Abstract
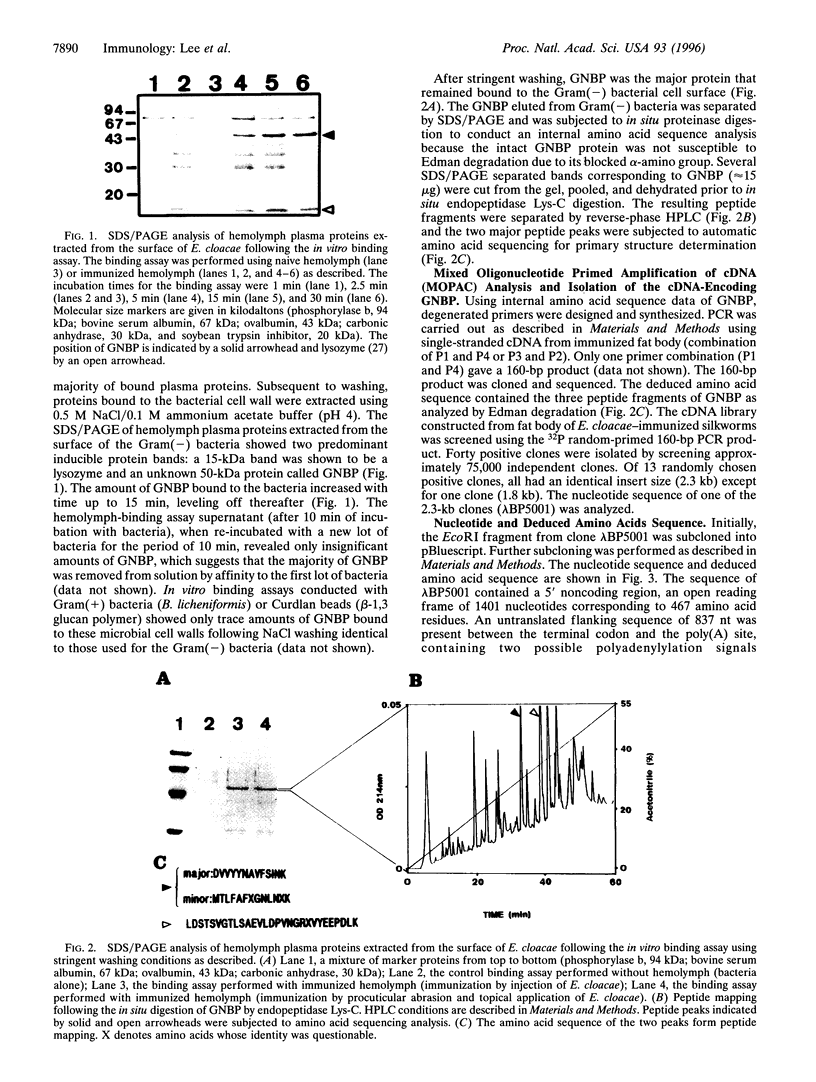
A 50-kDa hemolymph protein, having strong affinity to the cell wall of Gram(-) bacteria, was purified from the hemolymph of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. The cDNA encoding this Gram(-) bacteria-binding protein (GNBP) was isolated from an immunized silkworm fat body cDNA library and sequenced. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence with known sequences revealed that GNBP contained a region displaying significant homology to the putative catalytic region of a group of bacterial beta-1,3 glucanases and beta-1,3-1,4 glucanases. Silkworm GNBP was also shown to have amino acid sequence similarity to the vertebrate lipopolysaccharide receptor CD14 and was recognized specifically by a polygonal anti-CD14 antibody. Northern blot analysis showed that GNBP was constitutively expressed in fat body, as well as in cuticular epithelial cells of naive silkworms. Intense transcription was, however, rapidly induced following a cuticular or hemoceolien bacterial challenge. An mRNA that hybridized with GNBP cDNA was also found in the l(2)mbn immunocompetent Drosophila cell line. These observations suggest that GNBP is an inducible acute phase protein implicated in the immune response of the silkworm and perhaps other insects.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P. Computer analysis of protein structure. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:751–776. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82058-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashida M., Brey P. T. Role of the integument in insect defense: pro-phenol oxidase cascade in the cuticular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10698–10702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazil V., Horejsí V., Baudys M., Kristofová H., Strominger J. L., Kostka W., Hilgert I. Biochemical characterization of a soluble form of the 53-kDa monocyte surface antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1583–1589. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G. Antibacterial peptides: key components needed in immunity. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):205–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90154-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H. G. Peptide antibiotics and their role in innate immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:61–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey P. T., Lee W. J., Yamakawa M., Koizumi Y., Perrot S., François M., Ashida M. Role of the integument in insect immunity: epicuticular abrasion and induction of cecropin synthesis in cuticular epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6275–6279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerenius L., Liang Z., Duvic B., Keyser P., Hellman U., Palva E. T., Iwanaga S., Söderhäll K. Structure and biological activity of a 1,3-beta-D-glucan-binding protein in crustacean blood. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29462–29467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cociancich S., Bulet P., Hetru C., Hoffmann J. A. The inducible antibacterial peptides of insects. Parasitol Today. 1994 Apr;10(4):132–139. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(94)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne K. E., Crisci A., Lublin D. M. Construction of synthetic signals for glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor attachment. Analysis of amino acid sequence requirements for anchoring. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6689–6693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimarcq J. L., Zachary D., Hoffmann J. A., Hoffmann D., Reichhart J. M. Insect immunity: expression of the two major inducible antibacterial peptides, defensin and diptericin, in Phormia terranovae. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2507–2515. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gateff E. Malignant neoplasms of genetic origin in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1978 Jun 30;200(4349):1448–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.96525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakala B. E., White C., Recklies A. D. Human cartilage gp-39, a major secretory product of articular chondrocytes and synovial cells, is a mammalian member of a chitinase protein family. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25803–25810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haziot A., Chen S., Ferrero E., Low M. G., Silber R., Goyert S. M. The monocyte differentiation antigen, CD14, is anchored to the cell membrane by a phosphatidylinositol linkage. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):547–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofemeister J., Kurtz A., Borriss R., Knowles J. The beta-glucanase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens shows extensive homology with that of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1986;49(2):177–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D. Immune reactions in Drosophila and other insects: a model for innate immunity. Trends Genet. 1993 May;9(5):178–183. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90165-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D. Insect immunology. Ancient relationships. Nature. 1994 Jan 13;367(6459):116–117. doi: 10.1038/367116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip Y. T., Reach M., Engstrom Y., Kadalayil L., Cai H., González-Crespo S., Tatei K., Levine M. Dif, a dorsal-related gene that mediates an immune response in Drosophila. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):753–763. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90495-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jomori T., Kubo T., Natori S. Purification and characterization of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein from hemolymph of American cockroach Periplaneta americana. Eur J Biochem. 1990 May 31;190(1):201–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jomori T., Natori S. Molecular cloning of cDNA for lipopolysaccharide-binding protein from the hemolymph of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Similarity of the protein with animal lectins and its acute phase expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13318–13323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalfayan L., Wensink P. C. alpha-Tubulin genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick R. B., Matico R. E., McNulty D. E., Strickler J. E., Rosenberg M. An abundantly secreted glycoprotein from Drosophila melanogaster is related to mammalian secretory proteins produced in rheumatoid tissues and by activated macrophages. Gene. 1995 Feb 14;153(2):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00756-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi A., Matsui M., Kubo T., Natori S. Purification and characterization of a 59-kilodalton protein that specifically binds to NF-kappa B-binding motifs of the defense protein genes of Sarcophaga peregrina (the flesh fly). Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4049–4056. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladendorff N. E., Kanost M. R. Isolation and characterization of bacteria-induced protein P4 from hemolymph of Manduca sexta. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1990;15(1):33–41. doi: 10.1002/arch.940150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Caskey C. T. Direct complementary DNA cloning using polymerase chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1992;216:69–72. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)16009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Wu X. W., Gibbs R. A., Cook R. G., Muzny D. M., Caskey C. T. Generation of cDNA probes directed by amino acid sequence: cloning of urate oxidase. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1288–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.3344434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. J., Brey P. T. Isolation and characterization of the lysozyme-encoding gene from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Gene. 1995 Aug 19;161(2):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00199-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugin J., Heumann I. D., Tomasz A., Kravchenko V. V., Akamatsu Y., Nishijima M., Glauser M. P., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. CD14 is a pattern recognition receptor. Immunity. 1994 Sep;1(6):509–516. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichhart J. M., Georgel P., Meister M., Lemaitre B., Kappler C., Hoffmann J. A. Expression and nuclear translocation of the rel/NF-kappa B-related morphogen dorsal during the immune response of Drosophila. C R Acad Sci III. 1993 Oct;316(10):1218–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samakovlis C., Asling B., Boman H. G., Gateff E., Hultmark D. In vitro induction of cecropin genes--an immune response in a Drosophila blood cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 16;188(3):1169–1175. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91354-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimming S., Schwarz W. H., Staudenbauer W. L. Structure of the Clostridium thermocellum gene licB and the encoded beta-1,3-1,4-glucanase. A catalytic region homologous to Bacillus lichenases joined to the reiterated domain of clostridial cellulases. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki N., Muta T., Oda T., Iwaki D., Kuma K., Miyata T., Iwanaga S. Horseshoe crab (1,3)-beta-D-glucan-sensitive coagulation factor G. A serine protease zymogen heterodimer with similarities to beta-glucan-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1370–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Faye I. Affinity purification and characterization of CIF, an insect immunoresponsive factor with NF-kappa B-like properties. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1992 Sep;103(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(92)90436-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Lindström I., Boman H. G., Faye I., Schmidt O. Hemolin: an insect-immune protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1729–1732. doi: 10.1126/science.2270488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniai K., Kato Y., Hirochika H., Yamakawa M. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of cecropin B cDNA clones from the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 24;1132(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90013-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teather R. M., Erfle J. D. DNA sequence of a Fibrobacter succinogenes mixed-linkage beta-glucanase (1,3-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase) gene. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3837–3841. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3837-3841.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Tobias P. S. Recognition of endotoxin by cells leading to transmembrane signaling. Curr Opin Immunol. 1994 Feb;6(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(94)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahata N., Watanabe T., Nakamura Y., Yamamoto Y., Kamimiya S., Tanaka H. Structure of the gene encoding beta-1,3-glucanase A1 of Bacillus circulans WL-12. Gene. 1990 Jan 31;86(1):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]