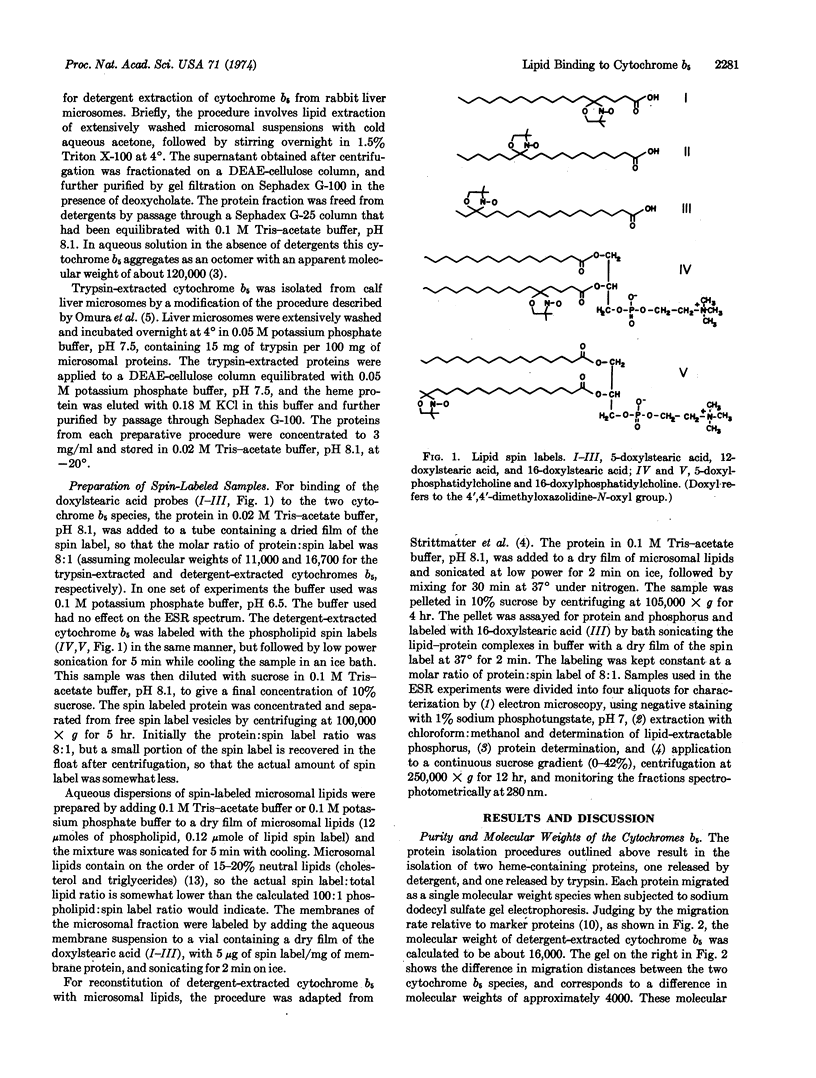
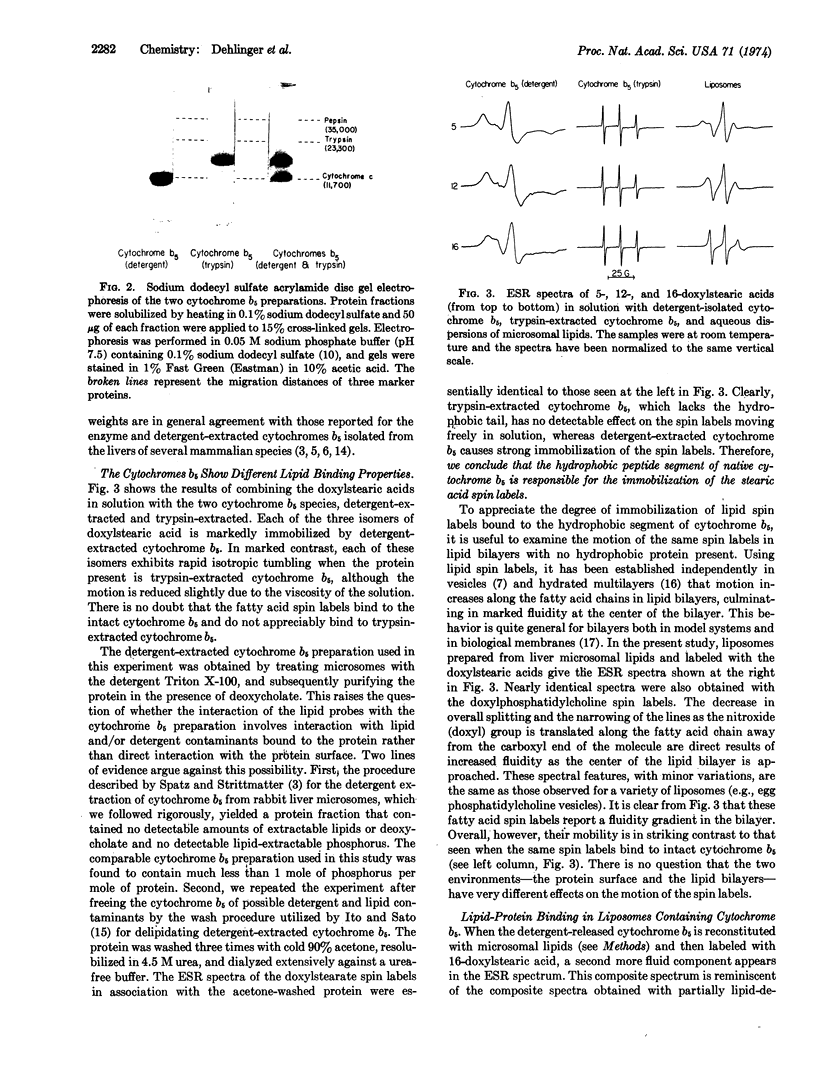
Abstract
The lipid binding properties of the membrane protein cytochrome b5 (detergent-extracted from calf liver microsomal preparations) were characterized by studying the interaction of spin-labeled lipids (5-, 12-, and 16-doxylstearic acid and 5- and 16-doxylphosphatidyl-choline, where doxyl refers to the nitroxide moiety) with cytochrome b5, using electron spin resonance spectroscopy. The intact cytochrome b5 molecule immobilizes all of the lipid spin labels, while the segment of cytochrome b5 released by trypsin does not affect lipid mobility. The immobilization of lipid spin labels on the hydrophobic surface of intact cytochrome b5 is not appreciably altered by associating the protein with liposomes. Differences in polarity of the lipid binding sites between cytochrome b5 and phospholipid vesicles were also observed. The lipid binding sites on cytochrome b5 are hydrophobic by conventional criteria, but are more polar than the interior of fluid phospholipid bilayers.
Keywords: electron spin resonance, lipid spin labels, endoplasmic reticulum membrane
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dallner G., Ernster L. Subfractionation and composition of microsomal membranes: a review. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Oct;16(10):611–632. doi: 10.1177/16.10.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. H., Dehlinger P. J., Van S. P. Shape of the hydrophobic barrier of phospholipid bilayers (evidence for water penetration in biological membranes). J Membr Biol. 1974;15(2):159–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01870086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. H., Jost P., Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. Boundary lipid and fluid bilayer regions in cytochrome oxidase model membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Dec 31;222:561–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb15287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A., Sato R. Purification by means of detergents and properties of cytochrome b5 from liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4922–4923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Capadil R. A., Vanderkooi G., Griffith O. H. Lipid-protein and lipid-lipid interactions in cytochrome oxidase model membranes. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(4):269–280. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P. C., Griffith O. H., Capaldi R. A., Vanderkooi G. Evidence for boundary lipid in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):480–484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost P., Libertini L. J., Hebert V. C., Griffith O. H. Lipid spin labels in lecithin multilayers. A study of motion along fatty acid chains. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):77–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90414-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajihara T., Hagihara B. Crystalline cytochrome b5. I. Preparation of crystalline cytochrome b5 from rabbit liver. J Biochem. 1968 Apr;63(4):453–461. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komai H., Capaldi R. A. On the subunit structure of cytochrome oxidase from beef heart mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1973 Mar 15;30(3):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80668-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omura T., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Turnover of constituents of the endoplasmic reticulum membranes of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2389–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRITTMATTER P., VELICK S. F. The isolation and properties of microsomal cytochrome. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jul;221(1):253–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz L., Strittmatter P. A form of cytochrome b5 that contains an additional hydrophobic sequence of 40 amino acid residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1042–1046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter P., Rogers M. J., Spatz L. The binding of cytochrome b 5 to liver microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7188–7194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugita A., Kobayashi M., Tani S., Kyo S., Rashid M. A. Comparative study of the primary structures of cytochrome b5 from four species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):442–447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
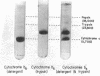
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]