z. Mutation of a cytoplasmic gene in Chlamydomonas alters chlorplast ribosome function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3551–3555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towers N. R., Dixon H., Kellerman G. M., Linnane A. W. Biogenesis of mitochondria. 22. The sensitivity of rat liver mitochondria to antibiotics; a phylogenetic difference between a mammalian system and yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Aug;151(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Rubin M. S., Sierra M. F. Biosynthesis of mitochondrial enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 12;301(1):71–104. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(73)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]