Abstract
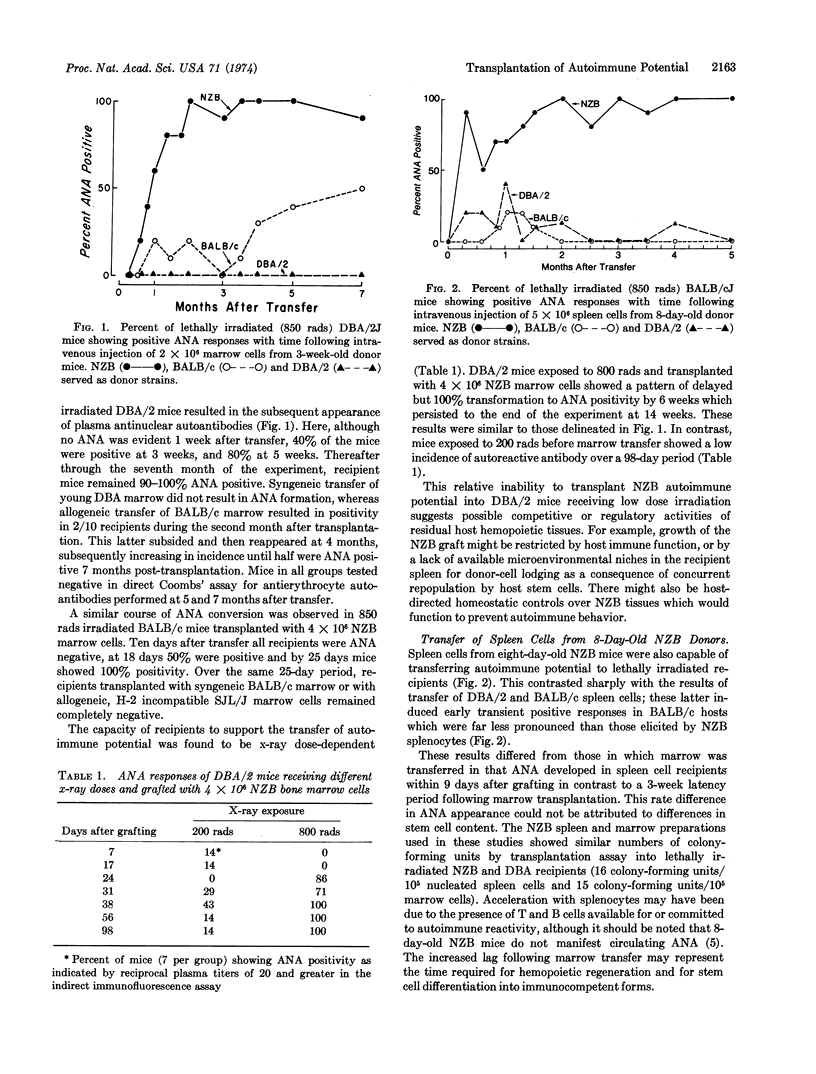
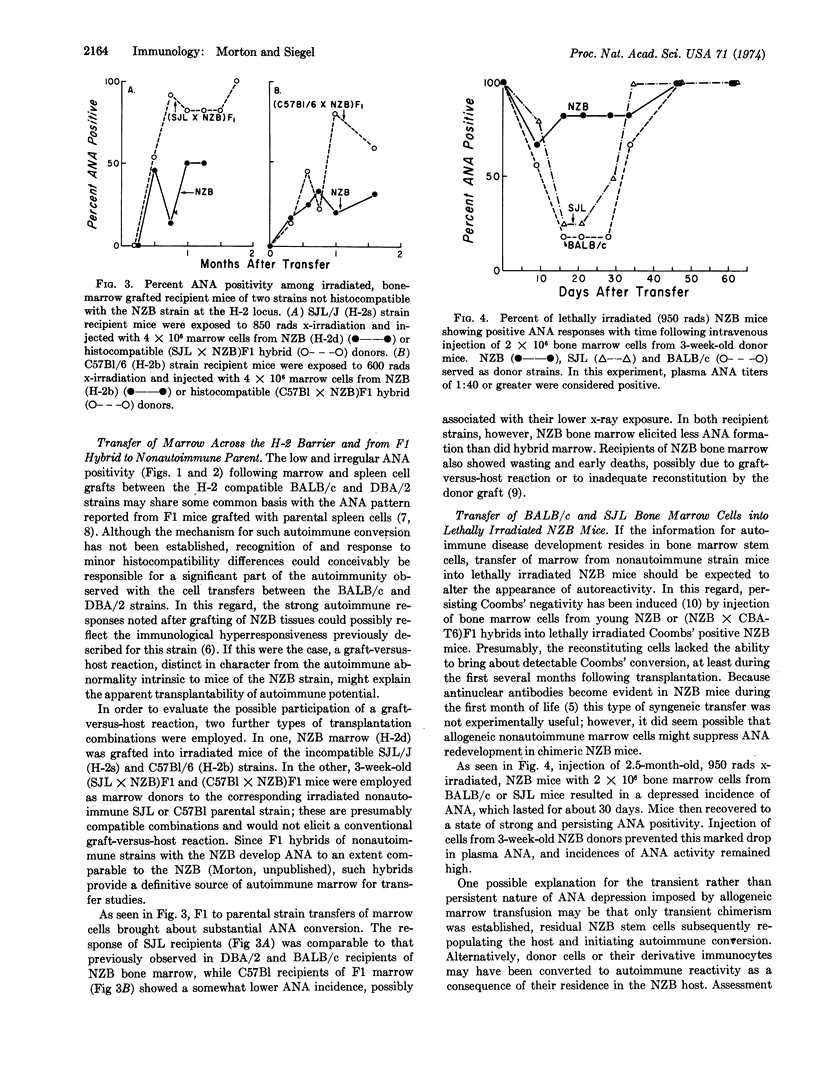
Antinuclear autoantibodies (ANA) appeared in the plasma of lethally irradiated H-2d histocompatible DBA/2 and BALB/c mice several weeks after intravenous transplantation of 2 to 4 × 106 bone marrow cells from 3-week-old animals of the autoimmune New Zealand Black (NZB) strain. Little or no ANA development was observed in DBA/2 or BALB/c strains when syngeneic or nonautoimmune allogeneic marrow was grafted, or when NZB marrow was injected into untreated DBA mice or mice receiving 200 rads of x-irradiation. Transfer of 5 × 106 spleen cells from 8-day-old NZB mice into lethally irradiated BALB/c mice effected substantial ANA formation by the ninth day after transfer, compared to a 20-day latency following transfer of the same number of bone marrow cells. This earlier conversion with splenocytes may have been due to the presence of immunocompetent T and B cells, since stem cell numbers of the two tissues were similar. Transplantation of NZB marrow to lethally irradiated H-2 incompatible SJL/J (H-2s) and C57B1/6 (H-2b) strains brought about less ANA conversion than the transfer of compatible (SJL × NZB)F1 and (C57B1 × NZB)F1 marrow cells to the respective nonautoimmune SJL or C57B1 parental strain. Graft-versus-host reactions thus did not appear to play a requisite or determining role in the autoimmune development observed following grafting of NZB hemopoietic tissues. Reconstitution of lethally irradiated NZB mice with BALB/c or SJL/J bone marrow depressed the recurrence of ANA for 30 days, compared to rapid ANA recovery following NZB marrow injection. The characteristics that ultimately provoke or permit spontaneous auto-reactivity are inherent in the hemopoietic stem cell population of the NZB strain.
Keywords: indirect immunofluorescence assay, hemopoietic stem cell, autoimmune disease
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cannat A., Varet B. Antinuclear antibodies in hybrid mice inoculated with parental spleen cells. Biomedicine. 1973 Mar 20;19(3):108–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denman A. M., Russell A. S., Denman E. J. Adoptive transfer of the diseases of New Zealand black mice to normal mouse strains. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Dec;5(6):567–595. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Gilchrist C., Allison A. C. Autoimmunity in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Apr;13(4):479–486. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey E. S., Woodruff M. F. Infusion of marrow and spleen cells in irradiated NZB-Bl mice: amelioration of autoimmune disease. Br J Haematol. 1968 Mar;14(3):255–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01495.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotzová E., Cudkowicz G. Resistance of irradiated F 1 hybrid and allogeneic mice to bone marrow grafts of NZB donors. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):791–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors R. C. Murine leukemialike virus and the immunopathologic disorders of New Zealand black mice. J Infect Dis. 1969 Oct;120(4):480–487. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.4.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. I., Siegel B. V. Radiation sensitivity of New Zealand black mice and the development of autoimmune disease and neoplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):124–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. I., Siegel B. V. Response of NZB mice to foreign antigen and development of autoimmune disease. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1969 Feb;6(1):78–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel B. V., Brown M., Morton J. I. Detection of antinuclear antibodies in NZB and other mouse strains. Immunology. 1972 Mar;22(3):457–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague P. O., Friou G. J. Antinuclear antibodies in mice. II. Transmission with spleen cells; inhibition or prevention with thymus or spleen cells. Immunology. 1969 Nov;17(5):665–675. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung L. L., Wyn-Evans T. C., Diener E. Ontogeny of the murine immune system: development of antigen recognition and immune responsiveness. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Apr;3(4):224–228. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


