Abstract
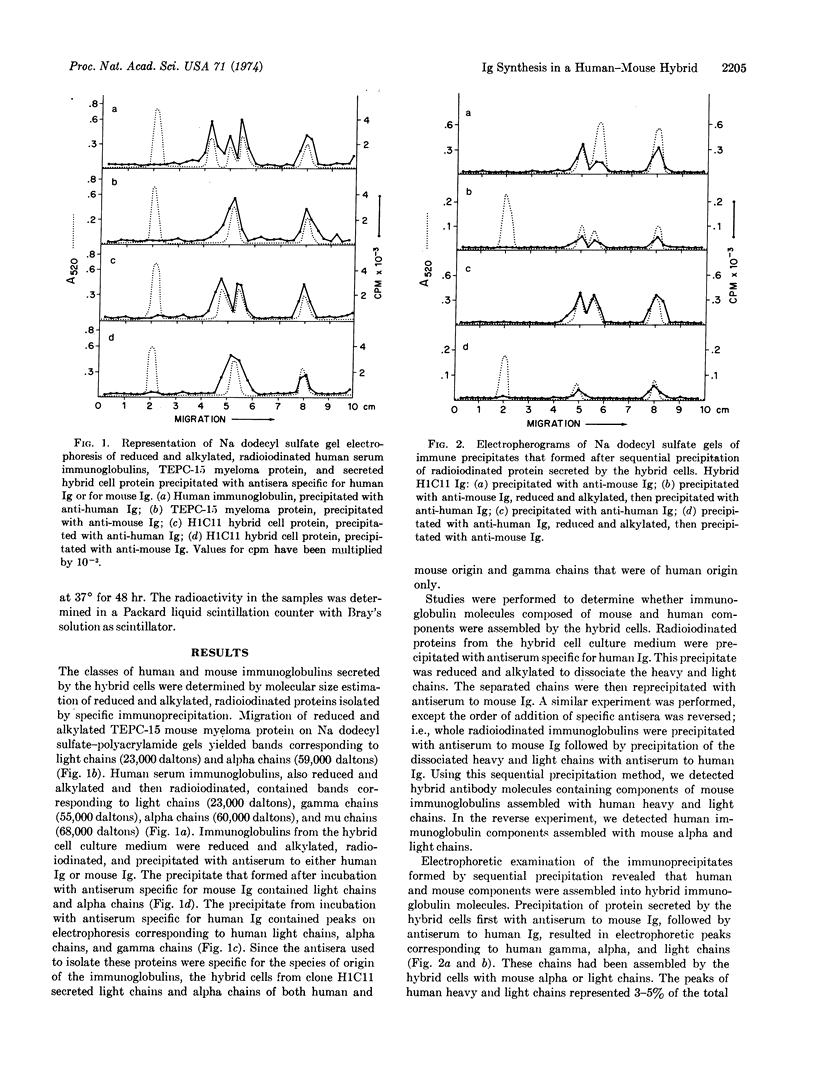
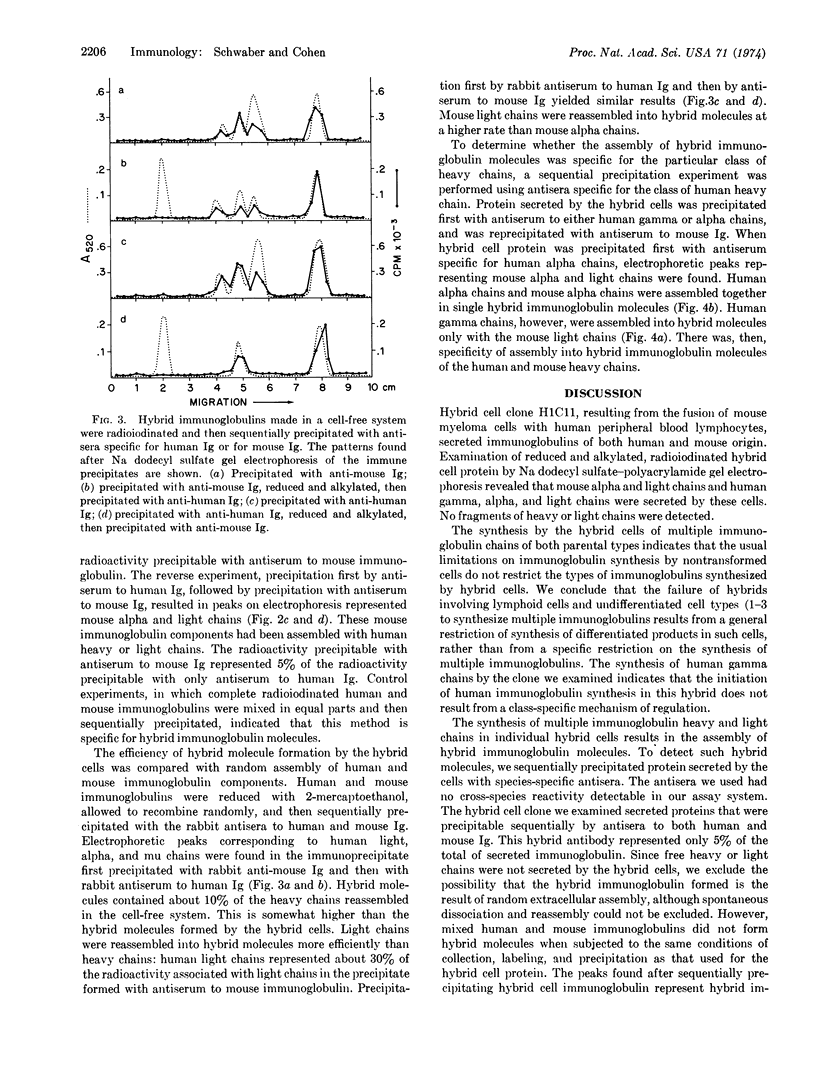
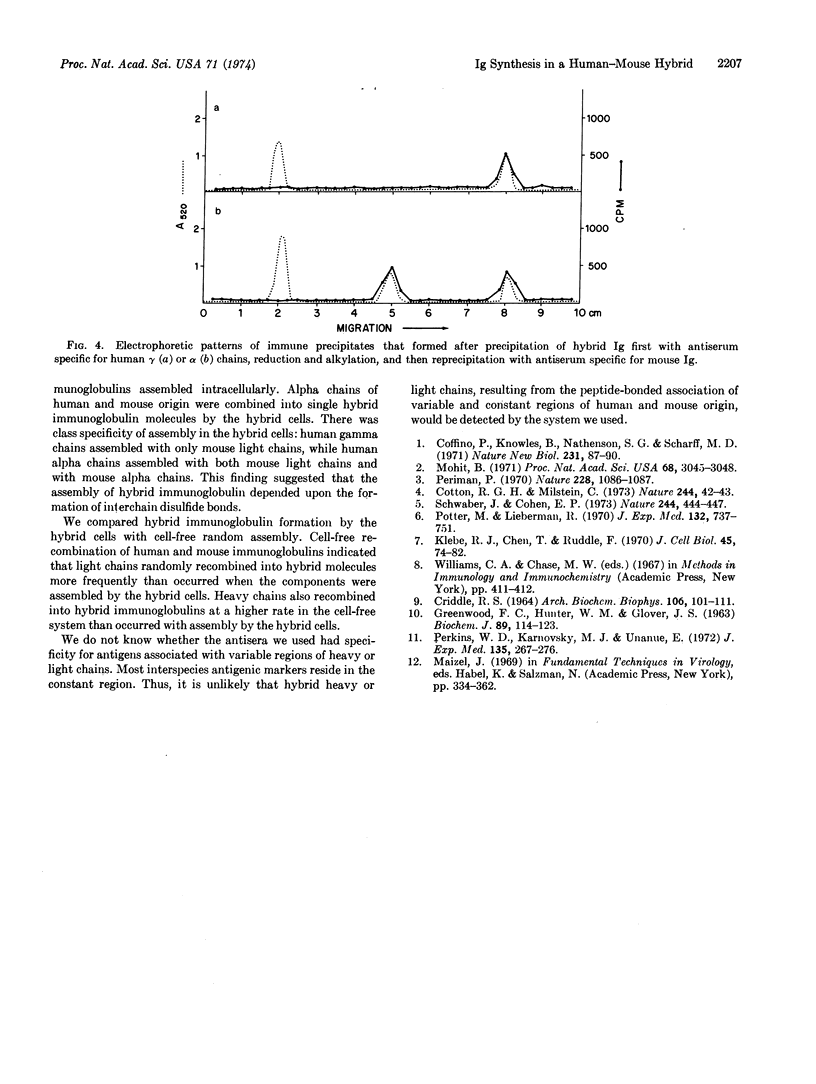
Fusion of human peripheral blood lymphocytes, not forming detectable immunoglobulins, with mouse myeloma cells (TEPC-15), secreting mouse immunoglobulin A with known antibody activity, yielded a somatic cell hybrid clone that secreted both human and mouse immunoglobulins. Analysis by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis indicated that human gamma, alpha, and light chains, as well as mouse alpha and light chains, were formed by the hybrid cells. To determine whether individual antibody molecules with both human and mouse components were secreted, medium from the hybrid cells was precipitated first with antibody against mouse immunoglobulin produced in rabbit, reduced, and alkylated, and then reprecipitated with antibody against human immunoglobulin produced in rabbit. Human gamma, alpha, and light chains were detected after electrophoresis of the immunoprecipitates on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, indicating that antibody molecules containing both human and mouse components were secreted by the hybrid cells. These data indicate that this somatic cell hybrid clone synthesized human gamma and alpha heavy chains and human light chains, as well as mouse alpha heavy chains and mouse light chains. Some of these immunoglobulin components were assembled as hybrid antibody molecules.
Keywords: hybrid cells, hybrid immunoglobulin
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRIDDLE R. S. DISSOCIATION AND SEPARATION OF GAMMA GLOBULIN INTO SUBUNITS. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul 20;106:101–111. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Knowles B., Nathenson S. G., Scharff M. D. Suppression of immunoglobulin synthesis by cellular hybridization. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 19;231(20):87–90. doi: 10.1038/newbio231087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton R. G., Milstein C. Letter: Fusion of two immunoglobulin-producing myeloma cells. Nature. 1973 Jul 6;244(5410):42–43. doi: 10.1038/244042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebe R. J., Chen T., Ruddle F. H. Controlled production of proliferating somatic cell hybrids. J Cell Biol. 1970 Apr;45(1):74–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohit B. Immunoglobulin G and free kapa-chain synthesis in different clones of a hybrid cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3045–3048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periman P. IgG synthesis in hybrid cells from an antibody-producing mouse myeloma and an L cell substrain. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1086–1087. doi: 10.1038/2281086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins W. D., Karnovsky M. J., Unanue E. R. An ultrastructural study of lymphocytes with surface-bound immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):267–276. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Lieberman R. Common individual antigenic determinants in five of eight BALB-c IgA myeloma proteins that bind phosphoryl choline. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):737–751. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaber J., Cohen E. P. Human x mouse somatic cell hybrid clone secreting immunoglobulins of both parental types. Nature. 1973 Aug 17;244(5416):444–447. doi: 10.1038/244444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


