Abstract
The hisT gene codes for an enzyme responsible for the conversion of uridine to pseudouridine (Ψ) in the anticodon region of many tRNA species in Salmonella typhimurium. We have previously shown that a hisT mutant has tRNAHis which lacks pseudouridine in this region and as a consequence has an altered chromatographic behavior. We show here a similar alteration in chromatographic behavior of all tRNALeu and one tRNAIle species from a hisT mutant. By contrast, tRNAVal, which contains no pseudouridine except for the one in the TΨCG sequence, is chromatographically unaltered in a hisT mutant.
The absence of pseudouridine in the anticodon region of tRNA in hisT mutants has been previously shown to cause derepression of the histidine operon. We show here that in hisT mutants the regulation of the leucine and the isoleucine and valine operons is also affected: the enzymes of these operons are refractory to repression by the branched chain amino acids. However, there is no difference between hisT and wild type in the pattern of derepression caused by isoleucine or valine limitation and only a slight difference in the enzyme levels in cells grown on minimal medium.
The alteration in the regulation of branched chain amino acid operons may also explain why hisT mutants are resistant to inhibition of growth by the amino acid analogues 5,5,5-trifluoroleucine, β-hydroxyleucine, and norleucine and by the oligopeptides glycylglycylnorleucine and norleucylnorleucine.
Keywords: amino-acid regulation, Salmonella typhimurium, tRNA chromatography
Full text
PDF
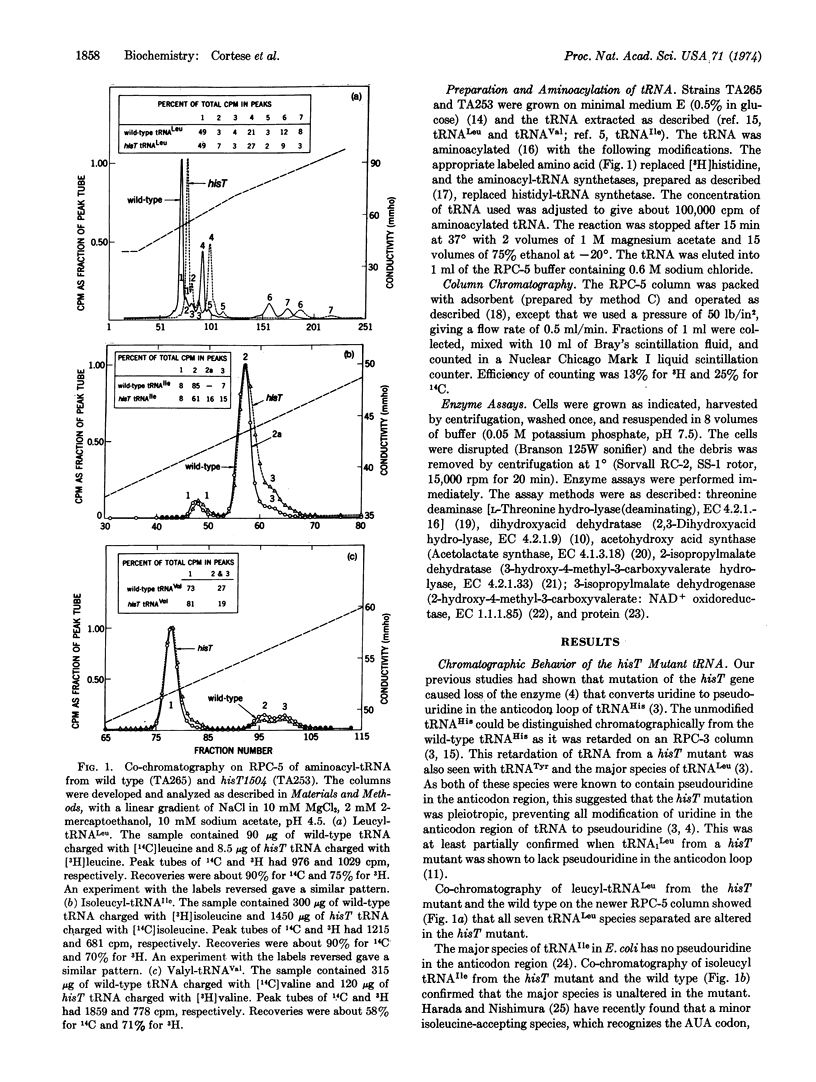
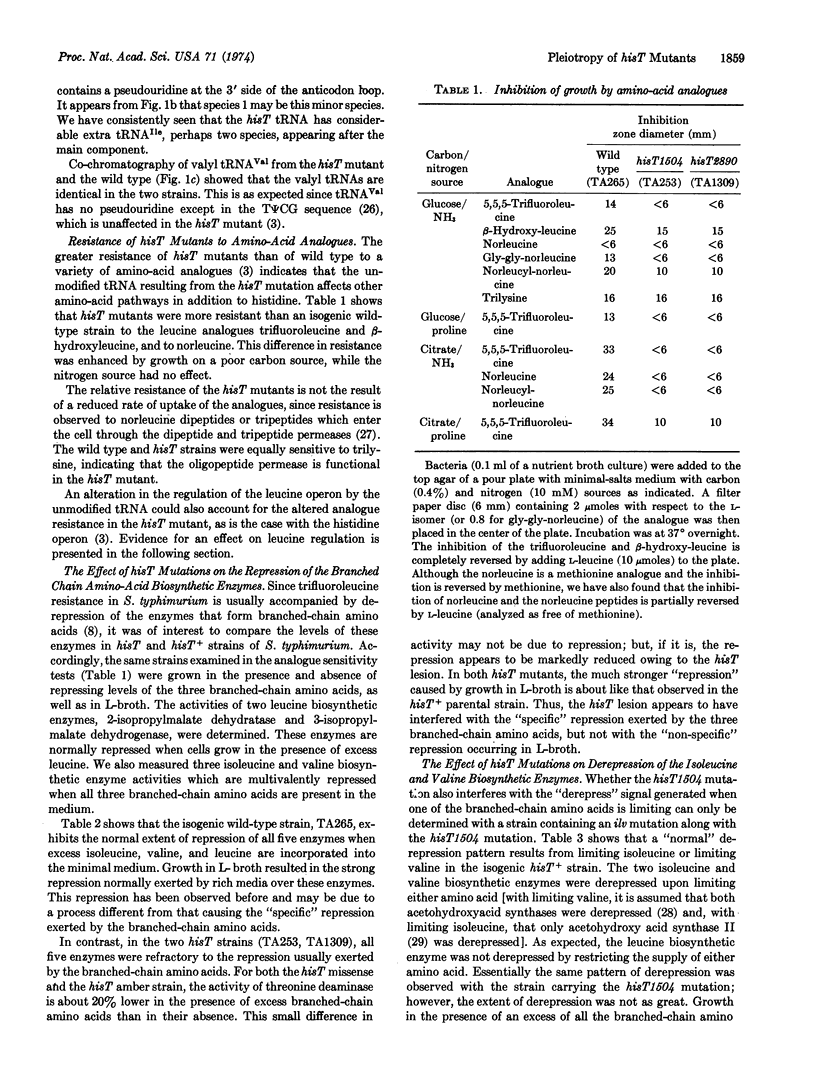
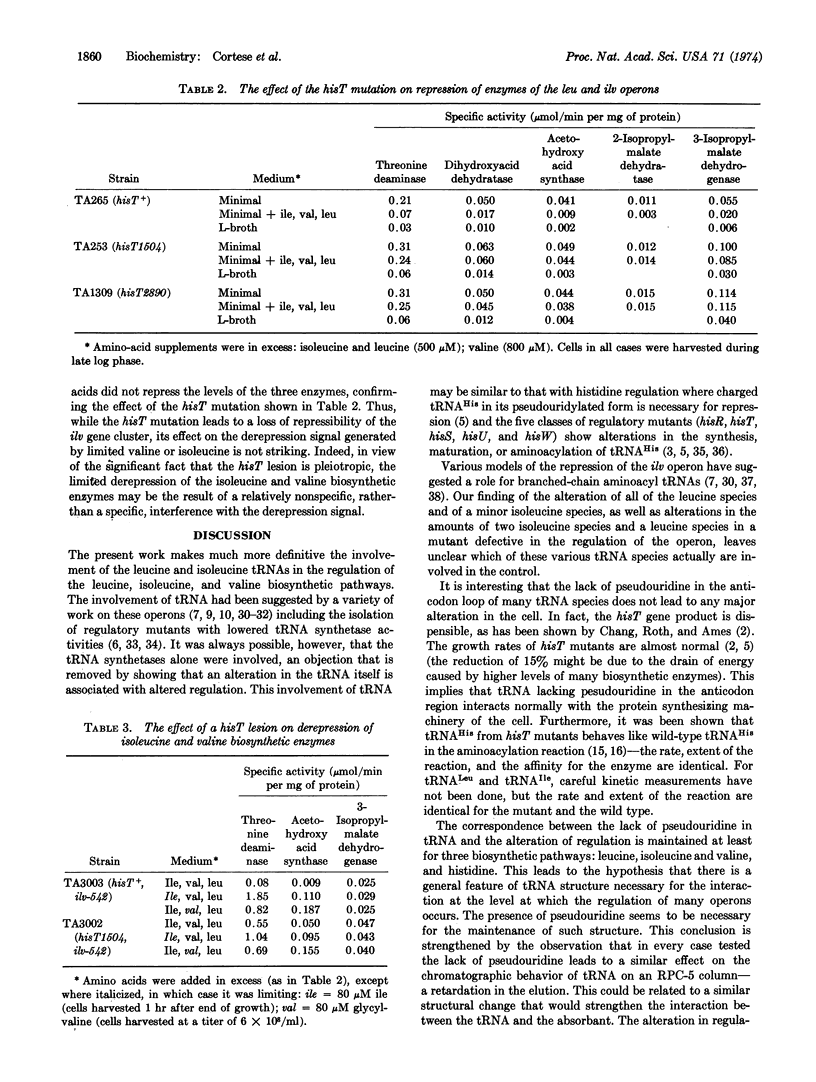

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander R. R., Calvo J. M., Freundlich M. Mutants of Salmonella typhimurium with an altered leucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):213–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.213-220.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allaudeen H. S., Yang S. K., Söll D. Leucine tRNA(1) from HisT mutant of Salmonella typhimurium lacks two pseudouridines. FEBS Lett. 1972 Dec 1;28(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80713-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Ames G. F., Young J. D., Tsuchiya D., Lecocq J. Illicit transport: the oligopeptide permease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):456–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1951 Sep;62(3):293–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.3.293-300.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNS R. O., UMBARGER H. E., GROSS S. R. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF LEUCINE. III. THE CONVERSION OF ALPHA-HYDROXY-BETA-CARBOXYISOCAPROATE TO ALPHA-KETOISOCAPROATE. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:1053–1058. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt J. M., Pledger W. J., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. XX. Multiple forms of acetohydroxy acid synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 25;48(2):444–450. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M., Ames B. N. Histidine regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. IX. Histidine transfer ribonucleic acid of the regulatory mutants. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1080–1088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M., Lewis J. A., Straus D. S., De Lorenzo F., Ames B. N. Histidine regulation in salmonella typhimurium. XIV. Interaction of the histidyl transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase with histidine transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4333–4339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A., Faiman L. E., Neidhardt F. C. Biochemical and genetic characterization of a mutant of Escherichia coli with a temperature-sensitive valyl ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1076–1082. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1076-1082.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. H., Hatfield G. W. Autoregulation: a role for a biosynthetic enzyme in the control of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2757–2761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvo J. M., Freundlich M., Umbarger H. E. Regulation of branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium: isolation of regulatory mutants. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1272–1282. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1272-1282.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang G. W., Roth J. R., Ames B. N. Histidine regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. 8. Mutations of the hisT gene. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):410–414. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.410-414.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese R., Kammen H. O., Spengler S. J., Ames B. N. Biosynthesis of pseudouridine in transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1103–1108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIDLIC L., NEIDHARDT F. C. ROLE OF VALYL-SRNA SYNTHETASE IN ENZYME REPRESSION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Mar;53:539–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich M., Trela J., Peng W. Evidence that the majority of leucine transfer ribonucleic acid is not involved in repression in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):951–953. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.951-953.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS S. R., BURNS R. O., UMBARGER H. E. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF LEUCINE. II. THE ENZYMIC ISOMERIZATION OF BETA-CARBOXY-BETA-HYDROXYISOCAPROATE AND ALPHA-HYDROXY-BETA-CARBOXYISOCAPROATE. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:1046–1052. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gefter M. L., Russell R. L. Role modifications in tyrosine transfer RNA: a modified base affecting ribosome binding. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan 14;39(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Nishimura S. Purification and characterization of AUA specific isoleucine transfer ribonucleic acid from Escherichia coli B. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):300–307. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield G. W., Burns R. O. Specific binding of leucyl transfer RNA to an immature form of L-threonine deaminase: its implications in repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1027–1035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iaccarino M., Berg P. Isoleucine auxotrophy as a consequence of a mutationally altered isoleucyl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):527–537. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.527-537.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelmers A. D., Novelli G. D., Stulberg M. P. Separation of transfer ribonucleic acids by reverse phase chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3979–3983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. A., Ames B. N. Histidine regulation in Salmonella typhimurium. XI. The percentage of transfer RNA His charged in vivo and its relation to the repression of the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1972 Apr 28;66(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B., Gates F., Goldstein T., Söll D. Isolation and partial characterization of temperature-sensitive Escherichia coli mutants with altered leucyl- and seryl-transfer ribonucleic acid synthetases. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):742–750. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.742-750.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C. Roles of amino acid activating enzymes in cellular physiology. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Dec;30(4):701–719. doi: 10.1128/br.30.4.701-719.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill J. P., Freundlich M. Effect of cyclopentaneglycine on metabolism in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):510–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.510-515.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oashi Z., Saneyoshi M., Harada F., Hara H., Nishimura S. Presumed anticodon structure of glutamic acid tRNA from E. coli: a possible location of a 2-thiouridine derivative in the first position of the anticodon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 24;40(4):866–872. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90983-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. L., Weiss J. F., Kelmers A. D. Improved separation of transfer RNA's on polychlorotrifuoroethylene-supported reversed-phase chromatography columns. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 11;228(3):770–774. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90748-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R., Ames B. N. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium II. Histidine regulatory mutants having altered histidyl-tRNA synthetase. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R., Antón D. N., Hartman P. E. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. I. Isolation and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):305–323. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer C. E., Smith G. R., Cortese R., Ames B. N. [Mutant tRNA His ineffective in repression and lacking two pseudouridine modifications]. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):72–74. doi: 10.1038/newbio238072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentirmai A., Szentirmai M., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism of Escherichia coli. XV. Biochemical properties of mutants resistant to thiaisoleucine. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1672–1679. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1672-1679.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentirmai A., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism of Escherichia coli. XIV. Effect of thiaisoleucine. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1666–1671. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1666-1671.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. J., Jr, Chen M. C., Lord R. C., Kotsiopoulos P. S., Tritton T. R., Mohr S. C. Transfer RNA: change of conformation upon aminoacylation determined by Raman spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):570–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91461-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaniv M., Barrell B. G. Nucleotide sequence of E. coli B tRNA1-Val. Nature. 1969 Apr 19;222(5190):278–279. doi: 10.1038/222278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., Barrell B. G. The sequence of nucleotides in tRNA Ile from E. coli B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 21;43(4):729–734. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90676-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


