Abstract
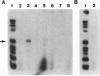
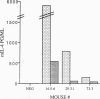
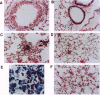
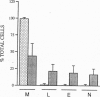
To investigate the contribution of interleukin-4 (IL-4) to airway inflammation in vivo and to explore directly its relationship to airway reactivity, we created transgenic mice in which the murine cDNA for IL-4 was regulated by the rat Clara cell 10 protein promoter. Expression was detected only in the lung and not in thymus, heart, liver, spleen, kidney, or uterus. The expression of IL-4 elicited hypertrophy of epithelial cells of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. Hypertrophy is due, at least in part, to the accumulation of mucus glycoprotein. Histologic examination of parenchyma revealed multinucleated macrophages and occasional islands of cells consisting largely of eosinophils or lymphocytes. Analysis of lung lavage fluid revealed the presence of a leukocytic infiltrate consisting of lymphocytes, neutrophils and eosinophils. Mice expressing IL-4 had greater baseline airway resistance but did not demonstrate hyperreactivity to methacholine. Thus, the expression of IL-4 selectively within the lung elicits an inflammatory response characterized by epithelial cell hypertrophy, and the accumulation of macrophages, lymphocytes, eosinophils, and neutrophils without resulting in an alteration in airway reactivity to inhaled methacholine.
Full text
PDF

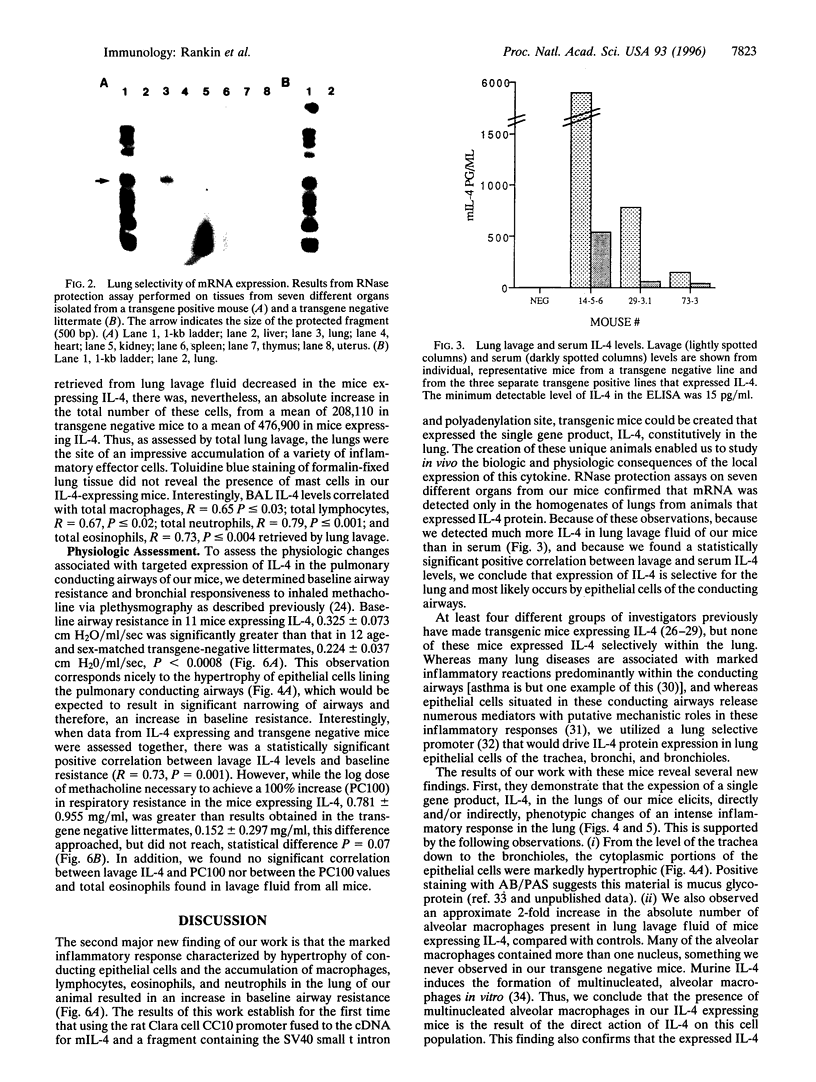
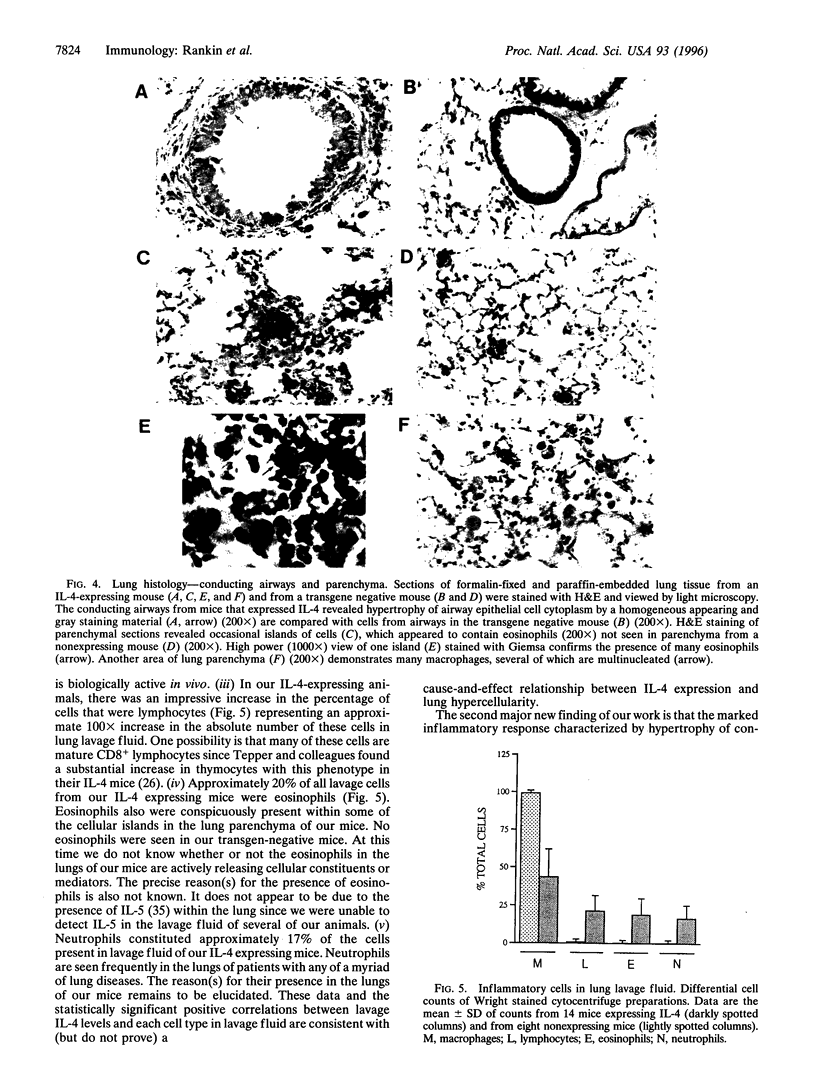

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMDUR M. O., MEAD J. Mechanics of respiration in unanesthetized guinea pigs. Am J Physiol. 1958 Feb;192(2):364–368. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.192.2.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Sasson S. Z., Le Gros G., Conrad D. H., Finkelman F. D., Paul W. E. Cross-linking Fc receptors stimulate splenic non-B, non-T cells to secrete interleukin 4 and other lymphokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1421–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay J. L., Paul W. E. The interleukin-4 family of lymphokines. Curr Opin Immunol. 1992 Jun;4(3):294–298. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(92)90079-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusselle G., Kips J., Joos G., Bluethmann H., Pauwels R. Allergen-induced airway inflammation and bronchial responsiveness in wild-type and interleukin-4-deficient mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995 Mar;12(3):254–259. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.12.3.7873190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse W. W., Coffman R. L., Gelfand E. W., Kay A. B., Rosenwasser L. J. Mechanisms of persistent airway inflammation in asthma. A role for T cells and T-cell products. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Jul;152(1):388–393. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.152.1.7599853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheever A. W., Williams M. E., Wynn T. A., Finkelman F. D., Seder R. A., Cox T. M., Hieny S., Caspar P., Sher A. Anti-IL-4 treatment of Schistosoma mansoni-infected mice inhibits development of T cells and non-B, non-T cells expressing Th2 cytokines while decreasing egg-induced hepatic fibrosis. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):753–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. D., Sensenbrenner L., Fan K., Run Q. Y. Murine recombinant IL-4 is a bifunctional regulator of macrophage growth induced by colony-stimulating factors. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):753–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. M., Finbloom D. S., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Meltzer M. S. B cell stimulatory factor-1 (interleukin 4) activates macrophages for increased tumoricidal activity and expression of Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):135–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCosmo B. F., Geba G. P., Picarella D., Elias J. A., Rankin J. A., Stripp B. R., Whitsett J. A., Flavell R. A. Airway epithelial cell expression of interleukin-6 in transgenic mice. Uncoupling of airway inflammation and bronchial hyperreactivity. J Clin Invest. 1994 Nov;94(5):2028–2035. doi: 10.1172/JCI117556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb K. J., Holtschke T., Muth K., Horak I., Schimpl A. T cell subset distribution and B cell hyperreactivity in mice expressing interleukin-4 under the control of major histocompatibility complex class I regulatory sequences. Eur J Immunol. 1994 May;24(5):1143–1147. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross A., Ben-Sasson S. Z., Paul W. E. Anti-IL-4 diminishes in vivo priming for antigen-specific IL-4 production by T cells. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2112–2120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B. Asthma and inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 May;87(5):893–910. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)90408-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Woods A., Becker-Dunn E., Bottomly K. Distinct functional phenotypes of cloned Ia-restricted helper T cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):188–201. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Yu C. C., Forbush K. A., Carpenter J., Sato T. A., Grossman A., Liggitt D. H., Perlmutter R. M. Interleukin 4 expressed in situ selectively alters thymocyte development. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):89–100. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacs N. W., Strieter R. M., Chensue S. W., Kunkel S. L. Interleukin-4-dependent pulmonary eosinophil infiltration in a murine model of asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1994 May;10(5):526–532. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.10.5.8179915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandler R., Finkelman F. D., Levine A. D., Snapper C. M. IL-4 induction of IgE class switching by lipopolysaccharide-activated murine B cells occurs predominantly through sequential switching. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):407–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. R., Gerard N. P., Galli S. J., Drazen J. M. Pulmonary responses to bronchoconstrictor agonists in the mouse. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Jun;64(6):2318–2323. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.6.2318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnes A., Rennick D. M. Interleukin 4 induces cultured monocytes/macrophages to form giant multinucleated cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):598–611. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Haldar S., Prystowsky M. B., Lammie P. Lymphokine regulation of inflammatory processes: interleukin-4 stimulates fibroblast proliferation. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Nov;49(2):292–298. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann T. R., Cherwinski H., Bond M. W., Giedlin M. A., Coffman R. L. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2348–2357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W., Kühn R., Rajewsky K. Major histocompatibility complex class II hyperexpression on B cells in interleukin 4-transgenic mice does not lead to B cell proliferation and hypergammaglobulinemia. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):921–925. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Interleukin-4: a prototypic immunoregulatory lymphokine. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):1859–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picarella D. E., Kratz A., Li C. B., Ruddle N. H., Flavell R. A. Insulitis in transgenic mice expressing tumor necrosis factor beta (lymphotoxin) in the pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10036–10040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plopper C. G. Comparative morphologic features of bronchiolar epithelial cells. The Clara cell. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Aug;128(2 Pt 2):S37–S41. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.2P2.S37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin J. A., Hitchcock M., Merrill W., Bach M. K., Brashler J. R., Askenase P. W. IgE-dependent release of leukotriene C4 from alveolar macrophages. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):329–331. doi: 10.1038/297329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Romberger D. J., Sisson J. H., Von Essen S. G., Rubinstein I., Robbins R. A., Spurzem J. R. Airway epithelial cells: functional roles in airway disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994 Nov;150(5 Pt 2):S27–S30. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/150.5_Pt_2.S27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J. Interleukin-5, eosinophils, and disease. Blood. 1992 Jun 15;79(12):3101–3109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seder R. A., Paul W. E., Dvorak A. M., Sharkis S. J., Kagey-Sobotka A., Niv Y., Finkelman F. D., Barbieri S. A., Galli S. J., Plaut M. Mouse splenic and bone marrow cell populations that express high-affinity Fc epsilon receptors and produce interleukin 4 are highly enriched in basophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2835–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stripp B. R., Sawaya P. L., Luse D. S., Wikenheiser K. A., Wert S. E., Huffman J. A., Lattier D. L., Singh G., Katyal S. L., Whitsett J. A. cis-acting elements that confer lung epithelial cell expression of the CC10 gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14703–14712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepper R. I., Levinson D. A., Stanger B. Z., Campos-Torres J., Abbas A. K., Leder P. IL-4 induces allergic-like inflammatory disease and alters T cell development in transgenic mice. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Heusser C. H., Moroni C. Production of the haemopoietic growth factors GM-CSF and interleukin-3 by mast cells in response to IgE receptor-mediated activation. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):150–152. doi: 10.1038/339150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., Mills F. C., Saxon A. Switch circles from IL-4-directed epsilon class switching from human B lymphocytes. Evidence for direct, sequential, and multiple step sequential switch from mu to epsilon Ig heavy chain gene. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 1;152(7):3427–3435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlotnik A., Fischer M., Roehm N., Zipori D. Evidence for effects of interleukin 4 (B cell stimulatory factor 1) on macrophages: enhancement of antigen presenting ability of bone marrow-derived macrophages. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4275–4279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]