Abstract
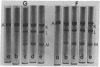
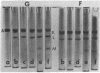
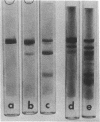
Under certain conditions actin can be split by thrombin. Actin prepared in the presence of excess Ca++ was found to be resistant to thrombin. However, if actin was purified without added Ca++, both G- and F- actin underwent thrombic digestion, although a considerable proportion of actin molecules remained intact. Similar results were obtained with actin (in 50% sucrose) devoid of nucleotide and divalent cations but retaining its native characteristic. The removal of tightly bound Ca++ from actin by EDTA accelerated the thrombic splitting and made the complete fragmentation of G-actin possible. Thrombin first cleaves actin into two pieces and subsequently one of them, fragment K (molecular weight 37,000 on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel), splits further, resulting in fragments L (molecular weight 27,000) and M (molecular weight about 10,000).
Keywords: clot retraction, contractile proteins, ATP-binding
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnone A., Bier C. J., Cotton F. A., Day V. W., Hazen E. E., Jr, Richardson D. C., Yonath A., Richardson J. S. A high resolution structure of an inhibitor complex of the extracellular nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus. I. Experimental procedures and chain tracing. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2302–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETTEX-GALLAND M., LUESCHER E. F. Extraction of an actomyosin-like protein from human thrombocytes. Nature. 1959 Jul 25;184(Suppl 5):276–277. doi: 10.1038/184276b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRAMBACH A., BARANY M., FINKELMAN F. The bound calcium of actin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 May;93:456–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T., Jr, Shaw E. Comparison of the esterase activities of trypsin, plasmin, and thrombin on guanidinobenzoate esters. Titration of the enzymes. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):2212–2224. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Bohak Z., De VriesA, Katchalski E. Thrombosthenin M. Purification and interaction with thrombin. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Sep;10(2):388–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elzinga M., Collins J. H., Kuehl W. M., Adelstein R. S. Complete amino-acid sequence of actin of rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2687–2691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLADNER J. A., FOLK J. E. Carboxypeptidase B. II. Mode of action on protein substrates and its application to carboxyl terminal group analysis. J Biol Chem. 1958 Mar;231(1):393–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASAI M., NAKANO E., OOSAWA F. POLYMERIZATION OF ACTIN FREE FROM NUCLEOTIDES AND DIVALENT CATIONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 29;94:494–503. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKI K., BOWEN W. J., CLARK A. The polymerization of proteins; adenosine triphosphate and the polymerization of actin. J Gen Physiol. 1950 May 20;33(5):437–443. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.5.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAKI K. The polymerization of proteins; the action of thrombin on fibrinogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Jul;32(2):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90277-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTONOSI A., GOUVEA M. A., GERGERLY J. Studies on actin. I. The interaction of C14-labeled adenine nucleotides with actin. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1700–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTONOSI A., GOUVEA M. A. Studies on actin. VI. The interaction of nucleoside triphosphates with actin. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1345–1352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTONOSII A., MOLINO C. M., GERGELY J. THE BINDING OF DIVALENT CATIONS TO ACTIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1057–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARUYAMA K., GERGELY J. Removal of the bound calcium of G-actin by ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Nov 29;6:245–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90371-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOMMAERTS W. F. H. M. The molecular transformations of actin. III. The participation of nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):469–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASMUSSEN P. S. Purification of thrombin by chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jan;16(1):157–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90194-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SGOURIS J. T., INMAN J. K., McCALL K. B., HYNDMAN L. A., ANDERSON H. D. The preparation of human fibrinolysin (plasmin). Vox Sang. 1960 Jul;5:357–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1960.tb03750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STROHMAN R. C. Studies on the enzymic interactions of the bound nucleotide of the bound nucleotide of the muscle protein actin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Apr;32:436–449. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90617-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R. Studies on reaction between thrombin and actin. Ser Haematol. 1973;6(3):392–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONOMURA Y., YOSHIMURA J. Removal of bound nucleotide and calcium of G-actin by treatment with ethylenediamine-tetraacetic acid. J Biochem. 1961 Jul;50:79–80. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. J. Binding of adenosine diphosphate to G-actin. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 3;9(5):1239–1246. doi: 10.1021/bi00807a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]