Abstract
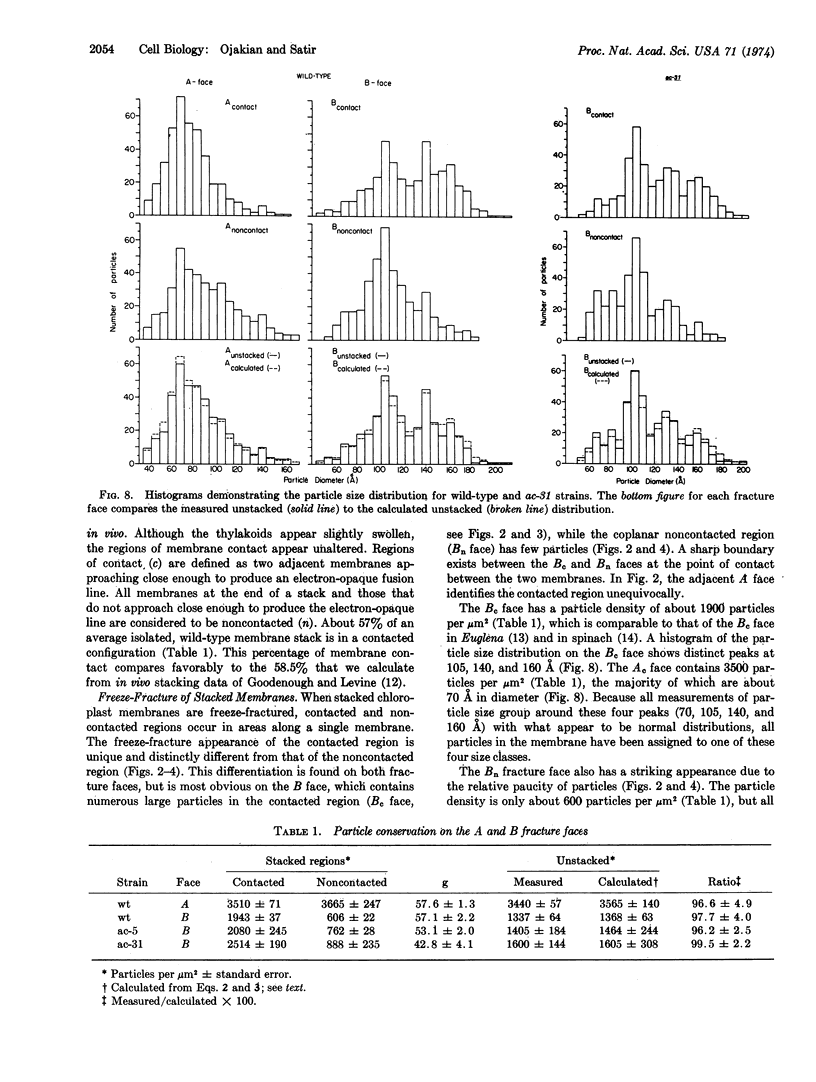
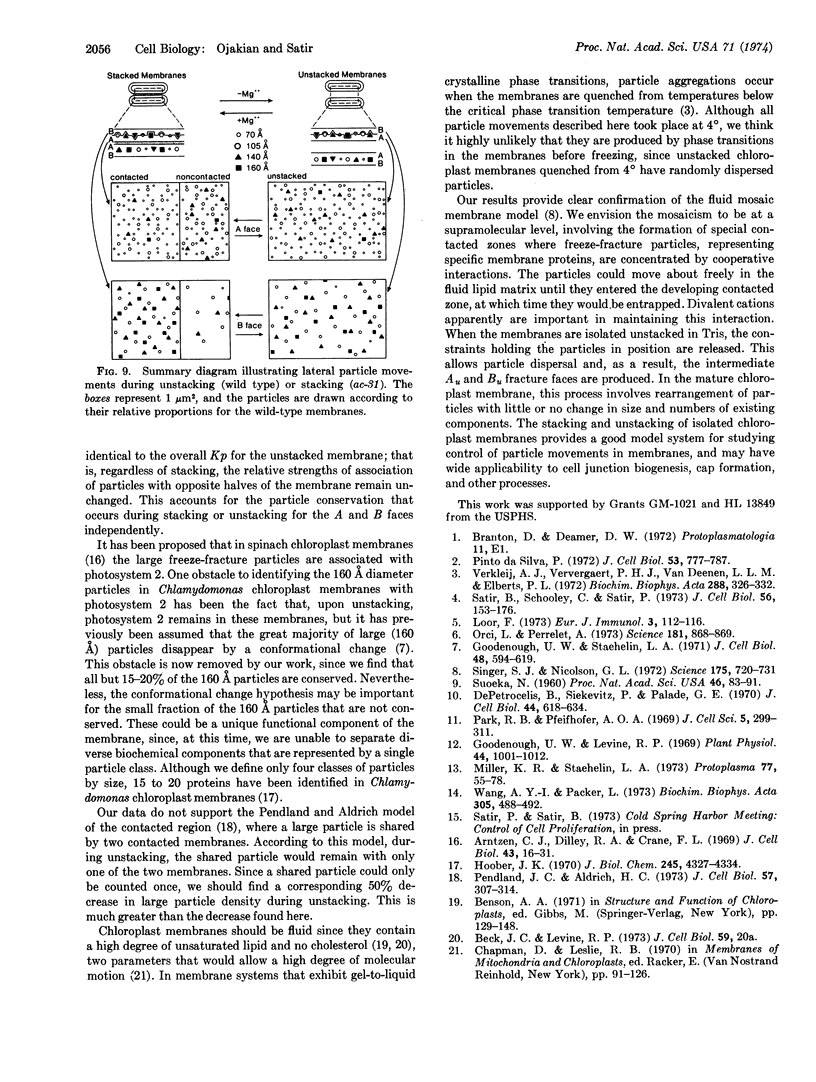
Stacked chloroplast membranes isolated from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii have differentiated particle arrays when examined by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. When the membranes are isolated unstacked, these particle arrays are lost and the fracture faces have a homogeneous appearance. The changes in appearance are due to rearrangement of existing membrane components by lateral particle movements in the plane of the fluid chloroplast membranes, since quantitative measurements demonstrate almost complete conservation of numbers and sizes of membrane particles during experimentally controlled stacking and unstacking.
Keywords: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, membrane interactions, chloroplast membrane structure
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Petrocellis B., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Changes in chemical composition of thylakoid membranes during greening of the y-1 mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. J Cell Biol. 1970 Mar;44(3):618–634. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.3.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough U. W., Armstrong J. J., Levine R. P. Photosynthetic Properties of ac-31, a Mutant Strain of Chlamydomonas reinhardi Devoid of Chloroplast Membrane Stacking. Plant Physiol. 1969 Jul;44(7):1001–1012. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.7.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoober J. K. Sites of synthesis of chloroplast membrane polypeptides in Chlamydomonas reinhardi y-1. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4327–4334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loor F. Lymphocyte membrane particle redistribution induced by a mitogenic-capping dose of the phytohemagglutinin of Phaseolus vulgaris. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Feb;3(2):112–116. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. R., Staehelin L. A. Fine structure of the chloroplast membranes of Euglena gracilis as revealed by freeze-cleaving and deep-etching techniques. Protoplasma. 1973;77(1):55–78. doi: 10.1007/BF01287292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Perrelet A. Membrane-associated particles: increase at sites of pinocytosis demonstrated by freeze-etching. Science. 1973 Aug 31;181(4102):868–869. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4102.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park R. B., Pfeifhofer A. O. Ultrastructural observations on deep-etched thylakoids. J Cell Sci. 1969 Jul;5(1):299–311. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.1.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendland J. C., Aldrich H. C. Ultrastructural organization of chloroplast thylakoids of the green alga Oocystis marssonii. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):306–314. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinto da Silva P. Translational mobility of the membrane intercalated particles of human erythrocyte ghosts. pH-dependent, reversible aggregation. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):777–787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rntzen C. J., Dilley R. A., Crane F. L. A comparison of chloroplast membrane surfaces visualized by freeze-etch and negative staining techniques; and ultrastructural characterization of membrane fractions obtained from digitonin-treated spinach chloroplasts. J Cell Biol. 1969 Oct;43(1):16–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satir B., Schooley C., Satir P. Membrane fusion in a model system. Mucocyst secretion in Tetrahymena. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jan;56(1):153–176. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sueoka N. MITOTIC REPLICATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID IN CHLAMYDOMONAS REINHARDI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Jan;46(1):83–91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkleij A. J., Ververgaert P. H., van Deenen L. L., Elbers P. F. Phase transitions of phospholipid bilayers and membranes of Acholeplasma laidlawii B visualized by freeze fracturing electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):326–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. Y., Packer L. Mobility of membrane particles in chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 30;305(2):488–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]