Abstract
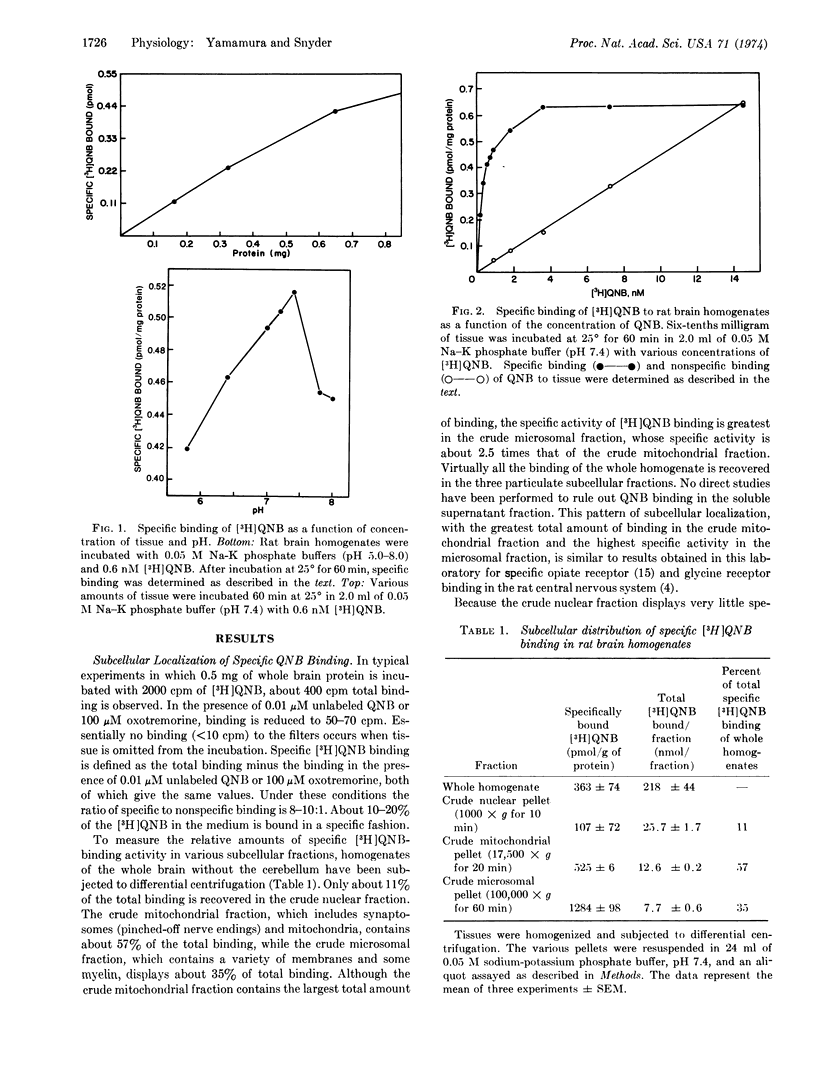
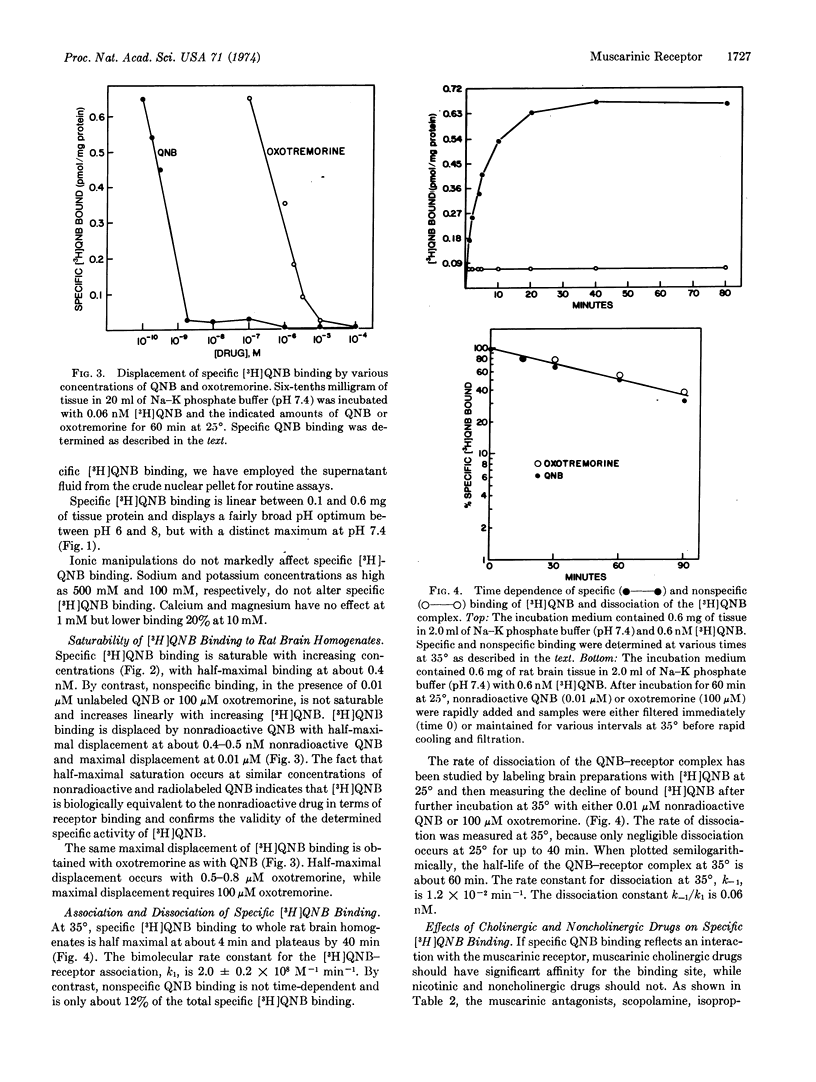
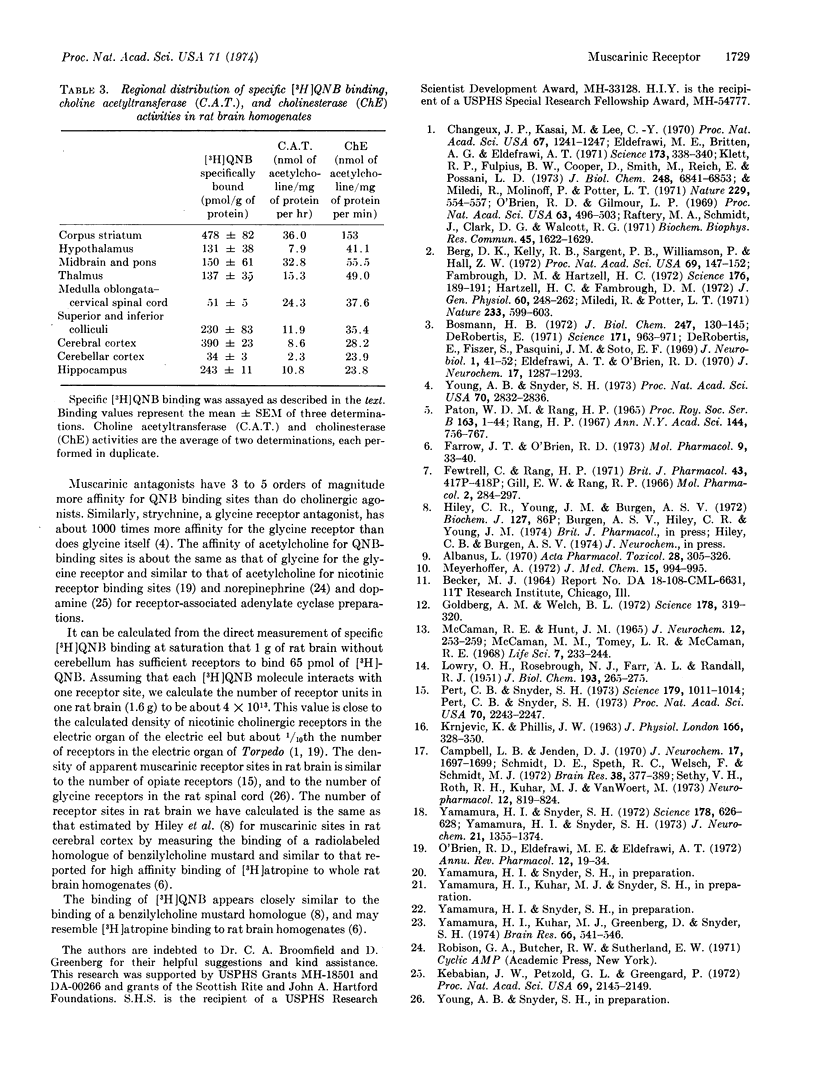
Binding sites with high affinity and specificity for [3H]quinuclidinyl benzilate (QNB) are present in homogenates of rat brain. The characteristics of the binding sites resemble those of muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Specific binding is saturable with respect to [3H]QNB and tissue concentration and is time-, temperature-, and pH-dependent. The bimolecular rate of association (2.0 × 108 M-1 min-1) and dissociation (1.2 × 10-2 min-1) at 35° indicate a dissociation constant of 60 pM and a density of 65 pmol/g of brain. Muscarinic antagonists and agonists displace specific [3H]QNB binding, while nicotinic and non-cholinergic drugs possess little affinity for [3H]QNB-binding sites.
Keywords: quinuclidinyl benzilate, receptors
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albanus L. Central and peripheral effects of anticholinergic compounds. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1970;28(4):305–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1970.tb00557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Kelly R. B., Sargent P. B., Williamson P., Hall Z. W. Binding of -bungarotoxin to acetylcholine receptors in mammalian muscle (snake venom-denervated muscle-neonatal muscle-rat diaphragm-SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B. Acetylcholine receptor. I. Identification and biochemical characteristics of a cholinergic receptor of guinea pig cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):130–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. B., Jenden D. J. Gas chromatographic evaluation of the influence of oxotremorine upon the regional distribution of acetylcholine in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1970 Dec;17(12):1697–1699. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb11396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Kasai M., Lee C. Y. Use of a snake venom toxin to characterize the cholinergic receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1241–1247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E., Fiszer S., Pasquini J. M., Soto E. F. Isolation and chemical nature of the receptor for d-tubocurarine in nerve-ending membranes of the cerebral cortex. J Neurobiol. 1969;1(1):41–52. doi: 10.1002/neu.480010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi A. T., O'Brien R. D. Binding of muscarone by extracts of housefly brain: relationship to receptors for acetylcholine. J Neurochem. 1970 Aug;17(8):1287–1293. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb03377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Britten A. G., Eldefrawi A. T. Acetylcholine binding to Torpedo electroplax: relationship to acetylcholine receptors. Science. 1971 Jul 23;173(3994):338–340. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3994.338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Hartzell H. C. Acetylcholine receptors: number and distribution at neuromuscular junctions in rat diaphragm. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrow J. T., O'Brien R. D. Binding of atropine and muscarone to rat brain fractions and its relation to the acetylcholine receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;9(1):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fewtrell C., Rang H. P. Distribution of bound 3 H-benzilylcholine mustard in subcellular fractions of smooth muscle from guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;43(2):417P–418P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill E. W., Rang H. P. An alkylating derivative of benzilylcholine with specific and long-lasting parasympatholytic activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Jul;2(4):284–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. M., Welch B. L. Adaptation of the adrenal medulla: sustained increase in choline acetyltransferase by psychosocial stimulation. Science. 1972 Oct 20;178(4058):319–320. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4058.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Fambrough D. M. Acetylcholine receptors. Distribution and extrajunctional density in rat diaphragm after denervation correlated with acetylcholine sensitivity. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Sep;60(3):248–262. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiley C. R., Young J. M., Burgen A. S. Labelling of cholinergic receptors in subcellular fractions from rat cerebral cortex. Biochem J. 1972 May;127(5):86P–86P. doi: 10.1042/bj1270086pa. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Petzold G. L., Greengard P. Dopamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in caudate nucleus of rat brain, and its similarity to the "dopamine receptor". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2145–2149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klett R. P., Fulpius B. W., Cooper D., Smith M., Reich E., Possani L. D. The acetylcholine receptor. I. Purification and characterization of a macromolecule isolated from Electrophorus electricus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6841–6853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Phillis J. W. Pharmacological properties of acetylcholine-sensitive cells in the cerebral cortex. J Physiol. 1963 May;166(2):328–350. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCAMAN R. E., HUNT J. M. MICRODETERMINATION OF CHOLINE ACETYLASE IN NERVOUS TISSUE. J Neurochem. 1965 Apr;12:253–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaman M. W., Tomey L. R., McCaman R. E. Radiomimetric assay of acetylcholinesterase activity in submicrogram amounts of tissue. Life Sci. 1968 Mar 15;7(6):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(68)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhöffer A. Absolute configuration of 3-quinuclidinyl benzilate and the behavioral effect in the dog of the optical isomers. J Med Chem. 1972 Sep;15(9):994–995. doi: 10.1021/jm00279a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Molinoff P., Potter L. T. Isolation of the cholinergic receptor protein of Torpedo electric tissue. Nature. 1971 Feb 19;229(5286):554–557. doi: 10.1038/229554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. D., Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Isolation of acetylcholine receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1972;12:19–34. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.12.040172.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. D., Gilmour L. P. A muscarone-binding material in electroplax and its relation to the acetylcholine receptor. I. Centrifugal assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):496–503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D., RANG H. P. THE UPTAKE OF ATROPINE AND RELATED DRUGS BY INTESTINAL SMOOTH MUSCLE OF THE GUINEA-PIG IN RELATION TO ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTORS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Aug 24;163:1–44. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Properties of opiate-receptor binding in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2243–2247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Schmidt J., Clark D. G., Wolcott R. G. Demonstration of a specific -bungarotoxin binding component in electrophorus electricus electroplax membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 17;45(6):1622–1629. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D. E., Speth R. C., Welsch F., Schmidt M. J. The use of microwave radiation in the determination of acetylcholine in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1972 Mar 24;38(2):377–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90720-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethy V. H., Roth R. H., Kuhar M. J., Van Woert M. H. Choline and acetylcholine: regional distribution and effect of degeneration of cholinergic nerve terminals in the rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology. 1973 Sep;12(9):819–823. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(73)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. Choline: high-affinity uptake by rat brain synaptosomes. Science. 1972 Nov 10;178(4061):626–628. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4061.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. High affinity transport of choline into synaptosomes of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Dec;21(6):1355–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Strychnine binding associated with glycine receptors of the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2832–2836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


