Abstract
Addition of nerve growth factor to a 105,000 × g supernatant of mouse brain induces the formation of a precipitate whose main constituent is the microtubule protein(s) (tubulin). The binding of nerve growth factor to purified tubulin is not inhibited by colchicine and does not appear to depend on the presence of GTP or Mg++. GTP, however, and divalent cations, exert a marked effect on the increased turbidity induced by interaction of nerve growth factor with tubulin. These findings are tentatively interpreted with the hypothesis that binding of the factor to tubulin and the induced aggregation is a sequential two-step process; the latter but not the former would be influenced by GTP or divalent cations.
Keywords: tubulin, divalent cations, colchicine, GTP
Full text
PDF
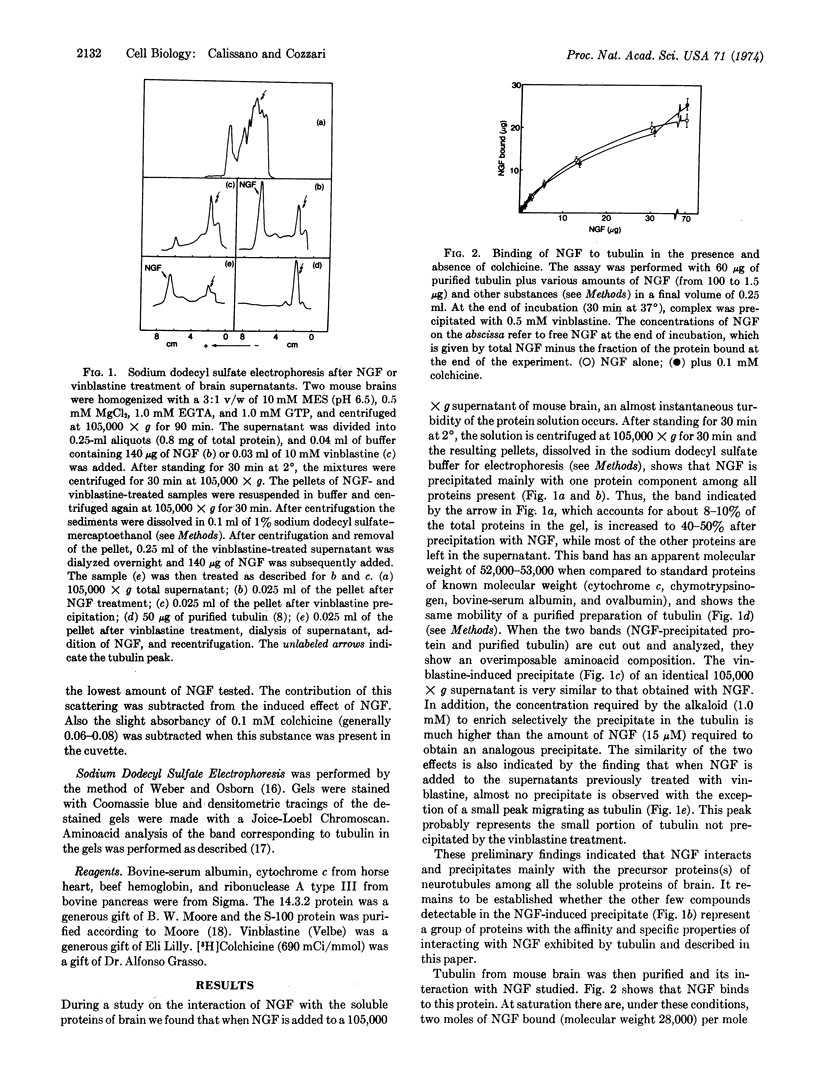
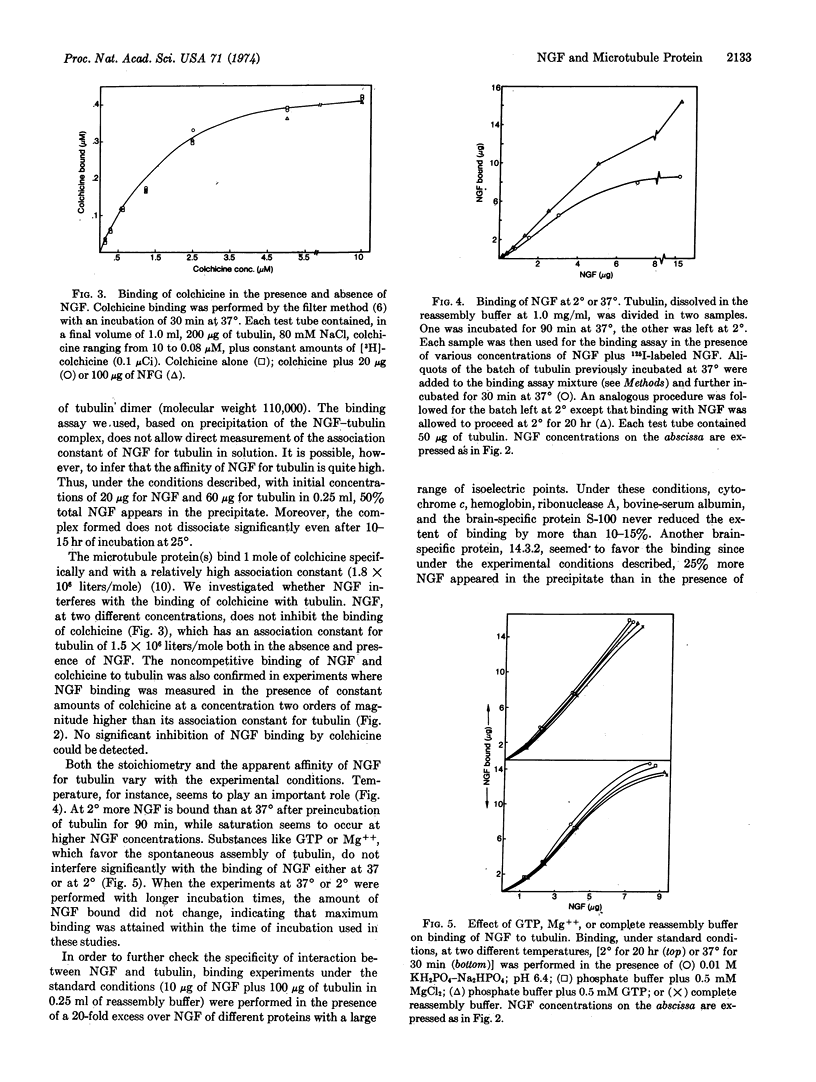
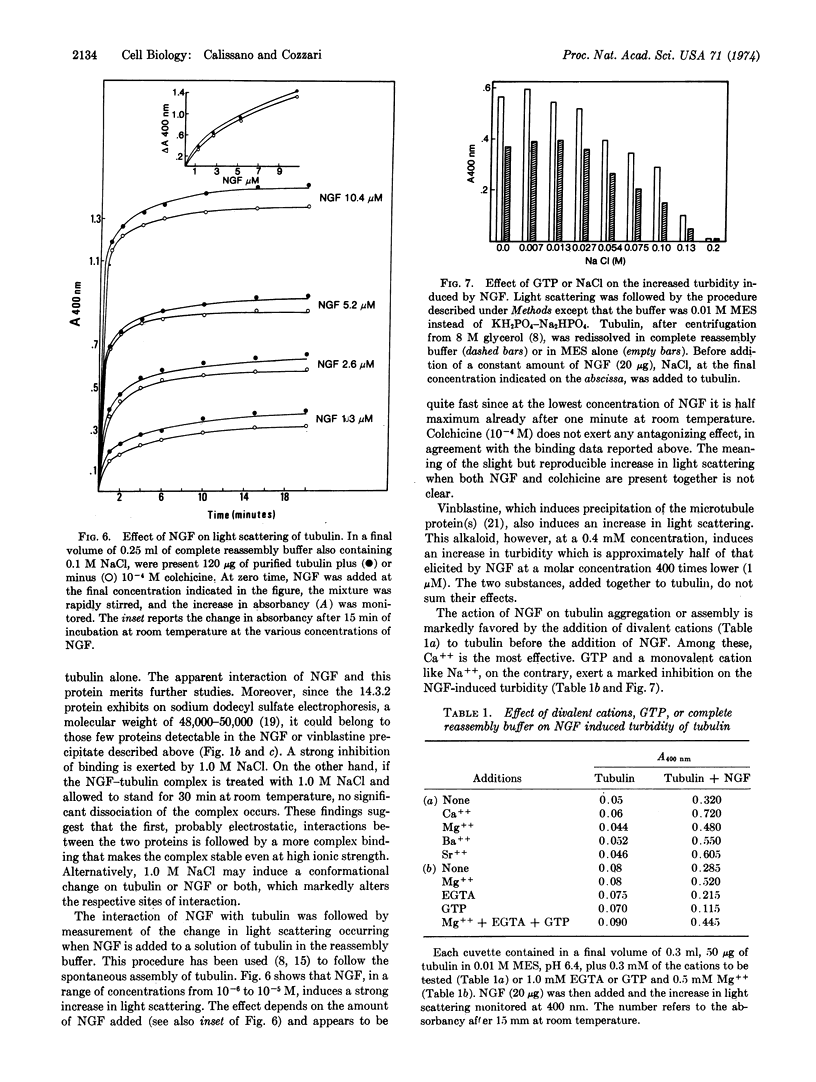

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angeletti R. H., Hermodson M. A., Bradshaw R. A. Amino acid sequences of mouse 2.5S nerve growth factor. II. Isolation and characterization of the thermolytic and peptic peptides and the complete covalent structure. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):100–115. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S. P., Snyder S. H., Cuatrecasas P., Greene L. A. Binding of nerve growth factor receptor in sympathetic ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2519–2523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K. G., Malawista S. E. Microtubular crystals in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):95–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisy G. G., Olmsted J. B., Klugman R. A. In vitro aggregation of cytoplasmic microtubule subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2890–2894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. Vinblastine and microtubules. II. Characterization of two protein subunits from the isolated crystals. J Mol Biol. 1972 Apr 28;66(1):157–168. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feit H., Barondes S. H. Colchicine-binding activity in particulate fractions of mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1970 Sep;17(9):1355–1364. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb06870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hier D. B., Arnason B. G., Young M. Studies on the mechanism of action of nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2268–2272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Purification of the sodium- and potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase from canine renal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4157–4165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Caramia F., Luse S. A., Angeletti P. U. In vitro effects of the nerve growth factor on the fine structure of the sensory nerve cells. Brain Res. 1968 May;8(2):347–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: its mode of action on sensory and sympathetic nerve cells. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:217–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marantz R., Ventilla M., Shelanski M. Vinblastine-induced precipitation of microtubule protein. Science. 1969 Aug 1;165(3892):498–499. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3892.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. W. A soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 9;19(6):739–744. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owellen R. J., Owens A. H., Jr, Donigian D. W. The binding of vincristine, vinblastine and colchicine to tubulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):685–691. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90546-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Franke W. W. Colchicine-binding proteins in chromatin and membranes. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):237–238. doi: 10.1038/newbio237237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberg R. C., Borisy G. G., Taylor E. W. The colchicine-binding protein of mammalian brain and its relation to microtubules. Biochemistry. 1968 Dec;7(12):4466–4479. doi: 10.1021/bi00852a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenberg R. C. Microtubule formation in vitro in solutions containing low calcium concentrations. Science. 1972 Sep 22;177(4054):1104–1105. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4054.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



