Abstract
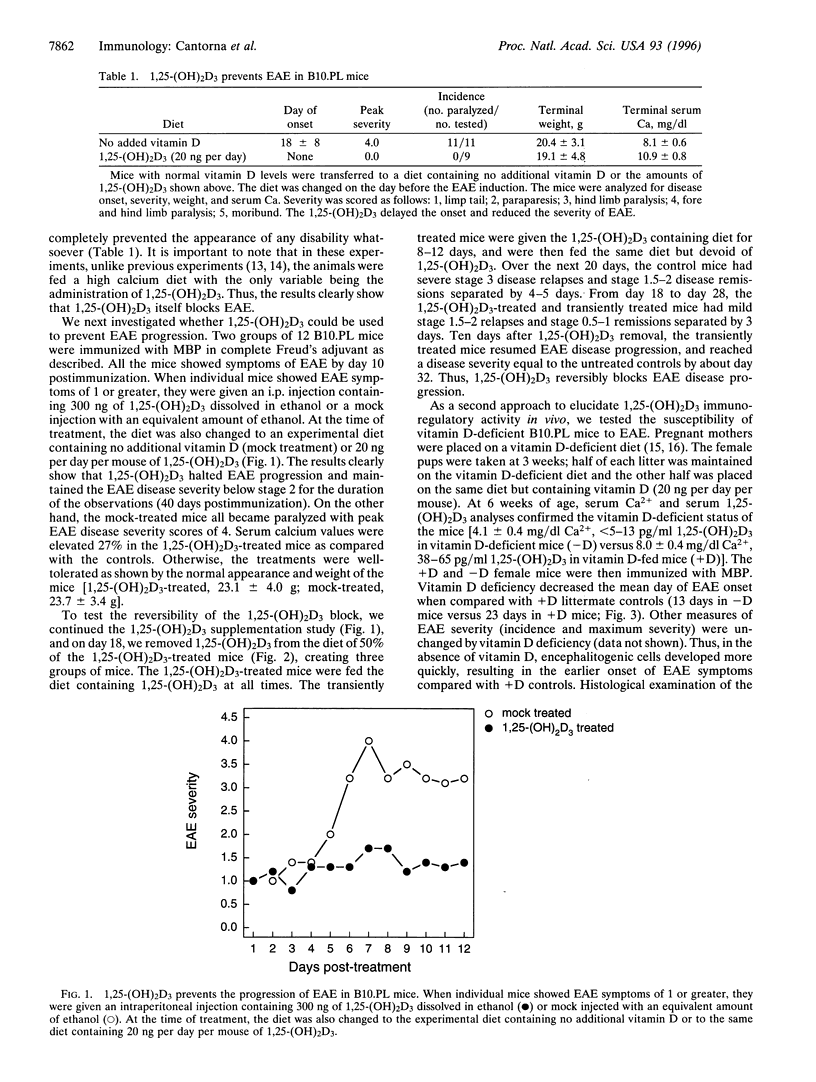
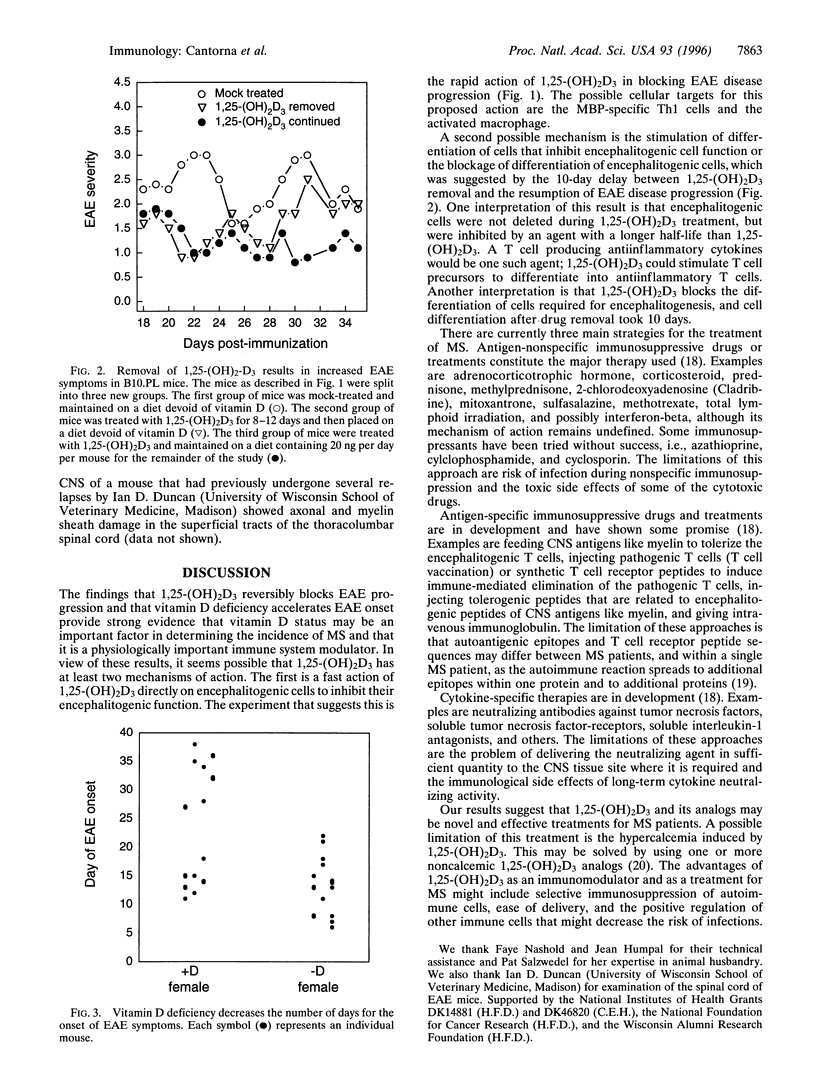
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an autoimmune disease believed to be a model for the human disease multiple sclerosis (MS). Induced by immunizing B10.PL mice with myelin basic protein (MBP), EAE was completely prevented by the administration of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 [1,25-(OH)2D3]. 1,25-(OH)2D3 could also prevent the progression of EAE when administered at the appearance of the first disability symptoms. Withdrawal of 1,25-(OH)2D3 resulted in a resumption of the progression of EAE. Thus, the block by 1,25-(OH)2D3 is reversible. A deficiency of vitamin D resulted in an increased susceptibility to EAE. Thus, 1,25-(OH)2D3 or its analogs are potentially important for treatment of MS.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhalla A. K., Amento E. P., Clemens T. L., Holick M. F., Krane S. M. Specific high-affinity receptors for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: presence in monocytes and induction in T lymphocytes following activation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Dec;57(6):1308–1310. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-6-1308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branisteanu D. D., Waer M., Sobis H., Marcelis S., Vandeputte M., Bouillon R. Prevention of murine experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: cooperative effects of cyclosporine and 1 alpha, 25-(OH)2D3. J Neuroimmunol. 1995 Sep;61(2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(95)00076-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daynes R. A., Enioutina E. Y., Butler S., Mu H. H., McGee Z. A., Araneo B A. Induction of common mucosal immunity by hormonally immunomodulated peripheral immunization. Infect Immun. 1996 Apr;64(4):1100–1109. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.4.1100-1109.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca H. F. New concepts of vitamin D functions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Sep 30;669:59–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb17089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibler G. E., Martenson R. E., Kies M. W. Large scale preparation of myelin basic protein from central nervous tissue of several mammalian species. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(2):139–165. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeffler H. P., Amatruda T., Ikekawa N., Kobayashi Y., DeLuca H. F. Induction of macrophage differentiation of human normal and leukemic myeloid stem cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its fluorinated analogues. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5624–5628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire J. M., Adams J. S., Sakai R., Jordan S. C. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses proliferation and immunoglobulin production by normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Clin Invest. 1984 Aug;74(2):657–661. doi: 10.1172/JCI111465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemire J. M., Archer D. C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 prevents the in vivo induction of murine experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1103–1107. doi: 10.1172/JCI115072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRae B. L., Vanderlugt C. L., Dal Canto M. C., Miller S. D. Functional evidence for epitope spreading in the relapsing pathology of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 1995 Jul 1;182(1):75–85. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. D., Karpus W. J. The immunopathogenesis and regulation of T-cell-mediated demyelinating diseases. Immunol Today. 1994 Aug;15(8):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K., Odum N., Bendtzen K. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 selectively reduces interleukin-2 levels and proliferation of human T cell lines in vitro. Immunol Lett. 1993 Feb;35(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(93)90088-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provvedini D. M., Tsoukas C. D., Deftos L. J., Manolagas S. C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in human leukocytes. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1181–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.6310748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby W. F., Denome S., Fanger M. W. Regulation of lymphokine production and human T lymphocyte activation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Specific inhibition at the level of messenger RNA. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1659–1664. doi: 10.1172/JCI113004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross T. K., Darwish H. M., DeLuca H. F. Molecular biology of vitamin D action. Vitam Horm. 1994;49:281–326. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)61149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Levy N. S., Hayes C. E. Impaired immunity in vitamin A-deficient mice. J Nutr. 1987 May;117(5):857–865. doi: 10.1093/jn/117.5.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L. Escape from "horror autotoxicus": pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune disease. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Watry D., Escobar S. S., Provvedini D. M., Dinarello C. A., Hustmyer F. G., Manolagas S. C. Inhibition of interleukin-1 production by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Jul;69(1):127–133. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S., Smith C., Prahl J. M., Luo X., DeLuca H. F. Vitamin D deficiency suppresses cell-mediated immunity in vivo. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 May 15;303(1):98–106. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



